We manufacture and organize the powder coating plant design for our powder painting customers. Cheap prices & Free Consultation & High Quality.
Powder coating plant design is a crucial aspect of setting up a successful powder coating operation. An efficient and well-designed plant layout can enhance productivity, minimize waste, and ensure a high-quality finish on coated products.
Key Elements of Powder Coating Plant Design
A well-designed powder coating plant typically comprises the following main areas:
- Surface Preparation Area: This area is dedicated to cleaning, degreasing, and preparing the substrate for powder coating. It should be equipped with appropriate cleaning equipment, such as blasting cabinets, degreasing tanks, and drying ovens.
- Powder Application Booth: The powder application booth is where the powder coating is applied to the prepared substrate. It should be equipped with a powder spray gun, filters to capture overspray, and a ventilation system to remove fumes and prevent airborne powder from settling.
- Curing Oven: The curing oven is where the powder coating is heated to its curing temperature to achieve a durable and long-lasting finish. It should be sized appropriately to accommodate the largest objects being coated and equipped with temperature and airflow controls.
- Powder Recirculation System: The powder recirculation system ensures efficient use of powder coating materials by capturing and returning overspray to the mixing reservoir. This system can include cyclone separators and filters to remove contaminants from the recycled powder.
- Warehousing and Material Handling: Adequate storage space is essential for powder coating materials, such as powder coating resins, catalysts, and hardeners. Efficient material handling systems, such as conveyors and elevators, streamline the movement of substrates and powder coating materials throughout the plant.
Factors to Consider in Powder Coating Plant Design
- Plant Size and Layout: The size and layout of the powder coating plant should be determined based on the expected production volume and the type of substrates being coated. Efficient material flow and workspace allocation are key considerations.
- Environmental Controls: A powder coating plant generates airborne powder particles, which can be hazardous if not properly contained. Effective ventilation systems, dust collection equipment, and air filtration systems are essential to maintain a safe and healthy work environment.
- Fire Prevention and Safety: Powder coating operations involve the use of flammable materials, so fire prevention measures are paramount. Proper ventilation, spark-resistant flooring, and fire suppression systems are essential to mitigate potential fire hazards.
- Material Handling and Storage: Efficient material handling and storage systems ensure smooth operation and reduce the risk of spills or contamination. Conveyors, elevators, and dedicated storage areas are crucial for managing powder coating materials and substrates.
- Operator Safety and Comfort: The powder coating plant should be designed to prioritize operator safety and comfort. Proper ventilation, ergonomic workstations, and safety equipment are essential to protect workers from airborne particles and dust.
- Compliance with Regulations: Powder coating operations should comply with all applicable environmental and workplace safety regulations. This may involve obtaining permits, adhering to waste disposal guidelines, and implementing safety training programs.
- Future Expansion: The powder coating plant layout should allow for potential growth and expansion. This may include incorporating additional booths, ovens, or storage areas to accommodate increased production or product diversification.
Considering Automation and Technology
Integrating automation and advanced technology into the powder coating plant can further enhance efficiency and productivity. Automated powder application systems, robotic handling equipment, and digital monitoring systems can streamline operations and reduce labor requirements.
Conclusion
Powder coating plant design is a complex process that requires careful consideration of various factors, including production volume, substrate types, environmental regulations, and operator safety. By carefully designing the plant layout, implementing appropriate equipment, and adhering to safety guidelines, businesses can establish a powder coating operation that achieves high-quality finishes while maintaining a safe and efficient workflow.
Powder Coating Plant Design
Powder coating plant design involves a comprehensive approach to planning and arranging the equipment, processes, and facilities for efficient and effective powder coating production. The design process considers various factors, including production volume, workpiece size and shape, powder coating requirements, environmental regulations, and safety standards.
Key Stages of Powder Coating Plant Design
- Define Production Requirements: Clearly define the production volume, workpiece types, powder coating specifications, and desired finish characteristics.
- Layout Planning: Develop a layout plan that optimizes workflow, minimizes material handling, and ensures efficient movement of workpieces through the powder coating process.
- Equipment Selection: Select the appropriate powder coating equipment, including powder booth, powder coating gun, curing oven, and workpiece handling system, based on production requirements and workpiece specifications.
- Pretreatment System Design: Design a pretreatment system that effectively cleans, prepares, and primes the workpieces for optimal powder adhesion.
- Powder Recovery System Integration: Incorporate a powder recovery system to collect overspray and reuse powder, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
- Ventilation and Exhaust System Design: Design a ventilation and exhaust system to remove harmful fumes and VOCs from the powder coating process, ensuring a safe working environment.
- Control System Integration: Integrate a control system to monitor and regulate the powder coating process, ensuring consistent powder application, curing parameters, and workpiece handling.
- Safety Compliance: Ensure the plant design complies with all applicable safety standards, including electrical safety, fire safety, and personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements.
- Environmental Considerations: Minimize environmental impact by incorporating energy-efficient equipment, powder recovery systems, and wastewater treatment solutions.
- Future Expansion: Consider future production growth and potential process enhancements when designing the plant layout and equipment selection.
Considerations for Different Production Scales
- Small-Scale Production: For small-scale production, manual or semi-automatic powder coating systems may be sufficient, with a focus on versatility and ease of use.
- Medium-Scale Production: For medium-scale production, semi-automatic or automated powder coating systems may be appropriate, balancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- High-Volume Production: For high-volume production, fully automated powder coating systems are essential to maximize productivity, consistency, and labor efficiency.
Conclusion
Powder coating plant design is a strategic process that optimizes production efficiency, ensures product quality, and promotes environmental sustainability. By carefully considering production requirements, workpiece specifications, equipment selection, and safety regulations, manufacturers can establish a well-designed powder coating plant that meets their specific needs and delivers high-quality powder coated products.
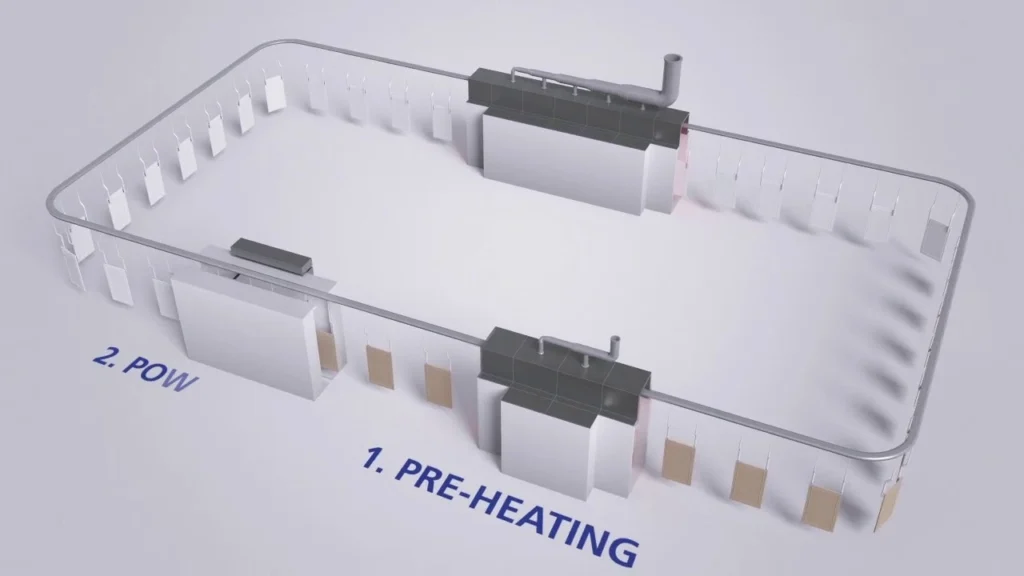
The powder coating plant design has the following elements:
The surface pretreatment of a powder coating plant design
The surface pretreatment of the powder coating plant layout is placed in the beginning part of the coating process. The chemical surface pretreatment is the first step on a powder spray conveyor line.

The powder coating pretreatment chemicals can either be acidic or alkaline. The acidic chemicals are more aggressive and they can damage the powder spray tanks if they were not manufactured with the proper material. We advise every customer a phosphate wash before powder coating for better surface quality.
Surface pretreatment is the first step in the powder coating process. It cleans and prepares the surface of the substrate to ensure that the powder coating adheres properly. There are many different surface pretreatment methods, but the most common are:
- Degreasing: This removes oils, grease, and other contaminants from the surface of the substrate.
- Blasting: This uses an abrasive material to remove rust, scale, and other imperfections from the surface of the substrate.
- Phosphate: This converts the surface of the substrate to a phosphate coating, which helps to improve the adhesion of the powder coating.
The specific surface pretreatment method that is used depends on the type of substrate being coated. For example, aluminum is typically degreased and blasted, while steel is typically phosphated.
Once the substrate has been pretreated, it is rinsed with water and dried. The dried substrate is then ready for powder coating.
Here are some of the benefits of surface pretreatment:
- Improved adhesion: Surface pretreatment helps to improve the adhesion of the powder coating to the substrate. This helps to prevent the powder coating from peeling or flaking off.
- Corrosion protection: Surface pretreatment can help to protect the substrate from corrosion. This is especially important for metals, such as steel and aluminum.
- Increased durability: Surface pretreatment can help to increase the durability of the powder coating. This makes the powder coating more resistant to scratches, chipping, and fading.
Overall, surface pretreatment is an important step in the powder coating process. It helps to ensure that the powder coating adheres properly, protects the substrate from corrosion, and increases the durability of the powder coating.
Here are some of the tips for choosing a surface pretreatment system:
- Consider the type of substrate being coated. Different substrates require different surface pretreatment methods.
- Consider the desired level of protection. Surface pretreatment can provide different levels of protection from corrosion and other damage.
- Consider the cost of the system. Surface pretreatment systems can range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars.
- Consider the ease of use of the system. Some surface pretreatment systems are easier to use than others.
Powder Coating Pretreatment Process
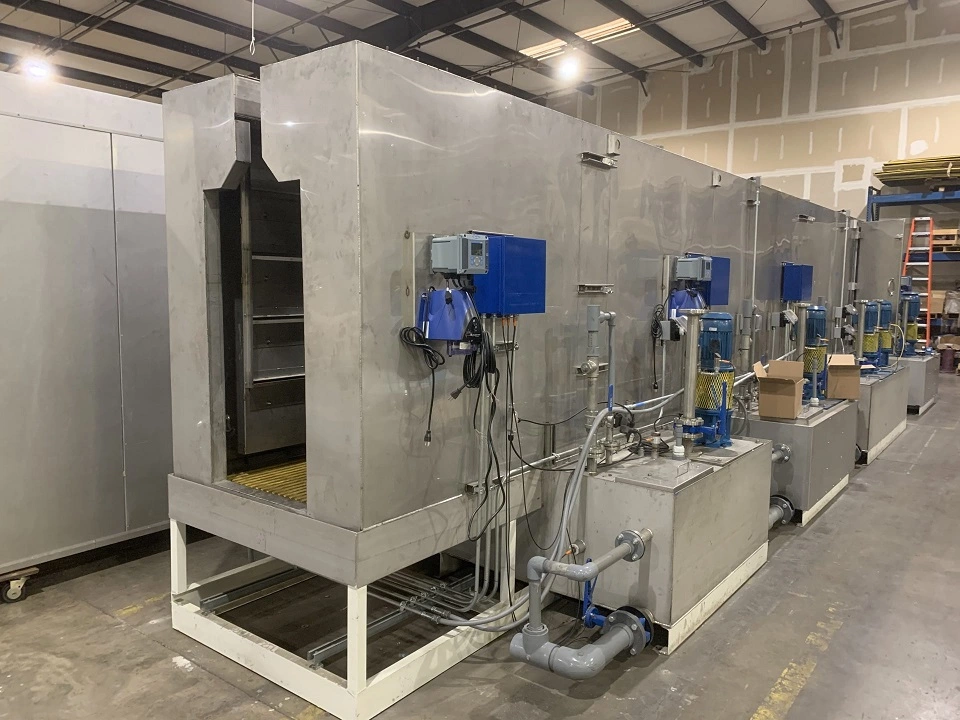

Powder coating pretreatment is a crucial stage in the powder coating process that ensures the proper adhesion of the powder coating to the substrate. It involves cleaning and preparing the surface to eliminate contaminants, imperfections, and surface oxides, creating a clean and uniform surface for the powder coating to adhere to effectively.
Surface Preparation Steps:
- Degreasing: The initial step involves removing any oils, grease, dirt, or other contaminants that could hinder the powder coating’s adhesion. This is typically achieved through solvent or electrolytic degreasing.
- Sanding or Abrasive Blasting: Abrasive blasting, such as grit blasting or soda blasting, removes rust, scale, and minor imperfections from the substrate’s surface. This creates a mechanically textured surface that provides better mechanical interlocking with the powder coating.
- Etching: Etching, using chemicals like phosphoric acid or hydrochloric acid, converts the surface of the substrate to a microscopically roughened state, further enhancing mechanical adherence of the powder coating.
- Water Rinse: Following each step, thorough rinsing with clean water removes any remaining contaminants or residues to prevent contamination of the powder coating.
- Drying: The substrate is then dried to remove any moisture or water droplets that could interfere with the powder coating’s flow and adhesion.
- Controlled Drying: Specialized drying chambers or ovens can optimize the drying process, ensuring that the substrate is completely dry and free from moisture before powder coating.
Pretreatment Significance:
- Adhesion: Proper surface preparation is essential for achieving strong adhesion between the powder coating and the substrate. This prevents the powder coating from peeling, cracking, or chipping over time.
- Corrosion Resistance: A well-pretreated surface provides a better foundation for the powder coating to adhere to, enhancing its corrosion resistance. This is particularly important for metals like steel or aluminum.
- Durability Enhancement: Surface preparation improves the overall durability of the powder coating, making it more resistant to scratches, chipping, and fading.
- Appearance Enhancement: A properly pretreated surface produces a smoother, more uniform appearance for the finished powder coating.
- Environmental Protection: Effective surface preparation minimizes the risk of contamination of the powder coating environment, ensuring the quality and consistency of the powder coating application.
Choosing the Right Pretreatment Method:
The specific pretreatment method depends on the type of substrate being coated. For instance, steel typically undergoes grit blasting or etching, while aluminum may require degreasing and phosphate conversion.
Safety Precautions:
- Respiratory Protection: Use appropriate respirators to protect against inhaling airborne particles and dust during blasting and drying.
- Eye Protection: Wear protective goggles or safety glasses to shield eyes from flying debris and contaminants.
- Avoid Flammable Materials: Powder coating operations involve flammable materials, so keep away from open flames or sparks.
- Handle Chemicals with Care: Handle chemicals used for etching or degreasing with care, following safety guidelines and using appropriate personal protective equipment.
- Regular Cleaning and Maintenance: Maintain equipment regularly to ensure proper functioning and prevent hazards.
- Training and Awareness: Provide adequate training and safety awareness to all personnel involved in the powder coating process.
By adhering to proper surface preparation and safety practices, powder coating applicators can ensure high-quality, durable, and aesthetically pleasing finishes that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
The powder coating pretreatment system can either be tunnel type or dipping type. The tunnel-type surface pretreatment needs a conveyor chain on or under the spray tunnel whereas the dipping-type tanks need a top crane to move the parts between the dipping tanks
No matter how you do, but a pretreatment before powder coating is vital.
Powder Coating Drying Oven
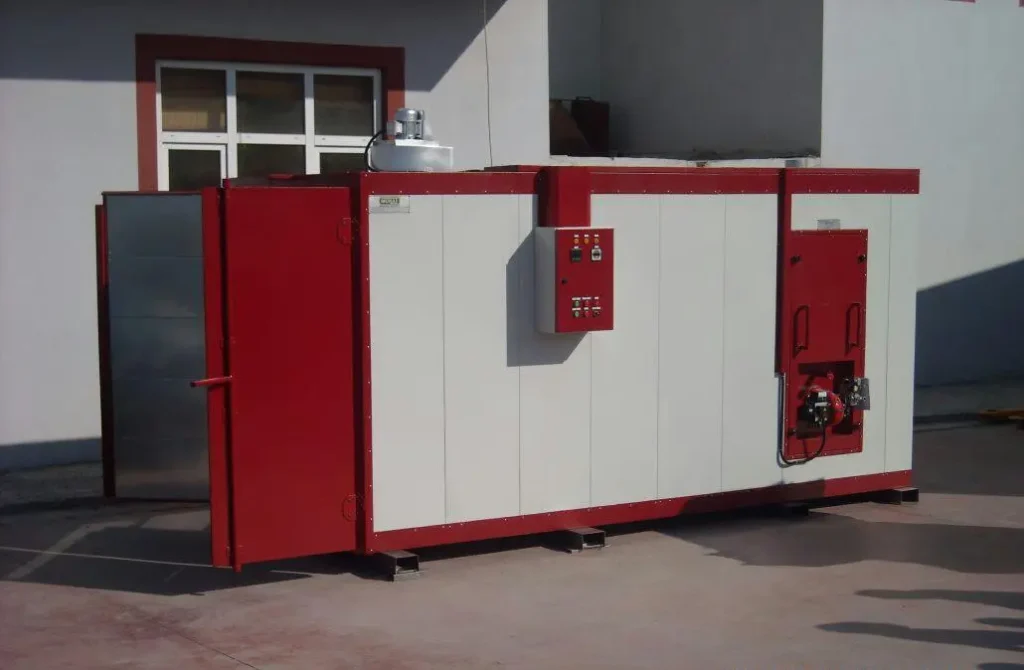

A powder coating drying oven is a specialized piece of equipment used to cure powder coating finishes on various objects. It provides a controlled environment with precise temperature, humidity, and air circulation to ensure the powder particles melt and fuse properly, resulting in a durable, long-lasting finish.
Key Components of a Powder Coating Drying Oven
- Heating System: The oven’s heating element generates heat to raise the temperature inside the chamber. Electric and gas are the most common heating sources.
- Air Circulation System: Adequate air circulation ensures even heat distribution throughout the oven chamber, preventing hot spots and ensuring proper cure of the powder coating.
- Temperature Controller: A precise temperature controller maintains the desired cure temperature throughout the curing cycle.
- Humidity Control: Controlling humidity levels is crucial for preventing premature curing and ensuring the powder coating fully cures at the specified temperature.
- Conveyor System (Optional): A conveyor system facilitates continuous batch processing, allowing for efficient handling of multiple items simultaneously.
Powder Coating Drying Oven Types
- Batch Ovens: These ovens hold a fixed number of workpieces and are typically used for smaller batches.
- Tunnel Ovens: These ovens continuously convey workpieces through the curing chamber, maximizing processing efficiency for larger batches.
- Infrared Ovens: These ovens utilize infrared radiation to heat the workpieces directly, resulting in faster curing times.
Applications of Powder Coating Drying Ovens
- Automotive Industry: Powder coating is widely used to protect and enhance the aesthetics of car parts, such as bumpers, spoilers, and wheels.
- Aerospace Industry: Powder coating provides excellent corrosion resistance and durability for aerospace components.
- Industrial Applications: Powder coating is used to protect and decorate a wide range of industrial equipment, tools, and machinery.
Safety Considerations
- Proper Ventilation: Powder coating ovens generate fumes and airborne particles that require adequate ventilation to protect workers from respiratory hazards.
- Temperature Control: Careful temperature control is essential to prevent burns and ensure the powder coating cures properly.
- Electrical Safety: Proper electrical grounding and safety precautions are crucial to prevent electrical hazards.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to ensure the oven functions safely and effectively.
The drying oven in the powder coating plant design is done either by a batch oven as indicated above or a tunnel-type drying oven, just as the surface pretreatment with a tunnel type. the same conveyor line moves through the surface pretreatment tunnels and carries the newly washed parts into the tunnel-type drying oven.
Powder Spray Booth Design
A powder spray booth is a controlled environment used to apply powder coating to metal or plastic objects. The booth is designed to capture and recycle overspray, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Key Components of a Powder Spray Booth
- Booth Enclosure: The booth enclosure provides a sealed environment to contain the overspray and direct it to the filtration system.
- Spray Guns: The spray guns apply the powder coating to the object being coated.
- Filtration System: The filtration system captures and removes overspray from the booth air, preventing it from escaping into the environment.
- Exhaustion System: The exhaustion system removes clean air from the booth, maintaining a negative pressure inside to prevent overspray from escaping.
- Powder Recovery System: The powder recovery system collects and reuses overspray, reducing waste and saving money.
Types of Powder Spray Booths
- Down Draft Booths: Down draft booths draw air downward, creating a dust cloud beneath the object being coated. This design is effective for capturing overspray from large objects.
- Side Draft Booths: Side draft booths draw air from the sides of the booth, creating a swirling airflow that captures overspray from all sides of the object being coated. This design is effective for smaller objects.
- Tunnel Booths: Tunnel booths are used for continuous coating of objects moving on a conveyor belt. The booth is enclosed with a tunnel-like structure that draws air from both sides and the top.
- Manual Booths: Manual booths are used for hand-held spray guns, typically for smaller objects or touch-ups.
- Automatic Booths: Automatic booths are integrated with robotic spray guns and conveyor systems for high-volume production.
Design Considerations for Powder Spray Booths
- Booth Size: The booth size should be adequate to accommodate the objects being coated while providing sufficient workspace for the operator.
- Airflow Velocity: The airflow velocity should be sufficient to capture overspray without disturbing the powder coating application.
- Filtration Efficiency: The filtration system should be designed to capture overspray particles of varying sizes, ensuring clean air is exhausted from the booth.
- Powder Recovery Efficiency: The powder recovery system should efficiently collect overspray for reuse, reducing waste and saving money.
- Safety Features: The booth should have safety features such as fire suppression systems, explosion-proof lighting, and emergency exits.
- Environmental Compliance: The booth should comply with local environmental regulations for air emissions and waste disposal.
The powder coating spray booth needs to be designed according to the actual situation on the spray line. If it is an automatic conveyor line, then the powder coat booth also needs to be an automatic one with openings on both sides for the reciprocators
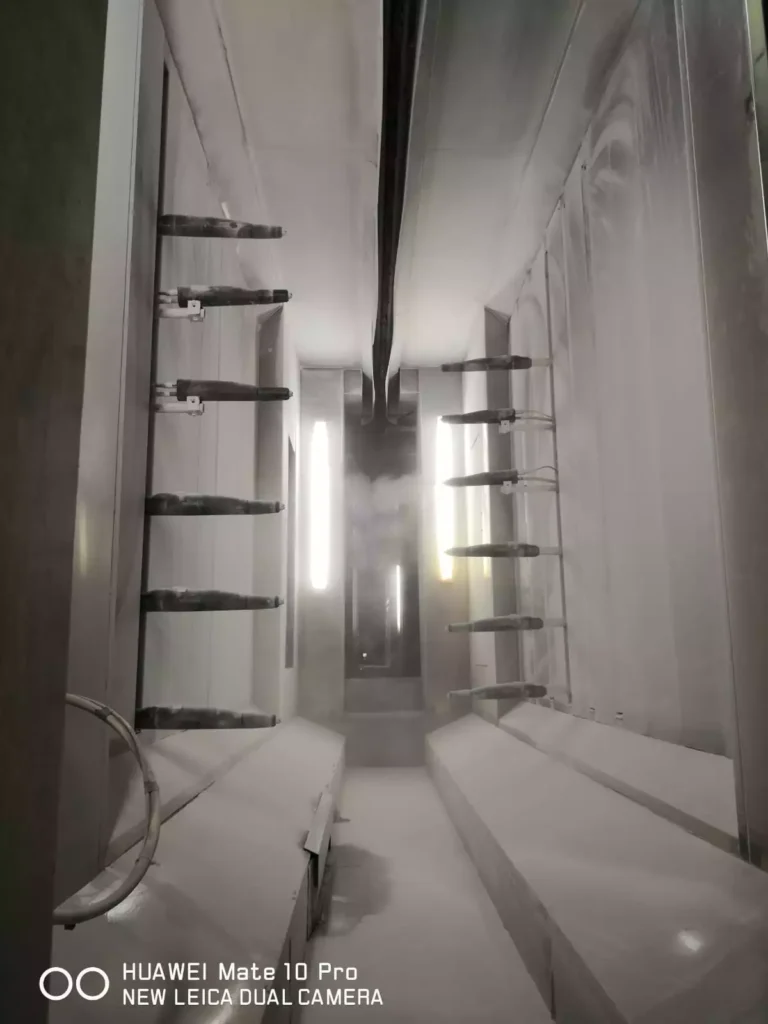

If it is a manual powder coating system, the booth can be a manual one with filters. We decide whether the line will be automatic or a manual one according to the coating capacity of the line.
Powder Coating: An In-Depth Guide to Equipment and Processes

Introduction
Powder coating is a popular finishing process used across various industries to apply a durable and protective layer to metal surfaces. Unlike traditional liquid paint, powder coating uses a dry powder that is electrostatically charged and applied to the surface, which is then cured in a high-temperature oven. This process results in a hard finish that is more resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading.
In this guide, we’ll explore the different components of a powder coating system, including ovens, machines, equipment, and entire production lines. Understanding these elements is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their production capabilities with powder coating technology.
Powder Coating Ovens

Definition and Purpose:
Powder coating ovens are essential for the curing process, where the powder adheres to the surface and forms a smooth, hard finish. These ovens provide the necessary heat to melt the powder, ensuring even and thorough coating.
Types of Powder Coating Ovens:
- Batch Ovens:
- Ideal for small to medium-sized production runs
- Flexibility to handle various part sizes
- Suitable for businesses with diverse product lines
- Conveyor Ovens:
- Designed for continuous production
- Higher throughput and efficiency
- Suitable for large-scale operations
Features and Specifications:
- Temperature Range: Typically between 325°F to 450°F
- Heating Source: Options include electric, gas, or infrared
- Size and Capacity: Varies based on production needs
- Energy Efficiency: Consider models with advanced insulation and airflow systems
How to Choose the Right Oven:
- Evaluate production volume and part sizes
- Consider energy consumption and operating costs
- Assess available space and installation requirements
- Consult with manufacturers for customized solutions
Powder Coating Machines
Overview of Different Machines Used:
Powder coating machines are used to apply the powder to the surface. They vary in complexity and functionality, catering to different production needs.
Manual vs. Automated Machines:
- Manual Machines:
- Suitable for small-scale operations
- Offers flexibility and control
- Requires skilled operators
- Automated Machines:
- Ideal for high-volume production
- Consistent and uniform application
- Reduced labor costs
Key Features and Specifications:
- Voltage and Power Requirements: Ensure compatibility with your facility
- Control Systems: Look for user-friendly interfaces and programmable settings
- Spray Gun Options: Different nozzles and gun types for various applications
Selecting the Right Machine for Your Needs:
- Determine the scale and complexity of your operations
- Evaluate budget constraints and long-term ROI
- Seek advice from industry experts and suppliers
Powder Coating Equipment
Essential Equipment for Powder Coating:
- Powder Coating Booths: Enclosed areas for applying powder
- Powder Recovery Systems: Capture and reuse overspray powder
- Air Compressors and Dryers: Ensure consistent airflow for optimal coating
Optional Equipment for Enhanced Performance:
- Pre-Treatment Systems: Clean and prepare surfaces before coating
- Curing Lamps: Speed up the curing process with infrared or UV lamps
Maintenance and Safety Considerations:
- Regularly inspect and clean equipment
- Train staff on proper handling and safety protocols
- Adhere to industry standards and regulations
Powder Coating Lines and Plants
Explanation of Powder Coating Lines:
Powder coating lines are integrated systems that automate the entire powder coating process, from pre-treatment to curing.
Components of a Powder Coating Line:
- Conveyor Systems: Move parts through the line efficiently
- Pre-Treatment Stations: Clean and prepare surfaces
- Powder Application Booths: Enclosed areas for powder coating
- Curing Ovens: Finalize the coating process
Design and Layout Considerations:
- Optimize workflow and space utilization
- Consider future scalability and expansion
- Ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations
Scalability and Customization Options:
- Modular designs for easy expansion
- Custom configurations to meet specific production needs
Benefits of Powder Coating
Environmental Advantages:
- Low VOC emissions compared to liquid paints
- Overspray can be recycled, reducing waste
- Complies with environmental regulations
Durability and Longevity:
- Resistant to corrosion, fading, and wear
- Suitable for outdoor and high-traffic applications
- Provides a high-quality, professional finish
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Reduces long-term maintenance and repainting costs
- Efficient use of materials minimizes waste
- High throughput and automation lower labor expenses
Considerations for Setting Up a Powder Coating Plant
Initial Investment and ROI:
- Assess capital requirements for equipment and infrastructure
- Calculate potential returns based on production capacity and demand
- Explore financing options and incentives
Regulatory Compliance:
- Adhere to industry standards and local regulations
- Implement safety protocols and employee training
- Monitor environmental impact and waste management
Market Trends and Future Outlook:
- Growing demand for eco-friendly coatings
- Advancements in automation and technology
- Increasing adoption in automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods sectors
Conclusion
Powder coating offers numerous advantages over traditional liquid painting methods, making it an attractive option for industries seeking durable and environmentally friendly finishes. By investing in the right equipment and understanding the intricacies of powder coating processes, businesses can enhance their production capabilities and meet the growing demand for high-quality coated products.
When setting up a powder coating plant, it’s essential to carefully consider your needs, budget, and long-term goals. Collaborating with experienced suppliers and industry experts can help you make informed decisions and achieve success in the competitive world of powder coating.
This comprehensive guide should provide valuable insights for your website visitors and help position your business as a knowledgeable and reliable source in the powder coating industry.
Installation process steps
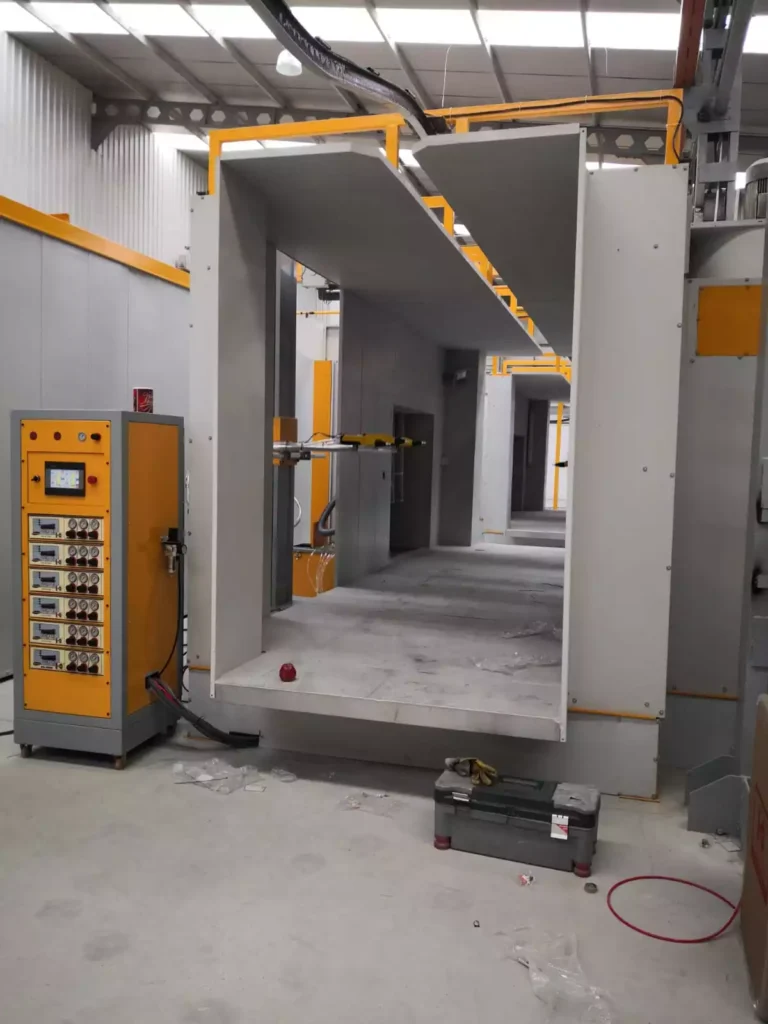

To provide a comprehensive guide on the installation process for powder coating systems, we’ll cover each step involved in setting up a powder coating plant. This includes planning, selecting equipment, site preparation, installation, testing, and staff training. Here’s a detailed outline and content for this section:
Outline for Installation Process Steps
- Planning and Design
- Assessing needs and capacity
- Layout and design considerations
- Budget and timeline
- Equipment Selection
- Choosing the right ovens, machines, and equipment
- Consulting with manufacturers and suppliers
- Site Preparation
- Preparing the facility for installation
- Ensuring compliance with regulations
- Installation Process
- Step-by-step installation guide
- Safety protocols and considerations
- System Testing and Calibration
- Testing each component
- Ensuring optimal performance
- Training and Support
- Staff training on operation and safety
- Ongoing maintenance and support
- Post-Installation Considerations
- Regular inspections and maintenance
- Upgrades and scalability
Installation Process Steps for Powder Coating Systems

Setting up a powder coating plant involves careful planning and execution to ensure a successful installation. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
1. Planning and Design
Assessing Needs and Capacity:
- Identify Production Requirements: Determine the types and sizes of parts you will be coating, and estimate your production volume.
- Analyze Workflow: Consider how materials will move through the plant, from pre-treatment to curing.
- Evaluate Space Requirements: Ensure adequate space for equipment, storage, and workflow efficiency.
Layout and Design Considerations:
- Optimize Workflow: Design a layout that minimizes bottlenecks and maximizes efficiency.
- Future Scalability: Plan for potential expansion or upgrades.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Ensure the layout meets all safety and regulatory requirements.
Budget and Timeline:
- Create a Detailed Budget: Account for equipment, installation, training, and operational costs.
- Establish a Timeline: Set realistic milestones for each phase of the installation process.
2. Equipment Selection
Choosing the Right Ovens, Machines, and Equipment:
- Powder Coating Ovens: Select between batch or conveyor ovens based on production needs.
- Powder Coating Machines: Choose manual or automated systems that match your operational scale.
- Additional Equipment: Consider powder booths, recovery systems, and pre-treatment stations.
Consulting with Manufacturers and Suppliers:
- Leverage Expertise: Work with manufacturers to choose equipment tailored to your specific requirements.
- Request Demonstrations: Evaluate equipment performance through demos or site visits.
- Negotiate Contracts: Ensure favorable terms and warranties with suppliers.
3. Site Preparation
Preparing the Facility for Installation:
- Infrastructure Readiness: Ensure adequate power supply, ventilation, and environmental controls.
- Space Optimization: Clear and organize the installation area for easy access and efficient workflow.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations:
- Local Permits and Licenses: Obtain necessary permits and ensure compliance with zoning regulations.
- Safety Standards: Adhere to occupational health and safety standards.
4. Installation Process
Step-by-Step Installation Guide:
- Site Inspection: Conduct a final inspection of the site to verify readiness.
- Delivery and Unpacking: Receive and unpack equipment carefully, checking for any damage.
- Positioning Equipment: Install each piece of equipment according to the layout plan.
- Electrical and Plumbing Connections: Ensure all electrical and plumbing connections are correctly made and tested.
- Calibration and Setup: Configure equipment settings and calibrate machinery to specifications.
Safety Protocols and Considerations:
- Install Safety Features: Implement necessary safety features such as emergency stops and protective barriers.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensure that all personnel have access to required PPE.
5. System Testing and Calibration
Testing Each Component:
- Conduct Trial Runs: Test each component individually and as part of the integrated system.
- Check for Performance Issues: Identify and resolve any performance or operational issues.
Ensuring Optimal Performance:
- Fine-Tune Settings: Adjust equipment settings for optimal coating quality.
- Document Results: Record all testing results and adjustments for future reference.
6. Training and Support
Staff Training on Operation and Safety:
- Conduct Training Sessions: Provide comprehensive training on equipment operation and safety protocols.
- Create Training Materials: Develop manuals and guides for ongoing staff reference.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support:
- Establish a Maintenance Schedule: Set up regular maintenance checks to ensure equipment longevity.
- Vendor Support: Engage with suppliers for ongoing support and troubleshooting.
7. Post-Installation Considerations
Regular Inspections and Maintenance:
- Implement Routine Inspections: Regularly inspect equipment and systems for wear and tear.
- Schedule Maintenance: Adhere to the maintenance schedule to prevent downtime and extend equipment life.
Upgrades and Scalability:
- Monitor Technological Advancements: Stay informed about new technologies and equipment improvements.
- Plan for Upgrades: Budget for future upgrades and expansion as business needs grow.
Conclusion
The installation of a powder coating system is a multi-step process that requires meticulous planning and execution. By following these steps, businesses can ensure a smooth setup and operation, maximizing efficiency and product quality. It’s crucial to work closely with experienced manufacturers and suppliers to tailor the installation process to your specific needs and to provide ongoing training and support for staff.
Installation cost estimate
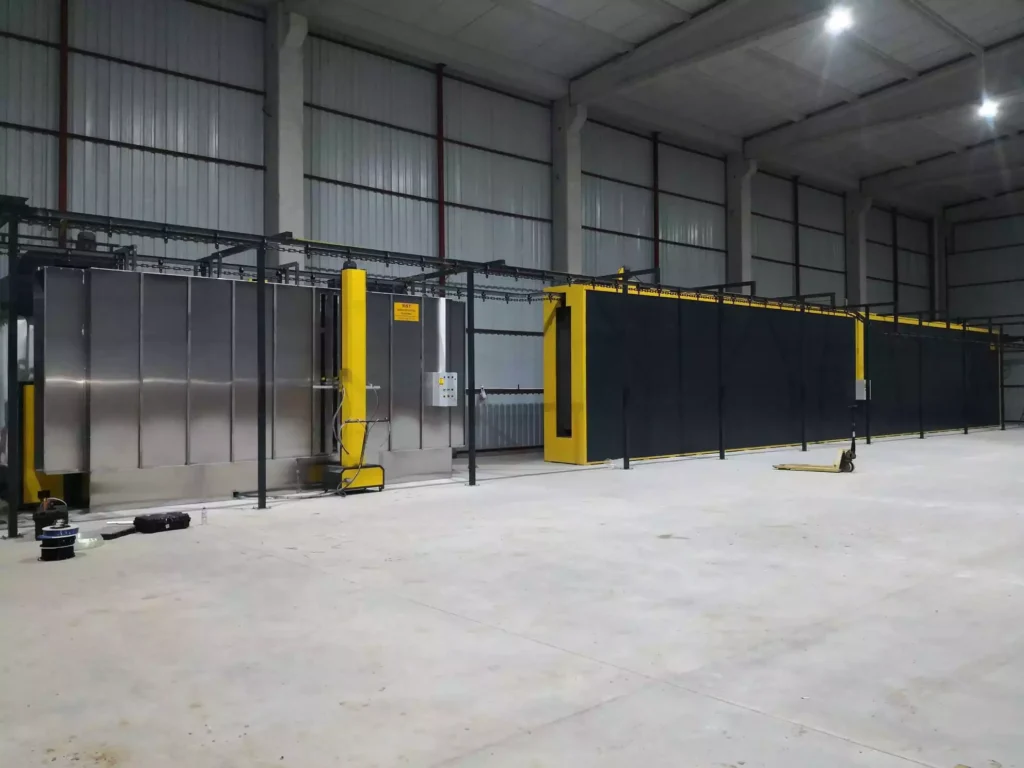

Estimating the installation cost of a powder coating system involves considering various factors, such as the size of the operation, the type of equipment, facility modifications, labor, and additional costs like permits and training. Here’s a detailed breakdown to help you understand the potential costs involved in setting up a powder coating plant.
Installation Cost Estimate for Powder Coating Systems
Factors Influencing Costs
- Type of Equipment and Technology
- Powder coating ovens (batch vs. conveyor)
- Coating machines (manual vs. automated)
- Auxiliary equipment (booths, recovery systems, pre-treatment stations)
- Scale and Capacity of the Operation
- Production volume
- Facility size and space requirements
- Facility Modifications
- Infrastructure updates (electrical, ventilation, plumbing)
- Space optimization and layout design
- Labor and Installation Services
- Skilled labor for installation
- Equipment calibration and testing
- Additional Costs
- Permits and regulatory compliance
- Staff training and support
- Maintenance and contingency expenses
Estimated Costs
Below is a general estimate of the costs associated with installing a powder coating system. Note that prices can vary significantly based on location, vendor, and specific requirements.
1. Equipment Costs
- Powder Coating Ovens:
- Batch Ovens: $1,000 – $50,000
- Conveyor Ovens: $10,000 – $200,000
- Powder Coating Machines:
- Manual Machines: $1,000 – $20,000
- Automated Systems: $20,000 – $100,000
- Auxiliary Equipment:
- Powder Booths: $2,000 – $30,000
- Recovery Systems: $3,000 – $15,000
- Pre-Treatment Systems: $10,000 – $50,000
2. Facility Modifications
- Electrical and Ventilation Upgrades: $10,000 – $50,000
- Space Optimization and Layout Design: $5,000 – $20,000
3. Labor and Installation Services
- Installation Labor: $10,000 – $30,000
- Calibration and Testing: $5,000 – $10,000
4. Additional Costs
- Permits and Compliance: $2,000 – $10,000
- Training and Support: $2,000 – $5,000
- Maintenance and Contingency: $5,000 – $15,000
Total Estimated Cost
The total estimated cost for installing a powder coating system can range from $70,000 to $500,000, depending on the size, complexity, and specific requirements of the operation. Here’s a breakdown by scale:
- Small-Scale Operations: $20,000 – $50,000
- Medium-Scale Operations: $50,000 – $100,000
- Large-Scale Operations: $100,000 – $500,000
Tips for Cost Management
- Conduct a Detailed Assessment:
- Evaluate your specific needs and choose equipment accordingly.
- Consider future scalability to avoid unnecessary upgrades later.
- Get Multiple Quotes:
- Request quotes from multiple vendors to compare prices and services.
- Negotiate terms and warranties to get the best deal.
- Plan for Contingencies:
- Set aside a contingency budget for unexpected expenses during installation.
- Regularly review and adjust your budget as the project progresses.
- Focus on Energy Efficiency:
- Invest in energy-efficient equipment to reduce long-term operational costs.
- Evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI) for each piece of equipment.
- Leverage Financing Options:
- Explore financing options, grants, or incentives available for industrial upgrades.
Conclusion
Setting up a powder coating plant requires a significant investment, but careful planning and strategic decision-making can help manage costs effectively. By considering your specific needs, working with experienced suppliers, and planning for the future, you can ensure a successful installation and operation of your powder coating system.
Let me know if you need further details or specific cost estimates tailored to your project!
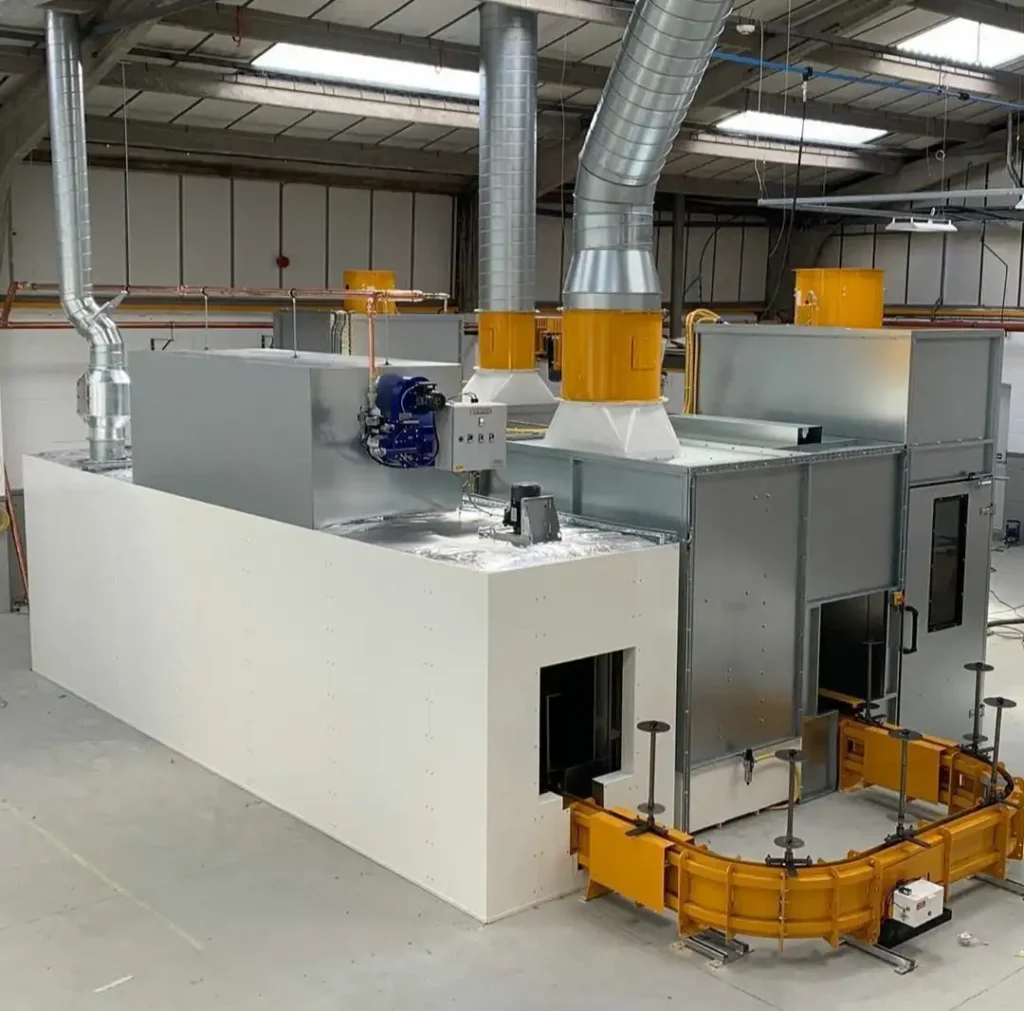
Components of a Powder Coating Plant

A powder coating plant consists of various components that work together to facilitate the coating process, from preparation to application and curing. Understanding these components is crucial for designing an efficient and effective system tailored to specific production needs. Below is a detailed overview of the key components of a powder coating plant:
Key Components of a Powder Coating Plant
- Pre-Treatment System
- Purpose: Cleans and prepares surfaces for powder coating to ensure adhesion and finish quality.
- Components:
- Washing Stations: Use chemical solutions to remove contaminants like grease, oil, dirt, and rust.
- Rinse Stations: Remove residual chemicals from the surface.
- Drying Ovens: Dry the parts after washing and rinsing to prepare them for powder application.
- Powder Coating Booths
- Purpose: Enclosed area where the powder is applied to the parts.
- Types:
- Manual Booths: Operators manually apply powder using spray guns. Ideal for small or custom jobs.
- Automatic Booths: Equipped with automated spray guns and reciprocators for high-volume production.
- Features:
- Ventilation Systems: Ensure proper airflow to capture overspray and maintain a clean environment.
- Powder Recovery Systems: Collect overspray powder for reuse, improving material efficiency.
- Powder Application Equipment
- Purpose: Applies the powder to the surfaces using electrostatic spray guns.
- Components:
- Electrostatic Spray Guns: Charge the powder particles and spray them onto the grounded parts.
- Control Units: Adjust settings like voltage, powder flow rate, and air pressure to ensure uniform coverage.
- Conveyor System
- Purpose: Transports parts through various stages of the powder coating process.
- Types:
- Overhead Conveyors: Hang parts from hooks or racks for continuous production.
- Floor Conveyors: Suitable for heavier or larger parts that cannot be suspended.
- Features:
- Variable Speed Control: Adjusts the speed of the conveyor to match production needs and curing times.
- Loading and Unloading Stations: Facilitate the movement of parts onto and off the conveyor system.
- Powder Coating Ovens
- Purpose: Cures the powder coating by melting and fusing it to the surface, forming a durable finish.
- Types:
- Batch Ovens: Suitable for smaller production runs and varied part sizes.
- Conveyor Ovens: Designed for continuous, high-volume production.
- Features:
- Temperature Control Systems: Ensure precise and consistent heating for optimal curing.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporate insulation and heat recovery systems to minimize energy consumption.
- Cooling and Inspection Stations
- Purpose: Cool the parts after curing and inspect them for quality assurance.
- Components:
- Cooling Zones: Allow parts to cool gradually to avoid warping or defects.
- Inspection Areas: Check for coating consistency, thickness, and finish quality before packaging or assembly.
- Control and Monitoring Systems
- Purpose: Manage and monitor the entire powder coating process for efficiency and quality control.
- Components:
- PLC Systems (Programmable Logic Controllers): Automate and synchronize various plant operations.
- Data Logging and Analysis Tools: Record production metrics and identify areas for improvement.
- Safety and Environmental Controls
- Purpose: Ensure the safety of workers and compliance with environmental regulations.
- Components:
- Fire Suppression Systems: Protect against powder fires or explosions in booths and ovens.
- Ventilation and Filtration Systems: Maintain air quality by removing dust, fumes, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide workers with necessary safety gear, such as masks, gloves, and goggles.
Optional and Auxiliary Components
- Advanced Pre-Treatment Systems: Utilize additional technologies like ultrasonic cleaning or nanotechnology for improved surface preparation.
- Curing Lamps: Use infrared or UV lamps for faster curing times and energy savings.
- Automated Robotic Systems: Enhance precision and efficiency in powder application and handling.
- Quality Control Instruments: Use advanced tools like thickness gauges, gloss meters, and adhesion testers for detailed quality assessment.
Layout and Design Considerations
- Workflow Optimization: Design the plant layout to minimize bottlenecks and ensure smooth transitions between stages.
- Space Utilization: Efficiently allocate space for equipment, storage, and movement of materials.
- Scalability: Plan for future expansion or upgrades to accommodate growing production demands.
Conclusion
A well-designed powder coating plant integrates these components to create an efficient, high-quality coating process. Understanding each element and its role in the system is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their powder coating capabilities. By investing in the right equipment and technology, companies can achieve superior finishes, increased productivity, and long-term success in the powder coating industry.
Detailed Components of a Powder Coating Plant
Certainly! To provide a detailed understanding of each component within a powder coating plant, we’ll delve into the technical specifications, functions, types, and key considerations for each element. This comprehensive breakdown will cover everything from the initial pre-treatment to the final inspection.
1. Pre-Treatment System
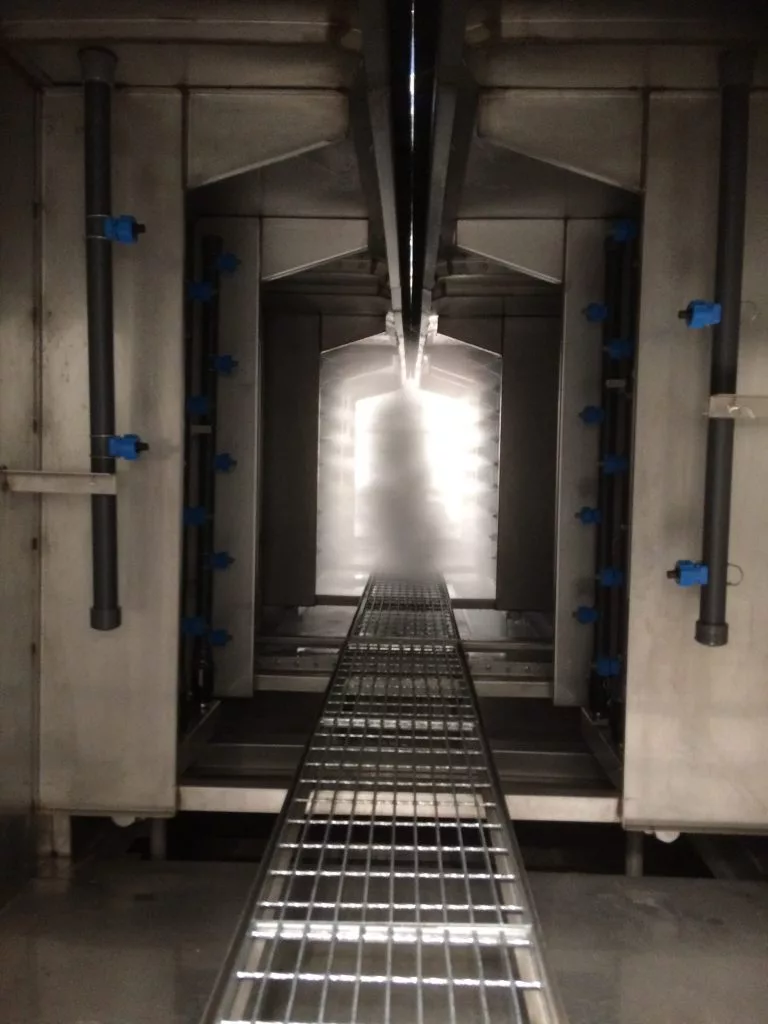

Overview
The pre-treatment system is crucial in ensuring that surfaces are properly cleaned and prepared for powder coating. This step enhances adhesion, improves finish quality, and increases the longevity of the coating.
Components and Process
1.1. Cleaning and Degreasing Stations
- Purpose: Remove oils, grease, and other contaminants from the surface.
- Methods:
- Alkaline Cleaning: Uses alkaline solutions to break down grease and oils.
- Solvent Cleaning: Employs organic solvents to dissolve contaminants.
- Ultrasonic Cleaning: Utilizes high-frequency sound waves for deep cleaning, especially effective for complex shapes.
- Equipment:
- Tanks and spray systems
- Heating elements to improve cleaning efficiency
- Agitation systems for even cleaning
1.2. Rinse Stations
- Purpose: Eliminate residual chemicals and contaminants from the cleaning stage.
- Types of Rinse:
- Freshwater Rinse: Basic water rinse to remove chemicals.
- Deionized Water Rinse: Prevents mineral deposits and spots on surfaces.
- Equipment:
- Spray bars and nozzles for thorough rinsing
- Closed-loop systems to recycle water and reduce waste
1.3. Surface Conditioning
- Purpose: Prepare the surface for subsequent conversion coating.
- Processes:
- Acid Etching: Removes oxides and prepares metal surfaces.
- Descaling: Removes scale and rust from the surface.
- Equipment:
- Immersion tanks or spray booths
- Automated dosing systems for precise chemical application
1.4. Conversion Coating
- Purpose: Apply a chemical layer that enhances powder adhesion and corrosion resistance.
- Types:
- Phosphate Coating: Iron or zinc phosphate for steel surfaces.
- Chromate Coating: Used for aluminum and zinc surfaces.
- Nano-Ceramic Coatings: Environmentally friendly option with superior adhesion and corrosion resistance.
- Equipment:
- Spray or immersion systems
- Temperature control for optimal reaction conditions
1.5. Drying Ovens
- Purpose: Remove moisture from parts to prevent defects in the powder coating.
- Features:
- Adjustable temperature settings
- Air circulation systems for even drying
- Equipment:
- Batch ovens for smaller production
- Conveyor ovens for continuous processing
Key Considerations
- Chemical Management: Ensure proper handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals used in pre-treatment.
- Environmental Compliance: Adhere to local regulations for effluent discharge and waste management.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and inspection of tanks and nozzles to prevent contamination.
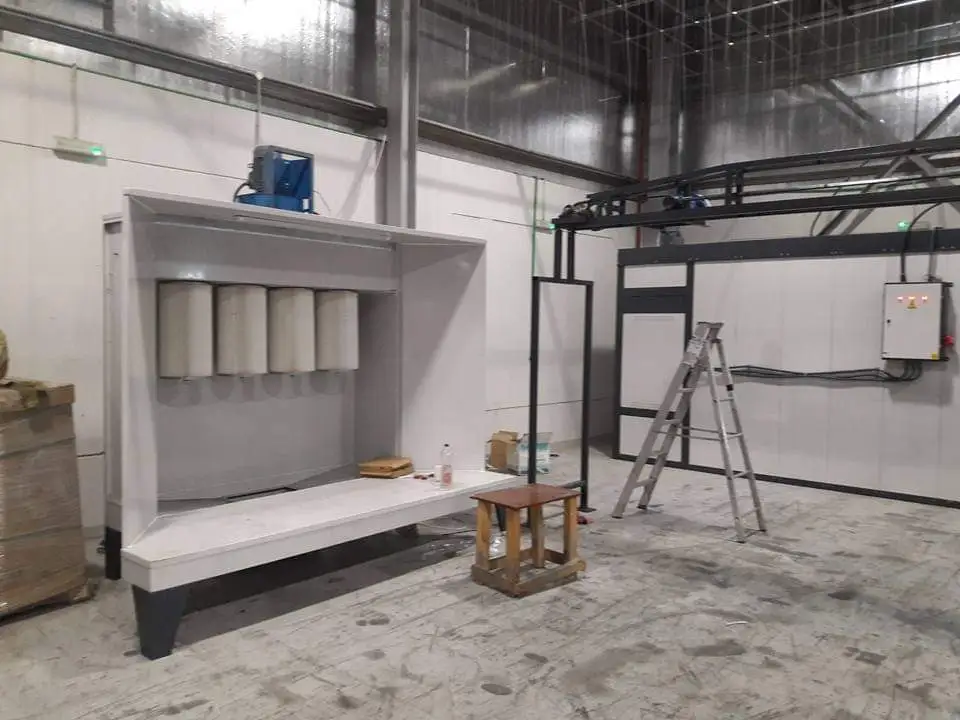
2. Powder Coating Booths

Overview
Powder coating booths provide a controlled environment for applying the powder. They ensure that the powder is applied evenly and that any overspray is efficiently managed and collected for reuse.
Types and Features
2.1. Manual Powder Coating Booths
- Purpose: Allow operators to manually apply powder using handheld spray guns.
- Applications: Suitable for small batches, custom jobs, and intricate parts.
- Features:
- Ventilation Systems: Maintain air quality and remove overspray.
- Lighting: Ensure visibility for precise application.
- Ergonomic Design: Facilitate operator comfort and efficiency.
2.2. Automatic Powder Coating Booths
- Purpose: Use automated systems to apply powder to parts, ideal for high-volume production.
- Applications: Suitable for standard parts and large-scale operations.
- Features:
- Robotic Arms and Reciprocators: Ensure consistent application across parts.
- Programmable Settings: Customize application parameters for different parts.
- Rapid Color Change Systems: Allow quick and efficient color changes with minimal downtime.
2.3. Powder Recovery Systems
- Purpose: Capture and recycle overspray powder to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
- Types:
- Cyclone Separators: Use centrifugal force to separate powder from the air.
- Cartridge Filters: Trap fine powder particles for reuse.
- Baghouse Filters: Employ fabric bags to capture powder, suitable for larger particles.
Key Considerations
- Airflow Management: Ensure proper ventilation to prevent contamination and maintain a clean environment.
- Color Change Efficiency: Invest in systems that allow quick and easy color changes to minimize downtime.
- Safety: Implement explosion-proof designs and fire suppression systems to prevent hazards.
3. Powder Application Equipment
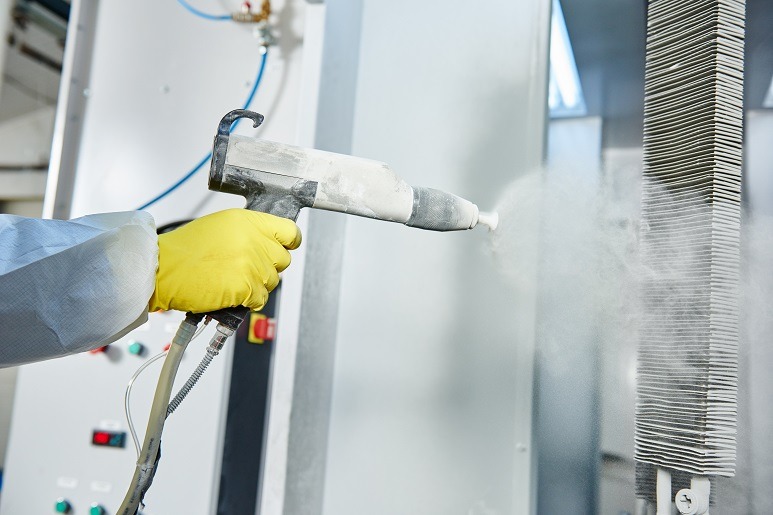

Overview
Powder application equipment is responsible for applying the powder coating to the parts. This equipment uses electrostatic principles to ensure uniform coverage and strong adhesion.
Components and Features
3.1. Electrostatic Spray Guns
- Purpose: Apply powder to the parts using an electrostatic charge.
- Types:
- Corona Guns: Use a high-voltage electrode to charge the powder.
- Tribo Guns: Charge the powder through friction, suitable for specific applications.
- Features:
- Adjustable Voltage and Current: Control the electrostatic charge for optimal coverage.
- Interchangeable Nozzles: Provide different spray patterns for various applications.
- Lightweight and Ergonomic Design: Ensure operator comfort during manual application.
3.2. Control Units
- Purpose: Manage and adjust the settings of the powder application equipment.
- Features:
- Digital Displays: Provide real-time feedback on settings and performance.
- Programmable Settings: Allow customization for different parts and powder types.
- Data Logging: Record application parameters for quality control and traceability.
3.3. Fluidized Bed Systems
- Purpose: Coat parts by dipping them into a bed of fluidized powder, typically used for thicker coatings.
- Applications: Suitable for specific applications requiring a thick and even coating.
- Features:
- Uniform Airflow: Ensure consistent fluidization of powder particles.
- Temperature Control: Maintain optimal conditions for coating.
Key Considerations
- Powder Compatibility: Ensure equipment is compatible with different powder formulations.
- Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training for operators to ensure efficient and safe use.
- Maintenance: Regularly clean and maintain spray guns and control units to prevent clogging and ensure consistent performance.
4. Conveyor System

Overview
The conveyor system is the backbone of the powder coating plant, transporting parts through each stage of the process, from pre-treatment to curing.
Types and Features
4.1. Overhead Conveyors
- Purpose: Transport parts by suspending them from hooks or racks, ideal for continuous production.
- Types:
- Monorail Systems: Simple looped tracks for straightforward applications.
- Power and Free Systems: Offer more flexibility with multiple paths and stopping points.
- Features:
- Variable Speed Control: Adjust the speed to match production needs and curing times.
- Load Capacity: Designed to handle different part sizes and weights.
- Integration with Other Systems: Seamlessly integrate with pre-treatment, application, and curing systems.
4.2. Floor Conveyors
- Purpose: Transport heavier or larger parts that cannot be suspended, suitable for specific applications.
- Types:
- Belt Conveyors: Use belts to move parts horizontally or on an incline.
- Roller Conveyors: Employ rollers to facilitate the movement of parts.
- Features:
- Heavy-Duty Construction: Designed to support large or heavy parts.
- Customizable Configurations: Adapt to different plant layouts and processes.
Key Considerations
- Layout Design: Plan the conveyor layout to optimize workflow and minimize bottlenecks.
- Load and Speed Requirements: Ensure the conveyor system meets production demands for speed and capacity.
- Safety Features: Implement safety measures such as guards, emergency stops, and regular inspections.
5. Powder Coating Ovens
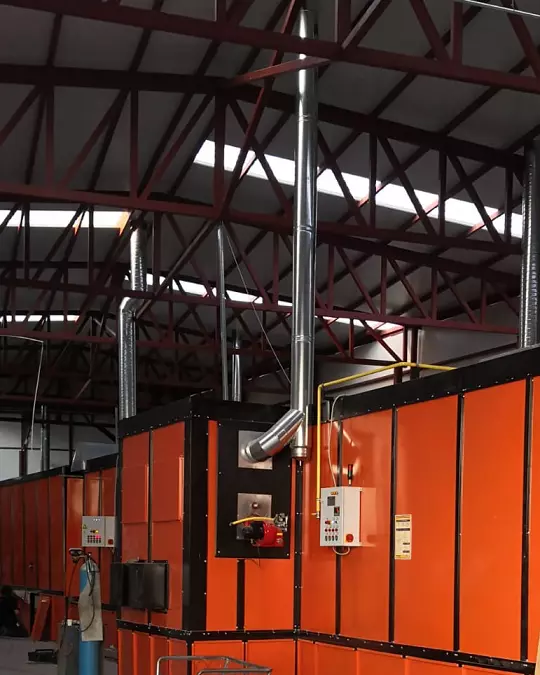

Overview
Powder coating ovens are responsible for curing the powder coating by melting and fusing it to the surface, resulting in a durable and attractive finish.
Types and Features
5.1. Batch Ovens
- Purpose: Cure parts in small batches, suitable for varied part sizes and low-volume production.
- Applications: Ideal for custom jobs, small businesses, and prototyping.
- Features:
- Adjustable Temperature Control: Precise control of curing conditions.
- Flexible Configuration: Accommodate different part sizes and shapes.
- Insulated Construction: Minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency.
5.2. Conveyor Ovens
- Purpose: Designed for continuous production, curing parts as they move through the oven.
- Applications: Suitable for high-volume production and standardized parts.
- Features:
- Consistent Temperature Distribution: Ensure even curing across all parts.
- Variable Conveyor Speed: Match curing times with production speed.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporate heat recovery systems and advanced insulation.
Key Considerations
- Oven Size and Capacity: Choose an oven that meets production demands without excessive energy use.
- Heating Source: Decide between electric, gas, or infrared heating based on cost and efficiency.
- Temperature Uniformity: Ensure consistent heat distribution to prevent defects in the finish.
6. Cooling and Inspection Stations
Overview
Cooling and inspection stations are crucial for ensuring the quality and consistency of the finished products. Cooling prevents defects, while inspection verifies the coating quality.
Components and Features
6.1. Cooling Zones
- Purpose: Gradually cool parts after curing to prevent warping or defects.
- Features:
- Controlled Airflow: Ensure even cooling and avoid thermal shock.
- Adjustable Cooling Rates: Customize settings for different materials and part sizes.
6.2. Inspection Areas
- Purpose: Conduct quality checks on coated parts to ensure consistency and adherence to standards.
- Features:
- Lighting and Magnification: Facilitate detailed visual inspections.
- Measurement Tools: Use instruments like thickness gauges and gloss meters for precise evaluation.
- Defect Detection Systems: Implement automated systems for detecting coating defects, such as thin spots or uneven coverage.
Key Considerations
- Quality Assurance Protocols: Establish standards and procedures for inspections to ensure consistent product quality.
- Training for Inspectors: Provide training to staff on recognizing defects and using inspection tools effectively.
- Feedback Loop: Use inspection data to inform process improvements and address recurring issues.
7. Control and Monitoring Systems

Overview
Control and monitoring systems automate and synchronize various plant operations, ensuring efficiency, consistency, and quality in the powder coating process.
Components and Features
7.1. PLC Systems (Programmable Logic Controllers)
- Purpose: Automate and control equipment functions throughout the plant.
- Features:
- Centralized Control: Manage multiple systems from a single interface.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Track performance metrics and adjust settings as needed.
- Data Logging: Record operational data for analysis and process optimization.
7.2. Data Logging and Analysis Tools
- Purpose: Collect and analyze production data to improve efficiency and quality.
- Features:
- Trend Analysis: Identify patterns and trends in production metrics.
- Performance Dashboards: Visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) for easy monitoring.
- Predictive Maintenance: Use data to anticipate equipment maintenance needs and prevent downtime.
Key Considerations
- System Integration: Ensure seamless integration with existing equipment and software.
- User Interface: Provide intuitive and user-friendly interfaces for operators.
- Cybersecurity: Implement security measures to protect sensitive data and control systems.
8. Safety and Environmental Controls
Overview
Safety and environmental controls are essential for protecting workers and ensuring compliance with regulations. These systems manage hazards and minimize environmental impact.
Components and Features
8.1. Fire Suppression Systems
- Purpose: Prevent and control powder fires or explosions in booths and ovens.
- Features:
- Automatic Detection and Suppression: Quickly identify and extinguish fires.
- Integration with Control Systems: Automatically shut down equipment in case of fire.
- Regular Testing and Maintenance: Ensure systems are operational and compliant with safety standards.
8.2. Ventilation and Filtration Systems
- Purpose: Maintain air quality by removing dust, fumes, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Features:
- High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Filters: Capture fine particles and contaminants.
- Exhaust Fans and Ductwork: Ensure proper airflow and ventilation.
- Regular Filter Replacement: Maintain efficiency and prevent clogs.
8.3. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Purpose: Provide workers with necessary safety gear to protect against hazards.
- Components:
- Respirators and Masks: Protect against inhalation of powder particles and fumes.
- Safety Glasses and Goggles: Shield eyes from dust and chemical splashes.
- Gloves and Protective Clothing: Prevent skin contact with chemicals and powders.
Key Considerations
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to local and international safety and environmental standards.
- Safety Training: Conduct regular training sessions on safety protocols and emergency procedures.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update safety measures to address emerging risks and regulations.
Conclusion
Each component of a powder coating plant plays a vital role in ensuring a successful and efficient coating process. By understanding the details and functions of these components, businesses can design and operate a plant that meets their specific needs and production goals. Investing in the right equipment and systems, along with proper training and maintenance, will lead to high-quality finishes, increased productivity, and long-term success in the powder coating industry.
Installation time estimate
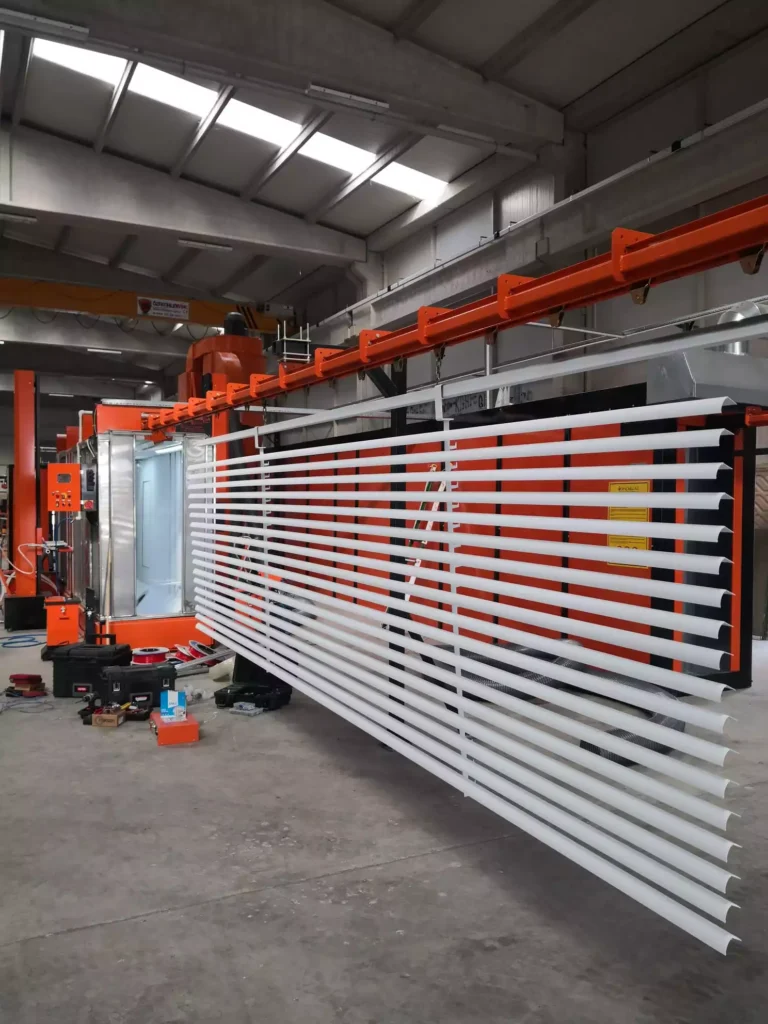

Estimating the installation time for a powder coating plant involves considering several factors such as the size of the operation, complexity of the equipment, facility preparation, and the efficiency of the installation team. Below is a detailed breakdown of the installation time estimate, including factors that can influence the timeline and strategies to ensure a smooth installation process.
Installation Time Estimate for a Powder Coating Plant
Factors Influencing Installation Time
- Scale and Complexity of the Plant
- Size and layout of the facility
- Number and type of equipment components
- Type of Equipment
- Manual vs. automated systems
- Batch vs. continuous production lines
- Site Preparation
- Existing infrastructure readiness
- Facility modifications needed
- Installation Team and Expertise
- Experience and skills of the installation crew
- Availability of necessary resources and tools
- Regulatory Compliance and Inspections
- Time required for permits and approvals
- Safety inspections and certifications
- Coordination and Scheduling
- Coordination between vendors, contractors, and stakeholders
- Availability of equipment and personnel
Estimated Installation Time by Component
Here is an approximate installation timeline for each major component of a powder coating plant. These estimates are generalized and may vary depending on specific project requirements.
1. Pre-Treatment System
- Time Estimate: 1 to 3 weeks
- Activities:
- Delivery and setup of washing, rinsing, and drying stations
- Plumbing and drainage installations
- Testing and calibration of chemical dosing systems
2. Powder Coating Booths
- Time Estimate: 1 to 2 weeks
- Activities:
- Assembly and installation of booth structures
- Integration of ventilation and powder recovery systems
- Setup of lighting and electrical connections
3. Powder Application Equipment
- Time Estimate: 1 to 2 weeks
- Activities:
- Installation of electrostatic spray guns and control units
- Calibration of application settings and nozzles
- Testing for uniform powder distribution
4. Conveyor System
- Time Estimate: 2 to 4 weeks
- Activities:
- Layout design and track installation
- Assembly of conveyor components and drives
- Testing for load capacity and speed control
5. Powder Coating Ovens
- Time Estimate: 2 to 3 weeks
- Activities:
- Installation of oven structures and insulation
- Setup of heating systems and temperature controls
- Testing for temperature uniformity and energy efficiency
6. Cooling and Inspection Stations
- Time Estimate: 1 to 2 weeks
- Activities:
- Installation of cooling systems and airflow management
- Setup of inspection stations and quality control tools
- Training staff on inspection procedures
7. Control and Monitoring Systems
- Time Estimate: 1 to 2 weeks
- Activities:
- Installation of PLC systems and control panels
- Integration with other equipment components
- Testing and validation of automation processes
8. Safety and Environmental Controls
- Time Estimate: 1 to 2 weeks
- Activities:
- Installation of fire suppression and ventilation systems
- Setup of safety barriers and emergency stops
- Safety audits and compliance checks
Total Estimated Installation Time
The total estimated installation time for a powder coating plant can range from 8 to 18 weeks, depending on the scale and complexity of the project. Here’s a breakdown by plant size:
- Small-Scale Operations: 8 to 10 weeks
- Medium-Scale Operations: 10 to 14 weeks
- Large-Scale Operations: 14 to 18 weeks
Strategies for Reducing Installation Time
- Detailed Planning and Coordination
- Develop a comprehensive project plan with clear timelines and milestones.
- Coordinate with vendors, contractors, and stakeholders to align schedules and resources.
- Pre-Fabrication and Pre-Assembly
- Opt for pre-fabricated components to reduce on-site assembly time.
- Pre-assemble equipment off-site where possible to minimize installation complexity.
- Experienced Installation Team
- Hire experienced professionals familiar with powder coating systems and processes.
- Conduct regular training and briefings to ensure the team is well-prepared.
- Efficient Site Preparation
- Ensure the facility is ready for installation before equipment arrives.
- Complete necessary infrastructure upgrades and modifications in advance.
- Streamlined Permitting and Inspections
- Obtain permits and approvals early in the project timeline.
- Schedule inspections and certifications to avoid delays.
- Contingency Planning
- Identify potential risks and develop contingency plans to address unforeseen issues.
- Allocate buffer time in the schedule for unexpected challenges.
Conclusion
The installation of a powder coating plant is a complex process that requires careful planning and coordination. By understanding the factors that influence installation time and implementing strategies to streamline the process, businesses can achieve a successful setup that meets their production goals and timelines.
Maintenance schedule tips
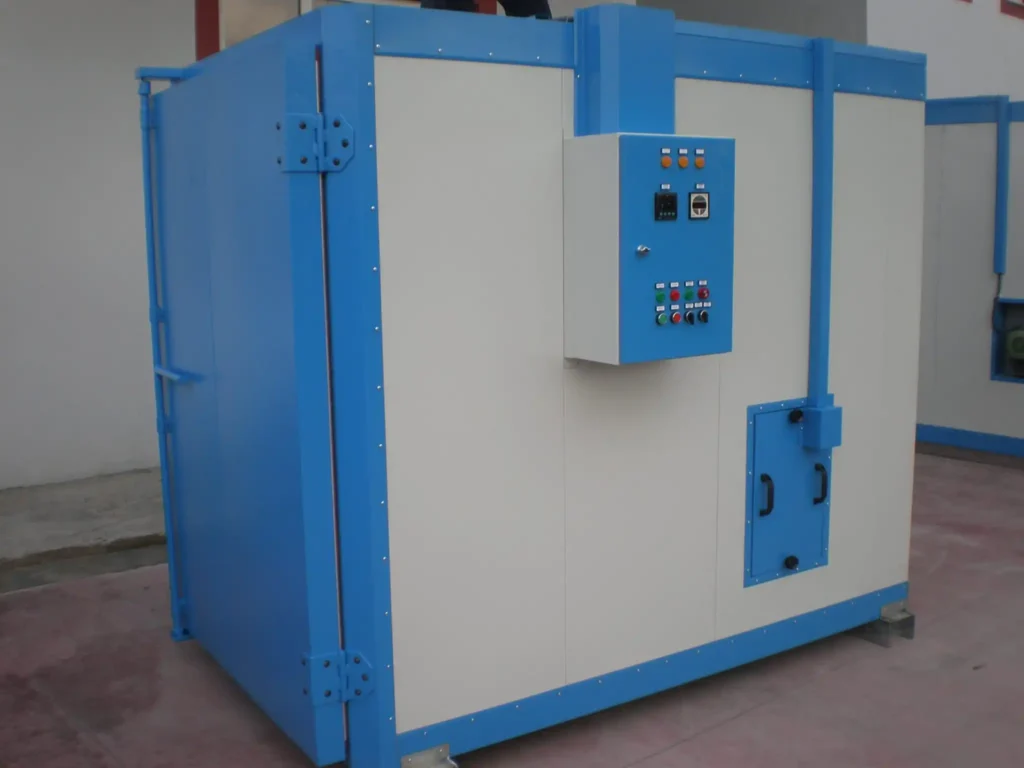

Creating a maintenance schedule for a powder coating plant is essential for ensuring efficient operation, minimizing downtime, and extending the lifespan of your equipment. A well-structured maintenance plan should address the needs of each component, including pre-treatment systems, powder coating booths, application equipment, conveyors, ovens, and safety controls. Here are some tips and guidelines to help you develop an effective maintenance schedule.
Tips for Creating a Maintenance Schedule for a Powder Coating Plant
1. Understand Equipment Requirements
- Read Manufacturer Guidelines: Start by reviewing the maintenance recommendations provided by the equipment manufacturers. These guidelines offer valuable insights into the specific needs and intervals for each component.
- Identify Critical Components: Prioritize maintenance for critical components that directly impact production quality and efficiency, such as spray guns, ovens, and conveyors.
2. Develop a Comprehensive Maintenance Plan
- Routine Inspections: Schedule regular inspections to identify wear and tear, leaks, or potential issues before they escalate. Inspections should cover all plant components, including electrical, mechanical, and safety systems.
- Preventive Maintenance: Implement a preventive maintenance schedule that includes tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, calibration, and parts replacement. This helps prevent unexpected breakdowns and maintains optimal performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilize data analytics and monitoring tools to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance based on condition and usage patterns.
3. Create a Detailed Maintenance Schedule
- Daily Maintenance Tasks:
- Check air pressure and filtration systems.
- Inspect spray guns and nozzles for clogs or wear.
- Clean work areas and remove powder buildup.
- Weekly Maintenance Tasks:
- Inspect conveyor systems for alignment and wear.
- Lubricate moving parts such as bearings and chains.
- Check temperature settings and calibrate sensors.
- Monthly Maintenance Tasks:
- Conduct a thorough inspection of pre-treatment systems.
- Inspect and clean ventilation and exhaust systems.
- Test and recalibrate control systems.
- Quarterly Maintenance Tasks:
- Perform a detailed inspection of the ovens for heat distribution and insulation integrity.
- Replace worn-out components such as belts and filters.
- Review and update safety protocols.
- Annual Maintenance Tasks:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of the entire plant.
- Audit compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
- Plan for equipment upgrades or replacements as needed.
4. Document Maintenance Activities
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, including dates, tasks performed, and any issues identified. This documentation helps track equipment performance and identifies recurring problems.
- Use Digital Tools: Consider using computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) to schedule, track, and analyze maintenance activities. Digital tools can provide reminders, automate scheduling, and generate reports.
5. Train and Empower Staff
- Employee Training: Train employees on the importance of maintenance and proper procedures. Ensure they understand how to identify and report issues and perform routine tasks.
- Empowerment: Encourage staff to take ownership of their equipment and be proactive in reporting potential problems.
6. Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Track KPIs: Monitor KPIs such as equipment uptime, mean time between failures (MTBF), and maintenance costs to evaluate the effectiveness of your maintenance program.
- Continuous Improvement: Use KPI data to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance maintenance strategies.
7. Plan for Spare Parts and Inventory
- Spare Parts Management: Maintain an inventory of critical spare parts to minimize downtime during repairs. Track usage patterns to ensure adequate stock levels.
- Vendor Relationships: Build strong relationships with equipment suppliers to ensure quick access to parts and technical support.
8. Evaluate and Adjust the Maintenance Plan
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review and update the maintenance schedule based on equipment performance, technological advancements, and changing production needs.
- Feedback Loop: Encourage feedback from maintenance staff and operators to identify pain points and improve processes.
Sample Maintenance Schedule Template
Here’s a sample template to help you structure your maintenance schedule:
| Frequency | Task | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Check air pressure | Ensure proper airflow for spray guns and equipment. |
| Inspect spray guns | Look for clogs, wear, and powder buildup. | |
| Clean work areas | Remove excess powder and debris from booths and equipment. | |
| Weekly | Inspect conveyor systems | Check alignment and wear of belts and chains. |
| Lubricate moving parts | Apply lubrication to bearings, chains, and gears. | |
| Calibrate temperature settings | Ensure accurate temperature readings in ovens. | |
| Monthly | Inspect pre-treatment systems | Check tanks, pumps, and chemical levels. |
| Clean ventilation systems | Remove dust and powder buildup in filters and ducts. | |
| Test control systems | Verify functionality and accuracy of control units. | |
| Quarterly | Inspect oven heat distribution | Check for even heat distribution and insulation integrity. |
| Replace worn components | Swap out belts, filters, and other wear-prone parts. | |
| Review safety protocols | Update safety measures and conduct training if needed. | |
| Annually | Conduct plant-wide inspection | Evaluate overall condition and performance. |
| Audit compliance with regulations | Ensure adherence to safety and environmental standards. | |
| Plan equipment upgrades | Assess the need for new equipment or technology upgrades. |
Conclusion
Implementing a well-structured maintenance schedule is vital for the smooth operation and longevity of your powder coating plant. By focusing on preventive and predictive maintenance, documenting activities, and involving your team, you can reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and maintain high-quality production standards.
Powder Coating Oven Types
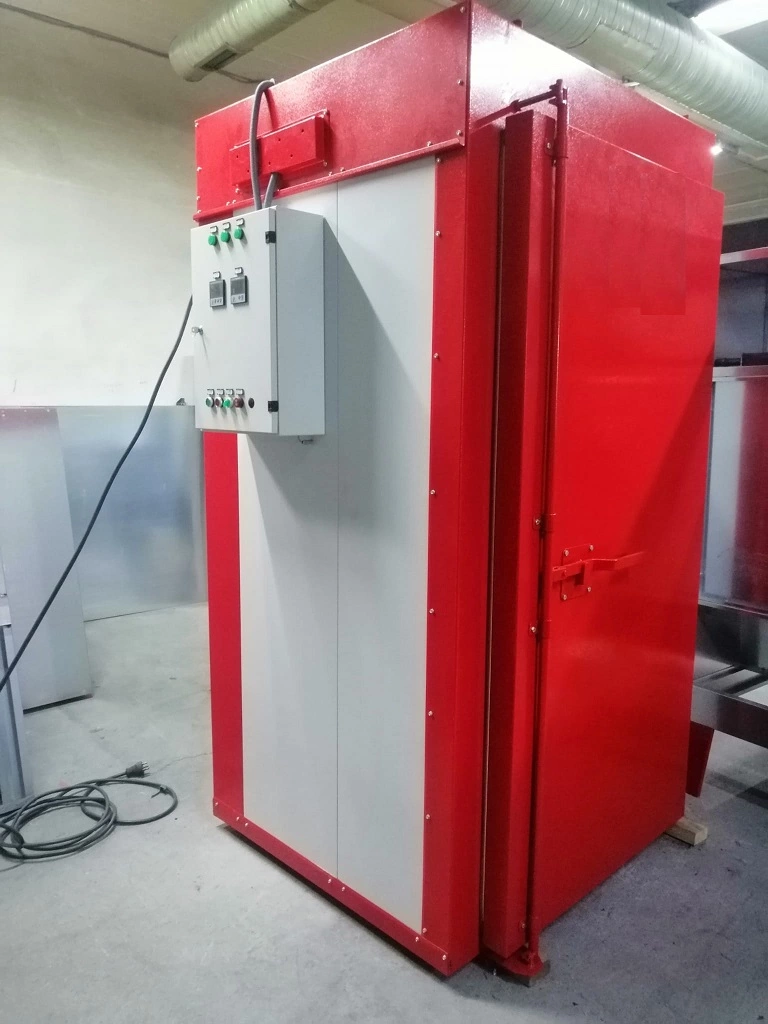

Powder coating ovens are a critical component of the powder coating process, providing the heat necessary to cure the powder and ensure a durable finish. There are several types of powder coating ovens, each designed to meet different production needs and efficiency levels. This guide will cover the various types of powder coating ovens, their features, benefits, and applications, helping you choose the right oven for your specific requirements.
Types of Powder Coating Ovens
1. Batch Ovens
Batch ovens are designed to cure powder coatings for small to medium-sized production runs. They are ideal for operations that require flexibility in coating different part sizes and types.
Features:
- Flexibility: Accommodates various part sizes and shapes.
- Energy Efficiency: Often includes insulation and heat recovery systems to reduce energy consumption.
- Manual or Semi-Automatic Operation: Suitable for low to moderate production volumes.
Benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Lower initial investment compared to continuous ovens.
- Versatile: Can handle a variety of coating tasks, including custom and complex shapes.
- Ease of Use: Simple to operate and maintain.
Applications:
- Small businesses and job shops
- Custom and prototype work
- Low to medium production volumes
Common Types of Batch Ovens:
- Walk-In Ovens: Large enough for operators to enter and load parts, suitable for oversized items.
- Cabinet Ovens: Smaller units ideal for small parts or lower-volume production.
- Truck-In Ovens: Designed for loading parts on racks or carts that can be rolled into the oven.
2. Conveyor Ovens
Conveyor ovens are designed for high-volume production and continuous processing. They automate the curing process, improving efficiency and consistency.
Features:
- Continuous Operation: Ideal for high production rates and large-scale operations.
- Automated Conveyor Systems: Transport parts through the oven for consistent curing.
- Variable Speed Control: Allows adjustment of conveyor speed to match curing requirements.
Benefits:
- High Throughput: Capable of processing large quantities of parts quickly.
- Consistent Quality: Ensures uniform curing across all parts.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automation reduces the need for manual intervention.
Applications:
- Automotive and aerospace industries
- High-volume manufacturing plants
- Standardized parts production
Common Types of Conveyor Ovens:
- Monorail Ovens: Parts are hung from an overhead conveyor and pass through the oven in a linear path.
- Chain-On-Edge Ovens: Parts are attached to fixtures on a conveyor chain, suitable for heavier items.
- Flat-Belt Ovens: Use a flat conveyor belt to transport parts, ideal for lightweight or flat components.
3. Infrared Ovens
Infrared ovens use infrared radiation to cure powder coatings, offering a fast and energy-efficient alternative to conventional ovens. They are often used in combination with other oven types to optimize curing.
Features:
- Fast Heating: Infrared radiation provides rapid heat-up and curing times.
- Energy Efficiency: Direct heating reduces energy consumption compared to convection ovens.
- Compact Size: Smaller footprint compared to traditional ovens.
Benefits:
- Quick Curing: Significantly reduces curing times, increasing throughput.
- Targeted Heating: Infrared heat can be focused on specific areas, reducing overall energy use.
- Improved Finish: Provides smooth and even curing, minimizing defects.
Applications:
- Automotive and consumer electronics
- Applications requiring quick turnaround
- Parts with complex shapes or heat-sensitive materials
Common Types of Infrared Ovens:
- Short-Wave Infrared Ovens: Provide intense heat for fast curing, suitable for thicker coatings.
- Medium-Wave Infrared Ovens: Balance between heat intensity and penetration, ideal for general applications.
- Long-Wave Infrared Ovens: Gentle heat suitable for heat-sensitive substrates.
4. Gas-Fired Ovens
Gas-fired ovens use natural gas or propane as a heat source. They are popular for large-scale operations due to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Features:
- High Heat Output: Efficiently generates high temperatures for rapid curing.
- Cost-Effective: Generally lower operating costs compared to electric ovens.
- Robust Construction: Designed to handle heavy-duty industrial use.
Benefits:
- Reduced Operating Costs: Lower energy costs compared to electric ovens, especially for large volumes.
- Reliable Performance: Consistent heating for uniform curing.
- Scalability: Suitable for large-scale production and expansion.
Applications:
- Automotive and heavy equipment manufacturing
- Large industrial operations
- High-volume powder coating lines
Common Types of Gas-Fired Ovens:
- Direct-Fired Ovens: Burners directly heat the air inside the oven chamber, providing fast and efficient heating.
- Indirect-Fired Ovens: Heat exchangers separate combustion gases from the oven air, offering cleaner operation.
5. Electric Ovens
Electric ovens use electrical heating elements to generate heat for curing powder coatings. They are commonly used in smaller operations due to their ease of use and installation.
Features:
- Precise Temperature Control: Offers accurate and consistent temperature settings.
- Easy Installation: No need for gas lines or combustion venting.
- Low Maintenance: Fewer moving parts compared to gas-fired ovens.
Benefits:
- Safe and Clean: No combustion gases, reducing emissions and improving air quality.
- Consistent Performance: Stable temperature control ensures uniform curing.
- Versatile: Suitable for various applications and materials.
Applications:
- Small to medium-sized businesses
- Custom and low-volume production
- Applications with strict environmental regulations
Common Types of Electric Ovens:
- Forced-Air Convection Ovens: Use fans to circulate heated air for uniform temperature distribution.
- Static Ovens: Rely on natural convection, suitable for delicate or sensitive parts.
6. Combination Ovens
Combination ovens integrate multiple heating methods, such as infrared and convection, to provide flexibility and optimize curing processes.
Features:
- Multi-Mode Operation: Allows switching between or combining different heating methods.
- Optimized Curing: Adjusts curing methods based on part size, shape, and material.
- Flexible Configuration: Customizable to meet specific production needs.
Benefits:
- Versatility: Capable of handling a wide range of parts and coatings.
- Improved Efficiency: Combines the strengths of different heating methods for optimal results.
- Enhanced Finish Quality: Provides tailored curing conditions to minimize defects.
Applications:
- Complex parts with varying geometries
- Industries requiring rapid production changes
- Specialized coating applications
Considerations for Choosing the Right Powder Coating Oven
When selecting a powder coating oven, consider the following factors:
- Production Volume:
- Choose batch ovens for low to medium production and conveyor ovens for high-volume operations.
- Part Size and Shape:
- Consider the size, weight, and geometry of the parts to determine the appropriate oven type.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Evaluate energy consumption and costs, especially for large-scale operations.
- Temperature Requirements:
- Ensure the oven can maintain consistent temperatures for your specific powder coatings.
- Space and Layout:
- Consider the available space and how the oven will fit into your production line layout.
- Budget and Cost:
- Balance initial investment with long-term operating costs and return on investment.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensure the oven meets local safety and environmental regulations.
Conclusion
Selecting the right powder coating oven is crucial for achieving high-quality finishes and efficient production. By understanding the features, benefits, and applications of each oven type, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their production needs and goals. Investing in the right oven will enhance productivity, reduce costs, and ensure a durable, attractive finish on your coated products.
Powder coating oven maintenance tips

Proper maintenance of powder coating ovens is crucial to ensure efficient operation, consistent curing quality, and the longevity of the equipment. A well-maintained oven minimizes downtime, reduces energy consumption, and prevents costly repairs. Below are comprehensive tips and guidelines for maintaining powder coating ovens effectively.
Powder Coating Oven Maintenance Tips
1. Regular Cleaning
Keeping the oven clean is essential to prevent powder buildup, which can affect performance and finish quality.
Cleaning Tips:
- Daily Cleaning:
- Inspect and Clean Interior Surfaces: Remove any powder buildup on oven walls, floors, and ceilings.
- Clean Heating Elements: Check and clean heating elements to ensure efficient heat transfer.
- Vacuum or Sweep the Floor: Remove any loose powder or debris from the oven floor.
- Weekly Cleaning:
- Clean Air Ducts and Vents: Ensure proper airflow and ventilation by cleaning ducts and vents regularly.
- Wipe Down Doors and Seals: Clean door seals and check for any damage that could affect insulation.
- Monthly Cleaning:
- Deep Clean Oven Interior: Use a non-abrasive cleaner to deep clean the oven interior and remove any stubborn residue.
- Inspect and Clean Exhaust Systems: Check and clean exhaust fans and filters to prevent blockages.
2. Routine Inspections
Regular inspections help identify potential issues before they become major problems, ensuring the oven operates at peak efficiency.
Inspection Tips:
- Daily Inspections:
- Check Temperature Settings: Verify that the oven reaches and maintains the correct curing temperature.
- Monitor Airflow: Ensure that fans and blowers are functioning correctly for even heat distribution.
- Inspect Doors and Seals: Check for gaps or damage that could lead to heat loss.
- Weekly Inspections:
- Inspect Electrical Components: Check wiring, connections, and control panels for signs of wear or damage.
- Check for Unusual Noises: Listen for any unusual noises that might indicate mechanical issues.
- Monthly Inspections:
- Inspect Insulation: Check oven insulation for any damage or wear that could reduce energy efficiency.
- Examine Conveyor Systems: For conveyor ovens, inspect belts, chains, and rollers for wear and alignment.
3. Calibration and Testing
Regular calibration and testing ensure that the oven operates at the correct temperature and settings, maintaining coating quality.
Calibration Tips:
- Temperature Calibration:
- Use Thermocouples: Place thermocouples at various points in the oven to verify temperature uniformity.
- Adjust Temperature Controllers: Calibrate controllers to maintain consistent curing temperatures across the oven.
- Testing Performance:
- Conduct Cure Tests: Perform test runs with sample parts to ensure that coatings are cured properly.
- Check Heating Elements: Test heating elements for consistent output and replace any that are faulty.
4. Preventive Maintenance
Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule helps prevent unexpected breakdowns and extends the life of the oven.
Preventive Maintenance Tips:
- Lubrication:
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply lubrication to bearings, chains, and other moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Component Replacement:
- Replace Worn Parts: Regularly check and replace parts like belts, seals, and filters that show signs of wear.
- Fan and Blower Maintenance:
- Inspect and Clean Fans: Check fans for balance and clean them to prevent vibration and noise.
- Replace Worn Bearings: Replace any bearings that are noisy or show signs of wear.
5. Safety and Compliance
Ensuring safety and regulatory compliance is critical for protecting workers and meeting industry standards.
Safety Tips:
- Fire Safety:
- Check Fire Suppression Systems: Ensure that fire suppression systems are operational and regularly serviced.
- Install Smoke Detectors: Regularly test smoke detectors and alarms to ensure they are functional.
- Electrical Safety:
- Inspect Wiring and Connections: Regularly check electrical wiring and connections for signs of wear or damage.
- Conduct Safety Audits: Perform regular safety audits to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
6. Documentation and Record Keeping
Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities helps track oven performance and identify trends or recurring issues.
Documentation Tips:
- Maintain a Maintenance Log: Record all maintenance activities, including inspections, cleaning, and repairs.
- Track Performance Metrics: Monitor metrics such as energy consumption, downtime, and repair frequency.
7. Staff Training and Awareness
Proper training ensures that staff are equipped to perform maintenance tasks safely and effectively.
Training Tips:
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Train staff on oven operation, maintenance procedures, and safety protocols.
- Encourage Proactive Maintenance: Empower staff to identify and report potential issues promptly.
Sample Maintenance Schedule for Powder Coating Ovens
Below is a sample maintenance schedule to help you organize and plan oven maintenance tasks:
| Frequency | Task | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Clean interior surfaces | Remove powder buildup from oven walls, floors, and ceilings. |
| Check temperature settings | Verify that the oven reaches the correct curing temperature. | |
| Inspect doors and seals | Look for gaps or damage that could lead to heat loss. | |
| Weekly | Clean air ducts and vents | Ensure proper airflow and ventilation. |
| Inspect electrical components | Check wiring, connections, and control panels for wear. | |
| Lubricate moving parts | Apply lubrication to bearings, chains, and other components. | |
| Monthly | Deep clean oven interior | Use non-abrasive cleaner to remove stubborn residue. |
| Calibrate temperature controllers | Verify and adjust temperature settings for consistency. | |
| Inspect insulation and conveyor systems | Check insulation integrity and conveyor alignment. | |
| Quarterly | Test heating elements and fans | Ensure consistent output and replace faulty components. |
| Review safety protocols and systems | Update safety measures and test fire suppression systems. | |
| Annually | Conduct comprehensive performance review | Evaluate overall condition and plan for upgrades. |
| Audit compliance with regulations | Ensure adherence to safety and environmental standards. |
A powder coating oven is a specialized industrial oven used to cure powder-coated parts. The oven applies heat to melt and fuse the powder coating onto a surface, creating a durable and uniform finish. These ovens are commonly used in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication industries.
Types of Powder Coating Ovens
- Batch Ovens – Used for small-scale or custom jobs where parts are coated in batches.
- Conveyor Ovens – Used in large-scale production lines for continuous processing.
- Infrared (IR) Ovens – Use infrared radiation for quick and efficient heating.
- Gas or Electric Ovens – Differ based on heating method; gas ovens are cost-effective for large-scale operations, while electric ovens offer precision.
Key Features
- Temperature Control: Typically ranges between 320°F and 450°F (160°C – 230°C).
- Even Air Circulation: Ensures uniform curing.
- Energy Efficiency: Insulated walls and efficient burners reduce energy consumption.
- Size Variations: Can be custom-built for different production needs.
Working Process
- Pre-Treatment: The part is cleaned and prepared to ensure adhesion.
- Powder Application: Electrostatic spray guns apply powder coating.
- Curing in Oven: The coated part is heated to melt and fuse the powder.
- Cooling: The part is allowed to cool and harden for final use.
A powder coating oven is an essential piece of equipment used to cure powder-coated parts by applying heat, allowing the powder to melt, flow, and form a durable finish. These ovens are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication, where high-quality surface finishes are required. The curing process typically occurs at temperatures between 320°F and 450°F (160°C – 230°C), depending on the type of powder used.
There are different types of powder coating ovens, including batch ovens, conveyor ovens, infrared (IR) ovens, and those powered by gas or electricity. Batch ovens are ideal for small-scale or custom jobs, while conveyor ovens are designed for continuous production lines. Infrared ovens use radiation to quickly and efficiently heat parts, making them suitable for fast-paced operations. Gas ovens are often preferred for large-scale production due to their cost efficiency, while electric ovens offer precise temperature control.
The effectiveness of a powder coating oven depends on factors such as even air circulation, proper insulation, and energy efficiency. A well-designed oven ensures consistent curing, preventing defects like orange peel, under-curing, or over-curing. The process starts with pre-treatment, where parts are cleaned to ensure proper adhesion. After powder application using an electrostatic spray gun, the parts are placed inside the oven, where the powder melts and fuses into a smooth, uniform coating. Once cured, the parts are cooled to harden and finalize the coating.
When selecting a powder coating oven, considerations include the size and type of parts being coated, production volume, energy efficiency, and budget. Custom-built ovens can be designed to fit specific needs, ensuring optimal performance. Proper maintenance, including regular cleaning of heating elements and air circulation systems, helps maintain efficiency and extends the oven’s lifespan. Would you like information on designing a powder coating oven or recommendations for a specific application?
In addition to the basic process and types of powder coating ovens, there are some key technical aspects to consider when operating or setting up a powder coating oven. One important factor is airflow management, which plays a crucial role in ensuring that the heat is distributed evenly throughout the oven. Proper airflow is critical to prevent uneven curing, which can lead to defects like color inconsistencies or patches on the coated parts. Typically, powder coating ovens are equipped with fans or blowers to circulate heated air throughout the chamber. The airflow ensures that the entire surface of the part is evenly exposed to the heat, promoting consistent curing and a high-quality finish.
Another important aspect is the temperature control system. Ovens are equipped with precise thermocouples and controllers that monitor and maintain the desired temperature. In some advanced models, a programmable temperature controller allows users to set different temperature profiles for various types of powders, ensuring that the curing process is optimized for different materials. Consistency in temperature is key because fluctuations can affect the quality and performance of the finish, such as causing under-curing (which might result in a soft or less durable coating) or over-curing (which can lead to discoloration or brittleness).
Energy efficiency is another key consideration for powder coating ovens, especially in large-scale operations where energy costs can be significant. Modern ovens are designed with high-efficiency insulation to minimize heat loss, ensuring that less energy is required to maintain the desired temperature. This is especially important in gas-powered ovens, where optimizing the combustion process can lead to significant cost savings over time. Electric ovens, while generally more precise, can be equipped with features such as programmable timers and energy-saving modes to reduce energy consumption during idle periods.
Furthermore, the size and configuration of the oven should be chosen based on the volume of production and the size of the parts being coated. Some ovens are modular and can be expanded as production needs increase, while others are more rigid in design. Conveyorized ovens, for example, are ideal for continuous production where parts move automatically through the oven, allowing for efficient high-volume operations. For smaller batches or custom jobs, a batch oven that can accommodate larger or irregularly shaped parts may be more suitable.
Finally, maintenance and safety are paramount in ensuring the long-term functionality of powder coating ovens. Regular cleaning of the oven’s heating elements, fans, and ducts is necessary to prevent the buildup of powder residue, which can lead to poor airflow or even safety hazards like fire. Additionally, safety features such as temperature alarms and overheat protection systems are often included in more advanced ovens to prevent accidents caused by excessive heat buildup.
In conclusion, choosing the right powder coating oven and maintaining it properly is critical for achieving high-quality, durable finishes while ensuring efficiency and safety. Whether for small-scale custom work or large-volume production, the key is to match the oven’s capabilities to the specific requirements of the parts being coated. Would you like additional details on energy-saving tips or specific maintenance practices?
Expanding on the operational side, there are several important considerations for optimizing the performance of powder coating ovens and ensuring consistent, high-quality results. One key factor is the cooling process after the parts exit the curing oven. Cooling is essential for solidifying the powder coating and preventing distortion. In many setups, a cooling zone follows the curing oven, which allows parts to gradually cool to room temperature, ensuring that the coating maintains its integrity. Some systems use forced air cooling to speed up the process, especially in high-volume production environments. Proper cooling helps avoid surface defects like warping, cracking, or an uneven finish.
The environmental conditions of the powder coating area also play a significant role in the process. For instance, the humidity and temperature in the room where the oven is located can affect the application of the powder and its ability to adhere properly. Excessive humidity can cause powder to clump or affect how it adheres to the part, leading to uneven coatings. It’s important to maintain stable, controlled conditions in the powder booth and oven area to avoid such issues. In larger operations, environmental control systems are often used to regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality to optimize the coating process.
Another consideration is powder selection. There are various types of powder coatings, including polyester, epoxy, polyurethane, and hybrid blends, each offering different properties such as corrosion resistance, UV stability, and flexibility. Depending on the type of product being coated and its intended use, choosing the right powder is crucial. For example, outdoor furniture or automotive parts may require a powder coating with high resistance to UV rays and weathering, while parts used in interior settings might not need such durable properties.
The application process itself can be fine-tuned for better results. While most powder coating systems use electrostatic guns to apply the powder, the application parameters (such as the distance between the gun and the part, air pressure, and voltage) can significantly affect the outcome. Optimizing these settings helps achieve an even coat and reduces powder waste. Additionally, pre-treatment is vital to ensuring proper adhesion of the powder. The surface of the part must be thoroughly cleaned, typically with a chemical wash or sandblasting, to remove oils, dirt, or rust, all of which can prevent the powder from sticking properly.
Automation in powder coating lines has become increasingly popular for large-scale manufacturing. Automated systems can include robots that apply the powder and conveyor systems that transport parts through the powder booth and curing oven. This automation helps improve consistency, speed, and precision, especially in high-volume operations. The automation can also reduce human error and make the process more repeatable, leading to fewer defects and a more uniform finish.
Additionally, recovery systems are an important part of modern powder coating setups. These systems capture oversprayed powder and recycle it, reducing waste and increasing cost efficiency. The powder that is captured can be filtered and reused, although it must meet certain quality standards to ensure it performs correctly during reapplication. Recovery systems typically use a combination of air filtration and mechanical systems to collect the powder, ensuring that only clean, uncontaminated powder is reused.
One other aspect worth mentioning is color changeover procedures. In production environments where different colors are frequently used, it’s important to have a streamlined process for switching between colors to minimize contamination or mixing of powders. Some powder coating systems come equipped with automated cleaning cycles or powder changeover mechanisms that help minimize downtime and powder waste.
In summary, optimizing the performance of a powder coating oven involves paying attention to many interconnected aspects, such as cooling, environmental control, powder selection, and automation. By carefully managing each of these factors, companies can maximize the efficiency of their coating processes, achieve high-quality finishes, and minimize production costs. Would you like more detailed information on automating powder coating lines or suggestions for specific applications?
Powder Coating Oven for Wheels
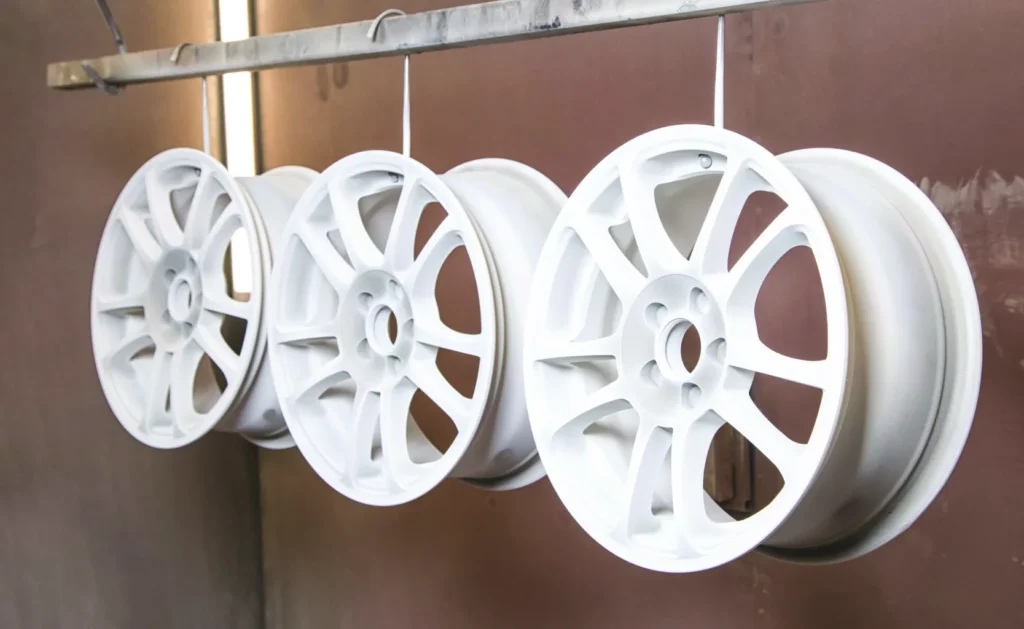

Powder coating ovens for wheels are specialized systems designed to provide a consistent and high-quality finish to wheel rims, commonly used in automotive, motorcycle, and bicycle industries. The process involves coating the wheel with a powdered paint that is then cured in the oven, creating a durable, uniform, and aesthetically pleasing finish. Given the high-performance and exposure requirements of wheels (which face weather, chemicals, and abrasion), a proper powder coating oven ensures that the finish will be both durable and visually appealing.
When setting up a powder coating oven specifically for wheels, a few key factors need to be considered:
1. Size and Shape of the Oven
Wheels come in various sizes, so the oven should be large enough to accommodate the size of the wheels being coated, with enough clearance for air circulation. This is especially important for larger wheels, such as those used in trucks or custom automotive applications. The oven may need to be customized to handle larger or uniquely shaped wheels, with a conveyor system or a batch process depending on the production volume.
2. Temperature Control and Uniformity
Wheels need to be cured at temperatures typically between 320°F and 400°F (160°C to 200°C). A precise temperature control system is critical to ensure that the powder coating melts, flows, and fuses correctly to the wheel surface. Temperature fluctuations or uneven heat distribution could result in poor adhesion, inconsistent finishes, or defects such as bubbling, cracking, or an uneven sheen.
Many modern powder coating ovens feature airflow systems designed to maintain even heat distribution across the entire surface of the wheel. Even air circulation ensures that the coating is consistently cured, particularly when the wheel may have intricate designs or spokes that need to be coated evenly.
3. Energy Efficiency
Since wheels are often coated in batches, optimizing energy consumption is important. Gas or electric ovens can be used, but energy-efficient options are critical for reducing operational costs. Insulated ovens help to maintain internal temperatures without wasting energy, and more advanced ovens may feature energy-saving modes during downtime, such as when the oven is not in active use. Gas-powered ovens are popular for their cost-effectiveness in larger operations, while electric ovens are known for offering better temperature control.
4. Airflow and Cooling
Proper airflow inside the oven ensures that heat is distributed uniformly around the wheel, preventing defects. Wheels, especially larger ones, require adequate space for airflow to reach all parts of the surface. Once the curing process is complete, the wheels need to be cooled gradually to prevent thermal shock, which could lead to cracks or other surface issues. A cooling zone after the oven, or forced air cooling, can help cool the wheels without causing any distortion or defects in the finish.
5. Pre-treatment and Cleaning
Before powder coating, wheels must be cleaned and pre-treated to ensure proper adhesion. This process typically includes removing dirt, grease, and rust, either by abrasive blasting (e.g., sandblasting) or using chemical cleaners. Without this crucial step, the powder coating may fail to adhere properly, resulting in defects or peeling over time.
6. Powder Coating Selection
For wheels, the powder coating must be able to withstand the rigors of outdoor exposure, chemicals, UV light, and abrasions. Polyester powder coatings are popular for automotive wheels because of their UV resistance and durability. Additionally, epoxy-based powders offer good corrosion resistance but may not be as UV stable, which is why they are typically used for indoor applications or parts that won’t be exposed to direct sunlight.
The ability to change colors quickly is also crucial for businesses offering custom wheels. Many powder coating systems designed for wheels feature a streamlined color change process that minimizes contamination and downtime, allowing for quick shifts between colors or finishes.
7. Automation and Production Flow
For high-volume production, conveyorized powder coating ovens are ideal, allowing wheels to be processed in continuous flow. Automated systems can handle parts from the pretreatment stage, through powder application, and into the oven, which streamlines the entire process. Automated spray guns can provide consistent application of the powder coating, reducing powder waste and improving efficiency. Conveyorized systems also ensure that the wheels are processed quickly and efficiently, increasing production rates.
8. Post-Curing Quality Control
After the wheels are removed from the oven and cooled, they should be inspected for finish quality. The coating should be smooth, even, and free from defects like orange peel, uneven thickness, or bubbles. Some operations include an additional step like UV light testing to ensure that the coating has cured properly and meets durability standards.
Key Features of a Powder Coating Oven for Wheels:
- Customizable Size for accommodating a variety of wheel sizes
- High Heat Capacity and Precision temperature control to ensure consistent curing
- Efficient Air Circulation and Ventilation for uniform coating
- Energy Efficiency with insulated walls and precise temperature management
- Powder Recovery Systems to minimize waste and save on coating materials
- Rapid Cooling Zones to reduce defects and ensure that the finish solidifies correctly
In conclusion, a powder coating oven for wheels must be well-suited for the specific demands of wheel finishes, including durability, consistency, and aesthetic appeal. Choosing the right oven and ensuring that all operational steps are streamlined will result in high-quality, long-lasting coatings. Whether you’re coating a few custom wheels or mass-producing them for a fleet of vehicles, the right oven setup can make a significant difference in quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
A powder coating oven for wheels is an essential piece of equipment designed to ensure that wheels receive a durable, high-quality finish. These ovens must be carefully selected and set up to handle the unique challenges posed by the coating and curing process. Wheels come in various sizes, and a proper oven should be large enough to accommodate different wheel diameters, with enough space for airflow to circulate evenly around the entire surface. This ensures that the powder coating is applied and cured uniformly, avoiding defects such as uneven coating or color inconsistencies.
The curing temperature for wheels typically ranges from 320°F to 400°F (160°C to 200°C), and precise temperature control is critical. The powder coating must melt, flow, and fuse onto the surface of the wheel without any temperature fluctuations that could result in under-curing or over-curing, both of which would negatively affect the quality of the finish. A good powder coating oven for wheels uses a robust system to maintain stable temperatures and provides even heat distribution across the wheel’s surface, including areas with intricate designs, such as spokes.
In addition to temperature control, the oven should have efficient airflow management to ensure that the heat is uniformly distributed. This is important for curing wheels consistently, especially in larger or more complex wheel designs. Some ovens are designed with adjustable airflow to accommodate different sizes and shapes of wheels. Proper cooling is also crucial after the curing process, as the wheels need to cool gradually to prevent any thermal shock that could cause warping or cracking in the coating. Cooling zones are often included after the oven to ensure the wheels are cooled uniformly.
The energy efficiency of the oven is another significant factor, particularly for high-volume operations. Gas-powered ovens are often preferred for their cost-effectiveness, especially when large quantities of wheels are being coated. However, electric ovens can offer more precise temperature control, and the most advanced models will incorporate insulation to minimize energy loss. Ensuring that the oven is well-insulated helps maintain heat levels and reduces energy consumption over time.
Before powder coating, the wheels must undergo thorough pre-treatment to remove contaminants like dirt, grease, and rust. This cleaning process is essential for ensuring proper adhesion of the powder to the wheel’s surface. The use of abrasive blasting or chemical cleaning is common to prepare the wheel for coating. Once pre-treated, the wheels are sprayed with the powder coating material, typically through an electrostatic spray process, which ensures that the powder adheres evenly to the wheel.
Powder coatings for wheels must be able to withstand a variety of challenges, including exposure to UV rays, chemicals, and abrasions. For this reason, coatings like polyester powders are often chosen for their superior UV stability and resistance to weathering. Epoxy-based coatings are also used in some cases but may not be as resistant to sunlight, making them better suited for indoor applications.
High-volume production often involves the use of automated systems, such as conveyorized ovens or robotic spray systems, which allow wheels to move seamlessly through the various stages of powder coating. These automated systems can significantly improve production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and ensure consistent quality across large batches. With conveyorized systems, wheels can be moved through the pre-treatment, powder application, curing, and cooling stages without needing manual handling.
The inclusion of powder recovery systems helps to minimize waste and reduce material costs. These systems capture oversprayed powder and filter it for reuse, ensuring that the powder used in the coating process remains clean and free from contaminants. This not only saves money on powder but also helps to maintain a clean, safe environment in the workplace by reducing airborne particles.
Once the wheels are cured and cooled, they should undergo quality control to ensure the finish meets the required standards. This might include checking for uniformity, color consistency, and the overall durability of the coating. Proper inspection ensures that the coating is smooth, without defects like bubbles, uneven thickness, or poor adhesion.
In summary, a powder coating oven for wheels needs to be precisely designed to handle the unique demands of coating wheels, with features such as uniform heat distribution, energy efficiency, pre-treatment, cooling, and post-cure inspection. Whether you’re coating a few custom wheels or running a high-volume production line, having the right equipment and setup will result in a high-quality, durable finish that can withstand the challenges of daily use and environmental exposure. Would you like to explore specific oven models or discuss further technical details for your production needs?
When it comes to optimizing the powder coating process for wheels, a few additional factors come into play that can significantly enhance the quality of the finish and improve production efficiency. One of the most important aspects is ensuring the uniform application of powder. Since wheels are often complex in shape, with spokes, rims, and other detailed features, it’s crucial that the powder is applied evenly across all surfaces. The electrostatic spray guns used in powder coating are designed to attract the powder to the wheel’s surface through an electrostatic charge, ensuring that the powder adheres well. However, getting the correct spray gun settings—such as voltage, air pressure, and distance from the part—can make a huge difference in the final outcome.
Optimizing the coating thickness is also key. If the coating is too thick, it can result in an uneven or brittle finish, while a coating that’s too thin might not offer sufficient protection against corrosion or wear. The coating thickness can be controlled through precise application and by using the right combination of powder type, air pressure, and curing time. Modern powder coating ovens often come with features that allow for automated coating thickness measurement to ensure that the correct amount of powder is applied.
In addition to this, environmental factors such as humidity and temperature within the coating facility can impact the final result. High humidity can cause the powder to clump or prevent it from adhering properly to the wheel, leading to an uneven finish. To prevent this, many powder coating facilities use humidity control systems or ensure that the temperature is stable within the production area to keep the coating process consistent.
Another consideration for wheel powder coating is finish variety. Depending on the requirements, wheels can be coated with different types of finishes, such as gloss, matte, satin, or textured. The oven and the powder coating system must be compatible with the specific finish desired. For example, some finishes might require slightly different curing times or temperatures to achieve the desired result, so a programmable oven that can handle multiple settings for different finishes can be a valuable asset.
Some advanced powder coating ovens for wheels also come equipped with advanced control systems, which can track and manage the entire coating process. These systems allow operators to monitor and adjust settings like temperature, air circulation, and curing time in real-time, ensuring the process stays within optimal parameters. These control systems can also generate data on the production process, providing valuable insights into efficiency and quality control.
For facilities handling larger production volumes, continuous conveyor systems can be used to move the wheels through different stages of the coating process. These conveyor systems are often fully automated, reducing the need for manual labor and ensuring that the wheels pass through the oven consistently. Automation helps reduce the risk of human error, improves throughput, and ensures uniform coating, which is especially important for large-scale production lines.
In terms of maintaining the oven, regular cleaning is essential to keep everything functioning properly. Powder buildup on the oven walls, heating elements, and air circulation systems can interfere with performance and lead to defects in the finish. Many powder coating ovens include features that make cleaning easier, such as removable filters and easy-to-access heating elements. It’s also important to inspect the oven regularly for any signs of wear, like cracks in the insulation or damage to the air circulation system, as these can negatively impact the oven’s performance.
The right oven setup for powder coating wheels can greatly enhance both the aesthetics and durability of the finish. Choosing the right oven involves not only considering the size and type of wheels you’re coating but also the overall production volume, the types of finishes desired, and the level of automation needed. Ensuring that the system is optimized for both energy efficiency and ease of operation will help keep costs down while producing high-quality, long-lasting finishes.
Expanding further, there are several considerations that can optimize both the quality of the powder-coated wheel finishes and the overall efficiency of the process. One of the most important is the maintenance of consistency throughout the entire production line. Even slight deviations in any part of the process—whether it’s the pre-treatment, powder application, curing time, or cooling—can lead to defects. Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure that every aspect of the coating line is regularly monitored and maintained. This consistency can be achieved through the use of automated monitoring systems that track critical parameters like temperature, humidity, and airflow, providing real-time feedback to operators and automatically adjusting settings as necessary.
Another factor to consider is the integration of additional features that could improve production efficiency. For example, integrating automated robotic arms for powder application can help achieve more precise coating, especially on complex wheel shapes. These robotic arms can consistently apply the powder with the correct amount of charge, reducing the likelihood of overspray or uneven coverage. Coupled with advanced electrostatic spray technology, robots can provide higher-quality finishes in less time, further improving productivity in larger-scale operations.
In addition, recovery systems should be incorporated into powder coating systems for wheels. These systems help capture oversprayed powder, clean it, and allow it to be reused. Not only does this reduce waste and lower material costs, but it also improves environmental sustainability by reducing the amount of excess powder that would otherwise be disposed of. The powder recovery system typically includes a filtration system to ensure that only high-quality, clean powder is reintroduced into the coating process, helping maintain the coating’s integrity.
Another advanced feature worth considering is the use of predictive maintenance technology. Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and machine learning to monitor the condition of equipment in real time, predicting when a part might fail or require servicing. For powder coating ovens, this could mean early detection of issues with the heating elements, airflow system, or cooling mechanism, allowing for maintenance before a major failure occurs. This can significantly reduce downtime, improve the reliability of the equipment, and extend the lifespan of the oven.
Moreover, some powder coating ovens for wheels come with advanced curing profiles, which are programmable settings that allow the operator to customize curing times and temperatures based on the specific type of powder being used. For example, wheels requiring a high-durability finish or those exposed to extreme temperatures may require a different curing profile than those with decorative finishes. Having the ability to store and recall different profiles for various coatings helps optimize the curing process for different materials, resulting in better finishes and more efficient operations.
Energy efficiency remains a top concern for any manufacturing operation, especially when considering large-scale production. One of the most innovative energy-saving features in modern powder coating ovens is the use of heat recovery systems. These systems capture heat from the exhaust air, which would normally be wasted, and reuse it to preheat incoming air or maintain the oven temperature. This process reduces the need for additional energy input, lowering energy costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Furthermore, the flexibility of the oven plays a significant role in accommodating varying production demands. In environments where different types of wheels (e.g., custom rims, automotive wheels, motorcycle wheels, etc.) are coated, a flexible oven design that can handle a range of sizes and shapes is crucial. Many modern ovens come with adjustable racking systems or modular designs that can be adapted depending on the size and configuration of the wheels being coated. This adaptability ensures that the coating process remains efficient, regardless of the diversity of the products being processed.
Post-coating inspection and quality assurance are essential for maintaining high standards. After the wheels are removed from the curing oven and cooled, a thorough inspection is necessary to check for any surface imperfections. In advanced systems, automated quality control systems equipped with cameras or sensors can detect defects like orange peel, pinholes, or inconsistencies in coating thickness. These systems can help identify defective wheels before they leave the production line, reducing waste and the need for rework.
Lastly, operator training and safety are key factors in the overall efficiency and success of the powder coating operation. Operators must be well-trained in oven settings, maintenance procedures, and the handling of hazardous materials (such as powder coatings and solvents). Safety features such as emergency shut-off systems, proper ventilation, and fire suppression systems are also important for protecting both the workers and the equipment. Additionally, providing ongoing training and maintaining a clean, well-organized workspace can help prevent operational errors and ensure smooth production.
To summarize, optimizing the powder coating oven for wheels involves incorporating features that increase the efficiency, quality, and sustainability of the process. This includes everything from advanced temperature and airflow control to automated robotic systems, predictive maintenance, energy-saving technologies, and rigorous quality control procedures. By implementing these features and technologies, manufacturers can achieve consistently high-quality finishes, reduce production costs, and improve the overall productivity of the powder coating process.
Large Ovens for Powder Coating
Large ovens for powder coating are designed to handle high-volume production and accommodate larger parts or products. These ovens are critical for industries like automotive, aerospace, furniture manufacturing, and other large-scale operations that require powder coating on bigger or bulkier items, such as car bodies, large metal components, or heavy machinery. The design of large powder coating ovens typically includes specialized features to ensure consistency, efficiency, and quality finishes across large surfaces.
Key Considerations for Large Powder Coating Ovens
- Size and Capacity: Large powder coating ovens need to be spacious enough to accommodate oversized parts or multiple parts in a batch. For example, in automotive production, car parts like bumpers or fenders are coated using large ovens. The oven’s interior dimensions must be customized based on the size of the parts to be coated. In some cases, manufacturers opt for modular oven designs that can be expanded or adjusted based on the changing needs of production.
- Temperature Control and Uniformity: One of the biggest challenges in large ovens is ensuring that the temperature is evenly distributed across the entire surface area. Large ovens should feature a high-efficiency airflow system that can circulate heat uniformly, even when the oven is filled to capacity. This includes airflow fans that distribute heated air evenly and help maintain consistent temperatures throughout the entire oven chamber. Maintaining uniform heat is crucial for curing the powder coating properly, as uneven temperatures can lead to defects such as streaking or inconsistent finishes.
- Energy Efficiency: Large ovens are energy-intensive, so it’s essential to invest in energy-efficient systems to minimize operating costs. Features like insulated walls and heat recovery systems can reduce the amount of energy required to maintain the oven temperature. Heat recovery systems capture the hot air from the exhaust and redirect it to preheat incoming air, which reduces the need for additional energy. Variable speed drives for fans and heating elements also help optimize energy use by adjusting power according to the needs of the oven.
- Curing Time and Temperature Control: Large ovens need to offer precise curing time and temperature control. Depending on the type of powder being used and the size of the parts, curing temperatures generally range from 320°F to 400°F (160°C to 200°C). Oversized parts may require longer curing times to ensure that the powder flows, fuses, and hardens correctly. A reliable and programmable digital control system allows operators to set and monitor the curing parameters for different types of powder and parts.
- Ventilation and Exhaust: Effective ventilation is crucial in large ovens to control the buildup of fumes and maintain a safe working environment. Exhaust systems must be powerful enough to remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other airborne particles created during the curing process. These systems are typically equipped with filtration units that trap any harmful particles before they are expelled from the oven. Proper ventilation helps keep the coating environment clean and prevents contamination of the powder.
- Automation: In large powder coating operations, automation plays a major role in improving both efficiency and consistency. Automated conveyor systems are commonly used to move large parts through the various stages of the coating process, including pre-treatment, powder application, curing, and cooling. Robotic arms or automated spray guns can be used for precise and uniform application of powder, reducing human error and improving finish quality.
- Cooling Zones: After parts are cured, they must be cooled down to room temperature. This is especially important in large ovens where high heat is involved. Large powder coating ovens may incorporate cooling zones at the end of the curing chamber, where forced air or water-cooled systems are used to gradually lower the temperature of the parts. Cooling is essential for ensuring the integrity of the coating, as rapid temperature changes could cause defects such as cracking or warping.
- Pre-treatment Areas: For large parts, the pre-treatment process is just as critical as the coating process itself. Before powder coating, parts typically need to be cleaned and pre-treated to remove dirt, oils, rust, and other contaminants. Pre-treatment can include methods such as sandblasting, chemical cleaning, or phosphating. Many large powder coating systems are designed to integrate pre-treatment booths or tanks with the oven for an efficient and streamlined process.
- Material Handling: Large powder coating ovens often require robust material handling systems to move parts in and out of the oven efficiently. These handling systems can include overhead conveyors, rotary tables, or forklifts to position parts accurately inside the oven. Having an efficient material handling system is key to reducing downtime between batches and increasing overall throughput.
- Customization and Flexibility: Large powder coating ovens can be customized for specific production needs. For example, manufacturers might need a dual-zone oven with separate heating and curing zones to handle different types of coatings or materials simultaneously. Flexibility in oven design also allows manufacturers to accommodate varying production volumes, whether they are running small, custom batches or large, high-volume orders.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: Given the large size of these ovens, regular maintenance is essential for keeping them running at peak performance. This includes cleaning the filters, heating elements, and airflow ducts, as well as inspecting insulation and ventilation systems for wear and tear. Preventive maintenance helps avoid costly downtime and ensures that the oven operates efficiently over time.
Types of Large Powder Coating Ovens
- Batch Ovens: These are typically used in facilities that do not require continuous production and are designed for larger parts that need to be processed in batches. Batch ovens can accommodate a wide variety of part sizes and allow flexibility in production, making them ideal for custom jobs or diverse product lines.
- Conveyor Ovens: For high-volume, continuous production, conveyorized ovens are often used. These ovens feature a moving conveyor belt that continuously transports parts through the coating process. Conveyor ovens are more efficient for large production runs and can handle many parts at once.
- Gas and Electric Ovens: Large ovens can be powered by either gas or electricity. Gas ovens tend to be more cost-effective in terms of operational expenses but may require more careful temperature management. Electric ovens offer precise temperature control and are easier to maintain, making them suitable for environments where fine control over the curing process is essential.
Conclusion
Investing in a large powder coating oven requires careful consideration of factors such as energy efficiency, temperature control, airflow, material handling, and automation. The right oven will not only improve the quality and consistency of the finishes but also help optimize production throughput, reduce waste, and lower operating costs. Whether you’re coating large automotive parts, heavy machinery, or other oversized items, selecting the right large powder coating oven system is essential for maintaining high production standards.
Large powder coating ovens are critical for handling high-volume production and large parts, making them essential for industries like automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery manufacturing. When selecting an oven for large-scale operations, several factors must be considered to ensure the system can handle the demands of high-throughput production while maintaining consistent coating quality.
Size and capacity are key considerations. Large ovens are designed to accommodate oversized parts such as automotive bodies, industrial equipment, or large furniture components. The oven must be spacious enough to allow for sufficient airflow and uniform heat distribution around the parts. The interior dimensions need to be customized based on the size of the items being coated, as oversized items often require greater space for efficient curing and coating application. Some manufacturers opt for modular designs, which allow the oven to be expanded or adjusted to accommodate changing production needs.
Temperature control and uniformity are particularly important in large ovens. Ensuring that the oven can maintain a consistent temperature across all parts, especially when filled to capacity, requires a robust airflow system. Powerful fans and strategically placed air ducts ensure that heated air circulates evenly throughout the chamber. This even distribution of heat helps avoid any areas of the parts that may be under-cured or over-cured, which can lead to defects in the finish. Precision temperature control also ensures that parts are properly cured at the optimal temperature, allowing the powder to melt, flow, and bond to the surface effectively.
Energy efficiency is another major consideration when dealing with large powder coating ovens. Large ovens consume significant amounts of energy, so it’s important to choose an oven system that can minimize operational costs. Insulation is key to maintaining heat within the oven, reducing the need for constant energy input. Additionally, energy-saving features like heat recovery systems capture hot exhaust air and reuse it to preheat incoming air, further reducing energy consumption. Adjustable speed controls for fans and heating elements also help optimize energy usage based on the specific needs of the oven during production.
Maintaining consistent curing times and temperatures is critical to achieving high-quality finishes. Oversized parts often require longer curing times due to their size and mass, and precise control over the curing cycle is essential to ensure proper adhesion and durability of the coating. Programmable control systems in modern ovens allow operators to set and adjust curing parameters for different powder types, ensuring the coating is applied uniformly and effectively. These systems also make it easier to switch between different coating types or finishes, allowing for a versatile coating process that can handle varying production requirements.
Ventilation and exhaust systems are also crucial in large powder coating ovens. The curing process generates fumes and airborne particles that must be properly vented to maintain a safe working environment. Efficient exhaust systems remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful substances, filtering them before they are expelled into the atmosphere. These systems help to prevent contamination of the powder and reduce environmental impact while ensuring a clean, safe environment for workers.
Automation plays a significant role in large-scale powder coating operations. Automated conveyor systems are commonly used to transport parts through the various stages of the coating process. These systems help move parts from pre-treatment to powder application, curing, and cooling, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing the chances of human error. Automated spray guns or robotic arms are also used to apply powder more consistently, especially on complex or large parts. The precision of these systems improves the quality of the coating and allows for more efficient production runs.
Cooling systems are essential after the curing process, especially for large parts. Rapid cooling can lead to defects such as warping or cracking, so many large ovens feature integrated cooling zones. These zones use either forced air or water-cooled systems to gradually lower the temperature of the parts, ensuring that the coating solidifies without introducing any stress to the surface. Cooling systems not only protect the integrity of the finish but also prepare the parts for further handling or packaging.
Pre-treatment is an essential step before powder coating, and many large ovens are designed with integrated pre-treatment areas to streamline the entire process. Parts must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any oils, dust, or contaminants that could prevent the powder from adhering properly. Methods such as sandblasting, chemical cleaning, or acid washing are commonly used for this purpose. The inclusion of pre-treatment areas within the oven system can reduce the time required to move parts between different processing stations and help ensure that all parts are prepared uniformly before coating.
Material handling is a critical component of large powder coating systems. Efficient material handling systems help move large or heavy parts into and out of the oven, reducing the risk of damage and improving throughput. Overhead conveyors, rotary tables, or forklifts may be used to position parts accurately within the oven. A well-designed handling system minimizes the time between batches, ensuring that production runs smoothly and reducing delays caused by manual handling.
For large-scale powder coating operations, flexibility is also important. Powder coating ovens for large parts often need to accommodate various part sizes, types, and finishes. Modular oven designs or adjustable racking systems allow for quick adaptation to different production runs, making it easier to coat multiple types of parts in a single batch. Some systems also allow for the use of different curing profiles, giving operators the flexibility to adjust curing temperatures and times based on the specific requirements of the coating material being used.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure that large powder coating ovens remain efficient and operate at peak performance. Cleaning the filters, inspecting the heating elements, and checking the airflow system are all part of routine maintenance that helps prevent downtime. Preventive maintenance ensures that any issues are caught early before they cause equipment failure, ultimately extending the life of the oven and reducing the risk of production delays.
In conclusion, large powder coating ovens are complex, highly specialized systems designed to handle oversized parts and high-volume production. Features such as temperature uniformity, energy efficiency, automation, and flexible design all contribute to the effectiveness of these ovens. By selecting the right equipment and optimizing various aspects of the coating process, manufacturers can achieve consistent, high-quality finishes while improving productivity and reducing operational costs.
Continuing from the previous points, large powder coating ovens are often seen as the backbone of high-capacity manufacturing environments, particularly when producing parts in large batches or dealing with oversized items. Their role is not just about coating parts but optimizing the entire production flow to ensure high efficiency, consistent quality, and minimized waste. To further enhance the overall powder coating process, some advanced features and strategies are becoming increasingly popular in large ovens.
For large operations, having a batch versus continuous production approach is an important distinction. In batch production, each item or set of items is coated and cured before the next batch begins. This approach works well when dealing with different part sizes, shapes, or custom orders. On the other hand, continuous conveyor ovens are ideal for mass production where parts can be continuously processed through the coating and curing stages. These conveyor systems are automated, reducing the need for manual handling and speeding up the process, which is essential for industries like automotive or heavy machinery, where hundreds or thousands of parts need to be coated daily.
Moreover, robust system integration is crucial in large powder coating facilities. Large ovens are rarely used in isolation; they are part of an entire line of equipment, including pre-treatment stations, powder recovery systems, and cooling zones. These ovens often come with integrated control panels or PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems that can monitor the entire process. Operators can adjust the settings across multiple stages, track energy usage, monitor throughput, and receive alerts if any part of the system is out of range. This interconnected approach helps ensure that the process remains efficient and that any issues can be spotted and resolved quickly without disrupting the entire operation.
In addition, smart technologies and data analytics are making their way into large powder coating systems. For instance, some ovens feature sensors that can monitor parameters like temperature, humidity, and even the thickness of the powder coating in real time. This data is fed into a central system that can alert operators to inconsistencies or variations before they result in defective parts. The use of AI and machine learning algorithms can also predict potential failures or maintenance needs, leading to more effective predictive maintenance rather than reactive repairs. These features can significantly improve uptime, reduce unplanned maintenance costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Another key area of focus for large powder coating ovens is environmental impact. Powder coating is already considered a more eco-friendly finishing method than traditional liquid coatings due to its low levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). However, large operations still need to manage energy consumption, waste, and emissions. Advanced ovens with integrated filtration systems help reduce airborne particulates, while advanced energy-efficient burners or electric-powered ovens help minimize energy use. Additionally, closed-loop powder recovery systems can reduce waste by capturing and reusing oversprayed powder, which not only cuts down on material costs but also minimizes the environmental footprint of the operation.
One of the often-overlooked yet crucial aspects of large-scale powder coating is product handling after curing. Once parts are coated and cured, they still need to be handled and stored carefully to avoid damage to the coating. A well-planned post-coating process includes automated cooling zones, inspection stations, and even automated packaging systems to ensure that the parts reach their next stage of production or shipment without compromising the quality of the coating. Automated inspection systems equipped with cameras and sensors can check for any defects in the coating immediately after curing, such as pinholes, uneven coverage, or discoloration, which helps ensure that only perfectly coated parts proceed to the next stage.
When it comes to flexibility, large powder coating ovens can often accommodate different types of coatings and finishing effects. Many systems are designed to handle a wide variety of powder types, from standard glossy finishes to more specialty coatings like textured or matte finishes. Depending on the requirements of the customer or the end-use application, the oven system might need to adjust its temperature, airflow, and curing time accordingly. Modern systems feature programmable settings that allow operators to quickly switch between different powder types or finish options without the need for manual adjustments or downtime. This is particularly useful for businesses that need to coat a variety of parts with different finishes or for operations that handle both custom and high-volume production runs.
Lastly, the maintenance and longevity of large powder coating ovens cannot be overstated. Given their size and the nature of their operation, these ovens undergo significant wear and tear over time. Regular cleaning, including removing powder build-up from heating elements, air circulation systems, and ducts, is crucial to maintaining consistent performance. Additionally, inspecting parts such as heating elements, fans, air filtration systems, and cooling systems should be a part of a comprehensive preventive maintenance plan. Scheduling regular maintenance and replacing worn-out components ensures that the oven continues to perform at peak efficiency and minimizes unplanned downtime.
In terms of customization, larger powder coating ovens can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a business. For instance, some ovens are designed with adjustable conveyor speeds, allowing for greater flexibility in the curing process, or with specialized racks and supports that can be configured to hold various types of products securely. Manufacturers may also opt for a dual-zone oven with separate temperature and airflow controls for different types of products or coating processes. This flexibility can enhance efficiency and allow for a more diverse range of products to be processed without the need to invest in additional equipment.
In conclusion, large powder coating ovens are not just about coating; they are integral to the overall manufacturing process. By optimizing every stage from pre-treatment to post-coating handling, integrating automation, and ensuring energy efficiency, manufacturers can achieve consistently high-quality finishes while improving productivity and reducing operational costs. The key to success in large-scale powder coating operations lies in selecting the right equipment and features that align with both current and future production needs.
Continuing with the conversation about large powder coating ovens, it’s important to delve deeper into some of the more advanced technologies and methods that are increasingly shaping the future of the powder coating industry. These innovations not only enhance the performance and capabilities of large ovens but also pave the way for more sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective operations.
One such advancement is the development of hybrid ovens, which combine both convection and infrared (IR) heating technologies. Hybrid ovens use both air circulation for even heat distribution and infrared radiation to deliver rapid surface heating, which is especially useful for large or dense parts that require faster curing times. Infrared heat is particularly effective at quickly heating the surface of parts, while convection heat ensures that the entire part reaches the desired temperature. By combining these two methods, hybrid ovens allow for more precise control over the curing process, leading to faster cycle times without sacrificing the quality of the finish. Additionally, hybrid ovens can significantly improve energy efficiency, as infrared heating requires less energy to heat surfaces directly compared to traditional convection-only ovens.
Modular oven designs are also becoming more popular, especially in large-scale operations that have fluctuating production demands. Modular ovens are built in sections that can be easily added, removed, or reconfigured, offering greater flexibility for scaling up or down as needed. This allows manufacturers to adapt to changes in production volume or new product requirements without having to invest in entirely new equipment. For example, if a company needs to increase capacity during peak seasons, they can add more modules to their existing system to accommodate the increased workload. Conversely, if demand drops, the system can be downsized by removing or reconfiguring modules. This scalability is a significant advantage in an industry where production needs can shift rapidly.
Another cutting-edge feature in large powder coating ovens is smart temperature and process monitoring systems. These systems use sensors embedded throughout the oven to continuously track and monitor critical parameters like temperature, humidity, airflow, and even powder thickness. The data collected by these sensors is transmitted to a centralized control system, where it can be analyzed in real time. This not only provides operators with greater visibility into the coating process but also allows them to make immediate adjustments to ensure optimal performance. For instance, if the system detects a deviation in temperature or airflow, it can automatically adjust the settings to correct the issue, helping prevent defects and maintain consistent quality.
In large-scale powder coating facilities, automated material handling systems are crucial for maintaining efficiency. These systems can move large parts through the pre-treatment, coating, and curing processes without requiring manual intervention. Overhead conveyors or automated trolleys are commonly used to transport items through the various stages of the process, reducing labor costs and minimizing the risk of damage to parts. By automating material handling, manufacturers can improve throughput and reduce cycle times, which is particularly important when working with high volumes of parts. Some advanced systems even include automatic part detection, allowing the system to adjust the speed of the conveyor or the positioning of parts to ensure that they are consistently processed.
Furthermore, large powder coating ovens are increasingly equipped with advanced filtration systems to maintain clean and efficient air quality. These systems capture fine powder particles and exhaust fumes, preventing contamination and ensuring that only clean, reusable powder is recirculated. Effective filtration also ensures that excess powder is removed from the air, which can otherwise cause environmental pollution or even health hazards to workers. HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters or cyclone separators are often used in conjunction with these systems to ensure that only the cleanest air is released into the environment. This is especially crucial in large facilities where high volumes of powder coating take place, as maintaining a clean work environment reduces the risk of contamination and health-related issues for employees.
The integration of robotic coating systems in large powder coating ovens is another game-changing development. In traditional powder coating setups, manual spray guns or stationary automatic spray guns are used to apply the powder to parts. However, robotic arms equipped with advanced spray guns can apply powder with high precision, reducing waste and improving the uniformity of the coating. These robots can be programmed to adjust their movements based on the size and shape of the parts, ensuring consistent coverage even on complex or irregularly shaped items. Additionally, robotic systems can work faster than human operators, leading to higher throughput and better overall efficiency. These robots are often used in conjunction with automatic powder recovery systems, which help minimize powder waste and ensure that oversprayed material can be reused.
Large powder coating ovens also benefit from advanced software solutions that improve the overall management of the coating process. Many modern systems are equipped with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software that tracks production schedules, inventory levels,
Powder Coating Plant Design
Designing a powder coating plant requires a careful and strategic approach to ensure that the facility meets production needs, adheres to safety regulations, and operates efficiently. The design process involves selecting the right equipment, ensuring proper workflow, and integrating systems that promote consistency, energy efficiency, and safety. Below is an overview of key considerations and best practices for designing a powder coating plant.
Key Considerations for Powder Coating Plant Design
- Space Planning and Layout: The layout of the plant should prioritize efficiency and ease of movement between different stages of the powder coating process: pre-treatment, powder application, curing, and cooling. The plant should have clearly designated zones for each step, allowing for smooth material flow and minimizing the risk of contamination. A typical plant layout may include:
- Pre-treatment area: For cleaning and preparing parts before coating.
- Powder coating booth: For applying the powder to parts.
- Curing oven: To heat and cure the powder coating onto the parts.
- Cooling area: To allow parts to cool down after curing before they are handled or packaged.
- Inspection area: To check the quality of the coating.
- Storage and packaging areas: To store finished parts before shipping.
- Pre-Treatment System: Pre-treatment is an essential step in powder coating. Parts must be cleaned to remove any oils, dirt, rust, or other contaminants before they are coated. The pre-treatment system could include various methods like:
- Phosphate washing (for corrosion resistance).
- Acid or alkaline cleaning.
- Blast cleaning or sandblasting.
- Water rinse to remove residual chemicals.
- Powder Coating Booth: The powder coating booth is where the powder is applied to the parts using an electrostatic charge, ensuring that the powder sticks to the surface of the part. The design of the booth should:
- Ensure proper ventilation: Exhaust fans and filtration systems must capture airborne powder particles to keep the booth clean and prevent contamination.
- Contain a high-efficiency powder recovery system: This system recycles oversprayed powder to reduce waste and increase material efficiency. Cyclone separators or cartridge filters are commonly used.
- Be spacious: There should be sufficient room for workers to move freely while applying the powder, and for larger parts to be coated.
- Allow for ergonomic application: The booth should be designed for ease of use and comfort for operators, with adjustable spray guns or automated systems for consistent coverage.
- Curing Oven: The curing oven is where the powder is heated to a high temperature to melt and bond to the surface of the part. The oven design should include:
- Precise temperature control: The oven must be able to heat evenly to the required temperature (typically between 320°F and 400°F, depending on the powder used).
- Uniform airflow: To ensure that the heat is distributed evenly across all parts, preventing defects such as uneven curing or poor adhesion.
- Energy efficiency: Ovens should be insulated to minimize energy consumption. Incorporating heat recovery systems can further reduce energy costs.
- Variable conveyor speed: The conveyor speed should be adjustable to accommodate different part sizes and curing times.
- Space for large parts: For larger parts, the oven should have sufficient clearance and the ability to adjust racks or hanging systems for proper curing.
- Cooling Area: After parts are cured, they need to be cooled down to room temperature before they can be handled or packaged. The cooling area may involve:
- Forced air cooling: Fans or ventilation systems help cool parts down after they come out of the curing oven.
- Water cooling systems: In some cases, water-cooled systems may be used for larger parts to quickly reduce their temperature.
- Quality Control and Inspection Area: After curing and cooling, parts should be inspected for defects. A dedicated inspection area is needed for:
- Visual inspection: For checking defects such as pinholes, uneven coverage, or discoloration.
- Thickness testing: Ensuring that the powder coating is applied at the correct thickness.
- Adhesion testing: Ensuring that the coating adheres to the part properly.
- Powder Recovery and Recycling System: Powder coating is an efficient process, but there will always be some waste due to overspray. A powder recovery system is crucial to reclaim excess powder and reduce material costs. Recovery systems can include:
- Cyclone separators: To separate and collect oversprayed powder from the airflow.
- Cartridge filters: To capture fine powder particles and ensure that the air in the booth remains clean.
- Automated powder handling: Systems that mix and recycle powder back into the coating process to minimize waste.
- Safety Considerations: Safety is a critical aspect in the design of any powder coating plant. Some key safety features include:
- Explosion prevention: Powder coating involves fine powders that can be flammable. The plant design should incorporate explosion-proof electrical systems, proper ventilation, and grounding systems to prevent static discharge.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Operators should be provided with appropriate PPE such as gloves, masks, and eye protection to avoid exposure to powders and fumes.
- Fire suppression systems: Fire extinguishers, sprinklers, and other fire safety equipment should be strategically placed throughout the plant.
- Environmental Controls:
- Ventilation and Air Quality: The plant should be equipped with powerful exhaust systems and air filtration units to capture and remove oversprayed powder, dust, and fumes from the atmosphere. HEPA filters are often used for fine particles.
- Waste Management: There should be a plan for disposing of waste materials, such as used powder, cleaning chemicals, and contaminated air filters. Closed-loop water systems for pre-treatment and cleaning can help conserve water.
- Energy Efficiency: Beyond insulation in curing ovens, the plant can incorporate energy-efficient lighting, heat recovery systems, and variable-speed drives to reduce energy consumption across the facility.
- Automation and Control Systems: A well-designed powder coating plant integrates advanced control systems to monitor and adjust every aspect of the process. Modern systems include:
- Programmable logic controllers (PLCs): For automating the coating process, managing conveyor speeds, oven temperatures, and other parameters.
- Touchscreen interfaces: For operators to easily set and monitor coating parameters in real-time.
- Data logging and analysis: To monitor production efficiency, energy usage, and quality control data.
- Storage and Packaging: The final stage of the powder coating process is packaging and shipping. A designated area should be set aside for:
- Finished product storage: Shelving or storage racks to organize coated parts.
- Packaging systems: To protect the coated parts during shipping, including wrapping, boxing, or other protective packaging methods.
Conclusion
Designing a powder coating plant requires thoughtful planning and careful integration of various equipment and systems to optimize performance. The layout must ensure smooth material flow, minimize downtime, and allow for future scalability. Ensuring energy efficiency, high-quality finishes, and safety standards are critical for a successful powder coating plant. By considering factors like pre-treatment, coating application, curing, cooling, inspection, and automation, a powder coating plant can be designed to meet both current production needs and future growth, while maintaining consistency and efficiency across all stages of the process.
In designing a powder coating plant, several critical factors must be carefully considered to create a seamless and efficient process that meets production needs while ensuring safety, quality, and sustainability. One of the first considerations is the layout of the plant, which should be optimized for smooth workflow between different stages, minimizing bottlenecks, and enhancing material handling. This means having a clear separation of the pre-treatment area, powder application booth, curing oven, cooling area, and inspection zones. The layout should also provide space for future expansion to accommodate increased production or the introduction of new processes.
Space utilization is also a key factor in the design, particularly for larger plants where room needs to be optimized for high-volume production. A layout that prioritizes efficient material flow—moving parts from one stage to the next without excessive handling—will help keep production moving smoothly. This can be achieved through automated conveyor systems, which guide parts from pre-treatment through to coating and curing. These conveyors need to be sized appropriately for the weight and size of the parts being processed, with careful consideration given to the type of products, whether they are small components or large, heavy items.
Pre-treatment systems should be robust and efficient, ensuring that parts are properly cleaned to remove oils, dirt, rust, or contaminants before coating. Depending on the parts, pre-treatment could involve processes like chemical cleaning, sandblasting, or acid etching. An efficient pre-treatment system is crucial for ensuring good adhesion and a high-quality finish. Once cleaned, parts must be dried thoroughly to prevent moisture from interfering with the coating process. This area should be designed for easy material flow, integrating washers, dryers, and perhaps even automated handlers to reduce human error and improve consistency.
For the powder coating booth, the design must take into account both the application process and the collection of overspray. The booth should be equipped with an effective exhaust system to maintain air quality and capture airborne powder particles. High-efficiency powder recovery systems like cyclone separators and cartridge filters are essential for recycling oversprayed powder, ensuring material efficiency and reducing waste. The booth must also be spacious enough to allow workers or robotic arms to apply powder evenly and efficiently. For larger or irregularly shaped items, it’s crucial to have adjustable spray guns or automated systems that ensure consistent coverage, even in hard-to-reach areas. The application booth should also have sufficient ventilation to keep the air clean and prevent harmful exposure to the powder.
The curing oven is another central piece of equipment in the design. It’s where the powder coating melts and bonds to the surface of the part, which requires precise temperature control. The oven must be capable of maintaining uniform heat throughout, ensuring the coating cures properly without hot or cold spots. Efficient airflow is essential for preventing defects such as uneven curing or incomplete bonding. Depending on the type and size of parts being coated, the oven may require adjustable conveyor speeds to allow different parts to be processed according to their individual requirements. The oven should also be energy-efficient, with good insulation and potentially heat recovery systems to minimize operating costs.
After curing, parts enter the cooling area where they must be allowed to cool before handling. Cooling can be achieved through forced air or, in some cases, water cooling systems for larger parts. This area should be designed to avoid any sudden temperature fluctuations that could cause defects in the coating, such as cracking or warping. It’s important to maintain proper airflow and manage cooling times to ensure that parts are handled correctly without affecting the finish.
Once cooled, parts must undergo inspection and quality control to ensure they meet the required standards. This area should be equipped with both manual inspection stations and automated systems for detecting coating defects like uneven coverage, pinholes, or discoloration. Thickness measurement and adhesion testing are also essential to verify that the coating has been applied properly and is durable. These quality checks are vital for ensuring that the final product meets both aesthetic and functional standards. Some plants use automated cameras or vision systems to inspect parts as they move through the process, helping identify defects early and reduce the need for rework.
In terms of safety and environmental controls, the design of the plant must prioritize worker safety and minimize environmental impact. Proper ventilation is a must throughout the facility, particularly in the powder application and curing areas, where fumes and dust can accumulate. Explosion-proof electrical systems and grounding should be integrated to prevent static discharge, which is a potential hazard due to the fine powders involved in the process. Fire suppression systems, including sprinklers and extinguishers, should be placed strategically around the plant to mitigate the risk of fire. Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as masks, gloves, and eye protection should be readily available for all personnel.
Environmental sustainability is also an increasingly important factor in plant design. Energy-efficient ovens, the use of closed-loop water systems in pre-treatment processes, and waste management practices for powder overspray and used chemicals all contribute to reducing the plant’s environmental footprint. Filtration systems help to capture and recycle oversprayed powder, and waste-to-energy systems can help to manage any residual waste in an eco-friendly manner.
In terms of automation, modern powder coating plants often integrate sophisticated control systems to manage the entire production line. PLC systems (programmable logic controllers) can automate tasks such as adjusting conveyor speeds, regulating oven temperatures, and controlling spray gun movements. This ensures that the coating process is consistent and reduces the potential for human error. Robotic coating systems are also becoming more common, as they can apply powder more evenly and efficiently than manual methods, especially for parts with complex geometries.
Lastly, storage and packaging play a crucial role in the final stages of the powder coating process. Finished parts must be carefully stored and packaged to prevent any damage to the coating. This may involve using automated packaging systems that wrap, box, or palletize parts for shipping. Parts should be stored in a clean, dry area to prevent contamination before shipping out.
Overall, the design of a powder coating plant is a complex and multifaceted process that involves much more than just selecting equipment. Every aspect of the layout, from pre-treatment to final inspection, must be carefully planned to ensure maximum efficiency, safety, and product quality. By focusing on automation, energy efficiency, quality control, and sustainability, a well-designed powder coating plant can not only enhance operational performance but also create a safer and more environmentally friendly working environment.
Continuing with the design of a powder coating plant, attention must also be given to integration of advanced technologies that can further enhance the efficiency and precision of the process. With the growing demand for customization and quicker turnarounds, modern powder coating plants are increasingly leveraging digital technologies to optimize their operations.
One major area of advancement is the use of smart manufacturing systems. These systems integrate Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, and data analytics to monitor and manage every aspect of the production process. For instance, sensors installed in the curing ovens and coating booths can continuously measure variables such as temperature, humidity, powder usage, and air quality. This real-time data is collected and analyzed, providing valuable insights into performance trends and enabling operators to make adjustments on the fly. By utilizing predictive maintenance tools, the plant can proactively address potential equipment issues before they lead to downtime or production delays, thereby improving overall efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Another key area where technology plays a role is robotics. Automated robots are being increasingly used in the powder coating process to ensure consistent coating quality and faster processing times. These robots can be programmed to coat parts with high precision and can even adapt to different sizes and shapes of products. By using robotic arms equipped with advanced electrostatic spray guns, parts are coated evenly, ensuring consistent powder distribution and reducing waste. The use of robotics can significantly speed up the coating process while reducing human error, leading to better productivity.
For powder recovery, more advanced systems are now available that can automatically adjust based on the amount of overspray collected. These recovery systems not only help reduce material waste but also ensure that the powder quality is maintained for reuse. The powder recovery system can be connected to the digital control system to monitor powder usage in real-time, making adjustments as necessary to optimize material savings.
As part of efforts to reduce waste and energy consumption, powder coating plants are also adopting closed-loop systems. These systems recycle water used in pre-treatment or cooling processes, thereby reducing water waste and minimizing the environmental impact of the plant. Additionally, energy-efficient lighting, such as LED fixtures, can be installed throughout the facility, contributing to lower electricity costs. By using variable-frequency drives (VFDs) for motors controlling conveyor speeds and air flow, the plant can adjust energy consumption based on the needs of the operation, ensuring energy is used only when required.
Beyond energy, sustainability is becoming increasingly important in powder coating plant design. In response to global environmental concerns, there is a shift toward using more eco-friendly powder coatings. Many manufacturers are choosing low-VOC (volatile organic compound) or zero-VOC powders that reduce emissions and are less harmful to both the environment and worker health. The design of the plant should incorporate systems that promote the use of these more sustainable coating materials and reduce waste disposal costs. For example, the powder recovery and filtration systems must be optimized to capture as much overspray as possible and prevent environmental contamination.
The layout and design must also accommodate workflow automation, not just within the core production stages, but also for functions like inventory management and shipping logistics. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) or conveyor systems can be used to move parts through the entire production line, ensuring consistent speed and reducing reliance on manual labor. These systems can be integrated with the plant’s central control software, allowing operators to track inventory, production schedules, and delivery deadlines in real time.
Another aspect of modern plant design is incorporating flexible workstations and ergonomic designs into the process. With some plants shifting towards a more customized approach, allowing different types of parts to be coated at the same time, workstations need to be adaptable for various sizes, part types, and coating requirements. Operators should have access to height-adjustable workstations, ergonomic spray guns, and adjustable settings for spray booths. This flexibility ensures both operator comfort and the ability to handle diverse product types without compromising coating quality.
Training and maintenance schedules are essential considerations in ensuring that the plant operates at peak efficiency. Regular training for operators and maintenance staff ensures that they are familiar with the latest technologies and best practices in powder coating processes. Routine maintenance is also critical to ensure that the equipment operates smoothly, and scheduled inspections of critical components like spray guns, recovery systems, and curing ovens help prevent unexpected downtime.
An emerging trend in plant design is the emphasis on data integration and process optimization. Plant managers are increasingly leveraging cloud-based software that can aggregate data from multiple sources, including powder recovery, oven performance, and material handling systems. This software allows for centralized monitoring and control, enabling decision-makers to access real-time information from anywhere, enhancing communication, and improving decision-making.
Additionally, quality management systems (QMS) integrated into the plant design help ensure that the finished products meet the highest standards. These systems can track every part through the coating process, recording detailed data at each stage—pre-treatment, coating, curing, and cooling. If any defects are identified, the system can trace back to the exact point in the process where the issue occurred, making it easier to isolate and address the root cause of the problem. This traceability is particularly important for industries with strict compliance regulations, such as the automotive or aerospace sectors.
The packaging and shipping areas should also be designed with efficiency in mind. With automated packaging solutions, parts can be quickly prepared for shipment without the need for extensive manual labor. Additionally, the design should incorporate storage solutions that prevent damage to coated parts, such as specialized racks or crates that secure parts in place and protect the coating during transportation.
Ultimately, the goal of any powder coating plant design is to create an efficient, sustainable, and safe production environment that produces high-quality finishes on time and within budget. The combination of automation, energy efficiency, quality control systems, and advanced technologies will help plant operators achieve this goal, ensuring that they can meet the demands of the industry while minimizing their environmental footprint and operational costs. By continuously incorporating innovations and focusing on best practices, powder coating plants can remain competitive and adaptive to the evolving needs of manufacturers and consumers.
Continuing further with the design of a powder coating plant, the integration of advanced technologies plays a pivotal role in optimizing overall performance. One key element of this is the adoption of advanced robotics and automation. Automated systems have become indispensable for achieving higher production rates, precision, and consistency in coating quality. These systems are particularly beneficial in industries that require high throughput or deal with parts that have intricate geometries, which are often difficult to coat uniformly by hand.
Robotic arms, equipped with electrostatic spray guns, are now commonly used to apply powder coatings to parts. These robots offer superior repeatability and precision compared to manual applications, ensuring consistent and uniform coverage. Robotic coating systems are capable of adjusting spray gun positions in three-dimensional space, allowing them to efficiently coat complex parts without requiring significant human intervention. This capability reduces the chances of coating defects such as uneven thickness, overspray, or poor adhesion, ultimately improving the quality of the final product.
The flexibility of robotic systems is also a key benefit. They can be programmed to coat a wide variety of parts, from small automotive components to large industrial machinery, without requiring extensive changes to the setup. This adaptability helps improve the versatility of the plant, allowing it to handle multiple product lines without major downtime between different production runs.
In addition to robotic arms for powder application, other forms of automation are becoming increasingly integral in material handling and part movement within the plant. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and conveyor systems ensure that parts are efficiently transported through different stages of the coating process, from pre-treatment to powder application and curing. By integrating these automated systems with advanced control software, plant managers can optimize workflow, reduce human error, and ensure that parts move through the facility at the right pace for the entire production cycle.
Material handling systems are also crucial in a powder coating plant, as they impact overall throughput. Conveyors, for instance, need to be robust enough to support the weight and size of the parts being coated. These systems should be designed for both speed and safety, with easy integration into the broader process to maintain efficiency. Using automated conveyors reduces the manual labor required to move parts and improves consistency, particularly in plants with high production demands.
Control systems within the plant should also be highly automated and centralized. With the rise of Industry 4.0 principles, digitalization and data integration are becoming standard practices. A robust plant management system can connect all aspects of production—from powder recovery to curing oven performance—through Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and cloud-based software. These systems collect real-time data on performance metrics like powder usage, curing temperature, and oven efficiency, which can then be analyzed for trends or potential issues.
This centralized control enables operators to monitor and make adjustments remotely, reducing the need for constant physical presence and streamlining the operation. Furthermore, the integration of predictive analytics and machine learning allows for identifying maintenance needs before they lead to equipment failure. This type of predictive maintenance relies on historical data and real-time monitoring to forecast when a piece of equipment is likely to require servicing. By addressing potential issues in advance, plants can minimize downtime, reduce repair costs, and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Additionally, data-driven decision-making becomes more feasible with the integration of big data systems. By analyzing vast amounts of operational data, powder coating plants can uncover areas of inefficiency or improvement that may not be immediately obvious. For example, data analytics can help pinpoint sections of the production line that are underperforming, identify patterns in defective parts, or even suggest better energy management practices based on usage trends. As a result, plant managers can continuously optimize operations, reduce waste, and ensure high levels of productivity.
While automation and digitalization streamline processes, operator training remains critical. Even in highly automated facilities, skilled operators are needed to manage equipment, perform quality control checks, and address troubleshooting tasks. An ongoing focus on training ensures that employees remain well-versed in the latest technologies and processes. Training programs can cover not only operational aspects but also safety procedures, especially considering the hazardous nature of some materials used in powder coating. Proper training helps reduce the risk of accidents and ensures that the plant runs efficiently and safely.
Energy efficiency continues to be a central concern in plant design. A powder coating plant can be energy-intensive, especially due to the high heat requirements of the curing ovens. To address this, the plant design should incorporate energy-saving solutions such as heat recovery systems. These systems capture waste heat from ovens or curing chambers and redirect it to other parts of the plant, like pre-treatment stations or the air handling systems. This helps reduce the demand for new energy input and lowers the facility’s overall energy consumption. Moreover, adopting energy-efficient lighting, such as LED fixtures, can also contribute to reducing electricity costs.
To further enhance sustainability, the plant should consider water conservation. Many plants use large amounts of water during the pre-treatment process, such as in phosphate washing or rinse tanks. By implementing closed-loop water systems, water usage can be minimized, and the need for constant water replenishment can be reduced. This not only helps cut down operational costs but also reduces the environmental impact of the plant. Additionally, the facility could explore using more eco-friendly pre-treatment chemicals or opting for alternative methods that are less water-intensive.
Waste management is another area where sustainability efforts can be strengthened. Powder overspray, cleaning solvents, and other waste products can accumulate during the powder coating process. Having a comprehensive waste management plan in place is crucial for keeping the plant’s environmental impact in check. Powder recovery systems can capture oversprayed material, reducing waste and allowing for the reuse of powder, which helps lower material costs. Furthermore, the plant should follow best practices for handling and disposing of any residual chemicals or contaminated filters, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
To enhance the final product’s quality, quality control systems should be integrated into every phase of production. Utilizing automated inspection systems equipped with vision cameras can ensure that parts are correctly coated and meet required specifications. These systems can perform checks such as verifying coating thickness, identifying defects like pinholes or surface imperfections, and ensuring that the adhesion of the coating is up to standard. These automated quality checks help reduce the need for manual inspection, increase accuracy, and improve the overall quality of the final product.
Lastly, the packaging and storage area should be designed to protect the finished products. After the coating has been applied and the parts have cooled, they need to be stored and transported carefully to avoid damage. Automated packaging lines can efficiently wrap and package parts, ensuring they are secure for shipment. This area should also be organized to handle parts according to size and type, minimizing the chances of damage or mix-ups during storage and distribution.
In conclusion, designing a cutting-edge powder coating plant requires a blend of advanced technologies, efficient workflows, and a strong focus on sustainability and safety. Through the use of automation, data integration, energy efficiency, and environmental stewardship, manufacturers can create highly productive and future-ready facilities that are capable of meeting the growing demand for high-quality powder-coated products. By continually improving these processes and embracing new technologies, powder coating plants can remain competitive and responsive to both market changes and regulatory requirements.
8x8x10 Powder Coat Oven

An 8x8x10 powder coating oven refers to the physical dimensions of the oven used in the powder coating process, where the internal space measures 8 feet in width, 8 feet in height, and 10 feet in length. This size of oven is typically used for coating larger or bulkier parts, such as automotive components, industrial equipment, or large machinery. Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects and considerations for an 8x8x10 powder coating oven:
1. Oven Size and Capacity
- Interior Dimensions: The oven’s interior size of 8 feet by 8 feet by 10 feet provides a relatively large area for processing multiple parts or larger items. This could accommodate a range of workpieces like large metal frames, automotive wheels, industrial parts, or other heavy components.
- Load Capacity: Depending on the type of materials being processed and the weight distribution, the oven must be designed to handle the load capacity efficiently, ensuring that the parts are adequately supported and moved throughout the curing process.
2. Heat Requirements
- The curing process involves heating the parts to a specific temperature, typically between 350-400°F (177-204°C), to melt the powder coating and allow it to bond to the surface. The size of the oven influences how heat is distributed.
- An oven of this size will likely have multiple heating elements (usually gas-fired or electric) to maintain consistent temperatures throughout the entire chamber. Air circulation within the oven is critical to prevent hot or cold spots, which can lead to uneven curing.
- Some larger ovens also feature heat recovery systems that help reduce energy costs by capturing and reusing heat.
3. Airflow and Circulation
- Uniform Heat Distribution: Proper airflow is crucial for ensuring that the heat is evenly distributed across the parts being coated. In an 8x8x10 oven, high-efficiency blowers or fans are typically used to circulate the air and prevent uneven curing or defects in the coating.
- Ventilation: Exhaust fans or ventilation systems are also necessary to remove fumes, gases, and any volatile compounds produced during the curing process. These systems should be well-designed to avoid contamination of the coating and ensure a safe working environment.
4. Energy Efficiency
- Given the size of the oven, energy consumption can be significant. Energy-efficient ovens often incorporate insulated walls and doors to minimize heat loss. Proper insulation reduces the need for additional energy to maintain the desired curing temperature, thus improving the overall energy efficiency of the plant.
- Control Systems: Modern powder coating ovens often come equipped with programmable temperature controllers to monitor and adjust the temperature throughout the curing process. These controls ensure that the oven maintains optimal temperatures for the required duration.
5. Automation and Conveyor Systems
- An oven of this size is typically integrated with an automated conveyor system that transports parts through the oven. Conveyors are usually designed to move the parts at a consistent speed to ensure even exposure to the heat.
- Entry/Exit Points: The layout of the oven may include entry and exit points to facilitate the continuous flow of parts, reducing downtime and increasing throughput.
6. Safety Considerations
- Temperature Controls: Ovens must have safety cut-offs and temperature alarms to ensure that the internal temperature does not exceed safe levels. This is essential to avoid potential hazards like fires or damage to the parts being coated.
- Explosion-Proof Design: Since powder coating involves the use of fine powders, there is a risk of static electricity or fire. Many large ovens incorporate explosion-proof designs or ATEX-rated equipment to prevent accidents.
- Personnel Safety: Operators working near the oven should be equipped with proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as heat-resistant gloves, masks, and safety glasses.
7. Applications of 8x8x10 Powder Coat Ovens
- These types of ovens are often used in industries where larger parts need to be powder coated, including:
- Automotive: Coating large car frames, wheels, or body parts.
- Industrial Equipment: Coating large machinery components or equipment frames.
- Architectural: Coating metal frameworks for buildings, gates, or fences.
- Furniture: Large outdoor or industrial furniture, such as tables and chairs.
- Aerospace: Large aerospace components such as brackets and structural elements.
8. Maintenance
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the oven is essential to maintain optimal operation and prevent any powder buildup inside the oven, which could lead to contamination of the next batch or even fire hazards.
- Regular Inspections: The heating elements, fans, and exhaust systems should be inspected periodically to ensure they are functioning properly. Any wear or malfunctioning parts should be replaced to maintain the oven’s performance.
- Calibration: The temperature control system and thermocouples need to be calibrated regularly to ensure accuracy and consistent performance in the curing process.
9. Customization
- Some powder coating ovens can be customized based on specific production needs, including modifications to the size of the opening, conveyor speed, or heat zones within the oven. Customization ensures that the oven can efficiently handle the types of parts being coated and meet particular processing requirements.
In summary, an 8x8x10 powder coating oven is a versatile and efficient piece of equipment designed for processing large or numerous parts. By ensuring precise temperature control, proper airflow, and energy efficiency, it can provide consistent, high-quality finishes. Proper safety measures and maintenance are critical to ensure the longevity and safe operation of the oven, making it an essential asset in a powder coating facility.
An 8x8x10 powder coating oven is designed to handle large parts or multiple smaller parts at once, allowing for efficient powder coating in industries that require a larger workspace. The size of the oven allows for versatility in terms of the types of parts that can be processed, from automotive components to industrial equipment and machinery. Ensuring that the oven has the appropriate heat distribution is critical for achieving consistent results. The internal temperature must be regulated effectively across the entire surface area of the parts being coated, so a high-quality fan or blower system is integral to maintaining an even temperature throughout the oven. This is crucial to avoid coating defects such as under-curing or over-curing, which could impact the quality and durability of the powder coating.
Heat recovery systems are often implemented in these ovens to help reduce energy consumption. These systems capture the waste heat from the curing process and redirect it to pre-heat the incoming air or to other parts of the facility, further improving the overall energy efficiency of the operation. A well-insulated oven minimizes energy loss, which is particularly important given the large volume of space needing to be heated. The material of the oven walls is typically designed for maximum insulation to keep energy consumption down while maintaining the right temperature for curing.
When considering the design and construction of a powder coating oven, one must also account for airflow dynamics. Proper airflow is necessary not just for heat distribution, but also for ensuring that fumes, gases, and dust are effectively removed from the environment. Efficient air handling systems and exhaust fans are key for keeping the environment inside the oven safe and for meeting local regulatory requirements for air quality. The exhaust system must be capable of handling the specific demands of the coating process, especially in the case of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that may be released from the curing powder.
Automation plays a significant role in improving the operational efficiency of an 8x8x10 oven. Automated conveyor systems are typically used to transport parts through the oven, ensuring they are consistently exposed to heat and maintaining the throughput of the facility. The integration of sensors and control systems within the oven helps optimize the curing process. Temperature sensors, for example, can provide real-time data on oven conditions, ensuring that any fluctuations are detected and corrected before they impact the coating process. These sensors can also interface with the plant’s central control system, enabling remote monitoring and management of the curing oven’s performance.
In addition to temperature monitoring, the oven’s control system allows for precise regulation of curing times. For different parts, varying times at specific temperatures may be required to achieve the desired coating quality. An effective control system ensures that each part is treated accordingly, maximizing the efficiency of the process and preventing defects. Moreover, the oven’s digital controls make it easier to track production schedules and provide traceability for quality control purposes. In industries where quality is paramount, the ability to monitor each batch of parts through every step of the coating process is crucial for maintaining high standards.
Safety considerations are paramount in the design of powder coating ovens. Given the flammable nature of powder coatings and the high temperatures used in the curing process, the oven must be equipped with appropriate explosion-proof features. This includes explosion venting, spark arrestors, and ground connection systems that prevent the accumulation of static electricity, which can trigger fires or explosions. The oven should also feature automatic shutdown systems in case of critical failures or unsafe conditions.
Maintenance plays a key role in ensuring that the oven operates effectively over time. Regular cleaning and servicing are essential to prevent powder buildup inside the oven, which could compromise both the efficiency of the oven and the quality of the coating. For instance, powder accumulation on heating elements could obstruct airflow and affect the oven’s ability to heat uniformly. In addition, proper calibration of temperature controls and the periodic inspection of components like fans, exhaust systems, and thermostats are necessary to ensure optimal operation. Preventive maintenance, such as checking for leaks in the insulation, ensures that the oven maintains the required performance levels over its lifespan.
While an 8x8x10 oven is designed for heavy-duty use, it’s important that it is used in conjunction with other equipment within a powder coating plant to form an efficient production line. For example, parts typically need to go through pre-treatment processes before entering the oven for coating. Pre-treatment removes dirt, oil, rust, and other contaminants, which could prevent the powder from adhering properly to the surface. These treatments might involve chemical baths or abrasive blasting. After curing in the oven, parts must then be properly handled and stored to avoid damage to the coating. Packaging systems ensure that the final product is ready for transport or installation.
The ability to process a variety of parts in an 8x8x10 powder coating oven also means flexibility in production. Powder coating ovens of this size can be used for diverse applications, from automotive parts to large appliances or structural components. Adjustments to temperature and curing times can be made based on the specific needs of the parts being coated, allowing manufacturers to meet a wide range of customer requirements.
Energy-saving features like LED lighting, variable frequency drives (VFDs) for motors, and high-efficiency heating elements all contribute to reducing the operational costs of an 8x8x10 powder coating oven. Incorporating sustainable practices not only improves the plant’s energy footprint but can also lead to significant cost savings in the long term. For example, minimizing energy use during off-peak hours or utilizing heat recovery systems can greatly reduce operating expenses, which is particularly beneficial for facilities running multiple shifts or processing large quantities of parts.
Lastly, an 8x8x10 powder coating oven can support a higher level of automation in facilities that require high-volume production. With parts moving through the oven in a constant, steady flow, large batches can be processed more efficiently, with less downtime between cycles. As the demand for quicker turnarounds and higher-quality finishes continues to increase, the capabilities of powder coating ovens will continue to evolve, incorporating more advanced automation, monitoring systems, and energy-efficient technologies.
In summary, an 8x8x10 powder coating oven serves as a vital piece of equipment in manufacturing processes where larger parts or higher volumes of parts need to be coated efficiently and consistently. Its design ensures optimal heat distribution, energy efficiency, and safety while offering flexibility and precision to meet a variety of production needs. Proper maintenance, automation integration, and advanced control systems make this size of oven ideal for high-throughput powder coating operations.
Continuing further, the design of an 8x8x10 powder coating oven should also factor in flexibility for adapting to various types of coatings and materials. Different powders, such as epoxy, polyester, or polyurethane, may have different curing requirements, and an oven of this size must be versatile enough to accommodate these variations. A programmable control system that allows the operator to easily adjust temperatures and curing times for different powders or materials can enhance productivity and ensure consistent results across different production runs.
Additionally, environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in the design and operation of powder coating ovens. In many regions, environmental regulations require manufacturers to reduce emissions and limit the environmental impact of their processes. VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) emissions are one of the main concerns when curing coatings in an oven, as the heating process can release potentially harmful gases. To meet these regulatory standards, powder coating ovens are often equipped with advanced filtration systems or scrubbers to capture or neutralize emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
The integration of digital monitoring systems offers significant advantages in terms of both quality control and troubleshooting. With digital sensors in place, plant managers and operators can receive real-time data on critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, airflow, and energy consumption. This data can be monitored remotely via cloud-based platforms, allowing for quick intervention in case of deviations from the ideal parameters. Moreover, having such detailed data readily available helps in making more informed decisions regarding maintenance schedules, process improvements, and product quality assurance.
In some setups, ovens of this size can also include multi-zone heating systems. This setup allows different sections of the oven to be independently controlled, providing more precise control over the curing process. For instance, if certain parts require higher temperatures in specific areas of the oven, multi-zone heating systems allow for those adjustments without affecting the rest of the oven. This added flexibility is useful when processing parts of various sizes or materials that have different temperature and time requirements.
The powder coating oven’s interior design is another important aspect. To ensure that parts are properly coated, the oven may need to be designed with adjustable shelving or hanging systems that can accommodate the specific shapes and sizes of the parts. Hanging racks or jigs are typically used to position parts inside the oven, and these racks should be designed to allow for optimal airflow around each piece. This helps achieve even coverage of the powder coating and ensures that all areas of the part are exposed to the correct curing conditions.
Furthermore, maintenance downtime can be minimized with thoughtful design features. Quick access panels for cleaning and servicing components like fans, heating elements, and air filters are important. These allow maintenance teams to perform regular tasks, such as cleaning, inspection, and part replacement, without disrupting production for extended periods. The use of modular components within the oven’s structure can also simplify repairs and replacements, reducing lead times when parts need to be replaced.
As part of ongoing efforts to improve sustainability, some powder coating ovens are now designed with a focus on reducing emissions and waste. The capture of overspray, for example, is a major area where energy and material savings can be realized. By incorporating powder recovery systems, excess powder that is not deposited on the parts can be collected, filtered, and reused. This helps reduce the amount of powder wasted in the process and lowers material costs. Powder recovery systems are especially useful in larger ovens, like the 8x8x10 size, where the volume of overspray can be significant.
A robust filtration system is essential for maintaining the cleanliness of the oven, particularly in environments where the process is high-volume. Dust and airborne particles generated by the powder coating process can accumulate inside the oven, potentially affecting air quality and the curing process. Advanced high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters or electrostatic filters are commonly used to capture fine particles before they are released into the atmosphere. These systems help ensure that the air inside the oven remains clean and that any contaminants do not interfere with the final coating quality.
In terms of integration with other processes, the 8x8x10 oven can be linked with upstream and downstream equipment to form a seamless production line. For example, pre-treatment stages such as cleaning, phosphating, or shot blasting can be designed to feed directly into the oven without interruption. After coating, parts can be moved automatically to a cooling station or storage area via conveyor belts, ensuring a smooth workflow and minimizing the need for manual handling. This level of integration increases efficiency, reduces errors, and improves overall throughput.
One other important consideration is the temperature uniformity within the oven. For an oven of this size, ensuring an even temperature throughout the entire curing chamber is critical for consistent powder coating quality. Uneven heating could result in parts that are under-cured or over-cured, leading to defects such as poor adhesion, color inconsistencies, or improper curing of the coating. Advanced temperature mapping tools are often used during installation or calibration to check for hot spots or cold zones within the oven. By mapping the internal temperature at various points within the oven, adjustments can be made to ensure a more even temperature distribution.
In conclusion, an 8x8x10 powder coating oven is a critical piece of equipment for handling large parts or high-volume production in industries requiring powder coating. The oven’s size allows for flexibility in accommodating various parts, while features like automated conveyor systems, precise temperature controls, energy-efficient systems, and sustainability measures further enhance its performance. Maintenance, air quality management, and integration with other production systems are essential for keeping the oven running smoothly and ensuring high-quality finishes. By leveraging advanced technology, data-driven decision-making, and sustainable practices, an 8x8x10 powder coating oven can provide long-term benefits, improving both the productivity and environmental footprint of the manufacturing process.
Continuing further with the 8x8x10 powder coating oven, as the demand for efficiency and precision increases in manufacturing processes, it’s important to consider future-proofing when designing such a system. With ongoing advancements in technology, an 8x8x10 oven should be designed with flexibility and scalability in mind, allowing it to integrate with future innovations in automation, energy management, and coating technologies.
One area where innovation is taking place is in smart technology integration. These ovens can be equipped with IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities, enabling operators to monitor and control the oven remotely through a mobile app or web interface. This remote access allows for real-time adjustments to temperature, airflow, and process settings without being physically present in the facility. This not only improves operator convenience but also allows for quicker troubleshooting and enhanced productivity, as problems can be identified and rectified before they result in significant downtime or coating defects.
With the increased use of big data and predictive analytics, these ovens can be further enhanced. The data collected from various sensors within the oven, such as temperature, humidity, and airflow readings, can be stored and analyzed to predict when certain components may need maintenance. This predictive maintenance model helps in avoiding unexpected breakdowns, reducing repair costs, and extending the lifespan of the oven. For instance, a sudden deviation in temperature or airflow can be flagged as an early sign that a fan, heating element, or insulation may need servicing before the issue escalates.
Energy management is another area where smart ovens are making a difference. The integration of variable-speed drives (VSDs) for fans and motors can allow for more efficient operation, adjusting the speed based on the load or process requirements. These systems can be controlled dynamically, so the oven only consumes the energy it needs, rather than running at full power continuously. This can significantly reduce energy consumption and lead to lower operational costs. Coupled with solar energy integration or other sustainable energy sources, such systems can provide a more eco-friendly solution to manufacturing plants.
The powder coating industry is also seeing developments in eco-friendly powders. These powders have a lower environmental impact, either by reducing the amount of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted during curing or by being composed of more sustainable materials. For example, some modern powder coatings are designed to be applied and cured at lower temperatures, which in turn helps reduce energy consumption. These eco-friendly powders may also be more resistant to environmental factors, leading to longer-lasting coatings that are better suited to demanding applications.
One significant improvement for large-scale powder coating ovens is reduced curing time. Traditional powder coating processes can take a relatively long time, especially for larger parts or multiple items. However, recent innovations have focused on speeding up the curing process. Infrared (IR) curing technology, for example, can significantly shorten curing times by using infrared radiation to heat parts more quickly than conventional convection heating. Incorporating IR curing into the oven design would allow for faster throughput and better productivity in high-demand production environments.
For businesses aiming to stay competitive, the ability to customize the coating process is becoming increasingly important. Features such as variable curing zones, which can be independently controlled within the oven, give operators the flexibility to tailor the process for different parts or product types. This ability to adjust the curing profile for each part is especially valuable in high-mix, low-volume environments, where different parts with varying coating requirements are processed in the same batch.
Further advancing the design of these ovens are modular heating systems, which allow manufacturers to scale up or down depending on their production needs. These modular systems allow for easy addition or removal of heating elements, giving flexibility in response to varying production demands. Whether a company needs to expand its production capacity or decrease energy consumption during slower periods, a modular system can accommodate these changes without the need for a complete overhaul of the equipment.
In terms of workflow optimization, integrating smart robotics with powder coating ovens is becoming more common. Robotic arms or automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can be used to load and unload parts from the oven, improving speed and reducing manual handling. By incorporating machine learning into these robotic systems, the robots can become more efficient over time, learning the best ways to handle parts and load them optimally into the oven for uniform coating. This eliminates human error, reduces physical strain on workers, and ensures that parts are positioned and coated as effectively as possible.
Additionally, there is a growing trend in the automotive industry where the 8x8x10 powder coating oven is being used for more customized finishes. As consumers demand higher-quality finishes with specific colors, textures, and gloss levels, manufacturers are adopting more sophisticated control systems within the oven to achieve precise results. Multi-stage coating processes can be utilized, where parts are coated with different layers or types of powders to achieve complex finishes. For example, a gloss layer followed by a matte or textured top layer. By incorporating customizable settings in the oven, manufacturers can meet increasingly specific customer requirements.
Customer demand is increasingly dictating the speed of production. To stay competitive in industries such as automotive, consumer goods, or industrial equipment, manufacturers must be able to provide quick turnaround times while still maintaining the highest quality standards. Advances in automation, along with improved heat and airflow control, help to achieve faster production speeds without sacrificing the quality of the finish. An 8x8x10 oven equipped with these features ensures that manufacturers can scale up their operations, manage varying product sizes, and meet market demands with ease.
The globalization of supply chains has also led to the need for more efficient powder coating systems. As companies source raw materials from different parts of the world and aim for just-in-time delivery, having a well-organized, high-efficiency oven in place becomes crucial to minimizing delays. To this end, an 8x8x10 oven equipped with sophisticated scheduling and tracking software can help manage the flow of parts through the system. Automated tracking systems can track the status of each part, ensuring that parts are processed in the right order, minimizing downtime, and preventing scheduling errors.
Lastly, regulatory compliance is an important consideration when designing and operating powder coating ovens. Local and international regulations often set strict limits on emissions, waste, and workplace safety. To comply with these regulations, the oven design should include emission controls, filtration systems, and safety protocols that meet or exceed the required standards. Regular environmental audits and performance assessments should be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with these standards.
In summary, as powder coating technology continues to evolve, the 8x8x10 powder coating oven is poised to benefit from a host of innovations. From automation and energy efficiency to eco-friendly materials and advanced curing technologies, the future of powder coating ovens promises improved production capabilities, sustainability, and customization. Integrating smart technologies, modular designs, and scalable solutions will allow manufacturers to stay competitive, meet customer demands, and enhance the quality of their products while minimizing operational costs. With ongoing advancements, the powder coating process will continue to play a pivotal role in a wide range of industries.
Electric Powder Coating Oven

An electric powder coating oven is a specialized oven used in the powder coating process to cure powder coatings on metal parts. Unlike traditional gas-fired ovens, electric powder coating ovens use electric heating elements to generate heat. These ovens are commonly used in manufacturing industries for coating parts like automotive components, industrial machinery, household appliances, and various metal items. Electric powder coating ovens have gained popularity due to their precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and environmental benefits. Here’s an overview of the key components, advantages, and considerations involved in electric powder coating ovens:
Key Components of Electric Powder Coating Ovens:
- Electric Heating Elements:
- Electric powder coating ovens rely on electric resistance heaters (such as coil or ceramic heaters) to heat the air inside the oven. These elements are strategically placed to provide even heat distribution throughout the oven chamber.
- The heating elements can be controlled by digital thermostats or PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers to maintain a precise and stable temperature, crucial for the curing process.
- Temperature Control System:
- One of the standout features of electric ovens is their precise temperature control. Most electric ovens come equipped with programmable temperature controllers that allow operators to set and maintain the oven at a specific temperature for the required curing time.
- These ovens are typically capable of maintaining consistent temperatures across the entire chamber, ensuring uniform coating quality. Temperature sensors throughout the oven relay data to the control system for real-time adjustments.
- Air Circulation System:
- Electric powder coating ovens are equipped with forced-air systems (usually fans or blowers) to circulate hot air evenly throughout the oven chamber. This ensures uniform heat distribution, which is essential for curing the powder coating evenly on all parts.
- Proper airflow can also help in reducing curing times by ensuring that the heat reaches every surface of the part evenly.
- Insulation:
- To maximize energy efficiency, electric powder coating ovens are designed with high-quality insulation. Insulated walls reduce heat loss and ensure that the oven operates at the optimal temperature with minimal energy waste.
- The insulation also helps maintain a stable environment inside the oven, protecting the coating process from external temperature fluctuations.
- Exhaust and Ventilation System:
- During the curing process, fumes and gases are emitted from the powder coating materials. Therefore, an effective exhaust and ventilation system is necessary to maintain air quality and remove hazardous fumes.
- The system usually includes fume extraction fans and filters to capture and filter out the fumes, ensuring that the working environment remains safe for operators.
- Cooling System:
- After the powder coating process, parts often need to be cooled before they can be handled or packaged. Some electric ovens are designed with cooling zones or integrated cooling fans to speed up the cooling process and improve throughput.
Advantages of Electric Powder Coating Ovens:
- Precise Temperature Control:
- Electric ovens offer exceptional control over the temperature, with minimal fluctuations during the curing cycle. This ensures that the coating is cured consistently across all parts, minimizing defects and ensuring high-quality finishes.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Electric ovens are more energy-efficient than gas-fired ovens, as they eliminate the need for gas combustion and reduce heat loss. The precise control over heating elements allows for energy consumption to be optimized, particularly when the oven is only heating specific zones or areas.
- Some ovens come equipped with energy-saving modes and heat recovery systems that reuse heat to pre-heat incoming air, further enhancing efficiency.
- Lower Operating Costs:
- Electric ovens often have lower operating costs compared to gas ovens because electricity is generally more cost-effective than gas in many regions, particularly for small-to-medium-sized operations.
- The absence of complex gas lines or fuel storage requirements can also lower initial setup and maintenance costs.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Since electric ovens don’t rely on gas combustion, they produce fewer emissions. This makes them an environmentally friendly option for powder coating operations, especially in areas with stringent environmental regulations.
- Electric ovens also tend to have fewer moving parts than gas ovens, which can reduce the likelihood of mechanical failures and increase the lifespan of the equipment.
- Compact Design and Flexibility:
- Electric powder coating ovens tend to have a more compact design compared to gas ovens, which can be advantageous in facilities with limited space. Their versatility makes them suitable for smaller workshops as well as large-scale industrial applications.
- Safer Operation:
- With electric ovens, the risk of gas leaks or combustion-related issues is eliminated, making electric ovens generally safer to operate than gas-fired ovens.
- Many electric ovens are equipped with overheat protection and safety shutoffs to prevent dangerous operating conditions.
- Reduced Emissions and Maintenance:
- Electric ovens have fewer concerns related to combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide, compared to gas ovens. This reduces the need for additional ventilation and ensures a safer workplace environment.
- The absence of a gas supply system also minimizes the risk of maintenance issues related to gas lines, burners, and exhaust systems.
Considerations for Electric Powder Coating Ovens:
- Power Requirements:
- Electric powder coating ovens require a stable and reliable electricity supply to operate effectively. Depending on the size and energy requirements of the oven, it may need a dedicated electrical circuit or even a high-voltage supply.
- It’s essential to ensure that the local power grid can support the oven’s energy demands without causing frequent outages or power fluctuations.
- Size and Capacity:
- Electric ovens come in various sizes, from small bench-top models for small batches to large custom-designed ovens for industrial-scale operations. When selecting an oven, it’s crucial to choose one that meets the size and throughput requirements of the specific manufacturing process.
- An 8x8x10 oven or larger would typically be suitable for heavy-duty operations that need to process larger parts or higher volumes of coated items.
- Curing Time:
- While electric powder coating ovens offer precise control over temperature, curing times can still vary depending on the type of powder, the thickness of the coating, and the size of the parts. Some powders require higher temperatures or longer curing times, so understanding the optimal parameters for each specific application is important.
- Initial Cost:
- The upfront cost of an electric powder coating oven may be higher than other alternatives, particularly for ovens with advanced features like programmable controllers, multiple heating zones, and custom temperature profiles. However, the long-term savings from energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs can offset the initial investment.
- Space and Installation:
- As with any industrial oven, proper installation is crucial for safety and performance. Electric ovens require sufficient ventilation, adequate electrical connections, and proper safety clearances to ensure safe operation.
- Some electric ovens may require specific installation conditions, such as ventilation for exhaust fumes or adequate space for airflow systems to operate efficiently.
Applications of Electric Powder Coating Ovens:
Electric powder coating ovens are used in a variety of industries, including:
- Automotive Manufacturing: For coating wheels, bumpers, and other parts.
- Appliance Industry: For coating metal parts of household appliances like washers, dryers, and refrigerators.
- Metal Fabrication: For coating industrial equipment and machinery.
- Architectural Coatings: For coating metal parts used in building facades, window frames, and doors.
- Custom Finishing: For smaller workshops and shops offering powder coating services for custom jobs like furniture, outdoor decor, and artistic creations.
Conclusion:
Electric powder coating ovens offer numerous benefits, including precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and lower environmental impact. They provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality powder-coated parts with minimal operating costs and maximum safety. By selecting the right oven size, ensuring proper installation, and maintaining the oven correctly, manufacturers can achieve consistent and high-performance powder coating results for a variety of applications. Whether for small-scale production or high-volume operations, electric ovens are an excellent choice for powder coating processes.
Electric powder coating ovens provide a highly efficient and environmentally friendly solution for curing powder coatings on metal parts. Their primary benefit lies in the precise control they offer over temperature, ensuring that the curing process is consistent and uniform across all parts. This is especially important for maintaining a high level of finish quality in industries like automotive, appliances, and metal fabrication. With electric heating elements, these ovens are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing operational costs while providing a safer and cleaner working environment. Unlike gas-powered ovens, electric models don’t require complex gas lines, reducing both installation and maintenance needs.
The energy efficiency of electric powder coating ovens also contributes to a lower environmental footprint. By eliminating the need for combustion and using electricity as the heat source, these ovens produce fewer emissions and have minimal environmental impact compared to traditional gas-fired ovens. Their compact design makes them versatile for various applications, from small shops to larger industrial settings, and they can be customized to fit the space and production needs of the business.
While electric ovens generally have lower upfront operating costs, they require a stable and reliable power source to function effectively. This is a key consideration, particularly when dealing with larger ovens or operations requiring high energy input. The ovens are equipped with advanced controllers that help monitor and maintain the ideal curing temperature, which is crucial for the powder coating’s quality. Additionally, the advanced air circulation systems inside electric ovens ensure even heat distribution throughout the oven, reducing the chances of uneven curing, which could result in defects such as inconsistent texture, color, or adhesion.
The precise nature of electric ovens makes them particularly suitable for industries where product quality and consistency are paramount. Manufacturers can expect enhanced productivity, as these ovens provide shorter curing times and greater flexibility in processing different types of parts. Whether it’s for high-volume operations or smaller, more custom jobs, the ability to control temperature and airflow with such precision translates to higher throughput without compromising on the finish quality.
One of the challenges of electric ovens lies in their need for a substantial power supply. The larger the oven, the higher the energy requirements, which may necessitate a dedicated power circuit to ensure stable performance. However, these energy needs can be offset by energy-saving features in newer models, such as heat recovery systems, programmable control systems, and energy-efficient fans. These systems can help lower energy consumption by optimizing how and when energy is used within the oven. The use of infrared heating elements in some models can also accelerate curing times and improve energy efficiency, making the process even faster and more cost-effective.
As powder coating technology continues to evolve, manufacturers are increasingly looking at ways to integrate smart technology into their ovens. With IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity, operators can remotely monitor the oven’s performance and make adjustments in real time. This can be particularly useful in large facilities or in operations where multiple ovens are running simultaneously, as it allows managers to oversee the process without needing to be on-site constantly.
Moreover, electric powder coating ovens can be designed with modular systems that allow for easy adjustments to heating zones. This is especially useful for processes that require different curing temperatures or times for various parts. The modular approach also makes these ovens adaptable to growing production needs. As the demand for coatings changes, manufacturers can scale the ovens up or down without needing to replace entire systems, which offers a level of flexibility that traditional ovens may not provide.
In addition, electric ovens are often integrated with advanced filtration systems that capture harmful fumes or airborne particles generated during the curing process. These systems help maintain air quality in the workplace, ensuring a safe environment for workers. The reduced need for ventilation systems compared to gas ovens, which emit combustion gases, further contributes to a safer working space and lower operational costs.
While the initial investment in an electric powder coating oven may be higher than gas-fired models, the ongoing cost savings and environmental benefits make it a worthwhile investment for many manufacturers. Over time, the energy efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements of electric ovens can provide significant long-term savings. Additionally, with the growing emphasis on sustainability in manufacturing, electric powder coating ovens can help companies meet environmental regulations and enhance their commitment to eco-friendly practices.
Ultimately, the choice to use an electric powder coating oven depends on a variety of factors, including energy availability, the scale of the operation, and specific coating requirements. Electric ovens are highly adaptable and capable of delivering consistent, high-quality results for a wide range of applications. As the technology behind these ovens continues to improve, manufacturers will benefit from even more efficient and customizable solutions to meet the increasing demand for high-quality, durable coatings in various industries.
As the demand for precision and efficiency continues to grow across industries, electric powder coating ovens are becoming more sophisticated, offering even greater advantages. One of the significant improvements in recent years is the integration of automated temperature control and sophisticated monitoring systems. These advancements allow for real-time adjustments based on the readings from multiple sensors within the oven. This means the system can automatically compensate for slight variations in temperature, airflow, or humidity, ensuring consistent results regardless of external factors.
In industries where rapid turnaround times are critical, such as in the automotive sector or for consumer goods manufacturers, electric powder coating ovens equipped with advanced heat recovery systems are becoming increasingly popular. These systems can reclaim and reuse heat from the oven exhaust, reducing the amount of energy needed to reach the desired curing temperature. This process not only cuts down on energy costs but also helps reduce the overall carbon footprint of the operation, making it an environmentally friendly solution.
Energy efficiency is further enhanced with the use of variable-speed fans and inverter technology in modern electric ovens. These systems adjust the airflow inside the oven depending on the specific requirements of the coating job, improving heat distribution and minimizing energy waste. The dynamic adjustment of fan speeds allows for a more responsive curing process, where the airflow is optimized for each individual part or batch, ensuring even curing without overexposing certain areas.
Another area where innovation is taking place is in the integration of smart sensors and cloud-based monitoring systems. These sensors continuously track critical factors like temperature, humidity, and even the thickness of the powder coating. This data can be analyzed in real-time to ensure the coating is applied and cured to exact specifications. With cloud integration, manufacturers can access this data remotely, providing insights into oven performance, energy consumption, and overall process efficiency. This capability can lead to better decision-making, predictive maintenance, and greater overall control of the powder coating process.
For companies that specialize in small-batch production or custom finishing, electric powder coating ovens offer another key advantage: flexibility. Electric ovens can be easily reprogrammed for different temperatures, curing times, and airflow configurations, allowing operators to quickly switch between various coating formulations or part types. This is ideal for operations that require fast customization of coatings, such as custom automotive parts or specialized consumer products. With electric ovens, manufacturers can experiment with different powder types and finishes without worrying about the constraints of traditional gas-fired ovens.
Automation in electric powder coating ovens is another growing trend. By integrating robotic arms or automated conveyors, parts can be loaded and unloaded with greater efficiency, reducing human intervention and the potential for handling errors. This also increases throughput and reduces labor costs while ensuring a consistent and repeatable coating process. Automation further enhances the precision of the process, as robots can position the parts optimally within the oven for uniform heat distribution and better coating adhesion.
Another noteworthy aspect is the reduction in downtime due to the simplicity and reliability of electric ovens. Gas-fired ovens may require more frequent maintenance, particularly with burners and combustion components, whereas electric ovens typically have fewer moving parts and are easier to maintain. The absence of complex gas lines, burners, and ventilation systems simplifies the overall maintenance process, which can reduce repair costs and operational interruptions.
As manufacturers continue to prioritize sustainability and regulatory compliance, electric powder coating ovens are poised to meet these growing demands. With lower emissions, no need for hazardous gas systems, and the ability to use cleaner energy sources, electric ovens are in a strong position to help businesses reduce their environmental impact while still meeting industry standards and customer expectations. With tighter environmental regulations and a shift towards greener manufacturing practices, companies are turning to electric solutions to stay ahead of the curve.
Electric ovens also provide a safer working environment, particularly when compared to gas-fired ovens. Without the need for fuel combustion, the risk of gas leaks or explosions is eliminated. Additionally, because electric ovens do not generate carbon monoxide or other harmful gases, they help maintain better air quality inside the facility. The elimination of these hazards contributes to a safer work environment and helps companies comply with stringent workplace safety regulations.
Finally, the versatility of electric powder coating ovens cannot be overstated. Whether a company needs to coat small custom parts or high volumes of larger components, these ovens can be designed to accommodate a wide range of product sizes and shapes. Many manufacturers offer customizable electric oven designs that can be tailored to meet specific production requirements. Whether it’s adjusting the oven’s internal size, adding additional heating zones, or incorporating a specific type of airflow, the adaptability of electric powder coating ovens allows them to fit into a wide variety of production environments.
As manufacturers continue to push for greater efficiency, quality, and sustainability in their operations, electric powder coating ovens will continue to evolve. The combination of precise temperature control, energy efficiency, environmental benefits, and flexibility makes them a valuable investment for any manufacturer seeking to improve their powder coating process. Whether used for large-scale production runs or more customized finishing, electric powder coating ovens represent the future of high-performance, sustainable manufacturing practices in many industries.
As the powder coating industry evolves, electric powder coating ovens are becoming increasingly advanced, offering more customization options and enhanced performance for manufacturers. The future of electric ovens is likely to feature continued integration of automation and intelligent technologies, enabling even higher levels of precision and efficiency in the curing process.
A key aspect of this progression is the advancement of IoT (Internet of Things) technology. In the future, electric ovens will likely be connected to smart factory networks, allowing operators to monitor and adjust parameters remotely through cloud-based interfaces. This would provide real-time insights into the oven’s performance, such as temperature fluctuations, energy consumption, and maintenance needs. The integration of smart sensors that can detect any abnormalities, like temperature spikes or irregular airflow, can alert operators immediately, minimizing the risk of quality issues and costly downtime. Additionally, this connectivity will enable predictive maintenance, where the oven’s software can forecast when maintenance or part replacement will be necessary, preventing unplanned disruptions.
With the push towards Industry 4.0, more manufacturers will embrace data analytics in their powder coating operations. The data collected from electric powder coating ovens will not only optimize the curing process but also improve the efficiency of the entire production line. By analyzing trends in energy usage, material consumption, and throughput, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, reduce waste, and further optimize their operations for cost savings and increased productivity. Data-driven insights can also lead to improved product quality by identifying and addressing potential issues before they arise.
Another notable future development is the use of advanced coatings and alternative curing technologies. With ongoing research into more environmentally friendly powder coating materials, the ovens will need to adapt to new curing requirements. These new powders may have different temperature or curing time requirements, necessitating ovens that can easily adjust and handle these variations. Additionally, advancements in LED curing technology may allow for more energy-efficient curing at lower temperatures. These changes could lead to the development of hybrid curing systems that combine electric heating elements with LED or infrared technology, offering even faster curing times and more flexibility.
In the coming years, energy efficiency will continue to be a significant focus, driven not only by economic factors but also by increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Sustainable manufacturing practices will become more critical, and electric ovens are well-positioned to play a key role in this transition. The inclusion of solar power or alternative energy sources to power electric ovens could become more common, making powder coating even more sustainable. With the rise of renewable energy sources and the growing push for carbon-neutral manufacturing, electric powder coating ovens could be designed to integrate seamlessly with green energy initiatives.
Modular designs will likely see more adoption, especially in large-scale operations that need to adapt quickly to changing production demands. Instead of investing in an entirely new oven system, companies could purchase modular components, such as heating zones, temperature controllers, or airflow systems, which can be added or removed based on specific job requirements. This approach will provide flexibility and reduce the need for costly, large-scale renovations to existing facilities. Companies can expand their capacity without significant new investments, allowing for more streamlined operations and greater scalability.
Additionally, as the demand for customized and high-performance finishes continues to grow, electric ovens will be designed with even more specialized features, such as the ability to handle a wider range of parts and materials. This could include ovens with adjustable racks or conveyors, enabling parts of various sizes and shapes to be processed simultaneously or in a more optimized arrangement. These innovations would allow manufacturers to offer a broader range of coatings, from highly durable finishes to more aesthetically focused solutions, such as matte or glossy effects, without compromising on production efficiency.
The trend toward enhanced worker safety will also influence the design of electric powder coating ovens. Future models will likely incorporate advanced safety features, such as automated fire suppression systems, enhanced alarm systems for overheating or electrical issues, and user-friendly interfaces that allow operators to monitor the oven’s operation more effectively. These features will reduce the risk of workplace accidents, ensuring that operators are alerted to any issues before they lead to hazardous situations.
As the global market for powder coating continues to expand, particularly in emerging economies, the demand for affordable yet reliable electric powder coating ovens will increase. This will drive manufacturers to develop ovens that are not only energy-efficient but also more accessible to small- and medium-sized businesses. Innovations in production efficiency and cost-effectiveness will make these ovens a viable option for companies of all sizes, particularly those in industries like automotive aftermarket, furniture manufacturing, and small-scale industrial coatings.
One area of potential growth is in the use of 3D-printed components within electric powder coating ovens. As 3D printing technology continues to advance, it may become possible to design more customized parts for ovens, such as specialized trays, racks, or even internal components, that offer improved airflow, temperature control, or load-bearing capacity. These components could be printed on demand, reducing lead times and allowing manufacturers to create ovens that are tailored to the unique needs of their operations.
Finally, the future of electric powder coating ovens will also involve greater emphasis on user-friendly interfaces. As operators become more accustomed to complex systems and automation, manufacturers will prioritize intuitive control panels and software that simplify the process of adjusting settings, monitoring performance, and maintaining the oven. Touchscreens, mobile apps, and voice-controlled systems will be integrated into electric ovens, making it easier for users to interact with the equipment, track performance metrics, and make adjustments as needed.
In conclusion, the future of electric powder coating ovens is one of continuous innovation, driven by advancements in automation, smart technology, energy efficiency, and sustainability. As manufacturers strive to meet growing demands for high-quality coatings, faster turnaround times, and reduced environmental impact, electric ovens will continue to play a central role in the evolution of powder coating processes. By embracing new technologies, optimizing energy use, and improving operational flexibility, electric powder coating ovens will remain a crucial component of modern manufacturing across a wide range of industries.
4x4x7 Powder Coat Oven
A 4x4x7 powder coat oven refers to a powder coating oven with internal dimensions of 4 feet by 4 feet by 7 feet (L x W x H), which provides a compact yet functional space for curing powder-coated parts. This size is suitable for medium-sized parts, small batches, or limited production operations. It can be used across various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, and custom fabrication, where parts need to be coated with durable powder finishes.
Here are some key aspects to consider when evaluating or setting up a 4x4x7 powder coat oven:
1. Capacity & Size
- Interior Dimensions: The internal dimensions of 4 feet by 4 feet by 7 feet provide ample space for various types of parts, from smaller components to moderately sized items like car rims, brackets, and metal panels. It’s a versatile size, especially for businesses that don’t require an oven large enough for industrial-scale production but still need to handle a range of medium-sized pieces.
- Load Capacity: Depending on the design and materials used in the oven, the load capacity can vary. Ensure the oven has adequate weight support for the items being processed.
2. Heating System
- Electric vs. Gas: A 4x4x7 oven can be equipped with either an electric or gas-powered heating system. Electric systems are typically more energy-efficient and easier to maintain, while gas systems can be more cost-effective in certain scenarios, depending on local energy rates.
- Heating Elements: Electric ovens are typically equipped with heavy-duty heating elements designed to maintain a consistent curing temperature. Gas ovens use burners that generate heat and require proper ventilation for safe operation.
- Temperature Range: These ovens generally have a temperature range of around 300°F to 450°F (150°C to 230°C), which is standard for curing powder coatings effectively. The exact range may vary depending on the oven and the type of powder coating.
3. Airflow and Circulation
- Air Circulation: Proper airflow is critical to ensure even curing of the powder coating. A forced air circulation system helps distribute heat evenly throughout the oven, minimizing the risk of hot or cold spots. In a 4x4x7 oven, it’s common to have a fan system that helps with air circulation.
- Airflow Control: Many ovens allow for adjustable airflow, which can be essential for handling different types of parts or materials that may require slight adjustments in temperature or airflow.
4. Energy Efficiency
- Insulation: High-quality insulation ensures that the oven retains heat effectively, reducing energy consumption and improving overall efficiency. Look for ovens that have ceramic fiber insulation or other advanced insulation materials that minimize heat loss.
- Heat Recovery Systems: Some modern powder coating ovens are equipped with heat recovery systems, which capture and reuse heat from the exhaust air. This can reduce energy costs over time and improve the oven’s environmental impact.
5. Temperature Control
- Digital Temperature Control: The oven should feature digital temperature controllers for precise temperature adjustments. A reliable temperature control system ensures that the oven stays within the optimal curing range for the powder coating, ensuring a smooth, durable finish.
- Thermocouples and Sensors: Thermocouples and other temperature sensors monitor the oven’s interior, providing real-time feedback to maintain consistent heat distribution.
6. Safety Features
- Safety Interlocks: These are essential to prevent accidents or unauthorized access during operation. The oven should have safety interlocks to ensure the doors can’t be opened while it’s heating.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial, especially for gas ovens, to remove any potentially harmful fumes. Even electric ovens should have good ventilation to ensure that no heat buildup occurs.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Depending on the facility’s regulations, a fire suppression system might be required to prevent fires in case of overheating or malfunction.
7. Applications
- Automotive: The 4x4x7 oven size is ideal for powder coating automotive parts like wheels, brackets, trim, and small body panels.
- Metal Fabrication: It’s well-suited for fabricators working with medium-sized steel, aluminum, or other metal parts that need to be powder coated for durability or aesthetic appeal.
- Furniture: Custom furniture manufacturers may use such ovens for powder coating metal frames, parts, and components.
- Appliance Parts: This size also works well for curing parts used in household appliances, from small components to larger structural pieces.
8. Cost Considerations
- Initial Investment: While a 4x4x7 powder coat oven is smaller compared to larger industrial ovens, the cost can still vary significantly based on the quality of components, whether it’s electric or gas-powered, and the presence of additional features like digital controls or heat recovery systems.
- Operating Costs: Over time, electric ovens may cost more to operate compared to gas ovens, but the efficiency and low maintenance requirements of electric ovens can offset the initial investment. Gas ovens may have a lower operating cost if the cost of natural gas is low in your area.
9. Customization Options
- Custom Racks and Racking Systems: Depending on the parts being coated, the oven may offer customizable racking systems to ensure optimal part placement for even heat distribution.
- Multiple Zones: Some ovens allow for adjustable temperature zones within the same chamber, providing further customization based on the type of coating or part.
Conclusion
A 4x4x7 powder coat oven is an excellent choice for medium-sized operations that require an efficient, reliable curing solution. With the right features—such as energy-efficient heating, good airflow, precise temperature control, and safety systems—this size oven can meet the needs of a wide range of industries while ensuring high-quality results. Whether you’re coating automotive parts, metal furniture, or custom fabrications, a 4x4x7 powder coating oven can offer the capacity and performance needed to complete the job efficiently.
A 4x4x7 powder coat oven is ideal for businesses that need a balance between space efficiency and capacity. It provides a practical size for various industries, offering enough space to handle medium-sized parts without taking up too much room in the shop. The compact size makes it suitable for smaller production lines or businesses just starting to incorporate powder coating into their processes, while still providing the flexibility to coat a wide range of parts, from automotive components to custom furniture frames.
When choosing a 4x4x7 powder coat oven, one of the critical aspects to consider is the heating system. Electric ovens are more common for this size, providing consistent and reliable heating. They’re typically more energy-efficient and easier to install than gas-powered ovens, which require gas lines and ventilation systems. Electric ovens have fewer maintenance requirements, which can save time and costs in the long run, and offer the advantage of precise temperature control, ensuring a uniform finish across all parts.
The air circulation inside the oven is another crucial factor. A well-designed forced air system helps distribute heat evenly throughout the chamber, ensuring the powder coat cures evenly on all surfaces of the parts being processed. This is especially important for parts with complex shapes or larger surface areas that might otherwise be prone to uneven curing. Even heat distribution ensures that the finish is smooth and consistent, reducing defects like bubbles, streaks, or dull spots.
One of the benefits of a 4x4x7 oven is the energy efficiency it offers. Smaller ovens generally require less energy to operate, making them more cost-effective in terms of electricity consumption. This can be especially advantageous for smaller businesses or those with fluctuating production volumes. Additionally, modern ovens come equipped with insulation that helps retain heat more efficiently, reducing heat loss and improving the overall energy use. Over time, this can lead to lower operating costs, which is crucial for keeping business expenses in check.
Temperature control is another essential feature in a powder coating oven. The digital controllers found in most modern ovens allow operators to set and maintain precise curing temperatures, typically between 300°F and 450°F (150°C to 230°C). This precise control ensures the coating achieves its full hardness and durability. With automatic temperature regulation, there is less need for constant monitoring, which improves the efficiency of the coating process and reduces human error.
Safety features are also critical in ensuring a safe working environment. Many ovens come equipped with safety interlocks to prevent the door from being opened while the oven is operating at high temperatures. Some ovens also include fire suppression systems, which are particularly important if the oven is used for long curing cycles or if there’s a risk of material overheating. Adequate ventilation is essential, especially in gas-powered ovens, but even electric ovens benefit from proper exhaust systems to prevent any build-up of fumes from the powder coating process.
The capacity of the 4x4x7 oven can be adjusted depending on the type of racking and loading systems used. The oven can handle small and medium-sized parts, and the internal space can be optimized with custom racking options, which allows for efficient loading and unloading. This flexibility makes the oven suitable for different types of jobs, whether it’s a batch of automotive wheels, custom metal furniture, or components for home appliances.
For companies that need more flexibility or are experiencing growth, this oven size can be a stepping stone toward larger, more automated systems. Some models offer the possibility to upgrade or expand their capabilities, such as adding more zones for independent temperature control or increasing the size of the oven. If future expansion is a consideration, choosing a flexible, modular oven system could provide an easier transition when scaling up production.
In terms of cost-effectiveness, the upfront price of a 4x4x7 powder coating oven is relatively moderate compared to larger ovens. The initial investment is lower, making it accessible for smaller businesses or startups that are getting into powder coating. Over time, the energy savings and reduced maintenance costs make this oven a good investment. While operating costs may be higher for electric models compared to gas-powered ovens in areas with low gas prices, the maintenance and safety benefits often outweigh these costs.
For those looking to expand their capabilities, automation options can be added to the 4x4x7 oven. Adding automated loading and unloading systems, or even integrating robotic arms to handle parts, can increase throughput and reduce manual labor. This is ideal for businesses that need to improve production efficiency, ensuring a high turnover of parts without sacrificing the quality of the finish. Automation can also help with repeatability and precision, crucial for businesses that require consistent and reliable powder coating results.
In summary, the 4x4x7 powder coat oven is a versatile and cost-effective solution for businesses that need an efficient curing system for medium-sized parts. Whether you’re in the automotive, metal fabrication, or furniture industries, this oven can deliver high-quality finishes with precise temperature control and energy efficiency. With options for customization and the ability to scale, it offers a reliable starting point for companies looking to add powder coating to their operations or expand their current capacity. With the right design, features, and maintenance, a 4x4x7 powder coating oven can provide years of reliable service and ensure high-quality, durable powder-coated finishes.
As businesses seek to optimize their operations, a 4x4x7 powder coat oven offers numerous advantages for small to medium-scale production runs. Beyond the obvious benefits of energy efficiency and space management, it’s important to note how advancements in oven technology contribute to overall process improvements. One significant factor in modern powder coating ovens is advanced temperature control systems. These systems can now be fine-tuned to maintain precise heat levels, which is critical for ensuring the integrity of the powder coating finish. Such control minimizes the chance of under- or over-curing, which can lead to defects such as uneven texture, poor adhesion, or reduced durability.
The airflow system in these ovens has also seen significant advancements, with many 4x4x7 models now incorporating variable-speed fans. This technology enables the oven to adjust the airflow based on the load or part type, further improving the evenness of the cure. For instance, more delicate or complex parts can be coated with less intense air movement, while larger or more rugged pieces might benefit from stronger airflow. This capability provides the flexibility to work with a wide variety of powder types and substrates, ensuring versatility for different types of projects.
Another growing trend is the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) into powder coating ovens, including models like the 4x4x7. These ovens can be connected to cloud-based systems that monitor and report data on parameters such as temperature, humidity, curing time, and even maintenance schedules. For businesses, this means real-time access to key performance metrics from any location. If something goes wrong with the process, such as a fluctuation in temperature or a mechanical issue, the system can send alerts to operators or managers, allowing them to address the issue quickly before it leads to a production delay.
With the rise of data-driven decision-making in manufacturing, businesses can analyze performance data collected by the oven to make improvements in the coating process. For example, the data could reveal patterns in energy consumption, helping operators adjust parameters for optimal energy efficiency. Furthermore, this data can support predictive maintenance, where the oven’s system alerts operators about wear-and-tear signs or component failures, reducing downtime and unexpected repair costs.
Heat recovery systems are also becoming increasingly popular in 4x4x7 ovens. These systems capture excess heat from the exhaust air and redirect it back into the oven, reducing the energy required to maintain the curing temperature. As manufacturers look for ways to reduce their carbon footprint and lower operational costs, heat recovery technology is an effective solution that aligns with sustainability goals while enhancing the oven’s efficiency. This innovation not only makes the process more environmentally friendly but also maximizes the oven’s performance by optimizing the energy used for each cycle.
For companies that are focused on sustainability or reducing their environmental impact, electric ovens in the 4x4x7 range can be a key part of the strategy. Unlike gas-powered ovens, electric ovens don’t emit carbon dioxide (CO2) or other pollutants associated with combustion, offering a cleaner operation. Additionally, the ability to integrate with renewable energy sources, such as solar power, could make these ovens even more eco-friendly. By leveraging clean energy, businesses can reduce their reliance on traditional power sources, contributing to a greener manufacturing process and aligning with modern environmental standards.
Customization is another significant advantage when it comes to 4x4x7 powder coat ovens. Depending on the needs of the business, these ovens can often be tailored with specific features such as adjustable racking systems, multiple heat zones, or specialized ventilation options. For example, if a company specializes in coating parts of different sizes or shapes, they may opt for customizable racks that can be easily adjusted to hold the parts securely in place, maximizing the use of space inside the oven.
The modular nature of some modern 4x4x7 ovens also allows for easier future upgrades. If production needs change and a business requires a larger capacity, they can often add extensions or more advanced features to the existing system. This level of flexibility helps businesses avoid large capital expenditures while maintaining the ability to scale operations as necessary.
Safety is a non-negotiable aspect of powder coating operations, and electric ovens in this size class typically come equipped with a variety of safety features. These include automatic door locks that prevent opening the oven while it’s in operation, as well as temperature overrun protection, which ensures the system shuts down if temperatures exceed safe limits. Additionally, fire suppression systems are increasingly common in ovens used for long curing cycles, offering an added layer of protection against potential hazards associated with the heating process.
Maintenance and longevity are other factors that businesses must consider. Electric powder coating ovens like the 4x4x7 are typically low-maintenance compared to gas-powered models, thanks to fewer moving parts and the absence of a combustion system. They require less frequent servicing, which can be a major advantage for businesses that don’t want to deal with complicated upkeep. Regular cleaning of the oven, replacing filters, and checking the heating elements are generally all that’s needed to keep the system running smoothly.
The future of 4x4x7 ovens will likely see even more integration with robotics and automation. Some manufacturers are already incorporating automated systems to load and unload parts, which can significantly increase throughput and reduce manual handling time. These systems can also improve consistency by ensuring that parts are placed and processed with precision, enhancing both the efficiency and quality of the powder coating process. Automated systems can also help with part positioning inside the oven, ensuring that heat is distributed as evenly as possible.
The user interface of modern powder coating ovens has also improved, becoming more intuitive and easier to navigate. Many of the latest models feature touchscreen controls that make it simpler for operators to set temperature, time, and airflow, reducing the risk of human error. In some cases, ovens are also equipped with remote monitoring capabilities, enabling operators to adjust settings or troubleshoot issues via mobile apps or desktop interfaces.
Overall, the 4x4x7 powder coating oven is a flexible, efficient, and reliable solution for a variety of coating needs. As technology continues to evolve, the benefits of these ovens will expand, offering more precise control, better energy efficiency, improved safety, and advanced automation options, all of which will help businesses improve production speed, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. Whether you’re a small operation or scaling up, this size oven is versatile enough to meet the needs of a wide range of industries.
In addition to all the previously mentioned advantages, a 4x4x7 powder coating oven can provide even more opportunities for enhancing production processes and expanding capabilities. One area where businesses can see significant improvements is in batch processing. This oven size is particularly suitable for batch processing, which is common in industries like automotive, furniture, and metal fabrication, where parts are coated in groups rather than individually. The controlled environment inside the oven ensures that each part in a batch receives an even and consistent finish, making it ideal for operations that need to coat multiple parts at once without compromising on quality.
Many businesses can also take advantage of multi-layer coating systems with a 4x4x7 powder coat oven. This feature allows manufacturers to apply different layers of powder coatings to the same part. For instance, a base layer can be applied and cured before another layer is applied on top to achieve specific finishes, colors, or durability properties. With precise control over the temperature and curing time, the oven ensures that each layer adheres correctly, resulting in a durable and high-quality multi-layer finish. This is particularly beneficial in industries like automotive and appliance manufacturing, where aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance are key priorities.
The flexibility in part size and configuration is another reason why the 4x4x7 oven is popular. While it is a medium-sized oven, it can accommodate parts of various shapes and sizes, especially when combined with customizable racking and hanging systems. Companies can adjust the positioning and orientation of parts to maximize the space within the oven. This flexibility helps businesses streamline operations by allowing them to coat different products on the same oven without having to invest in multiple ovens or changeovers. This adaptability becomes especially useful when there is a need to handle diverse orders and product types on a short production timeline.
For businesses that need to meet strict quality standards or certifications, a 4x4x7 powder coat oven can be equipped with advanced monitoring systems that ensure compliance with industry regulations. For example, ovens can include features like data logging capabilities that track the curing cycle in real-time, ensuring that the temperature and curing time are within the specifications required for optimal performance. This is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing, where stringent quality and safety standards must be met. Data from the oven can also be used for traceability, helping businesses maintain detailed records of the coating process for future reference, audits, or customer requirements.
In terms of productivity, businesses operating with a 4x4x7 oven can achieve a quicker turnaround on powder coating jobs. Since the oven is generally sized for medium-scale production, it can accommodate multiple parts per cycle, leading to higher throughput. When coupled with automated loading and unloading systems, businesses can achieve even greater efficiency. Automation can reduce manual labor, increase production speed, and free up human resources for more critical tasks within the coating process. It can also reduce the risk of operator error, ensuring that parts are loaded and unloaded in the correct orientation for optimal curing.
A key factor in maintaining a smooth and efficient production line is the integration of maintenance-friendly design elements. Many modern 4x4x7 powder coat ovens are built with ease of maintenance in mind. Features like removable panels for easy access to internal components, self-cleaning filters, and digital alerts for routine maintenance tasks make these ovens easier to maintain and service. For businesses with limited staff, this is an essential benefit as it minimizes downtime for maintenance while ensuring the oven remains in peak operating condition.
Another consideration is space optimization. The 4x4x7 oven’s compact size allows it to fit within small to medium-sized production facilities. Its relatively small footprint means it can be installed in areas with limited space without requiring significant reorganization of the facility. This is especially important for businesses that are growing but have constraints on the physical size of their production space. The compact design doesn’t compromise the oven’s ability to coat larger parts or handle multiple items at once, making it an excellent choice for small operations looking to maximize their productivity in a confined space.
As for the future of powder coating technology, we can expect continuous advancements in both the materials used for powder coatings and the oven technology that cures them. The development of more specialized powder coatings—such as those that are more resistant to UV degradation, extreme temperatures, or chemicals—will require corresponding advancements in oven technology to ensure that the curing process remains optimal. The 4x4x7 oven’s flexibility and precise control over temperature and airflow make it well-positioned to accommodate these new materials and powder types.
In particular, eco-friendly coatings are becoming more popular as industries move toward sustainability. The demand for low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) or zero-VOC coatings is rising, as manufacturers and customers alike seek products with less environmental impact. These coatings often require specific curing profiles, which the precise temperature control systems in a 4x4x7 oven can provide. By adapting to these new materials, businesses can remain competitive in the growing eco-conscious market.
Moreover, custom finishes are another area of growth. The rise of custom coatings that offer specialized textures, colors, or effects has opened new opportunities for businesses using powder coating ovens. For example, unique textures like metallic finishes, wrinkle or matte textures, or smooth glossy coatings are in demand for consumer goods, automotive, and architectural applications. The 4x4x7 oven, with its adaptable design and customizable settings, allows businesses to experiment with different effects and finishes, offering a range of possibilities to meet customer demands for unique products.
For businesses considering expansion into new markets or increasing production capacity, upgrading to a larger, more automated oven system may eventually be necessary. However, the 4x4x7 oven remains an excellent solution for businesses that need a reliable, efficient, and scalable option. The modular nature of some powder coating ovens allows businesses to upgrade in stages, adding more features, automation, or capacity as needed without having to invest in entirely new systems.
Ultimately, the 4x4x7 powder coating oven is an excellent choice for companies looking to balance space, energy efficiency, and production needs. It provides the flexibility to coat various parts, works with different materials and finishes, and integrates well with modern technologies, helping businesses maintain a competitive edge while ensuring high-quality results. As the powder coating industry continues to evolve, this oven size will likely remain a reliable and effective tool for businesses of various scales and industries.
Small Powder Coating Oven

A small powder coating oven is an ideal solution for businesses or hobbyists who need an efficient, compact, and cost-effective option for powder coating small to medium-sized parts. These ovens are typically designed for operations that don’t require large-scale production but still need reliable performance for high-quality finishes. Small powder coating ovens are popular in industries such as automotive restoration, custom furniture, small appliance manufacturing, and even prototyping or home-based powder coating businesses.
Key Features of Small Powder Coating Ovens:
- Compact Size: The main advantage of a small powder coating oven is its space-saving design. These ovens are typically designed to fit into smaller shops or garages without taking up much space. Their compact dimensions make them ideal for businesses that need to keep their production area organized while still accommodating a range of parts for coating.
- Energy Efficiency: Small ovens often use electric heating systems, making them energy-efficient. These ovens heat up quickly and maintain temperature stability with minimal energy consumption, which is beneficial for smaller businesses with tighter budgets. Additionally, they typically require less electricity to operate compared to larger ovens, making them cost-effective to run.
- Temperature Control: Just like larger ovens, small powder coating ovens are equipped with precise temperature controls, usually with digital displays and adjustable thermostats. These controls are crucial for ensuring the parts are cured to perfection. The typical curing temperature for powder coating is between 300°F and 400°F (150°C – 200°C), and maintaining consistent heat is essential to achieve a durable and smooth finish.
- Even Air Circulation: Small powder coating ovens are designed with efficient forced air circulation systems to ensure even heat distribution. Proper airflow is critical to achieving uniform curing, especially when coating parts with intricate shapes or various sizes. Some models include fans that can be adjusted to regulate airflow, further improving coating consistency.
- Quick Heat-Up Time: Small ovens typically heat up faster than larger ones, allowing for quicker turnaround times. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with lower production volumes, as it reduces downtime between coating cycles and improves overall productivity.
- Capacity and Versatility: While they are small in size, these ovens can still accommodate a range of parts, depending on their internal dimensions and the configuration of the racks or hooks used for hanging parts. Parts like small automotive components, custom metal works, or furniture pieces can easily be coated in these ovens. Some small ovens come with adjustable racking systems to maximize space and allow for different part sizes to be processed simultaneously.
- Safety Features: Small ovens often come with safety interlocks, preventing the door from being opened while the oven is at high temperatures. Additionally, many models are equipped with overheat protection systems to ensure the oven does not exceed safe temperatures, reducing the risk of accidents or damage to the parts being coated.
- Portability: Some small powder coating ovens are designed with portability in mind. These ovens can be moved around easily within the shop, and some even feature casters for smooth transportation. This makes them ideal for businesses that might need to move the oven between workstations or across different locations.
Benefits of Using a Small Powder Coating Oven:
- Ideal for Low to Medium Volume Production: Small ovens are well-suited for small-scale operations, such as a one-person shop or a business that processes parts in small batches. They allow companies to offer high-quality powder coating without needing to invest in expensive, large-scale equipment.
- Cost-Effective: These ovens generally cost less to purchase and operate than larger units. For businesses just starting or those working on a tight budget, the small powder coating oven offers an affordable solution to get into the powder coating process. The cost savings come from lower initial investment, reduced energy use, and fewer maintenance requirements.
- Faster Curing Time: The smaller size and efficient heating systems allow for faster curing times, reducing the time it takes to coat a part and get it back into production or ready for sale. This is beneficial for businesses that need to maintain a quick turnaround.
- Small Footprint: A small powder coating oven is perfect for shops or garages with limited space. It allows businesses to add powder coating to their operations without needing a large area dedicated solely to curing parts. This is especially useful for small businesses or even hobbyists who do powder coating as part of a side operation.
- Improved Finish Quality: Just like larger ovens, small powder coating ovens ensure that parts are uniformly coated with a smooth, durable finish. The ability to control the temperature and airflow ensures that the powder cures consistently, resulting in a high-quality finish on every part.
Applications of Small Powder Coating Ovens:
- Automotive Parts: Small powder coating ovens are commonly used in automotive customization shops, where parts like wheels, rims, bumpers, and brackets are coated. These ovens are perfect for shops that focus on custom work or small batches.
- Metal Furniture: Many businesses that produce custom metal furniture pieces, such as tables, chairs, and decorative objects, use small powder coating ovens. The ovens provide an even, durable coating that enhances the appearance and durability of the furniture.
- Home Appliances: Small powder coating ovens can be used in the production of small home appliances, such as appliances with metal components like ovens, refrigerators, and microwave parts.
- Prototyping: For businesses that produce prototypes or low-volume products, small powder coating ovens are a great tool for applying protective or decorative coatings to metal prototypes without requiring large, industrial-scale equipment.
Maintenance and Upkeep:
While small powder coating ovens are generally low-maintenance, proper care is necessary to ensure they operate at their best. Regular tasks include:
- Cleaning: Keeping the oven clean ensures proper airflow and prevents buildup of powder residue. Cleaning the interior and exhaust systems regularly will prevent any issues with airflow or overheating.
- Routine Inspections: Checking the temperature controls, fans, and heating elements periodically helps prevent malfunctions. Ensure all components are in good working order and that the oven is running at optimal performance levels.
- Calibrating Temperature Sensors: Over time, temperature sensors may drift, so it’s a good idea to calibrate them periodically to ensure the oven’s temperature remains accurate and within the necessary curing range.
Conclusion:
Small powder coating ovens are an excellent choice for businesses or individuals who need a space-saving, cost-effective solution for applying high-quality powder coatings. These ovens offer flexibility, efficiency, and reliability while maintaining a relatively low upfront cost. Whether for automotive customization, metal furniture production, or other small-scale applications, a small powder coating oven can deliver the results businesses need to ensure high-quality finishes and satisfy customer expectations.
A small powder coating oven is an ideal solution for businesses or individuals looking to achieve professional-quality finishes without the need for large, expensive equipment. Their compact size makes them perfect for businesses with limited space or those that don’t require the large output capabilities of industrial-sized ovens. Despite their smaller size, these ovens offer a range of advanced features that ensure efficient, consistent, and high-quality coating results.
One of the primary benefits of a small powder coating oven is its space efficiency. These ovens can fit in smaller workshops, garages, or production areas, making them a great choice for businesses with tight floor space or those operating in home-based environments. This allows smaller businesses to add powder coating services to their offerings without having to invest in a dedicated, expansive coating facility. This compactness also means they can be moved around more easily, providing flexibility in the layout of a workshop.
Another major advantage is energy efficiency. Small powder coating ovens are generally equipped with electric heating elements that provide fast, consistent heat. They require less power compared to their larger counterparts, resulting in lower energy consumption and operating costs. This makes them an affordable option for businesses with limited budgets, as they can minimize ongoing operational expenses while still achieving high-quality results. Their faster heat-up time further adds to this efficiency, allowing businesses to reduce downtime between coating cycles.
Despite being smaller in size, these ovens maintain precise temperature control. Temperature is critical in powder coating, as it directly impacts the curing process, and small ovens are designed to maintain the exact temperatures required for curing the powder effectively. Many models come with digital temperature controllers, making it easy to set and maintain the desired curing temperature, which typically ranges between 300°F and 400°F (150°C – 200°C). By ensuring an even and stable temperature throughout the entire curing cycle, small ovens produce high-quality, consistent finishes across all coated parts.
Air circulation is another key feature of small powder coating ovens. Proper airflow is necessary to ensure even heat distribution and to avoid the formation of hot or cold spots inside the oven. Many small ovens are designed with forced air circulation systems that promote uniform heat flow, ensuring that each part receives the same level of heat during the curing process. This is especially important for businesses that are coating multiple parts at once or parts with complex shapes, ensuring that every part has a consistent, durable finish.
Additionally, small powder coating ovens offer the flexibility to coat a variety of parts. While their capacity is smaller compared to larger models, they can still accommodate a range of parts, including automotive components, custom furniture pieces, and small metal works. The adjustable racking systems or hooks in these ovens allow businesses to maximize available space, enabling them to coat multiple parts in a single cycle. This versatility is crucial for businesses that need to handle different part sizes and configurations, offering more flexibility in production runs.
The quick curing time of small powder coating ovens helps businesses maintain high productivity. Because these ovens heat up quickly and have shorter curing cycles, they reduce the amount of time parts need to spend inside the oven, which accelerates the overall production process. For small businesses, quick turnaround times can improve customer satisfaction and increase the number of orders fulfilled within a given time frame.
Despite their small size, these ovens often include advanced safety features. Overheat protection, automatic door locks, and temperature monitoring are standard in many models to prevent accidents. These safety features ensure that the oven operates securely, even in environments where operators may be handling multiple tasks. The inclusion of fire suppression systems and safety interlocks further enhances the safety of the oven, reducing the risks of accidents during the powder coating process.
Small powder coating ovens also require less maintenance than their larger counterparts, making them a practical choice for businesses with limited resources for ongoing equipment upkeep. Regular cleaning of the oven, such as removing excess powder from the interior and exhaust system, ensures consistent performance and prevents potential issues with airflow or overheating. Additionally, periodic inspections and calibrations of temperature sensors ensure the oven continues to perform at its best, maintaining the quality of the finished products.
Another significant factor is the low initial investment. Small powder coating ovens are generally more affordable than larger, industrial models. This lower upfront cost makes them accessible for small businesses or individuals just starting out in powder coating or those looking to expand their service offerings without making a large capital investment. Despite the smaller price tag, these ovens still provide professional-grade results, making them a great investment for businesses focused on high-quality finishes at a competitive price.
Small powder coating ovens are also ideal for custom work or prototyping. Businesses that specialize in custom coatings for specific customer orders or prototypes for new products can benefit from the flexibility and control offered by small ovens. These ovens allow operators to experiment with different powder types, colors, and finishes, catering to unique customer requests or new product designs. Their small size allows businesses to quickly switch between different projects without the need for major equipment adjustments, making them well-suited to high-variability, low-volume work.
For businesses considering sustainability or reducing their environmental impact, small powder coating ovens are also a step in the right direction. Unlike gas-powered ovens, which can release harmful emissions, electric ovens are more environmentally friendly, producing fewer greenhouse gases and pollutants. Some models can be further optimized with energy-saving features, such as heat recovery systems, to capture and reuse excess heat, making them even more eco-friendly.
The ease of operation is another attractive feature of small powder coating ovens. Most models are designed with user-friendly interfaces, often featuring digital control panels with simple touch-screen displays or knobs for temperature, time, and airflow adjustments. These intuitive controls allow operators to adjust settings quickly and with precision, ensuring consistent and reliable results. Additionally, some ovens include remote monitoring options, allowing operators to track the status of the curing process from a mobile device or computer, enhancing convenience and efficiency.
Small powder coating ovens are also well-suited for batch production. For businesses that operate on a smaller scale or need to coat multiple items in a batch, these ovens can handle multiple parts simultaneously, reducing production time. This is particularly useful for businesses that produce limited runs of products or need to coat items in small quantities, such as custom-designed automotive parts, furniture, or home decor.
In conclusion, small powder coating ovens provide a cost-effective, efficient, and versatile solution for businesses of all sizes. Whether for automotive applications, small-scale manufacturing, custom work, or prototyping, these ovens offer reliable performance, energy efficiency, and high-quality finishes. Their compact design, ease of use, and lower operating costs make them an excellent choice for businesses seeking to add powder coating capabilities or improve their existing processes without the need for large, industrial ovens. With their flexibility, quick turnaround times, and safety features, small powder coating ovens are an essential tool for businesses looking to achieve professional results while maintaining an efficient and manageable operation.
Expanding further on the versatility and benefits of small powder coating ovens, they offer numerous advantages that make them highly suitable for various industries and applications.
One of the significant benefits of small powder coating ovens is their scalability. As businesses grow or expand their operations, these ovens can be adapted to meet increasing production demands. If a business initially operates on a smaller scale but anticipates future growth, a small powder coating oven can often be integrated into larger systems or combined with additional equipment. Many small ovens are designed with modular components, making it easier to add features like automated loading and unloading systems or expand the curing capacity. This scalability ensures that businesses can start small but have the option to upgrade and increase their production capacity without having to invest in entirely new equipment.
Another area where small powder coating ovens excel is customization. Because they are often used for niche markets or specialized industries, these ovens can be customized to fit specific needs. For example, businesses can opt for special racking systems that allow for the efficient coating of oddly shaped or oversized parts. Customized shelves or hooks can help organize parts, ensuring they are coated evenly and reducing the risk of parts interfering with one another during the curing process. Additionally, some small powder coating ovens can be configured to support different curing profiles, allowing businesses to coat a range of materials with various powder types and finishes. This flexibility is critical for industries that deal with unique projects or a wide range of products.
In terms of environmental considerations, small powder coating ovens are often more eco-friendly than larger counterparts, particularly when using electric heating elements. The lower energy consumption of small ovens helps to reduce carbon footprints, making them a great choice for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact. Moreover, many powder coating ovens are designed with energy-saving features such as recycled heat systems, which capture and reuse heat generated during the curing process. This type of energy efficiency not only reduces energy bills but also supports sustainability efforts, which is increasingly important to both customers and regulatory bodies.
Small powder coating ovens are also notable for their ease of installation and operation. Many models are designed to be user-friendly, requiring minimal setup time. Since they are smaller and lighter, they can be installed in a variety of locations without the need for complex infrastructure. Once set up, these ovens are often simple to operate, with intuitive controls that allow users to easily adjust curing parameters to meet the specific requirements of each job. Even for businesses that are new to powder coating, small ovens are often easy to learn and operate, with many manufacturers providing detailed user manuals and customer support to ensure smooth operation.
Maintenance for small powder coating ovens is generally less demanding than larger, industrial ovens. Because of their simpler design and fewer complex components, these ovens require less regular maintenance and are less prone to breakdowns. Routine tasks such as cleaning the interior to remove powder residue and checking the heating elements for wear can be easily performed. Over time, the temperature calibration may need to be checked, and some ovens include self-diagnostic features that alert users when maintenance is needed. This ease of maintenance is especially beneficial for small businesses that may not have dedicated maintenance personnel.
Furthermore, transportability can be a significant advantage of small powder coating ovens, especially for mobile operations. For businesses that work at multiple locations or have clients who require on-site powder coating, small ovens can often be transported to different sites. Their portability makes them perfect for businesses offering mobile coating services or those working on remote job sites. Their small size and manageable weight make setup and takedown quicker, reducing downtime and improving flexibility.
Small powder coating ovens are often used in combination with manual or automated powder coating guns. For smaller batches, businesses may prefer manual coating, as it allows for more control over the application process. However, for increased speed and consistency, some businesses opt to automate the powder application process with advanced powder coating systems. This combination of small ovens and automated powder coating guns provides a perfect balance between precision, efficiency, and scalability, allowing businesses to coat more parts in less time while still maintaining high-quality finishes.
Quality control is another area where small powder coating ovens shine. The ability to precisely control temperature and airflow ensures consistent and high-quality finishes, which is essential in industries where product appearance and durability are critical. For businesses offering custom finishes, such as automotive restoration or decorative metalwork, the consistency provided by a small powder coating oven can help meet client expectations while delivering superior results.
For small manufacturers or entrepreneurs looking to enter the powder coating business, these ovens offer an affordable entry point. They provide professional-grade results at a fraction of the cost of larger industrial ovens, allowing businesses to build their reputation and expand their customer base without significant upfront investment. Small powder coating ovens can be a stepping stone for those looking to scale up their production capabilities over time, and many companies find that starting with a smaller oven offers a low-risk way to enter the market.
Finally, customer service and support from manufacturers of small powder coating ovens can be a deciding factor in choosing the right equipment. Many manufacturers offer robust customer support services, including training on how to use the oven effectively, troubleshooting assistance, and tips for optimizing performance. Whether it’s offering guidance on achieving specific finishes or helping with technical issues, the support provided by oven manufacturers can be invaluable in ensuring smooth operations.
In conclusion, small powder coating ovens offer numerous advantages to businesses, ranging from space efficiency and energy savings to high-quality finishes and scalability. They are an excellent choice for companies seeking to enter the powder coating industry, those requiring a reliable system for small to medium-sized production runs, or businesses focused on customization. Their versatility, affordability, and ease of use make them a smart investment for a wide range of applications, from automotive restoration to custom furniture and beyond. As businesses grow or their needs evolve, small powder coating ovens can often be expanded or integrated with other equipment to meet future demands, making them a long-term solution for many companies.
Building upon the advantages and versatility of small powder coating ovens, there are several additional key factors and considerations that make these ovens an invaluable asset for many businesses.
One of the essential aspects to consider when using a small powder coating oven is time efficiency. These ovens heat up quickly due to their smaller size, which reduces the overall time required for both the preheating and curing phases of powder coating. This is especially beneficial for businesses that need to maximize throughput while maintaining high-quality finishes. For example, shops that handle smaller batches of parts or perform custom work can get more parts coated in a shorter amount of time, which ultimately increases productivity. Faster curing times also allow businesses to reduce customer wait times, improving service and satisfaction. This time-saving characteristic is crucial for companies working under tight deadlines or those looking to speed up their production cycles without compromising quality.
Additionally, the ease of integration with other powder coating equipment and processes is another strong point for small powder coating ovens. These ovens can be seamlessly integrated into existing powder coating systems, especially when paired with manual or automatic spray booths and powder application guns. Many small ovens are compatible with pre-treatment systems or blast cabinets, which allow parts to be cleaned and prepared for coating prior to entering the oven. The combination of these systems leads to a smoother workflow, enabling businesses to complete all necessary coating processes in-house without needing to outsource any portion of the work. This integration further streamlines operations and enhances overall efficiency, making the production process more cohesive and minimizing downtime.
A major consideration when selecting a small powder coating oven is the type of powder coating material that will be used. Powder coating comes in various formulations, including epoxy, polyester, hybrid, and urethane, each with distinct properties and ideal curing conditions. Small ovens are often designed to accommodate various powder types, but it’s important to ensure the oven you choose can consistently handle the temperature and curing needs of the specific powder coatings your business plans to use. Some ovens are optimized for specific powder types, so ensuring compatibility with your coatings will help you achieve the best finish and durability.
For businesses in the automotive industry, for example, where parts may be subject to extreme conditions, ensuring the oven can effectively cure automotive-grade powder coatings is critical. Automotive powder coatings often require high durability and weather resistance, which can only be achieved through precise temperature control and even curing. In such cases, even a small powder coating oven, when properly equipped, can deliver results that are as reliable as larger ovens.
Oven ventilation is another important consideration in small powder coating ovens. Many models are designed with ventilation systems that remove fumes, dust, and other pollutants that may be generated during the curing process. Proper ventilation is crucial for both safety and product quality, as the build-up of fumes can not only affect the environment but can also compromise the finish of coated parts. In some small ovens, ventilation can be connected to an external exhaust system, ensuring that pollutants are removed from the workspace while keeping the coating area clean and efficient. Furthermore, the proper filtration and extraction of particles also contribute to a safer work environment, reducing the risk of respiratory issues for operators working near the oven.
Another key consideration is durability and material quality. Although small in size, these ovens are designed to withstand the high temperatures required for curing powder coatings, which can reach up to 400°F (200°C). Therefore, the materials used in constructing the oven—such as the steel exterior, the insulation inside, and the heating elements—need to be of high quality to ensure the oven’s long-lasting performance. High-quality ovens will resist wear and tear, corrosion, and temperature fluctuations over time, providing dependable service for many years. Ensuring that the oven is made with materials that can handle the stress of repeated high-temperature cycles is vital to maintaining its operational lifespan.
Upgrading capabilities should also be considered. While small powder coating ovens are typically designed for low-to-medium volume production, businesses that anticipate growing their operations in the future might want to look into ovens with upgradeable features. Some small ovens allow for the addition of features like more powerful heating elements, automated conveyor systems, or improved air circulation technology. Being able to enhance the oven as the business grows or as customer demands change can extend the useful life of the equipment and allow the business to scale more easily.
Small powder coating ovens can also be used in educational or training environments. For schools, colleges, or vocational training centers offering courses on metalworking, automotive repairs, or industrial coatings, these ovens provide a great way to introduce students to powder coating technology. They are simple to operate and can be used to teach students about the entire powder coating process, from surface preparation to curing. This allows trainees to gain hands-on experience with professional-grade equipment while learning about the technical aspects of powder coating and its applications in various industries.
Regulatory compliance is another important factor when choosing a powder coating oven. Depending on the region or country in which the business operates, there may be specific environmental and safety regulations regarding emissions, heat output, and materials used. Small powder coating ovens, when properly selected, can help businesses meet these regulations. For instance, choosing an oven with a certified filtration system can ensure that the exhaust gases and particulate matter are effectively removed from the air. This helps the business comply with health and safety standards while maintaining a safe and healthy working environment for employees.
For businesses focused on the DIY or small-scale manufacturing markets, the compact size and affordability of small powder coating ovens allow hobbyists or entrepreneurs to experiment with different powder coating processes at a low cost. Whether for personal projects, such as coating household items, or for launching a small business producing custom metal goods, these ovens offer an entry point into the powder coating industry without a significant investment in large-scale equipment.
Lastly, customer satisfaction plays a pivotal role in the success of small powder coating ovens. Providing a consistently high-quality product is essential for building a strong customer base and reputation in the market. Small ovens, when used correctly, ensure that every piece is coated with precision, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Businesses in fields like automotive restoration, custom furniture design, or industrial equipment manufacturing often rely on the consistent, attractive finishes produced by powder coating. Small ovens allow businesses to meet customer expectations for quality finishes, which in turn helps drive repeat business and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
In conclusion, small powder coating ovens are an essential tool for many businesses, providing cost-effective, efficient, and high-quality powder coating solutions. Their ability to handle diverse applications, from automotive parts to small-scale manufacturing, makes them an invaluable asset. These ovens offer significant flexibility, allowing businesses to work in small batches, experiment with different finishes, and maintain consistent, durable results. Their energy efficiency, ease of use, and relatively low maintenance requirements make them ideal for businesses of all sizes—from hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts to entrepreneurs and established companies. With proper selection and operation, small powder coating ovens can deliver professional-grade results, ensuring that businesses can meet customer demands and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
A portable powder coating oven is a compact, mobile solution designed for businesses or individuals who require the ability to cure powder-coated items at various locations or in smaller spaces. These ovens are especially beneficial for businesses offering on-site services, those operating in temporary facilities, or for those with limited shop space. Their portability does not mean sacrificing performance, as they are designed to provide high-quality curing capabilities while maintaining ease of use and efficiency.
Key Features and Benefits of Portable Powder Coating Ovens:
- Portability: As the name suggests, a portable powder coating oven is lightweight and easy to transport. These ovens are typically built with wheels or handles, making them simple to move between locations. This makes them an excellent choice for businesses that offer on-site powder coating services, such as automotive shops, small manufacturers, or service providers working on-site at construction projects or industrial sites.
- Compact Size: These ovens are designed to be space-efficient, allowing them to fit in smaller spaces or be easily stored when not in use. Their smaller footprint is perfect for businesses with limited room or for those operating out of a garage or small workshop. This compact size also allows for easy placement in tight areas without taking up too much floor space.
- Energy Efficiency: Many portable powder coating ovens are electric-powered, making them more energy-efficient compared to their larger, gas-powered counterparts. They generally consume less power and heat up quickly, which results in lower operating costs and faster turnaround times. The energy efficiency is especially useful for small to medium-sized businesses that want to minimize operating expenses while achieving professional-grade results.
- Fast Setup: These ovens are designed for easy setup and operation. They are typically ready to use with minimal assembly or installation, which is ideal for businesses that need to move quickly between projects or locations. Their simplicity allows users to start the powder coating process without delay, leading to increased productivity. This feature is also beneficial for those in industries where time-sensitive projects are common.
- Adjustable Temperature Control: Portable powder coating ovens often come equipped with precise temperature controls, which are crucial for ensuring that the powder coating cures correctly. Most ovens have adjustable thermostats or digital controllers that allow users to set and maintain the ideal curing temperature, typically between 300°F and 400°F (150°C to 200°C), depending on the powder being used. This level of control ensures that parts are coated evenly and effectively, without under-curing or over-curing the powder.
- Even Heat Distribution: These ovens are designed with advanced airflow and heating systems to ensure that heat is evenly distributed throughout the interior. This consistent heat flow prevents hot spots, which could lead to uneven curing or defects in the finished coating. Whether the oven uses electric heating elements or gas burners, the system is designed to ensure uniform temperature across the oven’s interior.
- Safety Features: Like larger ovens, portable models come with a variety of safety features to protect the operator and the equipment. These may include automatic shut-off mechanisms, overheat protection, and thermal cutoffs. Some portable ovens also include a built-in exhaust system to remove fumes and fumes produced during the curing process, contributing to both the safety of the operator and the overall health of the workspace.
- Versatility: Portable powder coating ovens are versatile and can accommodate a wide range of parts. They typically come with adjustable racks, hooks, or shelves that allow for the coating of different sizes and shapes of objects. From small automotive parts to custom furniture pieces, a portable oven can handle various items with ease, making it suitable for businesses in industries such as automotive restoration, metalworking, or custom product design.
- Durability: While designed to be lightweight and portable, these ovens are built to last. Made with robust materials like steel, insulated walls, and high-quality electrical components, portable powder coating ovens are designed to withstand frequent use and transportation. Many are equipped with corrosion-resistant surfaces to maintain their appearance and performance, even when exposed to high temperatures and powder residue over time.
- Affordability: Portable powder coating ovens are generally more affordable compared to larger, industrial-sized ovens, making them accessible for small businesses, hobbyists, or startups. They provide a cost-effective solution for companies that need the functionality of a full-sized powder coating oven but do not have the capital or space to invest in such equipment. The lower upfront cost, coupled with reduced energy consumption, makes these ovens an attractive option for budget-conscious businesses.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: The maintenance of portable powder coating ovens is relatively straightforward. Regular cleaning of the interior to remove any leftover powder residue, especially in the exhaust system, is necessary to maintain airflow and prevent clogs. Periodically checking the heating elements and temperature sensors ensures the oven continues to perform at its best. The simplicity of these ovens often means they are easier to maintain than larger, more complex systems.
- Suitable for Low to Medium Production Volumes: These ovens are ideal for businesses that don’t require high-output production runs. They are often used in custom or low-volume operations where quality is more important than quantity. For example, a small shop specializing in custom wheels or metal art might only need a portable oven to coat a handful of items at a time. The oven provides flexibility and consistent results, without the need for a large, expensive industrial setup.
- Regulatory Compliance: Portable powder coating ovens are designed with built-in safety standards to comply with various regulations. This includes meeting local fire codes, environmental regulations for air quality, and electrical safety standards. Some ovens come with certifications or documentation to prove that they adhere to the required safety and performance standards, which is especially important for businesses that operate in regulated industries.
- Customization Options: Some manufacturers offer the option to customize portable powder coating ovens to meet the specific needs of the business. This could include adjusting the oven’s size, adding extra shelves or racks for specific parts, or incorporating additional safety features such as a fire suppression system. Customization ensures that businesses can get the most out of their oven, tailoring it to their unique requirements.
Applications of Portable Powder Coating Ovens:
- Automotive and Motorcycle Restoration: Small shops offering custom automotive or motorcycle parts restoration often use portable ovens to coat various components such as wheels, frames, bumpers, and suspension parts.
- Metalworking and Fabrication: Metal fabricators and welders who need to apply powder coatings to their custom metal works or products can utilize portable ovens to cure coatings on-site.
- Furniture and Home Décor: Businesses involved in custom furniture or home décor often use portable ovens to coat metal furniture, lighting fixtures, or other decorative pieces in a wide range of finishes.
- Small Manufacturers and Startups: Small manufacturers or startups with limited space and budgets can use portable ovens for powder coating parts in smaller batches, allowing them to scale their operations without a huge investment in large-scale equipment.
- Mobile Powder Coating Services: Companies offering mobile powder coating services can use portable ovens to provide on-site coating solutions for customers, particularly in industries like automotive repair, custom metalwork, or construction.
Conclusion:
Portable powder coating ovens offer the perfect combination of flexibility, performance, and convenience. Their compact size, mobility, and affordability make them a great solution for businesses with limited space, those offering on-site services, or anyone in need of a high-quality, low-cost powder coating option. Despite their smaller size, they provide excellent curing capabilities, energy efficiency, and consistent results, making them a valuable addition to any shop or service provider’s toolkit. Whether for custom projects, automotive restoration, or small-scale manufacturing, a portable powder coating oven can help businesses achieve professional finishes with ease and reliability.
Portable powder coating ovens offer a versatile solution for businesses or individuals who need the flexibility of curing powder-coated parts in different locations or smaller spaces. These ovens are designed to be compact and easy to move, making them ideal for companies providing on-site powder coating services, those with limited shop space, or small-scale manufacturers. While their size is smaller compared to industrial ovens, portable powder coating ovens still deliver high-quality curing and can be used across a wide range of applications. Their mobility is one of their strongest points, enabling businesses to transport the oven between job sites, workshops, or mobile operations with ease.
Even though these ovens are compact, they maintain energy efficiency, typically powered by electricity, which helps reduce operational costs compared to larger, gas-powered systems. The energy-efficient heating elements allow for faster heat-up times and more efficient curing, making them a great choice for small to medium-sized production runs. Many portable ovens come with adjustable temperature controls, allowing operators to set the oven to the precise temperature required for different powder types, typically ranging from 300°F to 400°F. This precise temperature control is crucial for ensuring the powder coating cures properly, achieving the desired durability and finish.
The ovens also feature a uniform heating system that ensures consistent results across various part sizes and shapes. Proper heat distribution is important in preventing defects such as uneven curing or poor adhesion. Whether curing automotive parts, metal furniture, or custom-made items, portable powder coating ovens are designed to provide even and thorough curing, which results in a high-quality finish.
For businesses that require mobility, such as mobile coating services or companies that need to operate in temporary locations, portable powder coating ovens offer the convenience of easy setup and use. Their lightweight design allows them to be transported quickly, set up in minimal time, and relocated as necessary. This flexibility is especially beneficial for businesses with fluctuating project locations, helping them complete jobs without requiring permanent installation in a fixed facility.
Despite their smaller size, portable powder coating ovens are durable and built to withstand the heat and conditions of the curing process. They are made from high-quality materials such as steel exteriors and insulated walls, which ensure they can handle high temperatures and frequent use over time. Many models are also corrosion-resistant, which helps them maintain their performance and appearance even after long-term exposure to powder residue, heat, and moisture. The ovens are also easy to maintain, requiring regular cleaning and checks to ensure their longevity, but with relatively low maintenance costs compared to larger, more complex systems.
For businesses with limited space, such as small shops or home-based operations, these ovens provide an efficient and cost-effective solution. Their compact design ensures they can fit in tight areas without taking up excessive floor space, making them an ideal option for those working in confined environments. Moreover, their affordability compared to larger industrial ovens makes them an accessible option for businesses that don’t need the capacity of a full-sized system but still want the professional-grade results that powder coating provides.
These ovens are also well-suited for low to medium production volumes. While they may not have the throughput of large industrial ovens, they are perfect for businesses that focus on custom work or small batches. Custom powder coating for products such as automotive parts, furniture, or art pieces often involves low-volume runs, making portable ovens the ideal solution. They allow businesses to provide quality, consistent finishes for a variety of different products, helping to maintain high standards for customer satisfaction.
A key factor when selecting a portable powder coating oven is ensuring it meets any regulatory standards and safety protocols required by local authorities. Most portable ovens are designed with built-in safety features such as automatic shut-offs, temperature alarms, and thermal protection to prevent overheating or accidents. Additionally, proper ventilation is essential to remove fumes and particulate matter from the curing process, especially in enclosed or confined spaces. Some portable ovens come equipped with integrated exhaust systems or can be connected to external ventilation units to help maintain a safe working environment.
Portable powder coating ovens are also a great tool for those new to powder coating or for educational purposes. Many smaller operations, training centers, or hobbyists use portable ovens to experiment with powder coating processes before investing in larger, more complex systems. These ovens provide a hands-on way to learn about the powder coating process, from surface preparation to the final cure, without requiring a significant upfront investment in industrial-scale equipment.
For small businesses or startups, portable powder coating ovens allow entrepreneurs to enter the powder coating market without the need for large capital expenditures. They provide an accessible entry point for entrepreneurs working with a limited budget, whether they are offering custom finishes or producing small batches of coated parts. Over time, businesses can scale up their operations by adding more ovens or integrating additional automated equipment as their demand and production capabilities grow.
In conclusion, portable powder coating ovens are a practical, efficient, and affordable solution for businesses that need flexibility and mobility in their coating operations. They provide consistent and high-quality finishes, ensure precise curing, and are easy to transport between locations. Whether used by small manufacturers, mobile service providers, hobbyists, or training centers, these ovens offer a cost-effective way to produce durable and professional-grade powder-coated finishes. Their compact size, energy efficiency, and durability make them a valuable tool for a wide range of industries, from automotive and metalworking to furniture and custom design.
Portable powder coating ovens continue to gain popularity due to their adaptability and ability to serve a wide range of industries and business types. These ovens are not just about mobility and compactness; they also offer significant operational benefits that make them an attractive option for businesses that require flexibility in their powder coating process.
One of the standout advantages of portable powder coating ovens is their ability to quickly integrate into existing workflows. For businesses that already have powder coating setups but need a mobile solution for specific jobs, the portability of these ovens means that they can be quickly added to an existing production line or used for specialized tasks. For example, a company that typically works in a large facility may still need to powder coat items on location for clients, like metal components in automotive repair or custom art pieces for installation. A portable oven can help these businesses cater to diverse needs without disrupting their core operations, providing a seamless expansion of their capabilities.
Another major benefit is customization and versatility in terms of size and design. Many portable powder coating ovens come with features that allow for adjustments based on the job at hand. Racks, shelves, or hooks can often be customized to accommodate different part sizes, ensuring that the oven can handle everything from small intricate parts to larger components. For instance, an automotive shop may need to coat wheels, frames, and engine components, all of which vary greatly in size and shape. The adjustable nature of portable ovens allows operators to adapt quickly and efficiently, avoiding delays or complications in setup.
While portability is the key feature, portable powder coating ovens can still manage to provide consistent results across a wide range of applications. Whether used for coating small metal brackets or larger automotive parts, the ovens maintain a consistent temperature distribution throughout the chamber, which ensures that each part receives an even coating. This consistency in temperature is vital for the curing process, as uneven heat can lead to poorly cured powder, resulting in defects such as bubbling, cracking, or poor adhesion. A portable oven designed with proper airflow and heat distribution systems ensures a flawless finish every time, even with frequent relocation or batch-to-batch variations in part size.
The reduced footprint of portable powder coating ovens makes them perfect for smaller businesses or operations that lack the space for larger equipment. Whether it’s a home-based business, a mobile service provider, or a small shop specializing in custom products, the smaller size of these ovens allows them to operate effectively in environments where space is at a premium. Their compact nature also ensures that they can be stored away easily when not in use, freeing up valuable floor space.
Portable powder coating ovens also help businesses reduce overhead costs by minimizing energy consumption. Since these ovens are generally smaller and more efficient, they require less energy to heat up compared to larger, fixed ovens. Many models are designed to heat up quickly, saving time and reducing the amount of electricity consumed per cycle. Additionally, the electric-powered design of most portable ovens eliminates the need for additional fuel sources like gas, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective in the long run.
For small-scale manufacturers or custom shops, the flexibility provided by portable powder coating ovens can be a game-changer. These businesses often work on short-run production or unique projects that require a high level of customization. Portable ovens allow these shops to offer a wide variety of coatings and finishes, from standard colors to custom textures or metallic finishes. They can quickly switch between jobs and maintain tight control over the curing process to ensure that each item is finished to a high standard.
Moreover, portable powder coating ovens have become increasingly accessible for DIY enthusiasts or hobbyists. Those who enjoy restoring old furniture, creating custom automotive parts, or experimenting with different finishes in their spare time can take advantage of portable ovens without needing to commit to a large, expensive industrial setup. Whether it’s for coating a few small pieces or tackling a larger project, these ovens provide an affordable and user-friendly way for individuals to achieve professional results at home or in a small workshop.
As with any type of equipment, proper maintenance is essential to ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of portable powder coating ovens. Fortunately, these ovens are generally straightforward to maintain. Regular cleaning to remove powder residue and checking the condition of the heating elements and temperature sensors can prevent malfunctions or inconsistent curing. Keeping the ventilation systems clear is also important to ensure proper airflow, as this affects both the safety of the workspace and the oven’s efficiency. Many manufacturers offer guides or customer service support to help users maintain their portable ovens in top condition, making it easier for businesses or hobbyists to keep their equipment running smoothly.
Safety is always a priority with any oven that involves high temperatures, and portable powder coating ovens are designed with this in mind. They come equipped with several safety features, such as overheat protection, automatic shut-off mechanisms, and durable insulation to prevent burns or other injuries during operation. In addition, proper ventilation and fume extraction are critical in preventing the buildup of harmful fumes or particulate matter. Some ovens are designed to include integrated filtration systems or can be easily connected to external exhaust systems to ensure that harmful particles are properly removed from the air, ensuring a safe working environment.
For businesses that operate in industries with strict regulatory standards, portable powder coating ovens can still offer the necessary compliance. Many models are built to meet or exceed local regulations for emissions, safety, and environmental impact. This is important for businesses that need to demonstrate compliance with health and safety laws, especially in highly regulated sectors such as automotive restoration, construction, or manufacturing. Portable ovens that are equipped with self-monitoring systems or certifications can provide the peace of mind that operations are adhering to the required standards.
Lastly, portable powder coating ovens also give businesses the ability to scale operations as needed. As demand grows or specific projects require more coating capacity, businesses can invest in additional portable ovens to meet production needs without committing to large fixed systems. This scalability ensures that small businesses can grow steadily and add more equipment as their customer base or project requirements expand. In some cases, companies can add automation features or integrate portable ovens into an existing production line to further improve efficiency and throughput.
In conclusion, portable powder coating ovens provide a flexible, cost-effective, and efficient solution for a wide range of businesses and applications. Whether you’re a small manufacturer, an automotive shop, a custom metalworker, or a DIY enthusiast, the portability, affordability, and consistent performance of these ovens make them a valuable tool for achieving high-quality finishes. They are designed to meet the needs of businesses with limited space, mobile operations, or low to medium production volumes, offering excellent flexibility and mobility without compromising the quality of the powder coating process.
Portable powder coating ovens continue to stand out as an essential tool for businesses in need of flexible and reliable curing solutions. Beyond the features already discussed, these ovens offer additional advantages that make them a valuable asset for a diverse range of industries.
One of the primary reasons businesses opt for portable powder coating ovens is their low initial investment and operational costs. Unlike larger industrial ovens, which can require significant capital investment for purchase, installation, and maintenance, portable ovens are much more affordable. This makes them an excellent option for startups, small businesses, or those who are just entering the powder coating market. The relatively low operating costs—due to energy-efficient design, quick heat-up times, and fewer maintenance requirements—further contribute to their cost-effectiveness. For businesses that need to coat a variety of parts on a limited budget, portable ovens provide the perfect balance of performance and affordability.
For businesses that experience fluctuations in production demand, mobility and flexibility become crucial. Portable ovens allow companies to adjust their capacity and operations depending on workload changes. This is particularly helpful for industries that operate on a project-by-project basis or those that require custom jobs. For example, a company that specializes in automotive restoration or custom-built furniture may not need a large, fixed oven all the time. However, with a portable powder coating oven, they can handle their needs during busy seasons or special orders without needing to invest in an entire factory setup. The ability to quickly scale operations with portable equipment allows businesses to remain agile and adaptable in a competitive market.
In addition, portable powder coating ovens are becoming more integrated with advanced technologies. As manufacturers strive to improve their processes, newer models come equipped with digital controls, temperature monitoring systems, and even mobile app connectivity. These technological advancements allow operators to have real-time data on temperature, humidity, and curing time, ensuring a more precise and consistent finish. Digital controls can help maintain the optimal curing temperature, reducing the chances of under-curing or over-curing parts, which can lead to poor adhesion or defects. Some advanced models even come with programmable settings, allowing operators to store specific curing profiles for different types of powder or materials, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving efficiency.
Another notable trend is the increasing use of environmentally friendly materials in the construction of portable ovens. With growing awareness around environmental impact, manufacturers are paying more attention to the materials used in these ovens, as well as the reduction of energy consumption and emissions. The insulation materials used in these ovens are more often made from eco-friendly substances, while the heating elements are designed to be more energy-efficient. Furthermore, the compact size of portable ovens inherently reduces the energy needed for heating, and they typically use electric power, which can be a cleaner energy source compared to gas-powered alternatives. This makes portable powder coating ovens a more environmentally conscious choice, helping businesses comply with environmental regulations and contributing to sustainability goals.
User-friendly features are another important aspect of portable powder coating ovens. These ovens are designed for ease of use, making them accessible to a wide range of operators. Many models feature intuitive controls and simplified interface systems, meaning that even those with minimal experience can use them without extensive training. This is a key factor for small business owners or hobbyists who may not have the technical expertise but still want to produce high-quality finishes. The design of the ovens often incorporates user-friendly elements such as clear temperature readings, easy-to-operate door latches, and straightforward maintenance procedures. This helps improve efficiency in the shop, reduces operator errors, and ultimately leads to better end results.
Additionally, portable powder coating ovens can be adapted for specific industry needs. For example, in the automotive or motorcycle restoration industries, businesses may need ovens that can handle parts with specific dimensions or materials. Manufacturers that cater to industries such as aerospace, military, or medical devices often have more specialized needs, such as specific temperature profiles or stricter safety requirements. Many portable powder coating ovens can be tailored to meet these specific needs, offering businesses the flexibility to coat a wide range of products with varying requirements. Some portable ovens can even be modified to handle custom powder types, such as heat-resistant coatings or high-gloss finishes, to meet the unique needs of specific industries.
Enhanced part handling capabilities are another benefit provided by portable powder coating ovens. These ovens typically come with adjustable racks, hooks, and trays that help organize parts during the curing process. This feature helps maximize space inside the oven and ensures that parts are evenly coated and cured. In many cases, the racks can be moved or repositioned to accommodate larger or more irregularly shaped items. The flexible design makes it easier to handle various sizes of parts, ensuring that businesses can coat multiple items simultaneously without compromising the quality of the finish. Some ovens may also be designed to allow for easy loading and unloading of parts, reducing downtime and speeding up the overall workflow.
As companies continue to diversify their offerings and seek innovative solutions, automating part of the coating process has become a more common feature in portable powder coating ovens. Some portable models now incorporate features like automated curing cycles, conveyor systems, or robotic arms for loading and unloading parts. These systems help improve consistency and reduce human error, increasing throughput and lowering labor costs. Automated features can also help businesses that want to scale their operations more efficiently, allowing them to handle higher volumes of coated parts with minimal manual intervention.
Lastly, reliable customer support is a key factor for businesses investing in portable powder coating ovens. Since these ovens are used in a variety of industries, many manufacturers offer extensive customer service and support for troubleshooting, maintenance, and operational guidance. Whether it’s a question about adjusting the temperature settings, troubleshooting an error code, or seeking advice on optimizing curing profiles, reliable customer support can help businesses keep their operations running smoothly. This support ensures that businesses can maximize the longevity of their ovens and get the most out of their investment.
In conclusion, portable powder coating ovens provide businesses with an adaptable, cost-effective solution for a wide variety of applications. From small manufacturers to DIY enthusiasts, their ability to combine portability, energy efficiency, and consistent performance makes them an invaluable tool for achieving high-quality finishes. With their user-friendly design, energy-saving features, and flexibility, these ovens are well-suited for businesses that require mobility, low to medium production volumes, or a more compact setup. Additionally, the continual advancements in technology and customization options ensure that portable powder coating ovens will remain an essential piece of equipment for a variety of industries looking to meet evolving needs and enhance productivity.
Powder Coating Machine and Oven

A powder coating machine and oven are both essential components of the powder coating process, which is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, furniture, and manufacturing. Powder coating offers a durable, high-quality finish for metal and other surfaces, and the combination of the machine and oven ensures a consistent, even, and long-lasting result.
Powder Coating Machine
A powder coating machine is used to apply a dry powder (often made of polyester, epoxy, or hybrid resins) onto the surface of parts or products. This machine uses an electrostatic charge to attract the powder to the surface, creating a uniform and efficient coating. The process involves several components, including:
- Powder Spray Gun:
- This is the primary component used to apply the powder. The spray gun is designed to atomize the powder particles and charge them electrically so they are attracted to the part being coated. The powder is stored in a hopper and fed through a hose to the gun. The spray gun allows for fine-tuned control over the powder’s application, making it possible to coat complex shapes and surfaces.
- Powder Recovery System:
- Any powder that doesn’t adhere to the part being coated is collected in a recovery system and sent back to the powder hopper. This system is designed to minimize waste, ensuring that unused powder is efficiently reclaimed for reuse. The recovery system typically includes a filter unit to remove contaminants, ensuring that the powder remains clean and usable for future coatings.
- Air Supply and Compressor:
- An air compressor provides the necessary air pressure to operate the powder coating gun and help atomize the powder. The airflow is crucial for controlling the powder’s distribution and ensuring an even coat on the part.
- Electrostatic Charge System:
- The electrostatic charge is applied to the powder as it is sprayed from the gun. The charged powder particles are attracted to the grounded part, creating a thin, even coating. This system is essential for ensuring that the powder adheres properly to the part, even in areas that are hard to reach.
- Powder Type and Selection:
- The type of powder used (epoxy, polyester, or hybrid) is chosen based on the requirements of the specific job, including factors such as durability, appearance, and environmental resistance. Each type of powder has its characteristics and curing needs, and the coating machine must be compatible with the selected powder type.
Powder Coating Oven
After the powder is applied to the part, it must be cured in a powder coating oven. This oven is designed to bake the powder-coated items at a specific temperature for a set amount of time to ensure the powder melts, fuses, and forms a hard, durable coating. The oven is a critical part of the process and has several key features:
- Temperature Control:
- Powder coating requires precise temperature control. The oven must reach and maintain the required curing temperature, which typically ranges from 300°F to 400°F (150°C to 200°C), depending on the type of powder. The oven has built-in thermostats and controllers to ensure the temperature is consistent throughout the curing cycle.
- Airflow and Circulation:
- A well-designed powder coating oven uses forced air circulation to evenly distribute heat across all parts of the oven chamber. This ensures that the powder cures evenly on all surfaces of the part. Proper airflow is also essential for preventing hot spots or cold spots in the oven, which could lead to uneven curing or defects in the coating.
- Size and Capacity:
- The oven size will depend on the type and volume of parts being coated. There are different oven sizes, from small tabletop models to large industrial ovens capable of handling large-scale production. The size should be chosen based on the part dimensions, the number of items being coated at once, and the production volume.
- Insulation:
- Insulated walls help the oven maintain a consistent temperature while reducing energy consumption. High-quality insulation minimizes heat loss, making the oven more energy-efficient and reducing operating costs.
- Exhaust and Ventilation:
- During the curing process, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and fumes may be released from the powder. A well-designed oven includes an exhaust system that helps remove these fumes from the curing chamber, ensuring a safe working environment. Proper ventilation helps prevent the buildup of harmful gases and ensures that workers remain safe.
- Curing Process:
- The curing process typically lasts anywhere from 10 to 20 minutes, depending on the thickness of the coating and the type of powder. During this time, the powder melts, flows out to form a smooth, continuous film, and then chemically reacts to form a hard, durable coating. The oven’s role is to maintain the required curing conditions to ensure the best results.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Modern powder coating ovens are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing the operational costs of heating and maintaining the oven temperature. Advanced features such as variable speed fans, heat recovery systems, and programmable temperature profiles help minimize energy consumption while maintaining the required temperature and curing times.
- Safety Features:
- Powder coating ovens are equipped with safety features such as overheat protection, automatic shut-offs, and temperature monitoring systems. These features help prevent accidents and ensure that the oven operates within safe parameters. Additionally, many ovens come with fire-resistant materials to reduce the risk of ignition.
Powder Coating Process Flow (Machine + Oven)
The powder coating process typically follows this sequence:
- Preparation of Parts:
- Parts to be powder-coated are cleaned and pretreated to ensure proper adhesion of the powder. Common preparation methods include sandblasting, chemical cleaning, or acid washing.
- Powder Application:
- Once the parts are clean and dry, they are placed in a powder coating booth where the powder is sprayed using the powder coating machine. The electrostatic charge applied to the powder ensures it adheres to the part’s surface.
- Curing:
- After the powder is applied, the parts are moved to the powder coating oven. The oven heats the parts to the required curing temperature, causing the powder to melt and form a smooth, hardened finish.
- Cooling and Inspection:
- After curing, the parts are removed from the oven and allowed to cool. Once cooled, the parts are inspected for quality, ensuring that the coating is smooth, consistent, and free of defects. Any imperfections can be addressed by re-coating or re-baking the part as needed.
Key Considerations for Selecting Powder Coating Equipment
- Production Volume: Consider whether the machine and oven can handle the expected production volume. For small-scale operations, a compact powder coating machine and oven will suffice, while high-volume production may require industrial-sized equipment.
- Part Size and Complexity: Ensure the machine and oven can accommodate the size and shape of the parts you intend to coat. Larger parts or irregularly shaped items may require a larger oven or specialized application equipment.
- Powder Type: Choose equipment compatible with the specific powder types you plan to use. Some machines may be better suited for certain types of powders (e.g., epoxy or polyester), so it’s important to consider your product requirements.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for equipment with features designed to reduce energy consumption, such as advanced insulation, energy-efficient heating elements, and precise temperature control.
- Safety Features: Ensure the equipment has built-in safety mechanisms to protect operators and prevent accidents during operation.
Conclusion
The powder coating machine and oven are two crucial components of the powder coating process that work together to produce high-quality, durable finishes. The powder coating machine applies the coating, while the oven cures it to create a smooth, long-lasting surface. Together, these pieces of equipment ensure consistent, reliable results across various industries, from automotive and metalworking to furniture and appliance manufacturing. Choosing the right powder coating machine and oven based on the specific needs of your operation can significantly improve the quality and efficiency of your coating process.
The powder coating machine and oven are integral components of the powder coating process, which is used to create durable, high-quality finishes on various materials, primarily metals. Powder coating is favored for its durability, smoothness, and ability to resist corrosion, making it popular in industries like automotive, construction, and appliances. These machines and ovens work together to achieve a flawless, long-lasting finish that provides a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective solution than traditional liquid coatings.
The powder coating machine functions by applying a dry powder to a part or product. This powder is typically made from resin systems such as polyester, epoxy, or hybrid resins, which can be selected based on the needs of the product being coated. The machine uses an electrostatic charge to attract the powder to the part’s surface, ensuring a uniform layer. The powder is stored in a hopper, and a spray gun, connected to a source of compressed air, is used to atomize and direct the powder onto the part. The electrostatic charge applied to the powder particles helps them adhere to the surface of the part, even in hard-to-reach areas. This method is both efficient and environmentally friendly, as it reduces overspray and powder waste, allowing unused powder to be collected and reused.
Once the powder is applied to the part, it must be cured in a powder coating oven. The oven’s role is to bake the powder at a specific temperature, which melts and fuses the particles together into a smooth, durable coating. The curing process typically involves heating the part to temperatures between 300°F and 400°F (150°C to 200°C) for a set amount of time. This ensures that the powder melts and forms a hard, chemically bonded coating that is resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading. The oven’s even temperature distribution is critical to ensure that all areas of the part receive the same level of heat, resulting in a uniform finish.
The powder coating oven is designed with features that support the precise curing process. One of the key elements is its ability to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the chamber. This is essential to achieving the desired finish, as any variations in temperature can lead to defects like uneven curing, poor adhesion, or bubbling. Many modern powder coating ovens are equipped with forced-air circulation systems to ensure that the heat is evenly distributed. This forced air helps maintain the right temperature and also prevents hot spots or areas that might remain under-cured.
A key advantage of using powder coating machines and ovens together is their energy efficiency. Since powder coating uses dry powder, there are no solvents involved, which makes it more environmentally friendly compared to liquid coatings. The ovens themselves are often designed with energy-saving features, such as advanced insulation, which helps maintain heat within the chamber and reduces the amount of energy required to reach and maintain the necessary temperatures. Furthermore, the precise temperature controls and monitoring systems in the oven help minimize energy waste by ensuring that only the required amount of energy is used during the curing process.
The combination of the powder coating machine and oven also offers a high level of flexibility and customization for different applications. Whether the goal is to achieve a high-gloss, matte, or textured finish, both the machine and oven can be adjusted to meet specific requirements. The powder coating machine allows for precise control over the powder application, while the oven can accommodate various curing times and temperatures based on the type of powder used. Additionally, the ability to adjust the size and configuration of the oven means that it can handle a variety of part sizes, from small components to larger, bulkier items.
The process of powder coating using these machines and ovens provides a smoother, more consistent finish compared to traditional wet painting methods. The electrostatic process ensures that the powder adheres evenly to the surface, which eliminates the need for multiple coats or excessive handling. This results in a more efficient process that reduces labor and material costs. Additionally, the durability of the powder coating means that products coated with this method can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making it an ideal choice for outdoor or high-use applications.
For businesses that specialize in custom work or smaller production runs, portable powder coating machines and ovens offer an excellent solution. These portable systems are compact and mobile, allowing businesses to coat parts on-site or in small workshops without the need for large, stationary equipment. These portable systems retain the same high-quality results as larger systems, with the added benefit of flexibility. The compact nature of these systems makes them ideal for businesses that need to coat items of varying sizes or handle smaller production volumes while still maintaining efficiency and consistency.
In conclusion, the powder coating machine and oven are both critical components of the powder coating process, ensuring that products receive a high-quality, durable finish. The powder coating machine applies a precise electrostatic charge to the powder, which adheres to the part, while the oven cures the coating, making it smooth and resistant to wear and tear. Together, these machines provide a flexible, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solution for coating a wide range of products across different industries. Whether in large-scale production or small custom operations, the combination of a powder coating machine and oven delivers exceptional results with minimal waste and maximum efficiency.
Building on the previous discussion, the powder coating machine and oven system offers numerous advantages in terms of efficiency, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. As powder coating becomes increasingly popular in various industries, the combination of these two pieces of equipment provides significant benefits over traditional liquid painting processes.
One of the key benefits of the powder coating process is its environmental friendliness. Unlike liquid paint, which contains solvents that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air, powder coating is a solvent-free process. This reduces the environmental impact and helps businesses comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. The absence of solvents also eliminates the need for hazardous chemicals or special waste disposal, further reducing the environmental footprint of the coating process. Additionally, the use of powder recovery systems in coating machines ensures that any excess powder is captured and reused, minimizing waste and maximizing material efficiency.
The durability of powder-coated finishes is another significant advantage. Once cured in the oven, the powder forms a hard, smooth, and highly resistant surface. The finish is not only scratch and chip-resistant but also more resilient to weathering, UV degradation, and chemicals compared to traditional paint. This makes powder coating particularly suitable for outdoor applications, such as automotive parts, exterior furniture, and industrial machinery, where durability and longevity are crucial.
Customization is also a major advantage of the powder coating process. The availability of a wide variety of powders allows for a range of finishes, from matte to glossy, textured to smooth. Businesses can select specific powder types depending on the part’s requirements, such as resistance to heat, corrosion, or abrasion. Furthermore, the powder coating process offers a consistent and uniform coating, which is often difficult to achieve with liquid paint. This consistency makes it especially valuable in industries where high-quality finishes are essential, such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
The speed of the powder coating process also plays a crucial role in improving overall productivity. The powder is applied in a single pass, and curing takes place quickly in the oven. The typical curing time can range from 10 to 20 minutes, depending on the part size and powder type. This quick turnaround time allows businesses to coat parts in high volumes and reduces downtime. In addition, the efficiency of the system ensures that multiple parts can be coated in the same batch, optimizing throughput.
One significant aspect of the powder coating oven is its ability to accommodate various part sizes and production volumes. While some ovens are designed for small, custom jobs, others can be scaled up to handle large, industrial applications. For example, conveyorized powder coating ovens are common in large-scale production facilities, where parts move through the oven on a conveyor belt. These systems are highly efficient and allow for continuous coating of parts at high speeds. Larger ovens can also be customized with multiple zones, allowing for different temperatures in different sections of the oven to accommodate various curing profiles.
For businesses focused on small batch or custom coating work, batch-style powder coating ovens provide more flexibility. These ovens allow operators to manually load and unload parts, making them ideal for companies that coat a wide variety of items in smaller quantities. Batch-style ovens can also be easier to operate and maintain, making them a popular choice for smaller operations or shops that don’t need the volume capacity of larger, conveyorized systems. Even though these ovens are smaller, they still offer precise temperature control and efficient heat distribution, ensuring high-quality results.
Another benefit of combining the powder coating machine and oven system is its low maintenance needs. Compared to liquid coating systems, which often require complex equipment for mixing, thinning, and cleaning, powder coating systems are simpler and require less maintenance. The powder coating machine, for instance, has fewer moving parts, and the powder recovery system helps ensure that the equipment stays clean. Similarly, the powder coating oven, though it requires periodic cleaning, has fewer components that need frequent servicing compared to other types of curing systems. This simplicity reduces downtime and helps businesses keep production costs low.
The consistency of the powder coating process is especially advantageous when working with parts that need a uniform finish. Unlike liquid coatings, which can show brush marks, drips, or variations in thickness, powder coating ensures a smooth, even application across all surfaces. The electrostatic charge applied during the powder application process attracts the powder to the surface evenly, allowing for a consistent coat. This is particularly useful when coating complex parts with intricate shapes, as the electrostatic method ensures that even hard-to-reach areas receive a uniform coating.
Energy efficiency is another factor that makes the combination of a powder coating machine and oven a highly cost-effective option for many businesses. Powder coating ovens are designed to minimize energy consumption, especially with features like advanced insulation, heat recovery systems, and efficient air circulation. This allows the oven to heat quickly, retain heat, and maintain consistent temperatures with less energy. The energy-efficient nature of these systems not only helps businesses reduce operational costs but also aligns with sustainability goals by reducing the overall environmental impact of the coating process.
The use of powder coating machines and ovens in industries such as automotive restoration, metal fabrication, or furniture manufacturing demonstrates their versatility. These systems are ideal for projects requiring high-quality finishes on both small and large parts. The flexibility to use different types of powders (such as matte, glossy, or textured finishes) makes it easy for businesses to meet various customer preferences or product requirements. Whether applying powder to automotive wheels, metal furniture frames, or intricate metal parts, these machines and ovens provide a reliable and efficient solution for creating high-performance coatings.
The advanced features found in modern powder coating machines and ovens also play a role in increasing production efficiency. Many systems now come with features such as programmable controls, allowing operators to set precise curing profiles for different powders or parts. These systems can be adjusted to account for variables like part size, material type, and coating thickness, ensuring the correct curing conditions are maintained. Some machines also offer automated powder application systems, which further enhance consistency and reduce human error.
Finally, safety remains a priority when working with powder coating equipment. Both powder coating machines and ovens are designed with safety in mind, featuring ventilation systems to manage fumes, temperature controls to prevent overheating, and protective features like thermal cutoffs and fire-resistant materials. These safety measures ensure a secure working environment and prevent accidents during the coating and curing processes.
In summary, the combination of the powder coating machine and oven is a powerful solution for businesses that want to achieve consistent, high-quality, and durable finishes. The machine applies a precise electrostatic charge to the powder, which is then cured in the oven, creating a smooth, hard finish that is resistant to wear, weather, and chemicals. With benefits ranging from environmental friendliness to energy efficiency, and from ease of maintenance to customizability, these systems offer businesses the tools they need to produce high-performance coatings efficiently and cost-effectively.
Top 5 Things To Consider When Buying A Powder Coating Oven
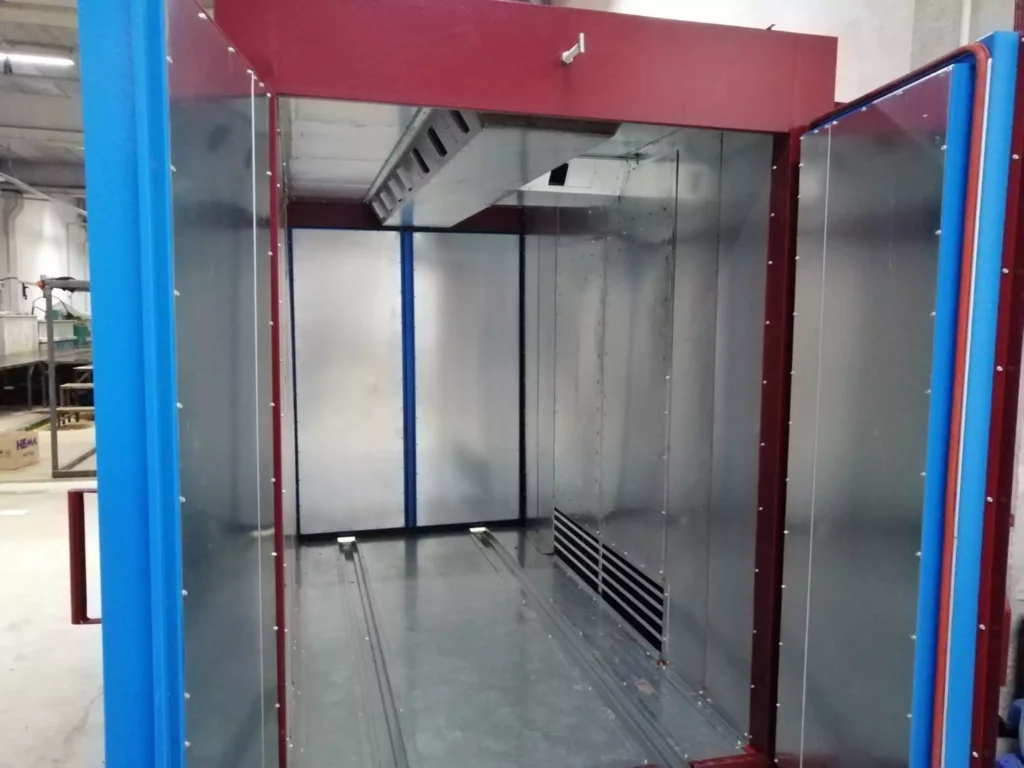

When buying a powder coating oven, it’s essential to choose one that meets the specific needs of your business, ensuring that it delivers the best results in terms of quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Here are the top 5 things to consider when purchasing a powder coating oven:
1. Size and Capacity
- Part Size: The size of the oven should be able to accommodate the parts you plan to coat. Whether you’re coating small components or large items, the oven must have enough space to allow for proper airflow and heat distribution. Oversized parts may require a larger oven with a more spacious interior.
- Production Volume: If you’re working with high-volume production, you’ll need a larger oven or even a conveyorized system that allows continuous operation. For smaller operations or custom jobs, a batch-style oven may be more suitable. Choosing the right size helps optimize production and energy efficiency.
2. Temperature Control and Consistency
- Precision in Temperature: Temperature control is one of the most critical features of a powder coating oven. The oven must be able to maintain a consistent, even temperature (usually between 300°F and 400°F / 150°C to 200°C) to ensure proper curing of the powder. Inconsistent heating can lead to defects like uneven finishes, poor adhesion, or improper curing, which may affect the quality of your coatings.
- Temperature Range: Check that the oven can achieve and maintain the required curing temperature for the type of powder coating you plan to use. Some powder types may require different curing temperatures, so having precise temperature controls and monitoring systems is essential.
3. Energy Efficiency
- Energy Consumption: Powder coating ovens can consume significant amounts of energy, especially during the curing process. Look for ovens with advanced insulation and heat recovery systems, which help retain heat and reduce energy costs by preventing unnecessary heat loss.
- Operating Costs: Energy-efficient ovens reduce the overall operational costs of your powder coating process. Consider ovens with programmable controls that allow you to set specific temperature profiles to optimize energy usage based on the parts you’re curing.
4. Airflow and Circulation
- Even Heat Distribution: Proper airflow is critical to ensure that the oven distributes heat evenly throughout the entire chamber. Uneven airflow can lead to hot spots or cold spots, causing parts to cure improperly or unevenly. Ensure that the oven has forced-air circulation or other systems designed to maintain consistent heat.
- Part Orientation and Loading: Airflow should not only be uniform but also efficient, allowing for the parts to be properly oriented within the oven. This ensures that each part receives an even coat of heat, essential for achieving uniform curing and the best finish.
5. Safety and Durability
- Safety Features: Make sure the oven includes built-in safety mechanisms, such as overheat protection, fire-resistant materials, and proper ventilation systems to manage fumes and gases. Safety features are critical to ensuring a safe working environment for operators and compliance with safety regulations.
- Long-Term Durability: Look for a well-built oven that is constructed with durable, high-quality materials designed to withstand prolonged use. Choose an oven with a robust frame and reliable heating elements that will continue to perform at a high level over time.
By considering these key factors—size and capacity, temperature control, energy efficiency, airflow, and safety and durability—you’ll be able to select a powder coating oven that aligns with your business’s specific needs, helping you achieve high-quality, consistent finishes while optimizing your production process.
When purchasing a powder coating oven, it’s important to evaluate the oven’s size and capacity to ensure it matches the parts you intend to coat and the scale of your production. The oven should be large enough to accommodate the items you’re coating, whether they are small components or larger parts like automotive bodywork or industrial equipment. Additionally, you should consider whether your production requires a high-volume, continuous operation or smaller, custom runs. Larger operations may benefit from a conveyorized system for continuous coating, while smaller operations might be better suited to a batch-style oven.
Temperature control and consistency are vital to achieving the best results in powder coating. The oven should have precise temperature controls to maintain a consistent heat throughout the curing process. This ensures that the powder coating cures evenly and forms a durable finish without defects. If the temperature fluctuates, it could result in an uneven or compromised coating, so look for ovens with reliable, consistent heating mechanisms. Be sure that the oven can reach and maintain the necessary curing temperatures for the type of powder you’re using, which generally ranges between 300°F and 400°F (150°C to 200°C). Some powder coatings may require specific curing profiles, so adjustability in temperature control is essential.
Energy efficiency is another key consideration. Powder coating ovens can be energy-intensive, so selecting an oven that’s energy-efficient can help reduce long-term operating costs. Look for ovens with advanced insulation and heat recovery features that minimize energy consumption by retaining heat within the chamber. This not only cuts down on energy bills but also ensures the oven reaches its desired temperature more quickly and maintains it without excessive energy use. In addition, ovens with programmable controls help you adjust temperature settings for different production needs, optimizing energy usage based on the specifics of the job.
Airflow and circulation are critical factors in achieving a uniform coating. The oven should be equipped with a reliable forced-air circulation system that evenly distributes heat throughout the oven chamber. Proper airflow ensures that the powder coating cures consistently across the surface of all parts, regardless of shape or orientation. Uneven airflow can lead to hot spots or cold spots, resulting in defects in the coating, such as incomplete curing or uneven finishes. The oven’s design should allow for efficient part loading and proper orientation, so the airflow reaches all areas of the parts being coated.
Finally, safety and durability are essential when selecting a powder coating oven. Ensure that the oven has safety features such as overheat protection, proper ventilation to manage fumes, and flame-resistant materials to protect operators and the workplace. These features are especially important when working with the high temperatures and powders involved in the coating process. In terms of durability, the oven should be constructed from high-quality materials designed to withstand constant use over time. Look for ovens with sturdy frames, reliable heating elements, and robust insulation, as these contribute to the oven’s longevity and consistent performance.
By keeping these factors in mind, you’ll be able to select a powder coating oven that fits your specific needs and provides the best results for your operations. Whether you’re focusing on quality, energy efficiency, or safety, these considerations will help ensure that the oven you purchase enhances your coating process and supports the growth of your business.
In addition to size, temperature control, energy efficiency, airflow, and safety, there are other factors that can further enhance your decision-making process when choosing a powder coating oven. For example, the ease of maintenance should be a priority. Over time, ovens require cleaning and maintenance to ensure they continue to perform efficiently. Look for ovens that are easy to clean, with removable filters, racks, or other parts that may need regular upkeep. Regular maintenance is essential for prolonging the life of the oven and ensuring it operates at peak efficiency, minimizing downtime and reducing repair costs.
The type of heating elements used in the oven is another important consideration. Powder coating ovens typically use either electric or gas heating elements, and each has its own advantages. Electric ovens are generally more energy-efficient and easier to control with precise temperature regulation. Gas ovens, on the other hand, can be more cost-effective in areas where gas is cheaper than electricity, but they may require more maintenance and have slightly less precise temperature control. Your choice of heating element will depend on your specific needs, such as energy costs, temperature consistency, and the overall scale of production.
Another factor to consider is the oven’s control system. Modern powder coating ovens come with advanced digital controls, which allow operators to set precise curing profiles, adjust temperature settings, and even track production schedules. This automation can improve efficiency by reducing human error and ensuring that each batch is cured to the correct specifications. Some ovens even have programmable settings for different types of powder or part sizes, which can save time and improve consistency across multiple runs.
Additionally, consider the oven’s ability to handle different types of powder coatings. Depending on your operations, you may be using various types of powders, such as polyester, epoxy, or hybrid coatings. Some ovens are specifically designed to work with specific powders, while others offer more versatility and can handle a range of coating types. Make sure that the oven you choose is compatible with the specific powder coatings you intend to use, and that it can provide the required curing conditions for each type.
For businesses that need flexibility in part handling, it may be beneficial to select an oven with adjustable racks or a conveyor system that can be customized to accommodate different part sizes or types. Conveyorized ovens are particularly useful for high-volume, automated production, as parts move through the oven on a conveyor belt, making it easy to coat large quantities of items at once. For smaller shops or custom projects, a batch-style oven might be better suited, as it allows for more flexibility in handling various part sizes and types.
Lastly, don’t overlook the importance of warranty and customer support when purchasing a powder coating oven. A solid warranty ensures that you’ll be covered in case of any defects or issues with the equipment. Good customer support can also make a significant difference when you need assistance with installation, troubleshooting, or general maintenance. Look for manufacturers or suppliers that offer reliable customer service and have a reputation for standing behind their products.
In conclusion, selecting the right powder coating oven is crucial for the success of your coating process. It involves evaluating a range of factors, including size, temperature control, energy efficiency, airflow, and safety, as well as considerations like ease of maintenance, heating elements, and control systems. By carefully assessing these features and ensuring the oven meets the specific needs of your business, you can improve efficiency, consistency, and quality in your powder coating operations. With the right oven, you’ll be able to achieve superior finishes while minimizing costs and maximizing productivity.
Powder Coating Kit with Oven
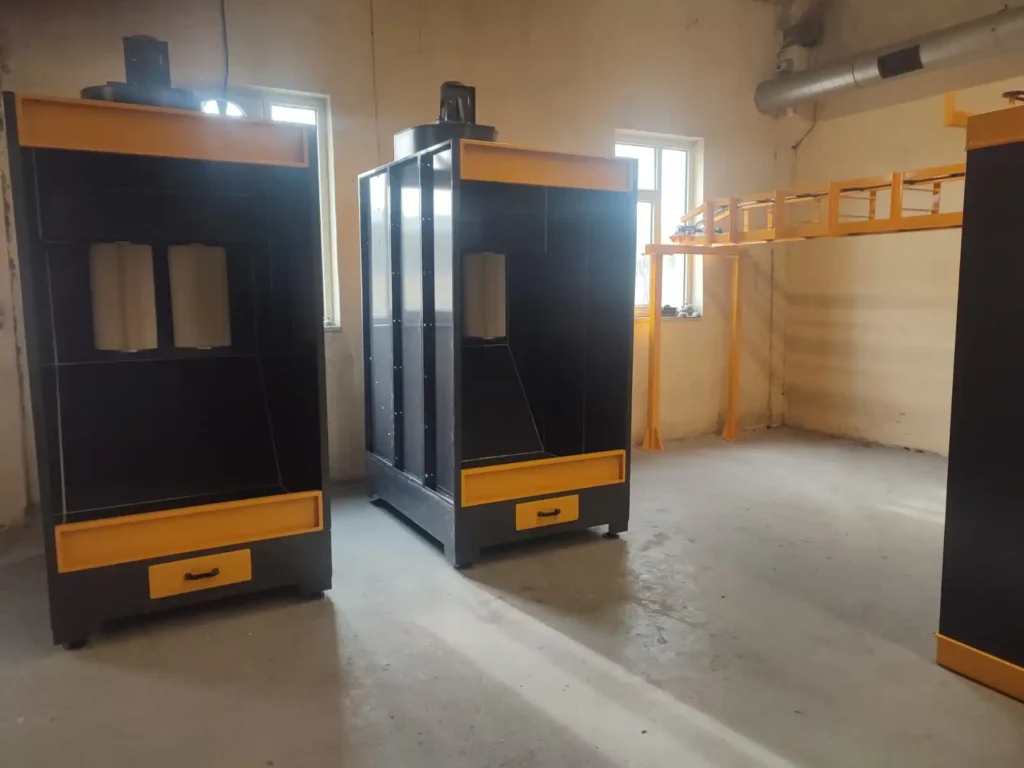

A powder coating kit with oven is a complete solution for individuals or small businesses looking to carry out powder coating projects efficiently and effectively. These kits combine all the necessary equipment needed for powder coating—specifically the powder coating machine, oven, and additional accessories—into one convenient package. They are ideal for custom projects, hobbyists, or small-scale production, offering a simple, cost-effective way to apply durable, high-quality coatings to metal surfaces. Here’s what you can expect from a powder coating kit with oven:
The powder coating machine in these kits typically includes a spray gun that applies an electrostatic charge to the powder particles, allowing them to adhere to the metal part. The machine usually comes with adjustable settings to control the powder flow and the electrostatic charge, helping ensure that the coating is even and smooth. This process is highly efficient because it minimizes powder waste, as excess powder can be recovered and reused.
The powder coating oven in the kit is designed to cure the powder coating once it has been applied to the parts. The oven heats up to the necessary curing temperature (typically around 350°F to 400°F or 175°C to 200°C) and maintains it consistently to melt and fuse the powder into a hard, durable finish. Many of these ovens are compact and portable, making them suitable for small spaces or home workshops. They typically offer adjustable temperature controls, ensuring the right curing conditions for a wide range of powder coatings.
In addition to the machine and oven, the kit may also include various accessories that can help improve the coating process. These accessories can include powder recovery systems, which capture excess powder for reuse, and grounding equipment to ensure proper electrical grounding during the coating process. Some kits also include stirring rods for mixing the powder, cleaning brushes for prepping parts before coating, and safety gear like gloves and masks to ensure the operator is protected from powder exposure.
When selecting a powder coating kit with oven, it’s essential to consider the following:
- Size and Capacity: Make sure the oven is large enough to accommodate the parts you plan to coat. Most kits are designed for small to medium-sized parts, so if you’re working with larger items, you may need a larger oven or a custom setup.
- Temperature Control: Ensure the oven has precise temperature control, as curing is crucial for achieving a durable and smooth finish. Some kits feature digital temperature controllers with timers, allowing you to set specific curing profiles for different powders or part sizes.
- Power Source: Check whether the kit operates on electricity or gas. Most small-scale kits use electric ovens, which are easy to set up and operate, but if you’re planning to work in a larger space or on a higher volume of parts, a gas oven may be more energy-efficient in the long run.
- Portability and Space Requirements: Many powder coating kits are designed to be portable and compact, making them ideal for home workshops or smaller businesses. Be sure to assess the space available in your shop or garage and choose a kit that fits comfortably while still allowing for efficient operation.
- Support and Warranty: Since powder coating equipment is an investment, it’s essential to choose a kit from a reputable manufacturer that offers reliable customer support, as well as a warranty that covers the oven and machine in case of defects or issues.
In conclusion, a powder coating kit with oven is an all-in-one solution that simplifies the process of powder coating. These kits are ideal for small businesses, custom shops, or hobbyists who want to create high-quality finishes on metal parts. By providing all the necessary tools in one package, these kits make it easier to achieve professional results while maintaining efficiency and flexibility.
A powder coating kit with oven is a convenient and complete solution for those looking to start powder coating in smaller-scale operations or even as a hobby. It typically includes everything you need to get started, from the powder coating machine to the curing oven, and even some accessories to help with the coating process. The powder coating machine is usually equipped with a spray gun that uses electrostatic charge to apply the powder evenly on metal parts. This system ensures the powder adheres well to the surface, minimizing waste and ensuring a smooth finish.
Once the powder is applied, the oven comes into play. It is designed to cure the powder by heating it to the right temperature, which causes the powder particles to melt and fuse into a hard, durable finish. These ovens are generally compact and portable, making them ideal for smaller spaces such as a home workshop or a small business. The ovens typically allow for precise temperature control, ensuring that the powder is cured effectively and consistently, which is critical for achieving a high-quality, durable finish.
One of the main advantages of using a kit is its convenience. Instead of purchasing separate machines and equipment, the kit provides everything in one package. It also often includes accessories that can make the powder coating process easier and more efficient, such as powder recovery systems to save and reuse excess powder, cleaning brushes for prepping parts before coating, and grounding equipment to ensure the proper electrostatic charge. In some cases, kits may also include safety gear like gloves and masks, ensuring the safety of the operator during the process.
When looking for a powder coating kit with oven, there are several factors to consider. The size and capacity of the oven are important depending on the parts you want to coat. Most kits are designed for small to medium-sized parts, so if you have larger pieces, make sure the oven can accommodate them. Temperature control is also crucial, as improper curing can lead to a poor finish. Kits with digital controls and adjustable timers offer more flexibility in setting precise curing profiles for different types of powder and part sizes.
Another important consideration is the power source. Many kits use electric ovens, which are easier to set up and generally more convenient for small-scale operations. However, gas ovens can be more energy-efficient, especially for larger volumes. Portability is another factor if you need the kit to be easy to move or store when not in use. Lastly, you should evaluate the support and warranty options provided by the manufacturer to ensure you have reliable service if any issues arise with the equipment.
In summary, a powder coating kit with oven is an all-in-one solution that simplifies the powder coating process for small businesses, hobbyists, or those just getting started. These kits offer ease of use, cost-efficiency, and professional results, with everything you need to get the job done right. With the right kit, you can achieve consistent, high-quality finishes that are durable and long-lasting, all while improving efficiency and reducing waste in your coating process.
When looking into a powder coating kit with oven, it’s essential to consider the specific features that will suit your operation or project needs. Many kits are designed to handle a variety of parts, from small household items to larger industrial components, so it’s important to choose one that matches the scale of your work. For example, if you plan on coating large automotive parts or bulk items, you may need a larger oven or a more industrial-grade setup. Conversely, if your work is more focused on smaller projects, a compact, portable kit will provide the flexibility to handle smaller parts while saving space.
The ease of setup and operation is another consideration. Some powder coating kits are ready to use out of the box, requiring minimal assembly, while others may involve a bit more setup. Kits with user-friendly features, like clear instructions and simple controls, can make the learning curve easier, especially for those new to powder coating. Additionally, digital controls for temperature, time, and even automated settings for curing can make the coating process more straightforward and precise. A well-designed kit can streamline your workflow, making the process smoother and less time-consuming.
Maintenance requirements are also worth noting. While powder coating ovens are generally low-maintenance, certain models may require periodic cleaning or component checks to maintain optimal performance. Kits with removable filters or parts that are easy to clean can save time and effort in maintenance. Additionally, ensure that the oven is equipped with features that help protect it from powder buildup or any potential damage due to excessive heat or material wear. Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of your oven and ensure your coating processes continue to run smoothly.
Durability is another crucial factor. You’ll want to invest in a kit made from high-quality materials that can handle frequent use, especially if you’re working with high temperatures or running multiple jobs a day. Durable ovens and machines are built to withstand the wear and tear of frequent powder coating applications, which means fewer repairs and a better return on investment over time. Look for kits with a reputation for lasting quality and a track record of reliability, so you know you’re getting a product that will stand the test of time.
Additionally, cost-effectiveness plays a significant role in selecting the right powder coating kit with oven. While there are premium options with advanced features, it’s important to balance cost with the level of capability you require. For smaller operations or hobbyists, a budget-friendly option might offer all the necessary features without the extra frills, while still providing great results. However, for businesses that rely on frequent production, investing in a higher-end kit with greater durability, energy efficiency, and advanced controls might prove more economical in the long run.
In conclusion, the key to selecting the right powder coating kit with oven is understanding your specific needs, whether you require a compact, versatile kit for small-scale operations or a larger, more robust setup for high-volume production. By evaluating factors like part size, ease of use, maintenance, durability, and cost, you can find a kit that matches your budget and enhances the efficiency and quality of your powder coating process. With the right equipment, you’ll be able to achieve professional results while saving time, money, and resources.
Used Powder Coating Oven
When considering a used powder coating oven, there are several factors to take into account to ensure you’re getting a reliable and functional unit at a good price. Purchasing a used oven can be an excellent way to save money, but it comes with risks, so it’s important to carefully evaluate the condition of the oven before making a decision.
Age and Condition are the first things to consider. The age of the oven can tell you how much wear it might have endured and whether it has outdated technology or components. Ideally, you want an oven that is relatively new or has been well-maintained, as this will reduce the likelihood of needing expensive repairs. Make sure to ask the seller about its usage history, including how often it was used, and check for any signs of wear, such as rust, worn-out insulation, or damaged heating elements.
Operational Check is crucial when inspecting a used oven. If possible, test the oven’s functionality before purchasing. This includes checking that it reaches the required temperatures and maintains heat consistency. Make sure the oven heats up evenly and stays at the desired temperature without fluctuations. Inconsistent or uneven heating could lead to poor curing, which affects the quality of the powder coating and the durability of the finish.
Heating Elements and Components are another vital consideration. The oven’s heating system—whether electric or gas—should be fully functional and in good condition. If the heating elements are worn out or damaged, replacing them can be costly. Additionally, check the condition of the insulation, as poor insulation can lead to energy inefficiency and uneven heating.
Size and Capacity are also important factors when buying a used powder coating oven. Ensure that the oven is large enough for the parts you plan to coat, and verify that the internal dimensions will accommodate the sizes of your typical workpieces. A smaller oven might be sufficient for hobbyists or small operations, but if you’re scaling up or plan to work with larger parts, you’ll need a larger oven.
Energy Efficiency should also be evaluated. An older oven may not have the same energy-saving features as newer models, and it could consume more power to operate. If the oven is a gas-powered model, check that it has no leaks, and ensure the burners and heat exchanger are in good condition. An inefficient oven will increase your operational costs, so try to balance the initial savings with the long-term energy expenses.
Upgrades and Parts Availability are additional factors to consider. Ask the seller whether any parts have been replaced or upgraded, as this could impact the oven’s performance and longevity. Additionally, check if replacement parts are still available for that model, as discontinued ovens may present a challenge if repairs are needed in the future. If parts are hard to find or no longer manufactured, it may be more cost-effective to buy a new oven instead.
Warranty and Support can sometimes be an issue with used equipment, as many warranties may no longer apply once the equipment is sold secondhand. However, if the oven was recently serviced or comes with a limited warranty, this can offer peace of mind. Be sure to inquire about any warranty options or service agreements available with the purchase.
Price is, of course, a major consideration when buying a used powder coating oven. While you can save a significant amount of money by purchasing a used unit, make sure the cost reflects the oven’s age, condition, and any necessary repairs. Don’t assume that a used oven is always the cheaper option if repairs or upgrades are needed right away. Compare the price of the used oven with the cost of purchasing a new one, considering factors like energy efficiency and expected lifespan.
Seller Reputation is another important factor. When buying used equipment, it’s critical to purchase from a reputable seller who can provide detailed information about the oven’s condition and history. If possible, ask for references or reviews from previous customers to ensure you’re getting an oven that has been properly maintained.
In conclusion, buying a used powder coating oven can be a cost-effective solution, but it requires careful evaluation to ensure the oven is in good condition and will continue to serve your business or personal needs. By thoroughly inspecting the oven, verifying its functionality, checking for energy efficiency, and making sure it suits your part sizes and production volume, you can make an informed decision that balances cost savings with long-term performance.
When purchasing a used powder coating oven, it’s essential to consider its overall condition and age. Older ovens might show signs of wear that could affect their performance, so it’s important to carefully inspect the unit for any issues that might need repairs soon. Look for any signs of rust, corrosion, or damage to key components such as the heating elements or insulation. If the oven is older, it might lack some of the modern energy-efficient features found in newer models, which could lead to higher operational costs. Additionally, make sure to check that the oven heats evenly and reaches the required temperatures for the type of powder you plan to use.
Before purchasing, it’s a good idea to test the oven’s functionality if possible. Ensure that it heats up properly and maintains consistent temperatures. Inconsistent heating can lead to uneven curing of the powder coating, affecting the final product’s durability and finish. A reliable oven should have precise temperature controls, and any signs of overheating or failure to maintain the right curing temperature should be a red flag.
Another crucial aspect to check is the heating elements and the condition of the oven’s internal components. Over time, heating elements can wear out, and replacing them can be costly. It’s important to check for any visible signs of damage or wear, as a malfunctioning heating system could require expensive repairs. The oven’s insulation is another factor to consider—if it’s damaged or degraded, it can result in inefficient heat retention, leading to increased energy usage and uneven curing.
In terms of size and capacity, ensure that the oven is large enough to handle the parts you plan to powder coat. Measure the interior dimensions to confirm it can accommodate your typical workpieces. A used oven that doesn’t meet your capacity needs may limit your ability to expand production or coat larger parts.
Energy efficiency is an important factor when considering any oven, whether new or used. Older ovens may not have the advanced insulation or heat recovery features that help save energy. If energy efficiency is a key concern, look for ovens that still have high-quality insulation and low energy consumption, as running an inefficient oven can drive up long-term costs. If you’re purchasing a gas-powered oven, be sure to check for leaks or wear in the gas lines and burners, as this could pose a safety hazard or lead to costly repairs.
Before buying, confirm that replacement parts for the oven are readily available. Some used ovens, particularly older models, may have parts that are no longer manufactured, making repairs or maintenance difficult or expensive. If parts are hard to find or discontinued, it might be better to consider a new oven or a more modern used model with accessible parts.
When purchasing a used powder coating oven, it’s important to also consider the reputation of the seller. A reliable seller will provide a full history of the oven, including how it was used and whether it has undergone any significant repairs or upgrades. If the seller can provide maintenance records or references from previous buyers, it can help reassure you that the oven has been well-maintained and is in good working order.
Lastly, while the initial price of a used oven may be attractive, it’s essential to factor in any potential future repairs, upgrades, or replacements. Sometimes, the cost of fixing an oven that requires a lot of work can outweigh the savings of buying used. Therefore, ensure that the price is fair for the oven’s condition and the amount of work that may be needed to get it up to full working capacity.
By carefully evaluating a used powder coating oven, you can make an informed decision that balances cost savings with the oven’s performance and potential longevity. If done right, purchasing a used oven can be an excellent investment, allowing you to get high-quality results at a fraction of the price of a new unit. However, it’s critical to thoroughly inspect the oven, test its functionality, and ensure that it meets your operational needs before finalizing the purchase.
Why You Need A Powder Coating Oven

A powder coating oven is essential in the powder coating process, as it plays a critical role in curing the applied powder to achieve a durable, high-quality finish. Without an oven, the powder would not properly adhere to the surface, and the coating would not achieve the desired hardness, resistance, or smoothness. Here are some key reasons why you need a powder coating oven:
- Curing Process: The primary purpose of a powder coating oven is to cure the applied powder coating. After the powder is sprayed onto a metal part, the oven is used to heat the part to a specific temperature, typically between 350°F and 400°F (175°C to 200°C), which causes the powder particles to melt and bond with the substrate. This curing process is essential for turning the powder into a hard, protective finish.
- Durability and Quality: Proper curing in a powder coating oven ensures that the coating is tough, long-lasting, and resistant to wear, corrosion, and chemicals. Without the oven, the powder coating would not cure properly, leading to a finish that is likely to be soft, prone to scratches, or unable to withstand harsh conditions.
- Consistent Results: A powder coating oven ensures even heating across the surface of the part, resulting in a uniform and consistent finish. This consistency is important for maintaining high-quality standards, especially in commercial or industrial applications. Without a proper oven, it would be challenging to achieve the level of control needed for consistent results.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern powder coating ovens are designed to be energy-efficient, with precise temperature controls that ensure the heat is evenly distributed throughout the oven. This allows for energy savings while ensuring that the curing process is carried out efficiently. In addition, ovens with good insulation help minimize heat loss, reducing energy consumption.
- Speed and Productivity: Powder coating ovens allow for faster curing compared to other methods of applying coatings. The quick curing process speeds up production cycles, which is crucial for businesses that need to coat large quantities of parts in a short amount of time. The oven’s precise temperature control ensures that each part is cured optimally, resulting in fewer reworks and higher throughput.
- Versatility for Different Parts: Powder coating ovens come in various sizes and configurations, allowing them to accommodate a wide range of part sizes and shapes. Whether you are coating small items like automotive parts or large pieces like industrial machinery components, a powder coating oven can handle a wide variety of jobs. The flexibility in oven size ensures that you can coat different parts effectively without needing multiple pieces of equipment.
- Improved Aesthetic Appearance: Proper curing in a powder coating oven results in a smooth, glossy, or matte finish, depending on the powder used. This uniform, polished appearance is a major selling point for many businesses, especially those in the automotive, appliance, and furniture industries, where aesthetics are important.
- Safety: Curing powder coating at high temperatures in a controlled oven is safer than trying to use alternative heat sources, like open flames or improper heating methods, which could lead to uneven curing or hazardous conditions. Powder coating ovens are designed to maintain safe temperatures and often include features like thermostats and safety shutoffs, minimizing risks during operation.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: In many industries, especially those dealing with metal parts exposed to harsh conditions (automotive, aerospace, manufacturing), powder coating is a regulated process. Having a proper powder coating oven ensures compliance with industry standards for quality, performance, and safety, helping businesses meet regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
In summary, a powder coating oven is crucial for achieving high-quality, durable finishes. It ensures proper curing, enhances productivity, and maintains consistency across different parts. Whether you’re operating a small-scale shop or a large manufacturing facility, having a powder coating oven is essential for delivering the best possible results in the coating process.
Additionally, a powder coating oven plays a significant role in reducing waste and improving efficiency in your coating process. By ensuring that the powder is properly cured, you eliminate the need for touch-ups or re-coating, which can be time-consuming and expensive. This not only saves materials but also reduces labor costs since you won’t need to reapply the coating or deal with defects caused by improper curing.
A powder coating oven also contributes to environmental sustainability. Powder coating itself is an eco-friendly process because it produces fewer emissions than traditional liquid coatings and does not require solvents. The use of a dedicated oven further enhances this benefit by providing an enclosed, controlled environment for curing, minimizing the chances of pollutants or overspray escaping into the atmosphere. Additionally, since the oven’s heat is directed at curing the powder, less energy is wasted compared to other methods of curing or drying.
Another reason you need a powder coating oven is that it allows you to work with a wide variety of powders. Depending on the type of powder coating you use—whether it’s epoxy, polyester, hybrid, or acrylic—you need a specific curing process that can be precisely controlled. A quality oven provides the ability to customize the curing temperature and time settings, ensuring that you can work with different powder types and achieve optimal results for each one.
In industries that demand high-performance finishes, such as automotive or industrial manufacturing, a dedicated oven is necessary to meet the coating’s required specifications. The oven ensures that parts are cured to the correct hardness, impact resistance, and chemical resistance levels, providing a finish that can withstand the demands of harsh environments, from high temperatures to corrosive elements.
Furthermore, a powder coating oven is designed to offer greater control and precision than other heat sources. Ovens have precise temperature regulation systems, with many modern units offering digital controllers that allow you to set exact curing times and temperatures. This precise control is vital for avoiding overheating or under-curing, which can lead to defects like blistering, peeling, or inconsistent finishes.
Having a powder coating oven also allows businesses to scale their operations. As your production grows, so will your need for consistent, high-quality finishes. A powder coating oven can handle larger volumes of parts efficiently, allowing for a more streamlined production process. If you’re working in an environment where high throughput is needed, an oven that can accommodate multiple parts simultaneously or larger items will help you meet deadlines and demand.
Finally, a powder coating oven contributes to the overall reliability and reputation of your business. By using a proper oven and ensuring consistent, high-quality finishes, you’re more likely to satisfy customers with long-lasting and aesthetically appealing products. Whether you’re coating wheels, automotive parts, or other metal items, the quality of the finish will directly reflect on your brand, helping you build a reputation for delivering top-tier, durable products.
In summary, a powder coating oven is essential not only for the curing process but also for ensuring consistent results, increasing efficiency, reducing waste, and improving environmental sustainability. It is a crucial piece of equipment for anyone looking to produce high-quality, durable finishes, whether on a small or large scale. Whether you’re a hobbyist or running a commercial operation, having the right oven will help you achieve professional results and keep your production process running smoothly.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance of powder coating ovens is essential for achieving high-quality finishes, maintaining production efficiency, and ensuring equipment longevity. By implementing a structured maintenance plan, conducting regular inspections, and training staff, businesses can minimize downtime, reduce costs, and maintain a safe working environment.
