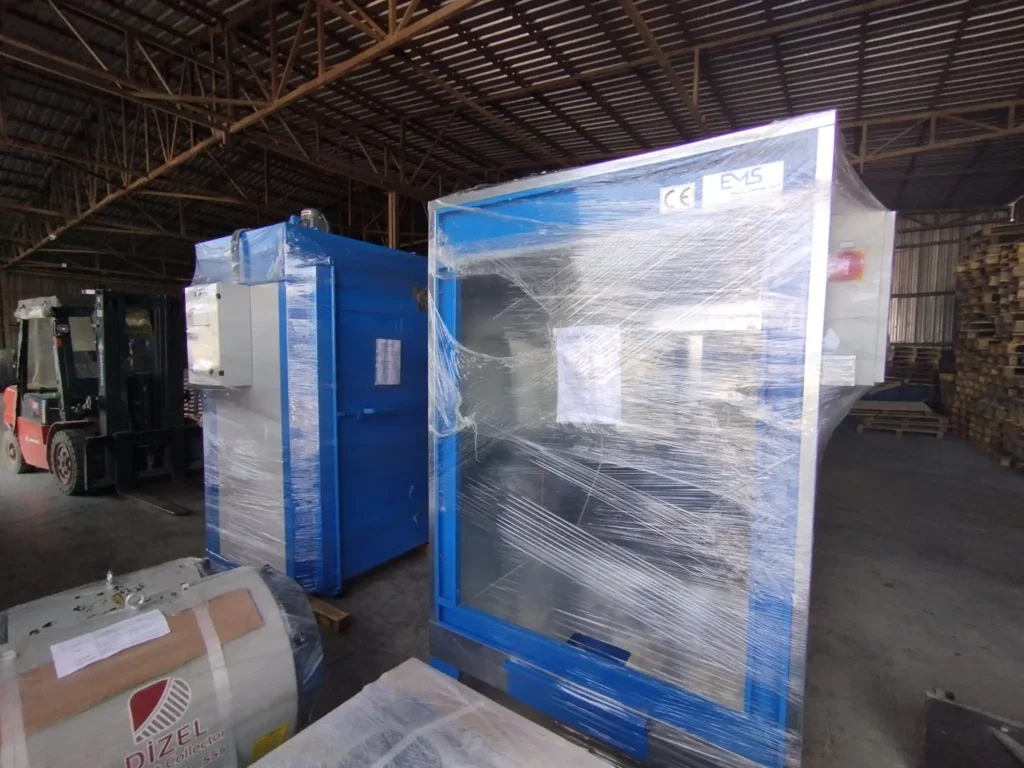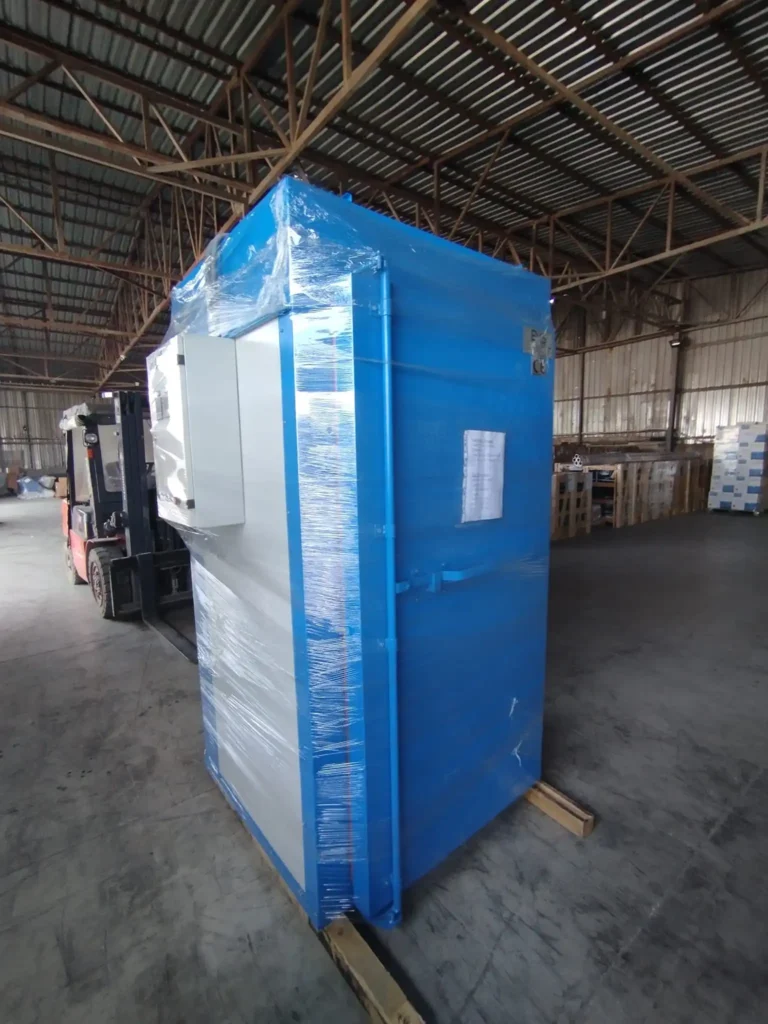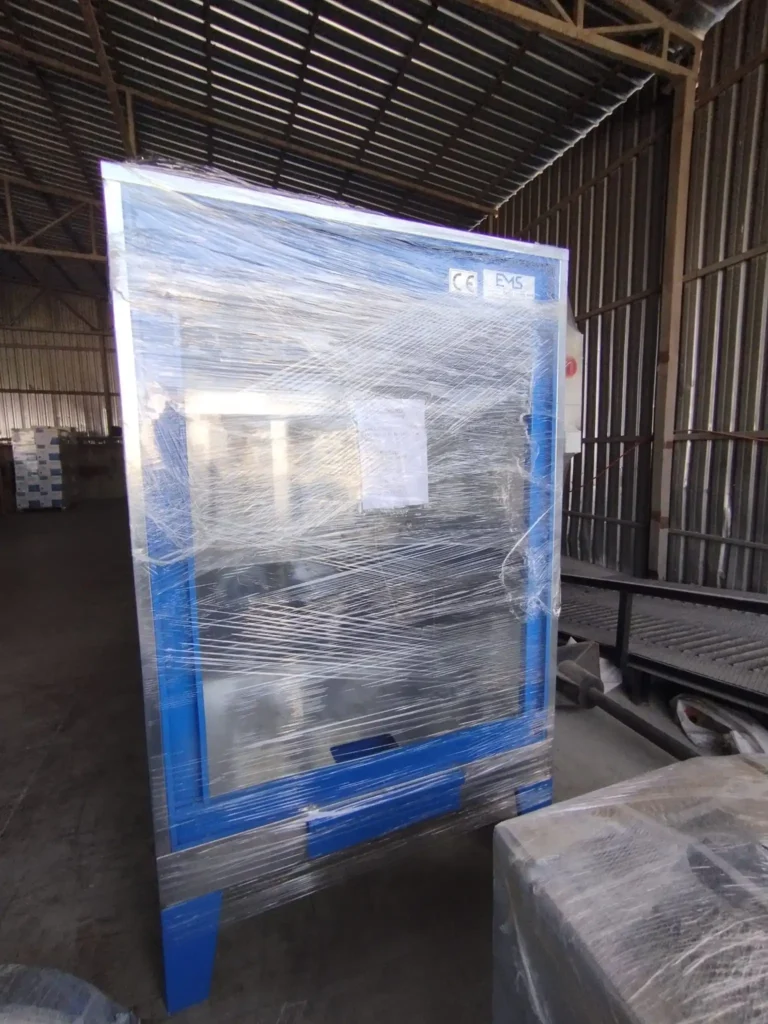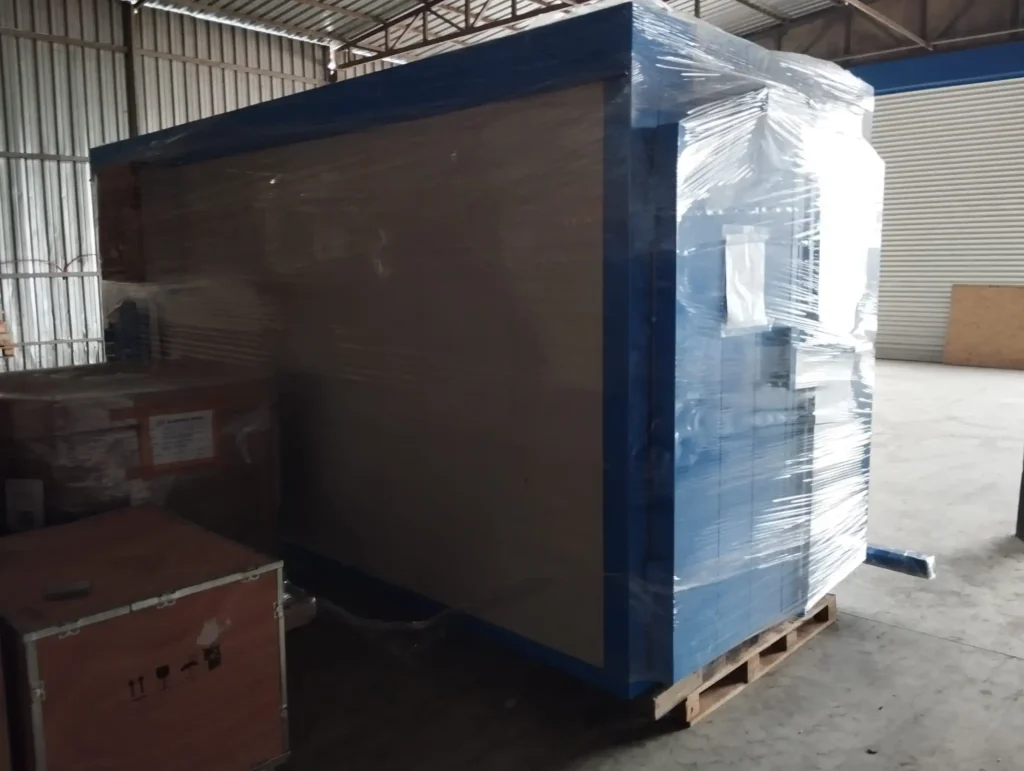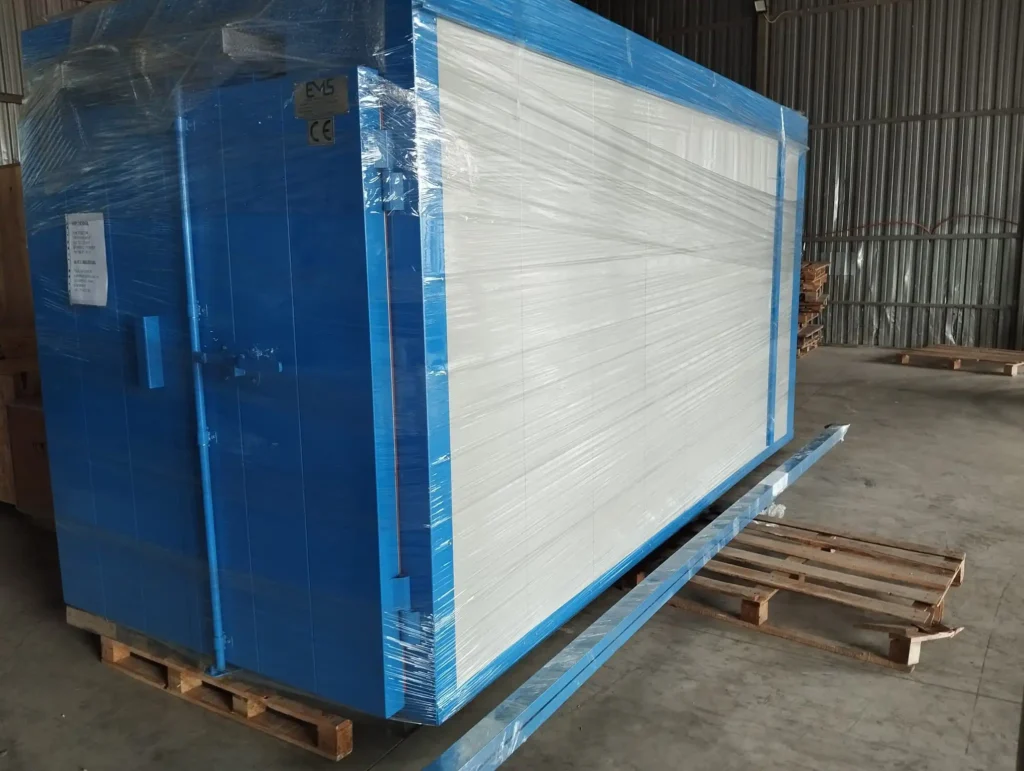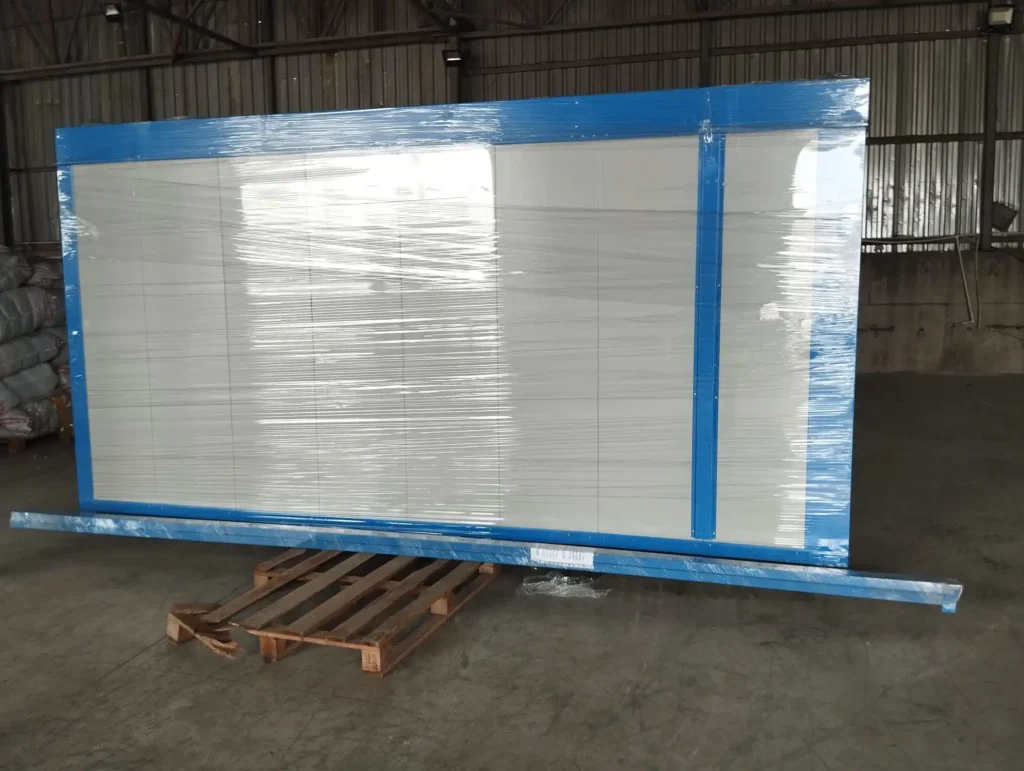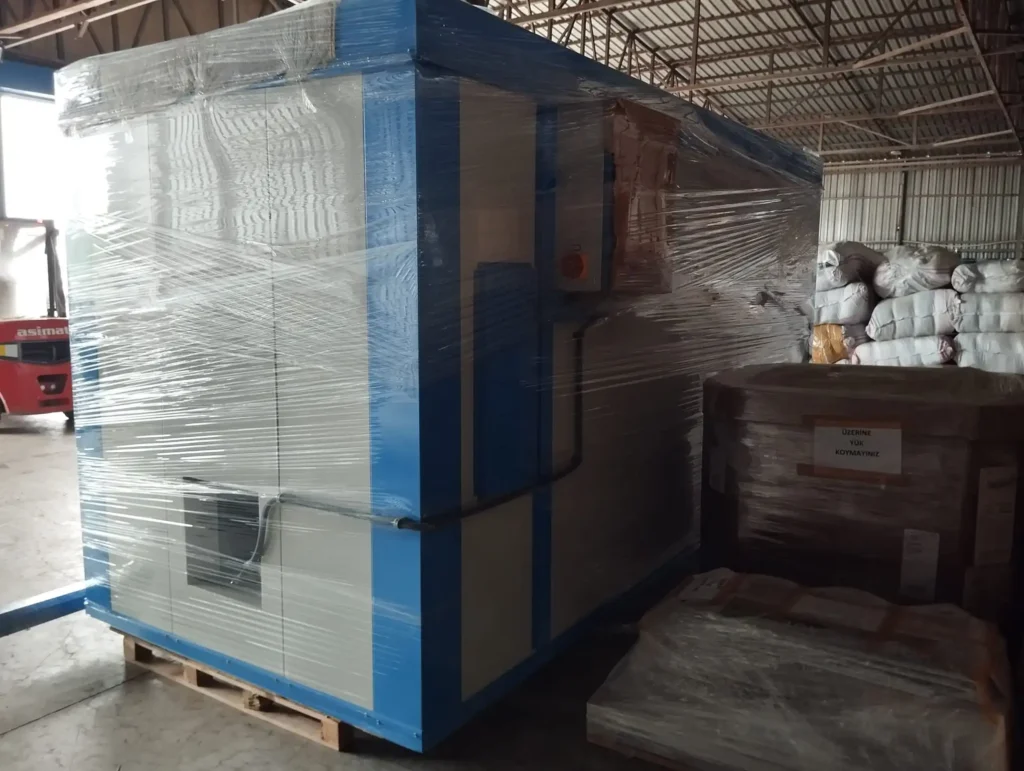
Automatic Painting and Powder Paint Coating Line for Small Parts: A fast coating machine for small metal items is a specialized industrial system engineered to apply protective or decorative coatings efficiently onto miniature or compact metallic components. These machines are designed with precision, speed, and consistency in mind, catering especially to manufacturers who handle high volumes of small parts such as screws, bolts, washers, pins, clips, hinges, fittings, and electronic hardware. Industries that benefit most from such machinery include automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods, and hardware manufacturing.
One of the most critical aspects of coating small metal items is ensuring uniform coverage across all surfaces — including hard-to-reach cavities or complex geometries — without over-coating, clumping, or waste. Fast coating machines achieve this through the use of automated spraying systems, fluidized beds, electrostatic powder guns, or dip-spin mechanisms. Each method can be adapted to suit different types of coatings, including powder coatings, liquid paints, epoxy resins, zinc-rich primers, or specialized corrosion-resistant finishes.
Speed and throughput are defining characteristics of these machines. Unlike manual or semi-automatic systems, fast coating machines are designed for continuous or batch operation, often incorporating rotary tables, conveyor belts, vibrating feed hoppers, or rotating baskets that can process thousands of items per hour. Their automation systems are typically managed by PLCs (programmable logic controllers), enabling precise timing, material flow, spray duration, and curing cycles.
The coating quality is maintained by integrating real-time monitoring systems, including sensors that check temperature, humidity, coating thickness, and curing profiles. This ensures not only rapid processing but also repeatable quality, which is essential for parts that must meet stringent technical standards — especially in critical sectors like aerospace or electronics.
Some fast coating machines also feature integrated pre-treatment units, such as ultrasonic cleaners, degreasers, or phosphate coating baths, allowing a complete surface preparation and coating line within a compact footprint. After coating, automated drying or curing ovens — often using infrared or convection heating — harden the finish quickly, reducing handling time and minimizing the risk of contamination or damage.
From a cost-efficiency standpoint, fast coating machines reduce material waste through closed-loop systems and precision application controls. Powder recovery systems, filtration units, and spray pattern optimization help conserve expensive coating materials. Moreover, the minimized need for human labor reduces operational costs and safety risks.
The footprint of these machines can vary. Compact tabletop units are available for laboratory-scale or prototyping work, while large industrial systems can handle multi-ton loads per hour in a fully enclosed and filtered environment. Modular design allows easy integration into existing production lines, and flexibility in design enables manufacturers to switch between different item sizes or coating materials with minimal downtime.
In summary, fast coating machines for small metal items represent a cornerstone of modern industrial finishing technology. They provide rapid, reliable, and high-quality coating performance while keeping operational costs low and ensuring compliance with environmental and safety regulations. For any manufacturer working with high volumes of small metal parts, investing in such a system can lead to significant improvements in product durability, aesthetic appeal, and production efficiency.
Fast coating machines for small metal items are essential in modern manufacturing environments where efficiency, consistency, and speed are critical. These machines are engineered to handle vast quantities of small metallic components such as screws, bolts, fasteners, clips, fittings, and other intricate pieces that require a protective or decorative coating. Their core function is to deliver a uniform finish across all surfaces of each item, even when those items have complex geometries or fine details that are traditionally difficult to coat evenly. By automating the coating process, these machines eliminate the inconsistencies often found in manual applications and greatly reduce the time needed for processing large batches. High-speed coating equipment typically utilizes rotary drums, vibratory bowls, or spin baskets that move items continuously or in timed cycles through the coating area, ensuring complete and even coverage. The application methods may vary from electrostatic powder spraying to dip-spin systems or even fluidized beds, depending on the coating type and end-use requirement.
These systems are often complemented by automated pre-treatment and drying units, including cleaning stages that remove oils, rust, and contaminants, and curing ovens that harden the applied material in a controlled thermal environment. Modern machines are equipped with smart sensors and digital controllers to monitor and adjust process variables such as temperature, coating thickness, and timing, ensuring each item meets precise specifications without the need for rework. Not only do they enhance the quality and longevity of the finished product, but they also increase production throughput while minimizing material waste through accurate dosing and closed-loop systems that recover excess coating material. Their compact and modular designs allow integration into existing production lines, and many offer quick-change features that enable manufacturers to shift from one type of product to another with minimal downtime. Whether in high-volume industries like automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, or home hardware production, fast coating machines serve as a vital solution to the challenges of coating small-scale metal items at industrial speed and scale. They help reduce labor costs, improve workplace safety, and support environmental compliance by reducing overspray, emissions, and hazardous waste. As demand for precision-coated micro-components grows, these machines continue to evolve, offering higher automation levels, better coating accuracy, and shorter cycle times — making them indispensable tools in any modern factory that handles small metal items requiring consistent, durable surface finishes.
The evolution of fast coating machines for small metal items continues to be driven by technological advancements and increasing demands for precision and sustainability. Manufacturers today seek not only speed and volume but also high levels of customization and control over the coating process. To meet these requirements, many machines are now equipped with advanced PLC or HMI interfaces, allowing operators to program exact coating recipes for different products. These settings can include spray angle, material flow rate, part rotation speed, and dwell time in pre-treatment or curing zones. This high degree of control ensures that even the smallest variations in item shape or material composition can be accommodated without compromising quality or wasting resources.
Another key advantage of these systems is their flexibility. With interchangeable drums, baskets, or trays, and modular attachments, the same machine can be adapted to coat a wide variety of items — from tiny fasteners to small stamped or turned components. The changeover between different items or coatings is made quick and efficient, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Many systems also include automated feeding and unloading systems, such as vibratory feeders, pick-and-place robots, or chute conveyors, which minimize the need for manual handling and reduce the risk of contamination or damage during transfer.
In industries with strict quality requirements, such as electronics or aerospace, fast coating machines are often integrated with inspection stations that use machine vision or laser measurement tools to verify the quality and consistency of the coating in real-time. Defective items can be automatically rejected or reprocessed without halting the entire production line. This level of quality assurance is essential when coating functions not only for appearance but also for electrical insulation, corrosion resistance, or mechanical protection.
From an environmental perspective, many modern coating machines are designed with sustainability in mind. Low-VOC or solvent-free coating systems are increasingly being used, along with highly efficient air filtration units and powder recovery systems. These features help manufacturers meet environmental regulations while also reducing material costs and energy consumption. Heat recovery systems may be employed in curing ovens to recycle waste heat, further lowering the machine’s overall energy footprint.
Maintenance and reliability are also central concerns for manufacturers operating 24/7 production lines. Fast coating machines are built with robust components and often feature predictive maintenance systems that alert operators to wear and tear before a breakdown occurs. Easy access panels, tool-free disassembly, and self-cleaning features make routine maintenance quicker and more manageable, ensuring minimal disruption to production.
In a world where product variety is increasing, delivery times are shrinking, and quality standards are rising, the role of the fast coating machine for small metal items is more critical than ever. These machines empower manufacturers to meet diverse customer demands while maintaining high throughput, consistent finish quality, and cost efficiency. They are not just pieces of equipment but essential parts of a highly synchronized production ecosystem, contributing directly to a company’s competitiveness, sustainability, and ability to innovate. As coating technologies continue to evolve, incorporating features like AI-assisted process optimization or hybrid coating capabilities, the machines will only become smarter, faster, and more indispensable in precision manufacturing environments.
Powder Coating System for Tiny Objects
A powder coating system for tiny objects is a highly specialized finishing solution designed to apply durable, uniform powder coatings onto miniature metal components such as screws, nuts, washers, pins, springs, connectors, clips, and other small hardware or precision parts. Unlike conventional spray booths or manual powder application methods, systems for tiny objects are engineered to process thousands of small items quickly and consistently, minimizing material waste and maximizing surface coverage even in complex or hard-to-reach geometries.
At the core of these systems is the electrostatic powder coating process, where dry powder particles are electrically charged and sprayed onto grounded metal objects. The powder adheres through electrostatic attraction and is then melted and cured in a high-temperature oven to form a tough, smooth, and even finish. For small objects, traditional spraying methods are often inefficient due to the items’ size, shape, and tendency to move or scatter during coating. To overcome this, dedicated systems employ methods like rotary drums, vibrating trays, tumblers, dip-spin coaters, or fluidized beds. These ensure constant motion and exposure of all surfaces while preventing clumping or uneven layering.
The dip-spin coating technique is particularly popular for fasteners and small bulk items. In this process, the parts are submerged in a powder slurry or powder cloud, then spun at high speed to remove excess coating. This ensures uniform distribution without pooling or bridging. Some systems use miniature spray chambers with rotary baskets, where the powder is sprayed into a rotating container filled with parts, allowing controlled deposition across all surfaces.
To ensure adhesion and finish quality, powder coating systems for tiny objects often include pre-treatment stages such as ultrasonic cleaning, degreasing, phosphating, or sandblasting to remove oil, dust, and rust. Once coated, the parts are typically conveyed or tumbled through a curing oven where the powder fuses into a smooth, solid film. Curing ovens for tiny objects must maintain very precise temperature control to avoid undercuring or overheating, especially when processing sensitive or thin-walled components.
Automation plays a key role in improving efficiency and consistency. Modern systems are equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that manage timing, rotation speed, spray duration, and oven temperatures. Sensors may monitor coating thickness, part temperature, or humidity, while integrated recovery units capture and recycle overspray powder, significantly reducing material loss.
One of the greatest advantages of powder coating for tiny objects is the ability to produce high-performance finishes—resistant to corrosion, abrasion, UV degradation, and chemicals—without solvents or hazardous emissions. Powder coatings also allow a wide variety of colors, gloss levels, and textures to be applied with excellent repeatability and minimal waste. This makes them ideal for sectors like electronics, medical devices, automotive parts, tools, and even decorative consumer goods where both appearance and durability are critical.
Scalability is another strength. From benchtop powder coating units for research labs or prototyping, to fully automated high-throughput systems for mass production, the technology can be adapted to meet a wide range of production volumes and part types. The choice of system depends on factors like part geometry, required finish quality, production rate, and available floor space.
In summary, powder coating systems for tiny objects are purpose-built to handle the challenges of finishing small, detailed, and numerous components efficiently and reliably. They combine precision handling, advanced application techniques, and tightly controlled curing processes to deliver high-quality, cost-effective finishes that meet the rigorous demands of modern industry.
Powder coating systems for tiny objects have become indispensable in industries where small metal parts require robust and aesthetically pleasing finishes. These systems are designed to overcome the unique challenges posed by the size and shape of miniature components. Because tiny parts can easily clump together or shift during coating, specialized equipment ensures consistent movement and exposure to the powder, preventing uneven coverage or defects such as bare spots or thick build-ups. Technologies such as vibrating feeders, rotating drums, or tumbling baskets are often integrated to maintain constant agitation and separate parts for uniform coating.
The application process is carefully controlled to achieve optimal electrostatic charge on the powder particles and ensure they firmly adhere to the grounded metal surfaces. Precise control over parameters like spray pressure, powder flow rate, and environmental conditions is critical because even minor variations can affect coating thickness and finish quality. The systems are often housed in enclosed chambers equipped with extraction and filtration units to contain powder overspray and maintain a clean work environment. This also helps protect operators from inhaling fine particles and ensures compliance with workplace safety regulations.
Another important aspect is the recovery and reuse of unused powder. Because powder coating materials can be costly, efficient recovery systems with filters and cyclones capture excess powder that falls off parts during application. This powder is then cleaned and recycled back into the process, significantly reducing material waste and operating costs. The level of automation in these systems helps minimize manual intervention, reducing labor costs and improving repeatability. Operators can program coating recipes that tailor the process to specific parts or batches, allowing for quick changeovers and high flexibility in production.
After coating, tiny parts are typically cured in specially designed ovens that ensure uniform heat distribution and precise temperature control. The curing process causes the powder to melt, flow, and chemically crosslink, resulting in a tough, seamless coating that adheres strongly to the substrate. For tiny objects, oven design often incorporates conveyors or rotating drums to prevent parts from sticking together or accumulating in one area, which could cause uneven curing or damage. The curing cycle is optimized to balance throughput with coating performance, avoiding overheating that might distort delicate parts or undercuring that could compromise durability.
These powder coating systems not only provide exceptional corrosion resistance and mechanical protection but also enable manufacturers to meet stringent industry standards related to environmental impact. Powder coatings are solvent-free and emit virtually no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making them an eco-friendly alternative to traditional liquid paints. Their durability also reduces the need for rework or replacement, contributing to sustainability through longer-lasting products.
In addition to standard finishes, powder coating systems for tiny objects can handle specialty powders with properties such as anti-static, conductive, flame retardant, or textured finishes, expanding their applicability across different sectors. This versatility is valuable for manufacturers who produce parts for electronics, automotive components, medical instruments, and consumer goods, where performance and appearance are equally important.
Ultimately, investing in a powder coating system tailored for tiny metal parts allows manufacturers to streamline their finishing operations, improve product quality, and reduce operational costs. As automation and coating technology continue to advance, these systems will offer even greater precision, higher throughput, and enhanced process control — enabling companies to keep pace with evolving market demands and maintain a competitive edge in industries reliant on small, high-quality coated components.
As powder coating systems for tiny objects advance, integration with smart manufacturing technologies is becoming increasingly common. These systems now often feature connectivity to industrial IoT platforms, enabling real-time monitoring, data collection, and process analytics. By tracking variables such as coating thickness, powder consumption, curing temperatures, and equipment status, manufacturers can optimize operations, predict maintenance needs, and quickly address quality issues before they escalate. This data-driven approach enhances yield, reduces downtime, and supports continuous improvement initiatives.
Customization is another growing trend. Manufacturers can fine-tune coating parameters to meet very specific requirements, whether it’s applying ultra-thin layers for electrical insulation or thicker coatings for enhanced corrosion resistance. This flexibility is critical as industries demand ever more specialized finishes for miniaturized components in sectors like aerospace, electronics, and medical devices, where even minor deviations can impact performance or safety.
Moreover, the development of new powder materials expands what can be achieved with these systems. Innovations such as hybrid powders combining different resin chemistries, powders with embedded nanoparticles for improved wear resistance, or powders formulated for rapid curing contribute to better functionality and faster production cycles. This continual evolution of coating materials works hand-in-hand with machine capabilities to deliver state-of-the-art finishes tailored for tiny parts.
Ergonomics and safety remain priorities in modern powder coating setups. Closed-loop systems minimize operator exposure to powder dust, while automated loading and unloading reduce repetitive strain injuries. Machine designs often include easy-to-clean surfaces and accessible components, making maintenance simpler and reducing downtime.
From a business perspective, powder coating systems for tiny objects provide manufacturers with a competitive edge by enabling fast turnaround times, consistent quality, and cost-effective use of materials. They support scaling production from prototype batches to full-scale manufacturing with minimal process changes, thus accelerating time-to-market for new products.
In conclusion, powder coating systems designed for tiny metal parts represent a fusion of precision engineering, material science, and automation technology. They address the unique challenges posed by small-scale components, delivering durable, high-quality finishes that meet demanding industry standards while promoting operational efficiency and sustainability. As these systems continue to integrate smart features and novel materials, their role in precision manufacturing will only grow more vital, helping companies innovate and excel in increasingly competitive global markets.
Fine Powder Coating Machine for Small Products

A fine powder coating machine for small products is a highly specialized industrial device designed to apply ultra-fine, uniform powder coatings onto small-scale metal or plastic components with precision and efficiency. These machines cater especially to manufacturers producing tiny parts such as fasteners, small fittings, electronic connectors, jewelry components, medical instruments, and other miniature items that require a smooth, durable, and aesthetically appealing finish. Unlike standard powder coating equipment, fine powder coating machines focus on delivering exceptionally controlled coating thicknesses and superior surface quality, which is critical when dealing with delicate or intricate small parts.
The technology behind these machines involves electrostatically charging fine powder particles so they adhere evenly to grounded parts. Due to the small size and often complex shapes of the products, these machines incorporate specialized application systems such as rotary baskets, tumblers, vibratory feeders, or fluidized bed systems. These mechanisms keep the small products in constant motion during coating, ensuring all surfaces receive equal powder coverage while preventing powder clumping or bridging between parts. The fine particle size of the powder itself allows for a smooth finish that enhances both the visual appeal and functional properties such as corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and wear protection.
Precision control is a hallmark of fine powder coating machines for small products. Modern units use programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) to regulate critical parameters like powder flow rate, spray gun voltage, part rotation speed, and coating time. This ensures repeatability and the ability to quickly switch between different product types or coating materials without compromising quality. Many machines also include advanced filtration and powder recovery systems to minimize waste, capturing overspray and recycling unused powder, which helps reduce operating costs and environmental impact.
Pre-treatment and curing are equally important components of the coating process for fine powder coating machines. Often integrated or designed to work seamlessly with the coating equipment, pre-treatment units clean and prepare the surfaces to maximize adhesion and coating performance. Following powder application, curing ovens precisely heat the coated parts to fuse the powder into a continuous, hard finish. For small and delicate parts, curing cycles are optimized to prevent overheating or distortion while achieving complete polymerization of the coating.
Fine powder coating machines are designed to be compact and adaptable to various production scales, from small-batch prototyping to high-volume manufacturing. Their modular construction allows integration into automated production lines or standalone operation, depending on the manufacturer’s needs. Safety features such as enclosed spray booths, proper ventilation, and operator safeguards ensure compliance with industry regulations and create a safer working environment.
In industries where small product quality and finish are paramount—such as aerospace, medical devices, electronics, and precision engineering—fine powder coating machines provide a reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly solution. By combining advanced powder technology, precision equipment design, and automation, these machines enable manufacturers to achieve superior coating results on small products while optimizing productivity and minimizing costs.
Fine powder coating machines for small products continue to evolve with the integration of new technologies that enhance precision, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. One significant advancement is the incorporation of real-time monitoring and feedback systems, which allow operators to track coating parameters such as thickness, powder consumption, and electrostatic charge during the coating process. This ensures that each batch meets stringent quality standards and reduces the likelihood of defects, rework, or waste. Automated adjustments can be made on-the-fly, optimizing the coating process without interrupting production.
The machines are also designed to handle a wide variety of powder types, including specialized powders that offer properties like anti-microbial resistance, electrical conductivity, or improved chemical resistance. This versatility allows manufacturers to tailor the coating process to specific application requirements, whether it’s protecting delicate electronic components or enhancing the durability of small mechanical parts. The fine particle powders used in these machines contribute to smoother finishes and better coverage in tight spaces, which is particularly important for products with intricate designs or tight tolerances.
Automation plays a critical role in fine powder coating systems, especially for small products that are difficult to handle manually. Automated feeding and unloading systems reduce human intervention, minimizing handling damage and contamination risks. Robotic arms, vibratory feeders, and conveyor systems can be synchronized with the coating operation to create continuous, high-throughput production lines. This level of automation also improves workplace safety by limiting operator exposure to powder dust and moving parts.
Maintenance and ease of use are key considerations in the design of these machines. Components such as spray guns, filters, and powder recovery units are made accessible for quick cleaning and replacement. Many machines include self-cleaning features that reduce downtime and help maintain consistent coating quality. Additionally, modular designs allow manufacturers to scale or customize their systems as production demands change, ensuring long-term flexibility and return on investment.
Energy efficiency is another important aspect. Modern fine powder coating machines often incorporate energy-saving features such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) on motors, efficient curing ovens with heat recovery systems, and optimized airflow management. These innovations help reduce operational costs and the environmental footprint of the coating process, which is increasingly important as manufacturers face stricter regulations and customer demands for sustainable production.
Ultimately, fine powder coating machines for small products provide manufacturers with a powerful tool to achieve high-quality finishes on delicate, intricate parts at scale. By combining advanced powder technology, precision application methods, and automation, these machines enhance productivity, reduce waste, and ensure consistent, durable coatings that meet or exceed industry standards. As the demand for smaller, more complex components grows across sectors like electronics, medical devices, aerospace, and consumer goods, fine powder coating systems will continue to play a crucial role in delivering finishes that protect and beautify these products while supporting efficient and sustainable manufacturing practices.
As the demand for even greater precision and efficiency grows, fine powder coating machines for small products are increasingly integrating cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms. These advancements enable the systems to analyze vast amounts of process data, identify patterns, and optimize coating parameters automatically. For example, AI can predict and correct deviations in powder flow, spray consistency, or curing temperature before they affect product quality. This predictive capability reduces downtime, lowers waste, and enhances overall throughput without the need for constant human oversight.
Additionally, innovations in powder formulation are expanding the capabilities of fine powder coating systems. Nano-sized powders and hybrid coatings offer enhanced properties such as superior adhesion, improved abrasion resistance, and multifunctional surfaces—like anti-fingerprint or self-cleaning effects—which are especially valuable for small, precision parts in electronics and medical devices. These new powders often require fine-tuned application and curing conditions, prompting further refinement in machine controls and sensor technology.
Customization remains a significant focus. Manufacturers can now specify coating parameters at a granular level, allowing for multilayer coatings or variable thicknesses on different parts of the same batch. This level of control opens doors to novel applications and finishes that were previously impractical or impossible with traditional powder coating methods. Fine powder coating machines often come with software platforms that facilitate recipe management, traceability, and integration with broader manufacturing execution systems (MES), enabling seamless production workflows and quality assurance.
Sustainability continues to drive innovation as well. Newer systems emphasize reducing energy consumption, minimizing powder waste through enhanced recovery systems, and using environmentally friendly powders free of heavy metals or hazardous substances. By aligning with green manufacturing principles, companies not only comply with stricter regulations but also meet growing consumer and industry expectations for responsible production.
In terms of design, ergonomic and user-friendly interfaces make these machines accessible even to operators without extensive technical training. Touchscreen controls, intuitive software, and guided maintenance alerts simplify operation and upkeep, increasing reliability and reducing operator errors. Safety features such as enclosed spray booths, automated powder containment, and dust extraction ensure compliance with health standards and protect workers from exposure.
Looking ahead, fine powder coating machines for small products are poised to become even more compact and modular, allowing easy integration into versatile production lines, including those for additive manufacturing or hybrid manufacturing processes. This adaptability will support the rapid prototyping and small-batch production demands typical of advanced manufacturing sectors.
In essence, these machines represent the convergence of material science, automation, and digital technology, delivering highly controlled, efficient, and sustainable finishing solutions tailored to the exacting needs of small product manufacturers. As industries continue to innovate and miniaturize their components, fine powder coating technology will be instrumental in providing the protective, functional, and aesthetic coatings that enable performance and longevity in the smallest of products.
Automatic Powder Coaters for Miniature Parts
Automatic powder coaters for miniature parts are advanced industrial systems designed to efficiently apply powder coatings to tiny components with high precision and consistency. These machines are engineered to handle the unique challenges posed by miniature parts such as screws, springs, electronic connectors, small fittings, and medical device components, which often have complex shapes and require uniform coating coverage without defects. Automation in these systems drastically reduces manual labor, improves throughput, and ensures repeatable quality across large production volumes.
The core technology behind automatic powder coaters involves electrostatic application, where powder particles are charged and sprayed onto grounded miniature parts. Because manual handling of small parts can lead to inconsistent coating, damage, or contamination, automatic systems use specialized fixtures, rotary baskets, tumblers, or vibratory feeders to keep parts moving and evenly exposed to the powder spray. These mechanisms prevent clumping and ensure complete surface coverage, including hard-to-reach areas.
Integrated conveyor systems and robotic arms automate the loading and unloading of parts, minimizing human intervention and increasing production speed. The coating parameters—such as spray duration, gun voltage, powder flow, and part rotation speed—are controlled via programmable logic controllers (PLCs) with user-friendly interfaces, allowing precise adjustment for different part geometries and coating materials. This level of automation also enables quick changeovers between product batches, enhancing manufacturing flexibility.
Pre-treatment stages, often included as part of the automated line, prepare the miniature parts by cleaning and activating their surfaces to improve powder adhesion. After coating, parts pass through curing ovens with controlled temperature profiles to melt and harden the powder into a durable, continuous film. For miniature parts, ovens are designed to maintain uniform heat distribution and prevent part deformation or sticking, which is critical for maintaining dimensional accuracy and functional performance.
Automatic powder coaters for miniature parts often incorporate powder recovery and filtration systems to capture and recycle overspray powder, reducing material waste and lowering operational costs. Environmental controls within the coating area help contain powder dust and maintain a clean workspace, contributing to operator safety and regulatory compliance.
These automated systems are highly valuable in industries such as electronics, aerospace, medical device manufacturing, automotive, and precision engineering, where high-quality finishes on small parts are essential for performance, longevity, and aesthetics. By combining automation, precise powder application, and integrated curing, automatic powder coaters provide a reliable, cost-effective solution to meet the demanding requirements of miniature part coating at scale.
Automatic powder coaters for miniature parts continue to evolve with a focus on enhancing efficiency, precision, and environmental sustainability. Their automation capabilities not only speed up the coating process but also reduce human errors and inconsistencies common in manual operations. By continuously moving parts through controlled coating chambers using rotating baskets, vibratory feeders, or tumbling mechanisms, these machines ensure uniform coverage even on complex geometries and tiny features. This movement prevents parts from sticking together or developing uneven coatings, which can compromise both appearance and functionality.
Advanced control systems play a critical role in optimizing the coating process. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to tailor coating parameters such as powder flow rate, electrostatic voltage, spray time, and part agitation speed to the specific requirements of each miniature part type. This adaptability is essential for handling diverse product lines or rapidly changing production schedules, making automatic powder coaters highly flexible. Furthermore, these systems can be integrated with factory-wide production management software for real-time monitoring, quality control, and data analytics, enabling manufacturers to maintain consistent product quality and quickly respond to any deviations.
The integration of automated pre-treatment modules streamlines the surface preparation process, ensuring that miniature parts are free from oils, dirt, and oxidation before coating. This step is vital for achieving strong powder adhesion and long-lasting finishes. After coating, parts move through precision curing ovens designed to provide consistent heat without overheating or warping delicate components. These ovens often include conveyors or rotating drums to maintain part separation and uniform exposure to heat, guaranteeing that coatings fully cure and develop their intended protective and aesthetic properties.
Environmental and safety considerations are integral to automatic powder coating systems for miniature parts. Efficient powder recovery units capture unused powder for reuse, minimizing waste and reducing material costs. Enclosed coating booths with advanced filtration prevent powder from escaping into the work environment, protecting operators and complying with health regulations. Many modern systems also focus on energy efficiency, employing heat recovery, variable-speed motors, and optimized airflow to reduce power consumption and operational expenses.
Automatic powder coaters are particularly valuable in industries requiring high volumes of small, precisely coated components, such as electronics, medical devices, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing. These systems enable manufacturers to produce consistent, high-quality finishes that enhance corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and aesthetic appeal while maintaining fast production cycles. By automating the entire coating process—from loading through curing—these machines reduce labor costs, increase throughput, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Looking forward, ongoing innovations are expected to further enhance the capabilities of automatic powder coaters for miniature parts. Developments in sensor technology, artificial intelligence, and machine learning will enable even smarter process controls and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving product quality. Additionally, advancements in powder materials, such as nano-enhanced coatings and hybrid formulations, will expand the functional properties and finishing options available for miniature parts.
In summary, automatic powder coating machines for miniature parts represent a sophisticated fusion of automation, material science, and process engineering. They address the specific challenges of coating tiny, complex components with speed, precision, and repeatability. As manufacturing demands continue to grow in complexity and scale, these systems will remain essential tools for delivering durable, high-performance coatings that meet stringent industry standards while supporting efficient, sustainable production.
As the market for miniature components expands, driven by trends like miniaturization in electronics, medical devices, and aerospace, automatic powder coaters are increasingly designed with modularity and scalability in mind. Manufacturers can configure systems to accommodate varying batch sizes, from small prototype runs to high-volume mass production, without sacrificing coating quality or efficiency. Modular designs allow quick adaptation or expansion, enabling companies to respond rapidly to changing product requirements or market demands.
Moreover, these machines often incorporate advanced robotics for material handling, reducing the risk of damage to delicate parts during loading, coating, and unloading stages. Collaborative robots (cobots) may be employed to work safely alongside human operators, enhancing flexibility and throughput while maintaining high safety standards. This integration of robotics also facilitates seamless transitions between different product types, allowing manufacturers to maintain continuous production with minimal downtime.
In terms of sustainability, automatic powder coaters continue to push boundaries by adopting green manufacturing principles. Powder recovery systems are becoming more efficient, capturing nearly all overspray for reuse, which reduces waste significantly. Some systems utilize powders formulated without heavy metals or other hazardous substances, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and corporate responsibility goals. Energy-efficient curing ovens, featuring infrared or convection heating combined with heat recovery, reduce overall energy consumption and carbon footprint.
The software aspect of automatic powder coating systems is also advancing rapidly. Integration with Industry 4.0 and smart factory platforms enables real-time process monitoring, predictive analytics, and remote troubleshooting. This connectivity helps manufacturers optimize resource usage, maintain consistent quality, and plan maintenance proactively, thereby minimizing unplanned downtime and production losses.
Quality control is enhanced by in-line inspection technologies that use machine vision and laser measurement tools to detect coating defects, thickness variations, or surface irregularities immediately after coating or curing. This immediate feedback allows for corrective action before products proceed further down the production line or reach customers, ensuring only parts that meet exacting standards are shipped.
Ultimately, automatic powder coaters for miniature parts represent a convergence of cutting-edge automation, advanced materials, and digital technologies. They provide manufacturers with the tools needed to meet the ever-growing demand for tiny, high-quality components with durable, uniform finishes. By improving efficiency, reducing waste, and enabling precise control, these systems play a vital role in modern manufacturing, helping companies innovate, compete globally, and deliver superior products in sectors where performance and reliability are paramount.
Precision Coating Line for Tiny Components
A precision coating line for tiny components is a highly engineered production system designed to apply consistent, high-quality coatings to very small parts with exacting control over every stage of the process. These components—which may include micro fasteners, miniature electronic connectors, medical device parts, or fine mechanical elements—demand flawless finishes to ensure performance, durability, and reliability in their final applications. The precision coating line integrates advanced automation, surface preparation, coating application, curing, and quality inspection into a seamless workflow tailored to the unique challenges of handling and finishing tiny components.
At the heart of such a line is the ability to maintain precise control over coating thickness, uniformity, and adhesion despite the minute size and complex shapes of the parts. Specialized handling systems like vibratory feeders, rotary baskets, or tumblers keep parts moving continuously and separated during coating to prevent damage or uneven coverage. Automated spray or dip coating stations utilize finely tuned parameters to apply coatings uniformly, often using electrostatic powder, liquid paints, or thin film deposition methods depending on the required finish and functional properties.
Pre-treatment modules are integrated to clean, activate, or chemically modify surfaces prior to coating, removing oils, contaminants, or oxides that could hinder adhesion. These stages might include ultrasonic cleaning, chemical baths, or plasma treatments carefully optimized for delicate parts to avoid damage. Following coating application, curing ovens with uniform temperature distribution solidify the coatings, often employing infrared, convection, or UV curing technologies based on the coating material and substrate sensitivity.
Precision coating lines incorporate real-time monitoring and process control through programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs), allowing operators to adjust parameters dynamically and ensure consistent quality. Advanced sensor systems track coating thickness, surface finish, temperature, and other critical variables, enabling immediate correction if deviations occur. Inline quality inspection stations using machine vision or laser scanning further verify that each tiny component meets strict specifications before packaging or assembly.
Automation is essential not only for consistency but also for efficiency. Automated loading and unloading systems minimize manual handling, reducing the risk of contamination, loss, or damage. Robotics and conveyors move components seamlessly through the various stages, enabling high throughput without sacrificing precision. Modular designs allow manufacturers to customize and scale their lines according to production volume and product diversity, supporting both small batch prototyping and large-scale manufacturing.
Environmental controls and powder recovery systems are incorporated to minimize waste and emissions, reflecting growing industry emphasis on sustainability. Efficient filtration and powder reclamation reduce material costs and improve workplace safety by limiting airborne particles. Energy-efficient curing ovens and optimized airflow reduce power consumption and carbon footprint, aligning with green manufacturing initiatives.
Precision coating lines for tiny components are widely used across industries such as aerospace, electronics, medical devices, automotive, and precision engineering. They provide the capability to apply protective, decorative, or functional coatings—ranging from corrosion-resistant powders and insulating paints to biocompatible films and optical coatings—with unmatched repeatability and speed. By delivering flawless finishes on small, complex parts, these lines enhance product performance and reliability while enabling manufacturers to meet increasingly stringent quality standards and market demands.
In summary, a precision coating line for tiny components combines sophisticated automation, advanced coating technologies, and rigorous quality control to solve the challenges of finishing miniature parts efficiently and consistently. It is a critical investment for companies aiming to produce high-value, small-scale components with exacting surface requirements, offering improved productivity, reduced waste, and superior product quality in a competitive global market.
Precision coating lines for tiny components represent the pinnacle of manufacturing technology where every step is carefully calibrated to handle the challenges posed by small size, delicate geometries, and strict quality requirements. These lines ensure that each component, no matter how minute, receives a coating that is not only visually flawless but also functionally effective, whether that means protecting against corrosion, enhancing electrical insulation, improving wear resistance, or adding aesthetic value. The continuous movement and separation of parts during coating are crucial to avoid defects like uneven thickness, bridging, or particle clumping, which can be disastrous in applications where tolerances are tight and performance is critical.
The integration of automation reduces human error and variability, allowing manufacturers to meet tight production schedules while maintaining consistency. Handling systems like vibratory bowls or rotary drums feed the parts steadily into coating stations, while robots or conveyors transport them through cleaning, coating, curing, and inspection stages without interruption. This seamless flow increases throughput and reduces the chances of contamination or damage that might occur with manual handling. Moreover, operators can program specific coating recipes for different products or batches, switching quickly between them to accommodate varying customer needs or product lines without sacrificing quality or speed.
Advanced sensor technologies embedded throughout the line monitor key parameters in real time, including coating thickness, temperature uniformity in curing ovens, powder flow rates, and environmental conditions. If any parameter strays from its set range, the system can automatically adjust process variables or alert operators to intervene, preventing costly defects or downtime. Inline inspection using machine vision or laser scanning can detect surface imperfections or thickness inconsistencies immediately after coating or curing, allowing defective parts to be rejected or reworked before further processing.
Sustainability is increasingly integral to these precision coating lines. Efficient powder recovery systems capture and recycle overspray, minimizing waste and reducing material costs. Enclosed booths with advanced filtration protect operators from powder inhalation and prevent environmental contamination. Energy-efficient curing ovens with heat recovery features help reduce electricity consumption and carbon emissions, supporting manufacturers’ environmental compliance and sustainability goals.
Customization and scalability make precision coating lines versatile for a wide range of production needs. Small-scale manufacturers can benefit from compact, modular lines that require minimal floor space and allow rapid changeovers, while large industrial operations can deploy fully integrated, high-throughput systems capable of processing thousands of tiny components per hour. This flexibility supports innovation and responsiveness in markets where product designs and volumes frequently evolve.
Ultimately, precision coating lines for tiny components combine cutting-edge automation, material science, and quality control to provide reliable, efficient, and environmentally responsible finishing solutions. They enable manufacturers to meet the increasing demand for high-performance, miniature parts across diverse industries, ensuring that each component performs flawlessly in its final application. As technology continues to advance, these lines will incorporate even greater levels of intelligence, connectivity, and adaptability, driving the future of precision manufacturing and coating technology forward.
As precision coating lines for tiny components advance, they increasingly incorporate smart manufacturing technologies that enhance control, flexibility, and productivity. Integration with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms allows for continuous data collection from sensors throughout the line, providing detailed insights into every aspect of the coating process. This data can be analyzed using artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict maintenance needs, optimize coating parameters, and detect quality issues before they occur, significantly reducing downtime and waste. Real-time dashboards and remote monitoring capabilities enable operators and managers to oversee multiple lines or facilities from a single interface, facilitating rapid decision-making and continuous improvement.
The use of robotics and advanced automation extends beyond material handling into areas such as adaptive coating application and precision inspection. For example, robotic spray systems equipped with vision guidance can adjust spray patterns dynamically to accommodate variations in part geometry or orientation, ensuring flawless coverage even on highly complex components. Automated inspection stations utilize high-resolution cameras, 3D laser scanners, or spectroscopic analysis to verify coating thickness, surface uniformity, and color consistency at high speeds, providing immediate feedback and quality assurance.
Emerging coating technologies, such as UV-curable powders or hybrid liquid-powder systems, are being incorporated into precision coating lines to expand their capabilities. These technologies enable faster curing cycles, lower energy consumption, and coatings with enhanced functional properties like improved adhesion, flexibility, or chemical resistance. The adaptability of modern coating lines allows manufacturers to experiment with and implement these innovations without extensive retooling, maintaining agility in a rapidly evolving market.
Sustainability remains a core focus, with continuous efforts to minimize environmental impact while maintaining productivity and quality. Advances in powder recovery and recycling systems reduce waste and raw material usage, while improved ventilation and filtration technologies protect worker health and ensure compliance with increasingly strict environmental regulations. Energy-efficient equipment designs, including ovens with optimized thermal insulation and heat recapture, contribute to reducing the overall carbon footprint of coating operations.
User experience and operational simplicity are also priorities. Intuitive touch-screen interfaces, guided maintenance prompts, and modular component design make the lines easier to operate and service, even for personnel with limited technical training. This reduces the learning curve, lowers the risk of errors, and ensures consistent performance over time.
The scalability and modularity of precision coating lines mean that manufacturers can start with smaller configurations for niche or prototype production and expand or customize their systems as demand grows or product portfolios diversify. This flexibility supports innovation, short product lifecycles, and the increasing trend toward personalized or small-batch manufacturing without compromising efficiency or quality.
In essence, precision coating lines for tiny components are becoming ever more intelligent, adaptable, and environmentally responsible. They play a vital role in enabling manufacturers to meet the stringent demands of industries like aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and automotive, where component quality, durability, and aesthetics are paramount. As these systems continue to integrate the latest technologies and innovations, they will remain indispensable assets in the competitive landscape of precision manufacturing.
Small Parts Powder Coating Equipment
Small parts powder coating equipment is specialized machinery designed to efficiently apply durable and uniform powder coatings to tiny metal or plastic components. These parts—such as screws, nuts, bolts, washers, pins, clips, and small fittings—require precise coating solutions that ensure full coverage without clumping, bridging, or missed areas, all while maintaining high production speeds and minimizing material waste. Unlike standard powder coating lines for larger items, equipment for small parts focuses on gentle handling, thorough surface exposure, and effective powder recovery to meet the unique challenges of miniature parts finishing.
The core components of small parts powder coating equipment typically include vibratory feeders or rotary baskets that gently agitate and separate the parts during coating, ensuring every surface receives equal exposure to the electrostatically charged powder particles. This motion prevents parts from sticking together and promotes uniform powder application. The powder spray is generated using electrostatic guns that impart a charge on dry powder particles, causing them to adhere to grounded parts effectively. Enclosed spray booths with efficient ventilation and filtration systems control overspray and maintain a clean working environment.
Pre-treatment modules often accompany small parts powder coating equipment to clean, degrease, and prepare the surfaces for optimal powder adhesion. Depending on the application, these modules may include ultrasonic cleaners, chemical baths, or phosphating systems designed specifically for delicate or complex small parts. Once coated, parts pass through curing ovens that provide controlled heat to melt and fuse the powder into a tough, continuous film. Curing ovens for small parts typically feature conveyors or rotating drums to ensure uniform heating and avoid part deformation or sticking.
Automation plays a significant role in these systems, with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) managing parameters such as spray duration, gun voltage, part agitation speed, and oven temperature. Automated feeding and unloading systems minimize manual handling, reducing labor costs and the risk of contamination or damage. Many systems also include powder recovery units that capture and recycle unused powder, reducing waste and lowering operating costs.
Small parts powder coating equipment is essential across industries such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, hardware manufacturing, and medical devices, where tiny components must meet high standards of corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and aesthetic finish. By providing consistent, high-quality coatings efficiently and sustainably, this equipment enables manufacturers to improve product performance, reduce production costs, and comply with environmental regulations. The modularity and scalability of these systems allow manufacturers to tailor their setups to specific production volumes and part types, making small parts powder coating equipment a versatile and valuable asset in modern manufacturing.
Small parts powder coating equipment continues to evolve with innovations that improve precision, throughput, and sustainability. One key advancement is the refinement of part handling systems, such as vibratory feeders, rotary drums, and tumblers, which are designed to maintain gentle but consistent agitation of parts throughout the coating process. This constant movement prevents parts from sticking together and ensures that powder particles reach every surface, including intricate recesses or undercuts that are common in miniature components. The careful design of these agitation mechanisms balances effective coating with minimizing damage or wear to delicate parts.
Automation and control technologies have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing manufacturers to customize coating recipes for different parts quickly and accurately. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) enable operators to adjust variables like powder flow, electrostatic voltage, spray duration, and part rotation speed in real time. This flexibility allows quick changeovers between product batches with minimal downtime, supporting diverse production schedules and product lines. Data logging and connectivity with manufacturing execution systems (MES) support traceability and quality assurance, which are critical in regulated industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Powder recovery and filtration systems are integral components that help reduce material waste and environmental impact. These systems capture overspray powder through high-efficiency filters and cyclone separators, allowing unused powder to be reclaimed and reused. This not only lowers raw material costs but also minimizes airborne powder in the facility, improving worker safety and maintaining a clean production environment. Modern powder recovery units are designed to integrate seamlessly with coating booths and spray guns, ensuring efficient collection without interfering with the coating process.
Pre-treatment and curing processes are carefully matched to the small parts coating line to maximize adhesion and finish quality. Pre-treatment stages may include ultrasonic cleaning, chemical degreasing, or phosphating tailored to the specific materials and contaminants involved. Curing ovens feature precise temperature control and gentle handling methods—such as conveyor belts with cushioned supports or rotating baskets—to prevent part deformation during the heat curing cycle. The oven design ensures uniform heat distribution to fully melt and cure the powder coating, resulting in durable, uniform finishes.
Small parts powder coating equipment is widely used in industries requiring high-performance finishes on miniature components. In electronics, coatings provide electrical insulation and protection against moisture. In automotive and aerospace sectors, powder coatings enhance corrosion resistance and mechanical durability. Medical device manufacturers rely on biocompatible powder coatings that withstand sterilization processes. Across these industries, the equipment’s ability to consistently deliver flawless finishes on small parts at scale directly impacts product quality, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
As manufacturing trends continue toward miniaturization and increased complexity, small parts powder coating equipment will further integrate smart technologies such as real-time quality monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive process controls. These innovations will drive higher productivity, lower costs, and improved environmental performance, ensuring that manufacturers can meet the evolving demands of precision coatings for small components. The combination of advanced material handling, precise powder application, effective recovery, and controlled curing makes small parts powder coating equipment an essential solution for modern manufacturing environments focused on quality, efficiency, and sustainability.
Looking ahead, the future of small parts powder coating equipment is shaped by the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, which enable greater connectivity, automation, and data-driven decision-making. Sensors embedded throughout the coating line collect continuous data on key process parameters such as powder flow rates, electrostatic charge levels, temperature, humidity, and part movement. This data feeds into centralized control systems or cloud-based platforms where advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms identify trends, detect anomalies, and recommend optimizations. Such smart monitoring enhances process stability, reduces defects, and allows predictive maintenance schedules to be implemented, minimizing unplanned downtime and extending equipment life.
Robotics and artificial intelligence are playing an increasing role in automating part handling and quality inspection. Robotic arms equipped with vision systems can load, orient, and unload tiny components with high precision, improving throughput and reducing human error or damage. Automated inspection stations use high-resolution imaging and laser scanning to detect coating inconsistencies, thickness variations, or surface defects at high speeds, ensuring only parts that meet strict quality criteria move forward. This real-time quality control capability supports zero-defect manufacturing and helps manufacturers comply with rigorous industry standards.
Material science advancements complement equipment innovations by providing next-generation powders designed for enhanced performance. Nano-engineered powders offer superior adhesion, scratch resistance, or antimicrobial properties, while hybrid powders combine features of both powder and liquid coatings for unique functional or aesthetic effects. The ability of small parts powder coating equipment to handle these advanced powders broadens the range of applications and industries served, from medical implants to precision electronics.
Sustainability remains a strong driver for future developments. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting powder coatings free of heavy metals and other hazardous substances to meet stricter environmental regulations. Equipment designs focus on maximizing powder recovery efficiency and minimizing energy consumption through innovations like infrared curing, variable frequency drives, and optimized airflow systems. These efforts reduce operational costs and environmental footprints while improving workplace safety by limiting operator exposure to powder dust.
User experience improvements are also key, with equipment featuring intuitive touchscreens, guided maintenance alerts, and modular components that simplify operation and servicing. This reduces training requirements and helps maintain consistent process performance over time, even in high-mix, low-volume production environments.
In summary, small parts powder coating equipment is evolving into highly intelligent, flexible, and sustainable manufacturing systems. By combining advanced automation, real-time monitoring, innovative powder materials, and efficient resource use, these systems enable manufacturers to meet the growing demand for high-quality, durable coatings on tiny components. They are critical enablers in industries where precision, reliability, and environmental responsibility are paramount, and they will continue to drive innovation and competitiveness in precision manufacturing worldwide.
Compact Powder Coaters for Small Items
Compact powder coaters for small items are specialized finishing machines designed to deliver high-quality powder coating on miniature parts within a small footprint. These systems are tailored for manufacturers who need efficient, consistent, and cost-effective coating solutions but have limited floor space or lower production volumes. Ideal for coating screws, nuts, bolts, electronic connectors, jewelry components, and other small metal or plastic items, compact powder coaters combine precision application, gentle part handling, and effective powder recovery in a streamlined, user-friendly package.
Despite their reduced size, these compact systems incorporate many features found in larger industrial coaters. They typically use rotary baskets, tumblers, or vibratory feeders to agitate parts continuously during powder application, ensuring uniform coating coverage across all surfaces, including intricate details and recessed areas. Electrostatic spray guns generate a charged powder cloud that adheres efficiently to grounded parts, minimizing powder waste and overspray. Enclosed spray chambers with integrated filtration systems help contain powder particles, maintain a clean work environment, and protect operators from inhalation risks.
Compact powder coaters often include pre-treatment options such as ultrasonic cleaning or chemical degreasing modules designed to prepare delicate small parts for optimal powder adhesion. After coating, parts are conveyed into curing ovens or heated chambers with precise temperature control that ensures thorough melting and bonding of the powder without damaging sensitive components. Some compact systems utilize infra-red or convection ovens optimized for fast curing cycles in limited spaces.
Automation and control are key elements, with many compact powder coaters featuring programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and touch-screen interfaces that allow operators to set and adjust parameters like spray time, powder flow rate, agitation speed, and curing temperature. These controls enable consistent repeatability and flexibility to switch between different parts or powder types quickly. Integrated powder recovery units capture and recycle unused powder, reducing material costs and environmental impact.
The advantages of compact powder coaters include lower capital investment, reduced energy consumption, and simplified operation, making them well-suited for small to medium-sized enterprises, prototyping facilities, and manufacturers with multiple product lines requiring frequent changeovers. Their compact design also facilitates easy integration into existing production environments without significant modifications.
In industries such as electronics, medical devices, automotive components, and precision hardware manufacturing, compact powder coaters provide a practical solution to achieve durable, corrosion-resistant, and visually appealing finishes on small items. They support manufacturers in meeting stringent quality requirements while optimizing space, reducing waste, and improving operational efficiency.
In summary, compact powder coaters for small items offer a balanced combination of precision, flexibility, and efficiency within a minimal footprint. They are essential tools for manufacturers aiming to deliver consistent, high-quality powder-coated finishes on miniature components without the need for large-scale industrial equipment, enabling cost-effective production and rapid response to market demands.
Compact powder coaters for small items continue to gain popularity as manufacturers seek efficient finishing solutions that fit limited spaces and support flexible production schedules. Their design emphasizes ease of use and quick setup, enabling operators to switch between different product types or coating colors with minimal downtime. The integration of modular components, such as interchangeable baskets or feeders, further enhances versatility, allowing the system to accommodate a wide variety of small parts with diverse shapes and sizes. This adaptability is crucial in industries where product runs can be short and changeovers frequent.
Despite their smaller scale, these systems do not compromise on coating quality. The agitation methods—whether rotary tumbling, vibration, or gentle tumbling drums—ensure that each small item is evenly coated, reducing the risk of bare spots or uneven thickness that could compromise performance or aesthetics. Electrostatic powder guns are often fine-tuned to optimize powder charge and spray patterns for small parts, improving transfer efficiency and minimizing waste. Advanced filtration and powder recovery units maintain a clean working environment while recycling excess powder, supporting sustainability goals and lowering operating costs.
Compact powder coaters often feature user-friendly interfaces with programmable controls, allowing operators to set precise parameters such as powder feed rate, spray duration, part rotation speed, and curing temperature. These programmable features not only improve consistency but also facilitate rapid switching between different coatings or products, enhancing production agility. Some models include data logging capabilities, enabling manufacturers to track process parameters for quality assurance and regulatory compliance.
The curing stage in compact powder coating systems is carefully engineered to provide uniform heat distribution and gentle handling, preventing damage to sensitive or intricate small parts. Compact curing ovens may utilize infrared or convection heating, balancing fast cure times with energy efficiency. Conveyor or basket systems ensure continuous movement of parts during curing to avoid sticking and promote even coating flow and polymerization.
These compact systems are especially advantageous for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), research and development labs, or specialized manufacturers who require high-quality finishing without the overhead of large industrial lines. Their relatively low capital investment and operational costs make them accessible to a broad range of users, while still delivering professional-grade coating results.
Industries such as electronics, medical devices, jewelry, automotive components, and hardware manufacturing benefit from compact powder coaters by achieving consistent, durable, and attractive finishes on small parts. The ability to produce corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and electrically insulating coatings enhances product performance and longevity, which is vital for customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
Looking forward, compact powder coating equipment is expected to incorporate more intelligent automation, real-time process monitoring, and integration with digital manufacturing systems, enabling smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable finishing operations. These advancements will empower manufacturers to meet evolving market demands while optimizing resource use and maintaining high standards of quality.
In essence, compact powder coaters for small items represent a practical, efficient, and versatile solution for precision finishing needs, delivering exceptional results in a small footprint that aligns well with modern manufacturing environments focused on agility, quality, and sustainability.
Building on their growing role in precision manufacturing, compact powder coaters for small items are increasingly incorporating smart technologies that enhance automation, process control, and connectivity. Integration with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms allows these systems to collect and analyze data from sensors monitoring powder flow, electrostatic charge, part movement, and curing conditions in real time. This connectivity enables predictive maintenance, reducing unexpected downtime, and facilitates continuous process optimization to maintain consistent coating quality.
Robotic handling solutions are becoming more common within compact systems, offering precise loading, orientation, and unloading of miniature parts. These automated material handling methods reduce manual labor, minimize the risk of part damage, and improve throughput. Advanced vision systems integrated with robotics provide real-time inspection capabilities, identifying coating defects or inconsistencies at early stages so corrections can be made promptly, improving yield and reducing waste.
The evolution of powder materials complements advances in compact coating equipment. New formulations such as ultra-fine powders, hybrid liquid-powder coatings, and functional powders with antimicrobial, anti-corrosive, or conductive properties broaden the range of achievable finishes. Compact coaters equipped to handle these advanced powders allow manufacturers to deliver highly specialized coatings that meet stringent industry standards across electronics, medical devices, aerospace, and automotive sectors.
Sustainability remains a priority, with ongoing improvements in powder recovery efficiency, energy use, and environmental controls. Equipment designs emphasize reducing powder loss and capturing overspray with enhanced filtration and cyclone systems, while curing ovens are optimized for minimal energy consumption without compromising cure quality. These efforts align with regulatory requirements and corporate sustainability goals, making compact powder coaters not only efficient but environmentally responsible.
User experience improvements continue to simplify operation and maintenance. Intuitive touchscreen interfaces, guided troubleshooting, and modular components reduce training requirements and minimize operator errors. The ability to quickly swap parts, clean equipment, and update software ensures high availability and adaptability, which is especially valuable for manufacturers handling multiple small part types or frequent product changes.
Compact powder coating systems also support lean manufacturing principles by minimizing footprint, reducing waste, and enabling just-in-time production. Their scalability allows manufacturers to start with smaller setups and expand capacity as needed without major capital investment, providing flexibility to respond to market fluctuations or new product introductions.
In summary, compact powder coaters for small items are evolving into intelligent, flexible, and sustainable finishing solutions that meet the precise demands of modern manufacturing. By combining advanced automation, innovative materials, and data-driven controls within a space-efficient design, these systems empower manufacturers to achieve superior coating quality on miniature components while optimizing productivity, cost, and environmental impact.
Automatic Powder Coating Machine for Tiny Metal Parts
An automatic powder coating machine for tiny metal parts is a purpose-built system designed to apply high-quality powder coatings to very small metal components with speed, precision, and consistency. These machines are essential in industries where large quantities of miniature parts—such as screws, nuts, bolts, clips, pins, electronic terminals, springs, and fasteners—need to be finished with protective or decorative coatings that are both durable and aesthetically uniform. Unlike manual methods, automatic machines streamline the entire process, reduce waste, and deliver repeatable results at high production volumes.
The coating process begins with careful feeding and handling of the tiny metal parts, often using vibratory bowl feeders, rotary tumblers, or perforated drums that agitate and separate the components to ensure even exposure. This movement is crucial to avoid sticking, overlapping, or clogging—common challenges when dealing with bulk tiny items. Once in motion, the parts enter an enclosed spray zone where electrostatic guns charge and disperse the powder particles. These charged particles adhere to the grounded metal surfaces, forming a uniform powder layer across all exposed surfaces.
A key advantage of automatic machines is their programmable control over all process parameters. Operators can set the powder output, spray duration, gun voltage, part agitation speed, and line speed through a digital control panel. This ensures that different part types can be coated under optimized conditions without needing manual adjustments or line reconfiguration. Such consistency is vital for manufacturers with strict quality requirements and a need for continuous, around-the-clock production.
Following the coating step, the parts are automatically transferred to a curing oven, where precise heat is applied to melt and fuse the powder into a smooth, hardened finish. Curing methods vary depending on part material and size but often include conveyorized infrared or convection ovens engineered for small items. These ovens are designed to provide even temperature distribution while preventing parts from fusing together or warping under heat.
To maximize efficiency and sustainability, most machines include integrated powder recovery systems. These systems capture unused powder from the spray zone, filter out contaminants, and return clean powder to the supply, significantly reducing material loss. This not only lowers operating costs but also minimizes the environmental impact of the process.
Automatic powder coating machines for tiny metal parts are designed to be compact yet modular, allowing manufacturers to tailor them to specific production needs. They are often integrated into larger automated lines or operated as stand-alone units for batch production. The machines are built for high durability and minimal maintenance, with features like quick-change powder hoppers, easy-to-clean spray chambers, and self-cleaning filters.
Used widely in industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, hardware, and medical devices, these machines play a critical role in improving product longevity, corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and visual appeal. Their ability to handle high-speed, high-volume production of miniature components with minimal human intervention makes them an indispensable asset in modern manufacturing.
In essence, an automatic powder coating machine for tiny metal parts combines gentle but precise material handling, electrostatic application, efficient curing, and intelligent process control to deliver superior coating results consistently. It is a compact yet powerful solution that aligns with the demands of high-precision industries requiring flawless finishes on even the smallest components.
As industries continue to prioritize efficiency, consistency, and sustainability, automatic powder coating machines for tiny metal parts are becoming more advanced, integrating smart technologies and refined engineering to handle the unique challenges of small-scale component finishing. One of the primary goals in designing these systems is to maintain total control over every variable in the coating process while minimizing waste and ensuring that each individual part, no matter how small, receives a complete, uniform, and defect-free coating. The movement of parts within the machine is crucial to achieving this. Continuous motion through rotary drums or vibrating bowls ensures that all surfaces are exposed to the powder spray, eliminating blind spots or uncoated areas. This constant agitation prevents parts from nesting together, which can otherwise lead to poor finishes or functional issues in assembled products.
Electrostatic powder guns used in these machines are carefully calibrated to deliver an optimal charge-to-mass ratio for very fine powder particles, ensuring maximum transfer efficiency and minimal overspray. The enclosed spray booth is designed to reduce turbulence while maintaining a uniform powder cloud, which is critical when working with tiny parts that can be sensitive to airflow changes. Additionally, the booth may be equipped with cyclone separators and multi-stage filters that capture and recycle unused powder, enhancing overall powder utilization and reducing operating costs. The reclaimed powder is often blended with fresh powder and automatically fed back into the system, maintaining coating quality and consistency from batch to batch.
The control systems of these machines are increasingly sophisticated. Modern units feature programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and touchscreen HMIs that allow operators to store multiple recipes for different part types, automate part tracking, and monitor production performance in real time. Parameters such as part throughput rate, dwell time in the spray chamber, powder density, gun voltage, and oven temperature are all adjustable and can be fine-tuned to accommodate different geometries, coating thickness requirements, or material sensitivities. Remote diagnostics and network connectivity also allow technicians to troubleshoot and update systems from offsite locations, reducing downtime and increasing machine availability.
Curing ovens integrated into these systems are designed with high airflow uniformity and precise temperature zones to ensure the powder melts and crosslinks evenly on all parts. Since tiny metal parts can be affected by even slight variations in heat, modern ovens use a combination of convection and infrared heating elements, sometimes in staged configurations, to gradually bring parts to the desired cure temperature without sudden thermal shock. Conveyorized curing ovens for continuous lines or rotating batch ovens for small-scale setups provide manufacturers with options depending on their throughput and footprint needs. The result is a smooth, durable coating that resists chipping, corrosion, and environmental degradation.
Compact automation is another strong feature of these machines. Auto-loading systems, robotic feeders, and gentle conveyor systems are used to minimize manual handling, which is especially critical when dealing with large volumes of very small items. Handling automation not only improves safety and speed but also helps maintain cleanliness and avoids the contamination or surface oils that could interfere with coating adhesion. Many systems also offer integrated pre-treatment stages, such as plasma cleaning or chemical baths, that prepare the part surface before coating, further enhancing the adhesion and performance of the final film.
From a production perspective, these machines offer significant scalability. A manufacturer can begin with a single machine for short runs or pilot production and then expand to multiple linked units as demand increases. Because of their compact footprint and modular architecture, they can be adapted to changing product lines or expanded for increased capacity without the need for major infrastructure changes. Additionally, they support lean manufacturing principles by enabling just-in-time production of coated parts, reducing inventory and floor space requirements.
Automatic powder coating machines for tiny metal parts also support strict compliance with environmental and workplace safety standards. The closed-loop nature of powder application and recovery drastically reduces powder emissions and exposure, while advanced filtration systems ensure that air quality remains within regulatory limits. Equipment enclosures, interlocks, and dust extraction systems contribute to safe operation, making them suitable even for facilities with tight health and safety requirements.
In conclusion, automatic powder coating machines for tiny metal parts represent a powerful convergence of precision engineering, automation, and materials science. They solve the longstanding challenges of coating small components by delivering reliable, repeatable, and scalable solutions that can be tailored to a wide range of production environments. These machines play an essential role in the global supply chain, ensuring that the smallest parts in our devices, vehicles, tools, and infrastructure are protected, functional, and built to last.
As demand for miniaturized components increases across nearly every advanced manufacturing sector, automatic powder coating machines for tiny metal parts are positioned as critical assets in achieving both volume production and high-quality standards. Their ability to coat thousands—or even millions—of parts per day without compromising consistency allows manufacturers to stay competitive in fast-moving industries like electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and precision hardware. These machines support not only high throughput but also unmatched repeatability, which is crucial when the failure of even a single small part can lead to costly product recalls or performance issues.
The design of these machines increasingly focuses on flexibility and modularity. This means that manufacturers can easily reconfigure the machine to handle different types of parts, adjust to changes in production volumes, or integrate additional processing steps like preheating, masking, or multi-layer coatings. Some systems are built with quick-swap tooling or interchangeable baskets, allowing operators to shift between product types in minutes instead of hours. This makes the machines especially well-suited to manufacturers who produce a broad range of parts in small batches or who work with short product lifecycles that demand frequent changeovers.
Another aspect of continued innovation lies in coating accuracy and material efficiency. New generations of powder guns now include real-time sensors that monitor the electrostatic charge and powder density during spraying, making micro-adjustments to maintain uniform output. This reduces the likelihood of coating defects like orange peel, pinholes, or thin spots. It also significantly cuts down on powder consumption—an important cost factor—while enhancing environmental responsibility. Some systems use dual-powder feed capability, which allows for seamless transitions between two powder types or colors, further supporting short-run production and specialty finishes.
These machines are also becoming increasingly compact while still offering industrial-grade capabilities. Smaller factories, research labs, or facilities with limited space can benefit from benchtop or miniaturized versions of these machines that deliver the same precision as larger, full-line systems. Despite their size, these compact versions often include automated loading systems, built-in curing chambers, and powder recycling features, making them ideal for startups, R&D departments, or companies producing low to mid-volume but high-value parts.
Global regulations and customer expectations around sustainability are also pushing machine developers to engineer systems that use less energy and emit less waste. Many automatic powder coating machines for tiny metal parts now feature low-energy curing ovens, optimized airflow paths, and high-efficiency motors. Manufacturers can choose to operate in enclosed cleanrooms or environmentally controlled zones, as some machines are designed to emit virtually no VOCs and very minimal particulate matter, making them compliant with the strictest environmental and workplace safety standards.
Maintenance has also been simplified with more intuitive diagnostics and modular part replacement. Smart sensors now detect wear in critical components, such as powder pumps, fans, or bearings, and notify operators in advance before breakdowns occur. This predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime and extends machine life. Additionally, many newer systems are built with open architecture and standard industrial protocols, meaning they can be integrated with factory-wide ERP and MES systems for better coordination and reporting across the production floor.
Ultimately, automatic powder coating machines for tiny metal parts are evolving from simple finishing tools into intelligent, connected systems that contribute to total manufacturing efficiency. Their precision, reliability, and scalability enable manufacturers to meet increasingly tight specifications while reducing material waste, energy use, and labor costs. Whether being used in high-speed mass production or in small-batch, high-value component lines, these machines help ensure that even the tiniest parts are finished to exacting standards—reliably, efficiently, and sustainably.
Fast Painting Line for Miniature Items
A fast painting line for miniature items is a specialized production system engineered to deliver rapid, consistent, and high-quality coatings on very small components. Miniature items—such as electronic connectors, tiny mechanical parts, jewelry pieces, and precision hardware—often require delicate handling and precise application of paint to ensure full coverage without defects like runs, sags, or uneven thickness. The fast painting line integrates automated handling, advanced spray technology, drying or curing stations, and quality control into a seamless workflow designed to maximize throughput while maintaining coating excellence.
Central to such a line is the material handling system, which typically includes vibratory feeders, rotary baskets, or conveyorized tumblers that gently agitate and separate miniature items during painting. This continuous movement ensures that paint reaches all surfaces evenly, preventing parts from sticking together and avoiding coating inconsistencies. The agitation mechanisms are carefully calibrated to handle fragile or complex shapes without causing damage or deformation.
Automated spray booths equipped with precision-controlled spray guns apply paint using methods like electrostatic spray, air atomization, or high-volume low-pressure (HVLP) spraying. Electrostatic systems charge paint particles, enhancing their attraction to grounded parts and improving transfer efficiency. This reduces paint waste, overspray, and environmental emissions, aligning with sustainable manufacturing goals. Spray parameters—such as flow rate, pressure, spray pattern, and gun voltage—are adjustable through programmable controls, enabling quick adaptation for different paints or miniature item types.
Following application, painted miniature items pass through fast drying or curing stations designed for rapid solvent evaporation or paint polymerization. These stations may employ infrared heaters, convection ovens, or UV curing lamps, selected based on the paint type and substrate sensitivity. Efficient drying ensures that parts are ready for subsequent handling, inspection, or assembly with minimal cycle time, supporting high throughput.
Quality assurance is integrated into the fast painting line through inline inspection systems that use machine vision, laser scanning, or thickness gauges to detect defects like paint runs, uneven coverage, or surface contamination. Immediate feedback allows process adjustments or rejection of defective parts, ensuring that only finished components meeting strict standards proceed down the line.
The entire line is typically controlled by centralized programmable logic controllers (PLCs) with human-machine interfaces (HMIs) that offer operators real-time monitoring, recipe management, and process control. This automation minimizes human error, enhances repeatability, and enables rapid changeovers between product batches, which is essential in industries with diverse product mixes or short production runs.
Fast painting lines for miniature items are widely used in electronics, medical device manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and precision engineering sectors. They provide manufacturers with the capability to produce durable, high-quality painted finishes on tiny components efficiently and sustainably. By combining gentle handling, precise application, and rapid drying, these lines help meet demanding production schedules without compromising coating performance or appearance.
In summary, a fast painting line for miniature items is a highly automated, flexible, and efficient system designed to deliver superior paint finishes on small parts. It balances speed with quality by integrating advanced material handling, spray technology, drying methods, and inspection into a streamlined process, enabling manufacturers to meet the challenges of coating miniature components in modern production environments.
Fast painting lines for miniature items continue to evolve with advancements in automation, materials, and process control that further enhance their speed, efficiency, and coating quality. One of the main challenges in coating miniature parts is ensuring uniform coverage on all surfaces, including tight corners, recesses, and complex geometries. To address this, modern systems employ multi-axis robotic arms or automated spray heads capable of precise, repeatable movement patterns that optimize paint deposition while minimizing overspray and waste. These robots can adjust their motion dynamically based on part shape and orientation, ensuring consistent finishes even on highly intricate components.
The material handling systems have also become more sophisticated. Vibratory feeders, rotary baskets, and tumblers are engineered to provide gentle yet continuous agitation that prevents parts from sticking together or sustaining damage. Some lines incorporate vision-guided robotic sorting and orientation to feed parts into the spray zone in optimal positions, increasing coating efficiency and reducing the need for rework. This level of automation reduces manual intervention, improving throughput and product consistency while enhancing worker safety by minimizing exposure to paint fumes and particulates.
Advances in spray technology contribute significantly to faster cycle times and improved finish quality. Electrostatic spray guns are fine-tuned to deliver highly charged paint particles that adhere efficiently to grounded miniature parts, increasing transfer efficiency and reducing paint consumption. High-volume low-pressure (HVLP) and airless spray systems may be used depending on paint type and finish requirements, offering flexibility in coating different materials or achieving specific surface textures. Spray booths are designed to optimize airflow and powder containment, ensuring environmental compliance and operator safety.
Drying and curing technologies have also progressed, enabling faster turnaround without compromising finish durability. Infrared curing systems provide rapid heat-up times and focused energy delivery, making them ideal for solvent-based or UV-curable paints. Convection ovens with carefully controlled temperature zones ensure even curing, preventing defects such as blistering or cracking that can arise from thermal stress on delicate parts. UV curing offers near-instantaneous polymerization of certain coatings, dramatically shortening cycle times and increasing throughput.
Integrated inline quality inspection systems are increasingly common in fast painting lines for miniature items. Machine vision cameras and laser scanners perform real-time checks for coating uniformity, thickness, color accuracy, and surface defects, allowing immediate corrective action. This proactive approach minimizes waste, enhances product reliability, and supports traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
The entire painting line is managed via centralized control software that enables operators to program multiple coating recipes, monitor equipment status, and log production data for quality assurance. Connectivity with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES) facilitates streamlined workflow management and inventory control, supporting just-in-time manufacturing and reducing lead times.
Environmental considerations remain paramount. Paint application systems minimize volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions through advanced filtration and exhaust control, while paint reclaim units recover and recycle overspray material. Energy-efficient curing ovens and optimized airflow designs contribute to reduced power consumption and operational costs.
In diverse industries such as electronics, aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and automotive, fast painting lines for miniature items provide a critical combination of speed, precision, and quality. They enable manufacturers to keep pace with demanding production schedules while meeting stringent finish requirements and environmental regulations.
Overall, these fast painting lines represent a blend of cutting-edge automation, material science, and process engineering. By delivering high-quality painted finishes on tiny, complex parts quickly and reliably, they help manufacturers achieve competitive advantage, operational excellence, and product excellence in today’s fast-paced industrial landscape.
As the demand for miniaturized and high-precision components grows, fast painting lines for miniature items are increasingly designed with scalability and flexibility in mind. Modular construction allows manufacturers to expand or reconfigure their lines as production needs evolve, supporting multiple coating processes, colors, or finishes within a single integrated system. This adaptability is essential for industries with frequent product changes or short production runs, enabling rapid changeovers and reducing downtime.
The integration of smart sensors and advanced analytics is transforming these painting lines into intelligent manufacturing hubs. Real-time monitoring of variables such as spray pressure, paint viscosity, environmental humidity, and temperature allows for proactive adjustments that maintain optimal coating conditions. Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze machine performance data to forecast wear or potential failures, minimizing unplanned stoppages and extending equipment lifespan. Operators receive instant alerts and actionable insights through user-friendly dashboards, improving responsiveness and process control.
Automation in loading and unloading processes is also advancing, with robotic arms, conveyor systems, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) reducing manual labor and increasing throughput. These automated systems are programmed to handle miniature parts delicately, minimizing the risk of damage or contamination. Automated part sorting and orientation systems ensure that components enter the painting zone in the correct position, further enhancing coating consistency and reducing scrap rates.
Material innovations complement these technological advancements. The development of fast-drying, low-VOC, and waterborne paints suitable for miniature parts enhances environmental sustainability and workplace safety. Specialty coatings with properties such as chemical resistance, biocompatibility, or enhanced adhesion expand the applications of fast painting lines across various high-performance sectors.
Energy efficiency remains a priority in line design. Modern drying and curing stations employ technologies such as variable frequency drives, heat recovery systems, and zoned heating to minimize energy consumption without sacrificing performance. This focus on sustainability aligns with global regulatory trends and corporate social responsibility goals.
Training and ease of use are enhanced through intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs), remote support capabilities, and augmented reality (AR) tools that assist operators in maintenance and troubleshooting. These features reduce the learning curve and help maintain consistent operation standards across shifts and facilities.
In summary, fast painting lines for miniature items are becoming more adaptable, intelligent, and environmentally friendly. By integrating advanced automation, real-time process control, and sustainable practices, these lines empower manufacturers to meet increasing production demands and quality standards efficiently. They play a vital role in producing the durable, high-quality finishes required for the next generation of miniature components across industries worldwide.
Automatic Paint Line for Small Products

An automatic paint line for small products is a highly engineered system designed to deliver fast, consistent, and high-quality paint finishes on small-scale components with minimal manual intervention. These lines are essential in industries such as electronics, automotive, medical devices, hardware, and consumer goods, where tiny parts—ranging from connectors and fasteners to precision mechanical components—require durable, uniform coatings that meet strict functional and aesthetic standards.
The heart of an automatic paint line for small products is its material handling system, which gently transports and agitates parts to ensure every surface is accessible for coating. Common handling mechanisms include vibratory feeders, rotary baskets, tumblers, and conveyor belts equipped with specialized fixtures that secure small items during processing. These systems maintain continuous, controlled movement that prevents parts from clustering or scratching, ensuring uniform paint application and reducing rework.
Coating application is performed using advanced spray technologies such as electrostatic spray, air atomization, or high-volume low-pressure (HVLP) systems. Electrostatic spraying is particularly effective for small products because it charges paint particles, improving their attraction to grounded parts and reducing overspray and paint waste. Spray booths are designed with optimized airflow and filtration to capture excess paint particles, maintain environmental safety, and ensure a clean working environment.
The paint used in these lines varies based on application requirements and can include solvent-based, waterborne, UV-curable, or powder coatings. Paint selection influences the type of drying or curing system employed. Drying ovens, infrared heaters, or UV curing stations are integrated to rapidly harden the coating, enabling quick cycle times without compromising finish quality or part integrity. These curing systems are precisely controlled to avoid damage to delicate parts while ensuring full polymerization and adhesion of the paint.
Automation and process control are central to the efficiency of automatic paint lines for small products. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) manage spray parameters, conveyor speeds, curing temperatures, and agitation rates, providing consistent and repeatable results. Touchscreen human-machine interfaces (HMIs) enable operators to select coating recipes, monitor line status, and perform quick adjustments or diagnostics. Some lines also incorporate real-time quality inspection systems using cameras or laser sensors to detect coating defects early in the process, improving yield and reducing waste.
Sustainability and environmental compliance are critical considerations. Modern automatic paint lines incorporate paint recovery systems that capture and recycle overspray, lowering material costs and minimizing environmental impact. High-efficiency filtration systems ensure operator safety and regulatory adherence by controlling volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and particulate release. Energy-efficient curing technologies reduce power consumption, further supporting green manufacturing initiatives.
Flexibility and scalability make these lines suitable for a range of production volumes—from small batch prototyping to high-speed mass production. Modular designs allow manufacturers to customize or expand their paint lines as product demands change, integrating additional pre-treatment stages, masking stations, or post-coating processes as needed.
In summary, an automatic paint line for small products offers a comprehensive, automated solution to the complex challenge of coating miniature components. By combining precise material handling, advanced spray technology, controlled curing, and intelligent process management, these systems enable manufacturers to achieve superior finish quality, maximize throughput, and maintain operational efficiency in today’s competitive markets.
Automatic paint lines for small products continue to advance with innovations that enhance precision, speed, and environmental sustainability while reducing operational costs. One key area of development is the integration of robotics and smart automation. Robotic arms equipped with multi-axis movement capabilities enable highly accurate and repeatable spray patterns, ensuring that every tiny part is coated uniformly, including hard-to-reach surfaces and intricate geometries. These robots can adapt dynamically to different part shapes and sizes, facilitating quick product changeovers and supporting high-mix manufacturing environments.
Material handling systems have become more refined to prevent damage or contamination of delicate small parts. Gentle vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, or cushioned conveyors keep parts separated and moving smoothly through each stage of the line. Some systems incorporate vision-guided automation that inspects and orients parts before coating, maximizing coverage efficiency and minimizing rejects. Automated loading and unloading further reduce manual labor and improve throughput consistency.
Spray technology improvements focus on optimizing paint transfer efficiency and minimizing waste. Electrostatic spray guns now feature real-time monitoring of charge levels and particle dispersion, allowing for fine adjustments that maintain consistent coating thickness and surface finish. The use of high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and advanced paint recovery units ensures that overspray is effectively captured and recycled, significantly lowering paint consumption and reducing environmental impact.
Drying and curing technologies integrated into automatic paint lines for small products continue to evolve, with infrared, convection, and UV curing options tailored to various paint chemistries and substrate sensitivities. These curing systems are designed for rapid cycle times while maintaining uniform temperature distribution to prevent defects such as blistering, cracking, or uneven gloss. Energy-efficient designs, including zoned heating and heat recovery, contribute to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
Process control and data management are central to modern automatic paint lines. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) coupled with user-friendly human-machine interfaces (HMIs) enable operators to store multiple coating recipes, monitor key process parameters in real time, and respond quickly to any deviations. Integration with factory-wide systems such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) facilitates comprehensive production tracking, quality assurance, and inventory management, streamlining workflow and improving traceability.
Environmental compliance and operator safety are paramount considerations. Enclosed spray booths with effective ventilation and filtration minimize worker exposure to hazardous fumes and particulates. Paint recovery and filtration systems reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, helping manufacturers meet stringent regulatory requirements and corporate sustainability goals.
Flexibility remains a defining feature of automatic paint lines for small products. Modular design allows for easy expansion or reconfiguration to accommodate new products, different coating types, or increased production volumes. This adaptability supports lean manufacturing principles and just-in-time production strategies, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to changing market demands without excessive downtime or capital expenditure.
In industries such as electronics, automotive, medical devices, aerospace, and consumer goods, these automatic paint lines are critical for producing durable, high-quality finishes on small components that meet exacting standards. By delivering consistent results with high throughput and minimal waste, they help manufacturers reduce costs, improve product reliability, and maintain competitive advantage.
Ultimately, automatic paint lines for small products represent the convergence of advanced automation, precision engineering, and sustainable manufacturing practices. Their ability to efficiently coat miniature parts with superior quality makes them indispensable in modern production environments focused on agility, quality, and environmental responsibility.
As technology continues to advance, automatic paint lines for small products are increasingly incorporating Industry 4.0 features, transforming traditional coating systems into intelligent, connected manufacturing platforms. Embedded sensors throughout the line collect vast amounts of real-time data on parameters such as paint viscosity, spray pressure, environmental conditions, and part throughput. This data is analyzed using machine learning algorithms to optimize process control, predict maintenance needs, and reduce variability, ensuring that every tiny part is coated to exact specifications with minimal defects.
The integration of digital twins—virtual replicas of the physical paint line—enables manufacturers to simulate and fine-tune coating processes before implementing changes on the actual line. This predictive capability minimizes trial-and-error adjustments, shortens setup times, and improves overall production efficiency. Remote monitoring and control further enhance operational flexibility, allowing experts to diagnose issues or adjust parameters from anywhere, reducing downtime and speeding up problem resolution.
Robotic systems within automatic paint lines are becoming more versatile and adaptive. Collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside human operators can handle delicate small parts safely and efficiently, providing a balance between automation and manual oversight. Advanced vision systems paired with artificial intelligence can detect minute surface imperfections, color deviations, or coating inconsistencies in real time, enabling immediate corrective action and minimizing waste.
The choice of coating materials is evolving as well, with a growing emphasis on environmentally friendly paints that meet increasingly strict regulations. Waterborne paints, UV-curable coatings, and low-VOC formulations reduce harmful emissions and environmental impact without sacrificing performance. Automatic paint lines are being optimized to handle these advanced materials effectively, ensuring thorough application and rapid curing while maintaining sustainability goals.
Energy efficiency remains a key focus, with the adoption of low-energy curing technologies such as LED-UV systems and infrared heaters that provide rapid curing with reduced power consumption. Improved insulation, heat recovery systems, and smart energy management help minimize operational costs and the carbon footprint of the painting process.
User experience and maintenance procedures are also being enhanced. Intuitive touchscreens, augmented reality (AR) support tools, and guided maintenance routines make operation and servicing easier and more accessible, reducing the learning curve and helping maintain consistent process quality across operators and shifts.
Modular designs allow paint lines to be easily reconfigured or expanded to meet changing production demands. Manufacturers can integrate additional stations for pre-treatment, masking, multi-layer coatings, or post-coating inspection without major disruptions. This flexibility supports diverse product portfolios and rapid product launches.
In sectors where precision and reliability are critical—such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics—automatic paint lines for small products enable manufacturers to meet stringent industry standards while optimizing throughput and reducing costs. The combination of advanced automation, real-time quality control, sustainable practices, and flexible design makes these lines indispensable tools for modern manufacturing.
In conclusion, automatic paint lines for small products are rapidly evolving into smart, adaptive, and eco-friendly systems that deliver exceptional coating quality and operational efficiency. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and process innovations, these lines empower manufacturers to produce flawless finishes on miniature components at scale, meeting the demands of today’s competitive and environmentally conscious markets.
Painting Machine for Small Items with Precision
A painting machine for small items with precision is a highly specialized piece of equipment engineered to deliver meticulous, uniform coatings on miniature components where accuracy and consistency are paramount. These machines cater to industries such as electronics, medical devices, aerospace, jewelry, and precision hardware, where even the smallest imperfections in coating thickness, coverage, or finish quality can lead to functional failures or aesthetic defects.
At the core of such a machine is an advanced material handling system designed to gently manipulate and orient tiny parts during the painting process. Mechanisms like vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, or precision conveyors ensure continuous agitation or controlled positioning, allowing every surface of each part to be exposed evenly to the paint. This constant, delicate movement prevents clustering or abrasion, which could compromise coating integrity.
Precision spray technology is central to these machines. Electrostatic spray guns are widely used due to their ability to charge paint particles, enhancing their attraction to grounded metal surfaces and improving transfer efficiency. These guns are finely calibrated to control particle size, spray pattern, and voltage, delivering an even, thin film with minimal overspray. Alternative technologies such as air-assisted airless spray, ultrasonic atomization, or micro-jet spraying may also be employed depending on the application and paint type, providing additional control over droplet size and coating uniformity.
The painting chamber is often enclosed to maintain optimal environmental conditions, controlling airflow, temperature, and humidity to stabilize paint behavior and drying characteristics. This enclosure also helps contain overspray and supports advanced filtration systems that recycle unused paint, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Curing or drying stations integrated with precision painting machines are designed to rapidly and evenly cure coatings without causing thermal damage to delicate small parts. Options include infrared ovens, UV curing systems, or convection dryers tailored to the specific paint chemistry and substrate sensitivity. Controlled curing ensures coatings develop their full mechanical and chemical properties, such as adhesion, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
Automation and digital process control are key features of precision painting machines. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and user-friendly human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to define and store multiple coating programs tailored for different parts or finishes. Real-time monitoring of parameters like spray pressure, powder feed rate, conveyor speed, and curing temperature helps maintain consistency across production runs. Some machines incorporate feedback loops where sensors detect coating thickness or surface quality and automatically adjust spray parameters to correct deviations.
The design often includes quick-change fixtures or modular components to facilitate rapid changeovers between different small item types, supporting flexible manufacturing environments and reducing downtime. Maintenance is streamlined through easy access panels, self-cleaning spray guns, and filter replacements, helping sustain high performance and minimize production interruptions.
From a sustainability perspective, these machines emphasize efficient paint usage, powder or liquid recovery systems, and low-VOC paint compatibility. Energy-efficient curing solutions and enclosed spray environments contribute to reducing environmental footprint and ensuring operator safety.
In summary, a painting machine for small items with precision combines gentle part handling, finely tuned spray application, controlled curing, and intelligent process management to achieve superior coating quality on miniature components. These machines are essential in producing durable, aesthetically flawless finishes that meet the rigorous standards of modern manufacturing across various high-tech and specialized industries.
Painting machines designed for small items with precision continue to evolve as manufacturers demand ever-higher quality finishes and greater process reliability. One of the key advancements is the integration of multi-axis robotic spray systems that enable highly controlled and repeatable motion paths. These robotic systems can maneuver spray nozzles around complex geometries of miniature parts, ensuring complete coverage while minimizing paint consumption and overspray. The ability to program and adapt motion sequences quickly makes these machines versatile for diverse product types and small batch production runs.
Material handling within these machines is engineered to balance gentle agitation with secure part positioning. Vibratory feeders and tumblers provide continuous movement to expose all surfaces evenly, while precision conveyors and rotary indexing tables hold parts in exact orientations for targeted spraying. Some systems incorporate vision-guided robotics that inspect and orient parts in real time, further enhancing coating uniformity and reducing rejects. Automation in loading and unloading also minimizes human handling, preserving part cleanliness and preventing damage.
Spray technologies have advanced to include ultrafine atomization methods such as ultrasonic spraying and electrostatic micro-jet systems. These approaches generate extremely small paint droplets that form smooth, uniform coatings with fine control over thickness and texture. This is especially important when coatings must meet stringent functional requirements like electrical insulation, biocompatibility, or optical clarity. Electrostatic charging remains a preferred method due to its ability to improve transfer efficiency and reduce environmental waste, making the process more cost-effective and sustainable.
The environmental controls within the painting chamber are optimized to maintain consistent temperature, humidity, and airflow, which directly affect paint behavior and finish quality. Sophisticated filtration systems capture overspray particles and recycle paint or powder, significantly reducing waste and emissions. Enclosed chambers also protect operators from exposure to harmful fumes and particulates, ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations.
Curing or drying stations integrated into precision painting machines utilize tailored technologies such as infrared, UV, or convection heating, carefully controlled to avoid thermal stresses that could deform or damage small parts. Rapid and uniform curing improves throughput and ensures the coating achieves its full mechanical and chemical properties, including adhesion, hardness, and resistance to corrosion or wear.
Process control is increasingly intelligent, with sensors and feedback loops monitoring key parameters such as spray pattern consistency, coating thickness, and environmental conditions. Advanced software can automatically adjust spray parameters in real time to correct for variations, ensuring consistent product quality. Data logging and connectivity features enable integration with factory-wide systems for traceability, quality assurance, and predictive maintenance.
Quick-change tooling and modular design principles support fast setup and changeover, reducing downtime when switching between different part types or coating specifications. Ease of maintenance is enhanced through features like self-cleaning spray guns, accessible filtration units, and remote diagnostics, helping maintain high uptime and consistent performance.
Sustainability remains a focal point, with machines designed to maximize paint transfer efficiency, recycle overspray, and operate with low energy consumption. Compatibility with waterborne and low-VOC paints further supports environmentally responsible manufacturing practices.
Overall, painting machines for small items with precision embody a blend of advanced automation, sophisticated spray technology, and comprehensive process control. They enable manufacturers to meet exacting quality standards for miniature parts, delivering durable, flawless finishes while optimizing efficiency, reducing waste, and ensuring safety. These capabilities are crucial in sectors where even minor coating defects can have significant functional or aesthetic consequences, making such machines indispensable tools in high-tech and specialized manufacturing.
Building on these capabilities, painting machines for small items with precision increasingly incorporate real-time quality assurance systems that further enhance coating reliability. High-resolution machine vision cameras, laser scanners, and spectroscopic sensors inspect coated parts immediately after application or curing, detecting surface defects, color variations, or insufficient coverage down to microscopic levels. This immediate feedback loop enables automated rejection of defective parts or on-the-fly process adjustments, minimizing scrap rates and ensuring that only parts meeting strict quality criteria move forward in the production chain.
The use of data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) is gaining momentum in these systems. By analyzing historical and real-time process data, AI algorithms can predict potential deviations or equipment failures before they occur, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing costly downtime. AI-driven optimization also helps fine-tune spray parameters for varying part geometries or environmental conditions, ensuring consistent coating thickness and finish quality without extensive manual intervention.
Customization and flexibility remain key design goals. Modular machine architectures allow manufacturers to add or remove stations such as pre-treatment (cleaning, etching, or priming), masking, multi-layer coating, or post-coating inspection depending on product requirements. This scalability enables cost-effective adaptation to evolving production volumes or new product lines without extensive retooling.
Operator experience is also enhanced through intuitive interfaces, touchscreen controls, and guided workflows. Augmented reality (AR) tools are emerging as valuable aids for training, maintenance, and troubleshooting, providing real-time visual overlays and step-by-step instructions that reduce errors and speed up service times. Remote support capabilities enable expert technicians to assist on-site staff quickly, even across multiple global facilities.
Environmental sustainability is increasingly embedded in machine design. Painting machines compatible with waterborne, low-VOC, or powder coatings reduce harmful emissions and operator exposure. Advanced overspray recovery systems and high-efficiency filtration ensure minimal paint waste and clean air discharge. Energy-efficient curing technologies, such as LED-UV systems or optimized infrared ovens, minimize power consumption while maintaining rapid throughput.
Furthermore, these precision painting machines are designed to integrate seamlessly into smart factories. Communication protocols and open architecture enable connectivity with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, facilitating full production traceability, resource management, and supply chain coordination. This integration supports lean manufacturing principles and enables manufacturers to respond swiftly to market demands.
In highly regulated industries like aerospace, medical devices, and electronics, these features help ensure compliance with strict quality and safety standards. Precise control over coating thickness, adhesion, and finish properties is critical to product performance and reliability, and these machines provide the necessary accuracy and repeatability.
In conclusion, painting machines for small items with precision represent a convergence of advanced automation, smart technologies, and sustainable engineering. They enable manufacturers to achieve flawless, durable coatings on miniature components efficiently and reliably. As industries continue to push the boundaries of miniaturization and quality, these machines will remain essential in delivering superior finishes that meet the demands of modern manufacturing.
Paint Systems for Small Components
Paint systems for small components are specialized solutions designed to apply high-quality coatings to miniature parts with exceptional precision, uniformity, and efficiency. These systems address the unique challenges posed by small-scale components, such as intricate geometries, delicate surfaces, and the need for consistent coverage on all sides. Industries including electronics, medical devices, aerospace, automotive, and precision hardware rely heavily on these systems to enhance product durability, functionality, and aesthetics.
At the core of paint systems for small components is a carefully engineered material handling mechanism that ensures continuous and gentle movement of parts throughout the painting process. Common handling methods include vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, precision conveyors, and automated fixtures that hold or orient parts securely. These mechanisms prevent parts from sticking together or getting damaged, enabling uniform exposure to paint and optimal coating quality.
Coating application technologies within these systems vary according to part requirements and paint types. Electrostatic spray coating is frequently employed because it imparts an electrical charge to paint particles, improving transfer efficiency by attracting them to grounded components. This method reduces overspray, minimizes waste, and enhances finish quality. Alternative technologies such as air atomization, ultrasonic spraying, or powder coating may be used based on the desired finish, environmental considerations, or material compatibility.
Enclosed spray booths maintain controlled environmental conditions, regulating airflow, temperature, and humidity to stabilize paint behavior and drying characteristics. Integrated filtration and overspray recovery systems capture excess paint, enabling recycling and reducing environmental impact. These booths also protect operators by minimizing exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter.
Drying and curing units are essential components, designed to harden and set the paint efficiently without damaging small or heat-sensitive parts. Technologies like infrared ovens, UV curing lamps, or convection dryers are selected based on paint chemistry and substrate properties. Precise temperature control ensures coatings achieve optimal adhesion, hardness, and resistance to wear or corrosion.
Automation and process control are central to modern paint systems for small components. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide operators with intuitive control over spray parameters, conveyor speeds, curing times, and other critical variables. Recipes for different parts or finishes can be stored and recalled, facilitating quick changeovers and consistent results. Inline inspection systems using machine vision and sensors enable real-time detection of coating defects, allowing immediate corrective actions.
Sustainability considerations drive the integration of low-VOC paints, efficient paint recovery, and energy-saving curing technologies. These features help manufacturers comply with environmental regulations and reduce operational costs while maintaining high-quality finishes.
Flexibility and modularity characterize these paint systems, enabling manufacturers to customize configurations based on production volumes, part complexity, and finish requirements. Systems can be scaled from benchtop units for small batch production to fully automated, high-throughput lines integrated into broader manufacturing processes.
In summary, paint systems for small components combine precise material handling, advanced coating technologies, controlled curing, and intelligent automation to deliver superior finishes on miniature parts. Their design addresses the challenges of coating tiny, often complex items, ensuring durability, aesthetics, and compliance with industry standards across a wide range of applications.
Paint systems for small components continue to evolve with technological advancements that enhance efficiency, quality, and environmental sustainability. One significant trend is the integration of robotics and intelligent automation, which allows for highly precise and repeatable paint application on even the most intricate miniature parts. Multi-axis robotic arms equipped with advanced spray nozzles can maneuver around complex geometries, ensuring thorough coverage while minimizing overspray and paint waste. This level of control supports a wide variety of part shapes and sizes without the need for extensive manual adjustments or custom tooling.
Material handling innovations focus on gentle yet effective agitation and orientation of parts throughout the painting process. Vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, and specialized conveyors maintain continuous movement to expose all surfaces evenly while preventing damage or surface contamination. Some systems employ vision-guided robotics and sensors to detect part orientation and adjust spray patterns dynamically, improving coating consistency and reducing rejects. Automated loading and unloading further enhance throughput and reduce labor costs.
Advances in spray technology contribute to improved paint transfer efficiency and finish quality. Electrostatic spraying remains a cornerstone due to its ability to charge paint particles, which enhances adhesion and reduces overspray. Other methods, such as ultrasonic atomization or high-volume low-pressure (HVLP) spraying, provide alternative options tailored to specific paint types or finish requirements. Spray booths are designed to optimize airflow, containment, and filtration, ensuring operator safety and environmental compliance.
Curing and drying equipment integrated into paint systems for small components utilize technologies like infrared, UV, and convection heating, selected based on coating chemistry and substrate sensitivity. These systems are engineered for rapid and uniform curing, reducing cycle times while preventing thermal damage or deformation of delicate parts. Energy-efficient designs with heat recovery and zoned heating minimize power consumption and operational costs.
Process control systems leverage programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and data analytics to monitor and adjust parameters in real time. Inline inspection using machine vision and laser sensors detects coating defects such as uneven thickness, runs, or color variations, enabling immediate corrective actions. Data connectivity with enterprise systems supports traceability, quality assurance, and predictive maintenance, contributing to lean manufacturing practices.
Sustainability is a core design consideration. Paint recovery and recycling systems reduce material waste, while low-VOC and waterborne paints minimize environmental impact. Closed-loop filtration systems capture and clean exhaust air, protecting worker health and meeting regulatory requirements.
Modularity and scalability allow paint systems for small components to be tailored to diverse production needs. Whether for prototype runs, small batch production, or high-volume manufacturing, these systems can be configured with optional modules such as pre-treatment, masking, multi-layer coating, and post-coating inspection stations. This flexibility supports quick changeovers and adapts to evolving product lines.
In industries demanding high precision and reliability—such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics—paint systems for small components ensure that finishes meet stringent performance and aesthetic standards. By combining advanced automation, sophisticated coating technology, and environmentally responsible design, these systems help manufacturers deliver durable, flawless coatings efficiently and sustainably, reinforcing product quality and competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Building on these advancements, paint systems for small components are increasingly adopting smart manufacturing technologies that enhance productivity and process intelligence. Embedded sensors throughout the system continuously monitor critical parameters like paint viscosity, spray pressure, environmental temperature, and humidity. This data feeds into advanced control algorithms and machine learning models that dynamically optimize the painting process in real time, ensuring consistent coating quality even as conditions vary.
Digital twin technology is also being incorporated, creating virtual replicas of the physical paint system that simulate operation under different scenarios. This enables engineers to test process changes, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance without interrupting production. Remote monitoring and control capabilities allow operators and technicians to access system diagnostics, perform adjustments, and conduct maintenance activities from anywhere, minimizing downtime and improving responsiveness.
Robotics within paint systems have evolved to offer greater dexterity and adaptability. Collaborative robots (cobots) can work safely alongside human operators to handle delicate small parts with precision, facilitating complex tasks such as selective coating or multi-stage painting. Vision-guided systems enable real-time part recognition, orientation, and defect detection, further improving process accuracy and reducing scrap.
Material innovations continue to expand the capabilities of paint systems. The adoption of environmentally friendly coatings—including waterborne, UV-curable, and low-VOC formulations—supports sustainability goals without compromising performance. Paint systems are designed or retrofitted to handle these advanced materials effectively, ensuring optimal application and curing.
Energy efficiency remains a priority, with drying and curing technologies incorporating features like zoned heating, heat recovery, LED-UV curing, and infrared systems that deliver rapid curing while minimizing energy consumption. These innovations reduce operational costs and support corporate environmental responsibility initiatives.
User experience improvements include intuitive touchscreens, customizable interfaces, and augmented reality (AR) tools that provide interactive guidance for setup, maintenance, and troubleshooting. These features help reduce operator errors, speed up training, and maintain consistent process quality across shifts and sites.
The modular architecture of modern paint systems allows manufacturers to configure lines that precisely meet production demands. They can add or remove components such as pre-treatment modules, masking stations, multi-layer coating setups, or inline inspection units as needed. This flexibility facilitates quick product changeovers, supports diverse part portfolios, and enables scalable growth.
Integration with broader manufacturing systems via standard communication protocols ensures seamless data exchange with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. This connectivity supports comprehensive production tracking, quality management, and supply chain coordination, contributing to lean manufacturing and just-in-time delivery strategies.
In highly regulated sectors, paint systems for small components provide the precision and traceability required to comply with strict industry standards. They ensure that coatings meet exact specifications for thickness, adhesion, chemical resistance, and aesthetics, which are critical for product safety and performance.
In summary, paint systems for small components are rapidly advancing through the convergence of automation, smart technologies, sustainable materials, and flexible design. These systems enable manufacturers to produce consistently high-quality coatings on miniature parts efficiently, sustainably, and with the agility needed to meet evolving market demands and regulatory requirements.
Automatic Painting Machine for Tiny Objects
An automatic painting machine for tiny objects is a highly specialized piece of industrial equipment designed to apply precise, uniform coatings on very small components with minimal human intervention. These machines are essential in industries such as electronics, medical devices, aerospace, and precision engineering, where tiny parts—ranging from micro-connectors and miniature gears to delicate surgical tools—require flawless paint finishes to ensure functionality, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
The core challenge in painting tiny objects lies in achieving complete and consistent coverage despite the parts’ small size and often complex geometries. To address this, automatic painting machines utilize advanced material handling systems such as vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, or precision conveyor belts that gently agitate or orient parts during coating. This continuous movement exposes every surface evenly to the paint, preventing issues like missed spots, runs, or uneven thickness.
Coating application is typically performed using precision spray technologies like electrostatic spray, micro-jet atomization, or ultrasonic spraying. Electrostatic spraying is particularly effective for tiny objects because it imparts an electrical charge to paint particles, which are then attracted to grounded parts. This enhances paint transfer efficiency, reduces overspray, and minimizes waste, resulting in sharper, cleaner finishes. Spray parameters such as particle size, spray angle, and voltage are finely controlled through programmable systems to tailor the coating process for different part shapes and paint types.
The painting chamber is designed to maintain optimal environmental conditions, controlling temperature, humidity, and airflow to stabilize paint behavior and drying characteristics. Enclosed booths with advanced filtration capture overspray and protect operators from exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter, supporting both safety and regulatory compliance.
Drying or curing stations integrated into the machine utilize technologies like infrared heaters, ultraviolet (UV) curing lamps, or convection ovens. These systems are carefully engineered to rapidly cure coatings without damaging heat-sensitive miniature parts, ensuring the paint fully adheres and achieves desired mechanical properties such as hardness, flexibility, and corrosion resistance.
Automation and digital controls are fundamental to the machine’s performance and usability. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) manage all aspects of the painting cycle, including part agitation, spray timing, paint flow, and curing parameters. Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide operators with intuitive control panels to select programs, monitor system status, and perform diagnostics. This level of automation guarantees repeatability, reduces human error, and facilitates quick changeovers between different part types or paint recipes.
Some automatic painting machines for tiny objects incorporate inline quality inspection systems using machine vision and laser sensors. These systems detect coating defects such as uneven coverage, color mismatches, or surface blemishes in real time, enabling immediate process adjustments or rejection of defective parts. This proactive quality control helps maintain high yields and reduces waste.
Sustainability features are increasingly integrated into these machines. Paint recovery systems capture and recycle overspray, while low-VOC or waterborne paints reduce environmental impact. Energy-efficient curing technologies and optimized airflow design contribute to lower power consumption and operational costs.
Modular design allows these machines to be customized or scaled to production needs, ranging from benchtop units suitable for prototype or low-volume runs to fully automated lines capable of high-throughput mass production. This flexibility supports manufacturers in meeting diverse market demands while maintaining coating quality and efficiency.
In summary, automatic painting machines for tiny objects combine precise material handling, advanced spray technology, controlled curing, and intelligent automation to deliver superior paint finishes on miniature parts. They enable manufacturers to achieve high-quality, consistent, and efficient coating processes critical to the performance and appearance of small, complex components in today’s advanced manufacturing environments.
Automatic painting machines for tiny objects have become increasingly sophisticated as manufacturers seek faster cycle times, greater precision, and enhanced reliability. One major development is the incorporation of multi-axis robotic systems that provide exceptional maneuverability and control over spray patterns. These robots can adjust nozzle positions dynamically to coat complex geometries fully, including recessed areas and undercuts that are difficult to reach with traditional spray setups. This adaptability minimizes paint waste and eliminates the need for multiple coating stages.
Material handling systems have also advanced to ensure gentle, consistent part movement while minimizing damage and contamination. Techniques such as vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, and cushioned conveyors keep tiny parts separated and continuously agitated to maximize surface exposure during spraying. Vision-guided robotic arms and sorting mechanisms can further optimize part orientation automatically, ensuring each component is positioned for optimal paint coverage and reducing rejects.
Spray technologies continue to evolve with improvements in atomization and electrostatic charging. Ultrasonic atomization and micro-jet spray methods produce extremely fine droplets, creating smooth, uniform coatings essential for delicate miniature parts. Electrostatic systems finely tune the charge level and spray parameters to improve paint transfer efficiency, reduce overspray, and lower environmental emissions. Advanced filtration systems capture airborne particles and VOCs, enhancing workplace safety and compliance with environmental regulations.
Drying and curing stations integrated into automatic painting machines are optimized for speed and uniformity. Infrared and LED-UV curing technologies enable rapid polymerization of coatings without exposing heat-sensitive parts to damaging temperatures. Zoned heating and convection systems maintain even temperature distribution, preventing defects such as blistering or cracking. Energy-efficient designs also contribute to lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact.
Automation and control are central to machine performance. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) coordinate every aspect of the process—from agitation and spraying to curing and inspection. Intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to select recipes, monitor real-time data, and troubleshoot quickly. Data collection and connectivity support integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES), enabling full traceability, quality management, and predictive maintenance that minimize downtime and maximize throughput.
Inline quality assurance systems employing high-resolution cameras, laser scanners, and spectral analysis detect coating defects immediately after application. These systems enable real-time feedback loops that adjust spray parameters or flag defective parts for removal, ensuring consistent finish quality and reducing waste.
Sustainability features such as paint reclaim units, low-VOC and waterborne coatings, and energy-saving curing technologies align these machines with modern environmental standards and corporate responsibility goals. Modular construction allows easy expansion or customization of the line to meet changing production requirements or incorporate new technologies.
Whether used for small batch prototyping or high-volume mass production, automatic painting machines for tiny objects provide the precision, efficiency, and reliability essential to meet the stringent demands of today’s industries. Their combination of advanced automation, sophisticated spray technology, and intelligent process control makes them indispensable tools for delivering flawless coatings on miniature parts that contribute to overall product quality and performance.
As automatic painting machines for tiny objects continue to evolve, their integration with Industry 4.0 technologies becomes increasingly prominent, driving smarter, more connected manufacturing environments. Embedded sensors throughout the system constantly gather data on parameters such as paint flow rate, spray pattern consistency, environmental conditions, and part positioning. This data is analyzed in real time using advanced algorithms and machine learning models to optimize the painting process, anticipate potential issues, and maintain the highest coating quality standards.
Digital twin technology allows manufacturers to create virtual models of their painting lines, enabling simulation and testing of process adjustments without halting production. This predictive capability reduces setup times and increases process robustness. Furthermore, remote monitoring and control capabilities enable experts to oversee operations and troubleshoot issues from anywhere, minimizing downtime and accelerating response times.
Collaborative robots (cobots) are increasingly used in these machines to enhance flexibility and safety. Working alongside human operators, cobots can perform delicate tasks such as precise part handling, selective painting, or multi-stage coatings with high repeatability. Vision-guided systems combined with AI enhance defect detection and part orientation, ensuring consistent results and reducing waste.
Innovations in coating materials further enhance the capabilities of these machines. Environmentally friendly waterborne, UV-curable, and low-VOC paints provide durable, high-performance finishes while minimizing environmental impact. Machines are engineered to handle these advanced coatings efficiently, ensuring proper application and curing.
Energy efficiency is prioritized through the use of low-energy curing technologies such as LED-UV lamps and infrared heaters with zoned temperature control. Heat recovery systems and optimized airflow reduce power consumption and operational costs, supporting sustainability goals.
Operator interfaces have become more intuitive and supportive, incorporating touchscreen controls, customizable displays, and augmented reality (AR) tools that assist in training, maintenance, and troubleshooting. These features reduce errors, shorten learning curves, and help maintain consistent production quality.
Modular designs offer scalability and adaptability, allowing manufacturers to tailor paint lines to specific product requirements and production volumes. Additional modules for pre-treatment, masking, multi-layer coatings, or post-coating inspections can be integrated seamlessly, facilitating rapid changeovers and supporting diverse product portfolios.
Seamless integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software ensures comprehensive production tracking, quality management, and supply chain coordination. This connectivity enables lean manufacturing, traceability, and just-in-time delivery.
In industries where miniature parts must meet exacting standards—such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics—automatic painting machines for tiny objects deliver the precision, efficiency, and reliability necessary to produce flawless, durable coatings. By combining cutting-edge automation, advanced spray technologies, and smart process control, these machines play a critical role in modern manufacturing, helping companies stay competitive while meeting environmental and regulatory demands.
Miniature Part Painting Equipment
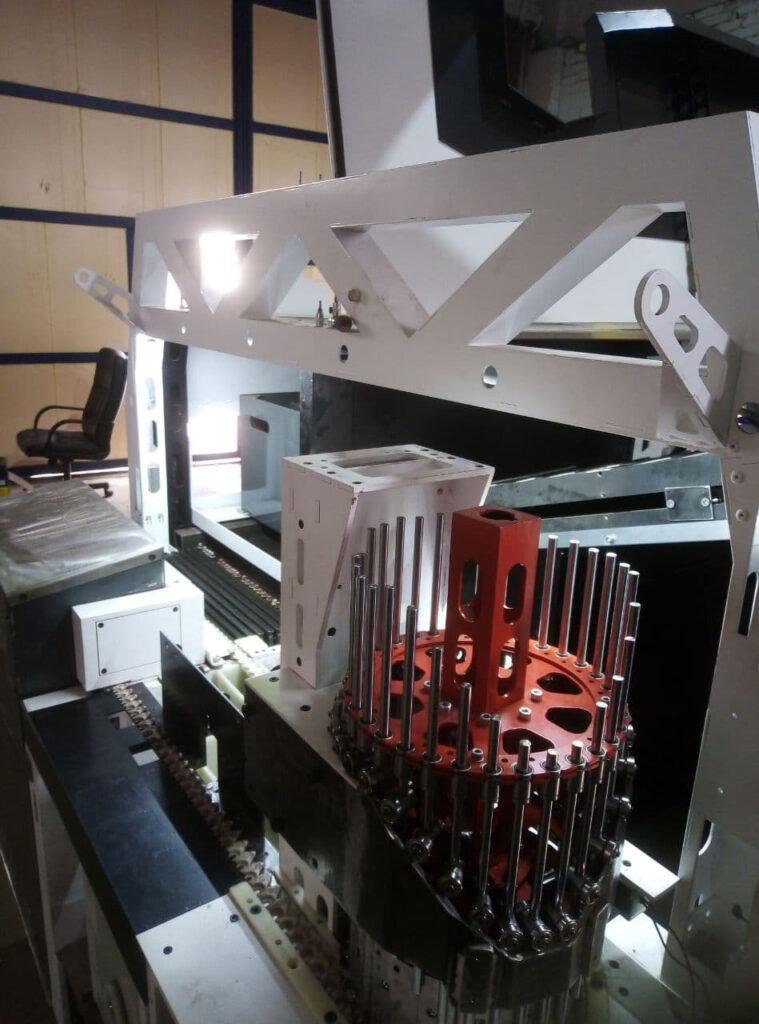
Miniature part painting equipment is precision-engineered to deliver highly uniform and controlled coatings on very small components used across industries like electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and precision instruments. As the demand for miniaturized and complex parts increases, these machines have become vital to ensure that even the tiniest surfaces receive consistent, durable finishes without compromising detail, quality, or throughput.
At the heart of miniature part painting equipment is a carefully designed handling system that accommodates the fragility and small size of the parts. Vibratory bowls, rotary baskets, indexing tables, and precision conveyors are commonly used to keep parts moving in a stable, non-abrasive environment. This constant, smooth motion ensures that all surfaces are evenly exposed during the spraying phase, which is critical for uniform coating distribution. Many systems include fixtures or nests to securely hold parts in the optimal orientation, while others use tumbling or rotation to guarantee complete coverage from all angles.
Paint application technologies used in these systems are tailored to handle fine detail and tight tolerances. Electrostatic spray guns are widely adopted due to their ability to charge paint particles, ensuring efficient adhesion to grounded metal parts and reducing material waste. For non-metallic or heat-sensitive components, HVLP (high-volume, low-pressure) or ultrasonic atomization methods may be employed to achieve ultra-fine droplet sizes that form thin, consistent films without flooding or pooling. These advanced spraying methods allow precise control over layer thickness, surface smoothness, and finish quality.
Curing or drying stations are integrated seamlessly into these machines, using methods like infrared heating, UV curing, or low-temperature convection drying, depending on the part material and coating chemistry. These curing systems are designed to work quickly and uniformly without damaging miniature parts, ensuring the paint hardens properly to deliver the desired mechanical, chemical, and visual characteristics. In sensitive applications—like electronics or medical instruments—rapid, low-heat curing is especially important to avoid deformation or performance degradation.
Miniature part painting equipment is often fully automated and run by programmable logic controllers (PLCs) with recipe management systems. Operators can program specific parameters for different parts or coating types, including spray time, air pressure, part speed, temperature, and more. These systems reduce human error and ensure repeatable results across long production runs. With the help of touchscreens and intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs), operators can monitor process variables, receive error alerts, and perform quick changeovers.
For quality control, many systems are equipped with in-line inspection stations that use high-resolution cameras, laser scanners, or optical sensors to detect coating defects like uneven thickness, drips, or uncovered surfaces. This allows real-time feedback and immediate rejection or correction, greatly reducing waste and improving overall yield.
Modern systems also incorporate sustainability features. Overspray recovery and recycling units capture unused paint for reuse, minimizing waste. Air filtration systems with HEPA or activated carbon filters ensure emissions are controlled, and compatibility with waterborne or low-VOC coatings supports eco-friendly production practices. Additionally, energy-efficient components such as LED-UV curing lamps and smart ventilation controls help reduce operating costs and environmental impact.
Scalability and flexibility are also key design considerations. These systems can be modular and customized to suit various production scales, from compact benchtop models for R&D and prototyping to high-speed, multi-station industrial lines for continuous mass production. Quick-change tooling and adjustable settings allow the same machine to handle a wide variety of part types, shapes, and sizes, supporting diverse product lines and reducing setup time between jobs.
In summary, miniature part painting equipment combines advanced part handling, precision spray technologies, efficient curing, and intelligent automation to meet the strict coating demands of small, detailed components. These systems enable manufacturers to achieve excellent finish quality, high process reliability, and low material waste—making them indispensable tools in the production of modern miniature parts across high-performance industries.
Miniature part painting equipment continues to advance in response to the growing complexity of parts and the demand for zero-defect quality. The systems now often incorporate robotics with multi-axis control that allows for exact spray gun positioning and dynamic adjustment to match intricate part geometries. These robotic arms can be taught or programmed using CAD data or vision systems to trace even the smallest features, resulting in extremely consistent finishes across high-volume production runs. This precision eliminates the inconsistencies that come with manual spraying and ensures each part is coated to the exact thickness required by design or regulatory standards.
Handling small parts efficiently requires not only delicate movement but also mechanisms that prevent surface damage, contamination, or misalignment. Automated loading and unloading modules are configured to pick and place components using soft grippers or vacuum suction, avoiding scratches or orientation errors. Some systems use nests machined to the exact shape of the part to hold items firmly during the process, while others utilize rotating platforms or tumbling baskets that gently agitate and expose the parts to uniform spray. These options can be easily swapped or adjusted, depending on the product, enabling rapid changeovers and batch customization.
The spraying process itself is finely tuned using digital controllers that govern air pressure, paint volume, nozzle aperture, and spray speed. These variables are monitored and adjusted automatically in closed-loop systems, compensating for viscosity changes, ambient conditions, or part geometry. This ensures high repeatability with minimal operator intervention. In some setups, dual or triple spray guns may be used simultaneously to apply primer, color, and topcoat in a single cycle, improving efficiency without sacrificing finish quality.
In-process monitoring has become more advanced, allowing miniature part painting equipment to detect anomalies as they occur. Cameras paired with AI-driven inspection software analyze each coated part for coverage completeness, thickness uniformity, gloss level, and potential flaws such as fisheyes, pinholes, or orange peel effects. Feedback from these inspections can immediately trigger process corrections or flag specific parts for rework or rejection, helping maintain extremely tight quality control tolerances and minimizing waste.
Energy consumption is another area where improvements have been made. The integration of low-energy UV curing, infrared lamps with zoned heating, and variable-speed ventilation systems reduces the environmental footprint of the equipment. Paint lines are increasingly equipped to handle waterborne and powder coatings, which further reduce volatile organic compound emissions. Advanced filtration units and recirculation systems ensure a clean working environment and minimize the release of hazardous materials, which is especially important in industries such as pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Operational interfaces are streamlined to make complex systems user-friendly. Touchscreen panels allow operators to select pre-loaded programs for different part types and initiate automatic cleaning cycles, maintenance prompts, or changeover steps. Augmented reality tools are being introduced for maintenance and training, overlaying real-time instructions on equipment via tablets or smart glasses to guide technicians through troubleshooting or part replacement. This improves uptime and reduces the need for specialized in-house expertise.
Scalability and modularity make miniature part painting equipment suitable for both small enterprises and large-scale manufacturers. A single system can be expanded with additional spraying stations, pre-treatment modules such as ionized air cleaning or plasma surface activation, or integrated with upstream and downstream automation like robotic sorting, packing, or labeling. This allows manufacturers to build flexible production cells that adapt easily to fluctuating order volumes, new part designs, or different finish requirements.
In sectors where coatings play a functional role—such as dielectric coatings in electronics, anti-corrosion layers in fasteners, or biocompatible coatings in surgical tools—the precision and repeatability of miniature part painting equipment are essential. These systems are not just about applying paint but about achieving a performance surface that affects how a product looks, behaves, and survives in its intended environment. As requirements continue to evolve, this equipment is designed to adapt—offering manufacturers a reliable, efficient, and highly controlled way to coat miniature parts at scale, without compromising quality or flexibility.
As demand continues to increase for products with miniaturized components—especially in electronics, medical devices, and micromechanical systems—manufacturers are turning to miniature part painting equipment not only for surface finishing but also for functional coating applications. These include ESD (electrostatic discharge) protective coatings, anti-microbial layers, conductive or insulating films, as well as wear-resistant or hydrophobic treatments. Applying such coatings to very small and detailed parts requires not only physical precision but also advanced process consistency, which this equipment delivers through high-end engineering and automation.
The ability to apply ultra-thin, uniform films becomes critical when tolerances are in the range of microns. High-resolution control over atomization, droplet trajectory, and electrostatic field strength ensures that even nano-coatings can be distributed evenly across complex micro-surfaces. In such cases, the choice of paint delivery system—whether needle-nozzle, diaphragm pump, or pressurized canister—can be tailored for specific flow characteristics and fluid behavior. Integration with real-time viscosity monitors ensures that each droplet behaves identically from the start of the run to the finish.
In addition to precision application, drying and curing systems have become increasingly compact and efficient. For example, miniature UV curing tunnels are now used to cure coatings within seconds, without affecting part dimensions or thermally sensitive substrates like plastics or composites. These UV systems are designed to emit in a controlled wavelength range tailored to specific photo-initiators in the coating material, ensuring full cure without overexposure. Infrared ovens and hybrid IR+air systems are also used to deliver consistent thermal profiles for coatings that require flash-off before full cure, avoiding bubbling, solvent popping, or surface dullness.
The integration of these curing systems directly into the paint line—either inline or in a carousel layout—ensures that parts pass through every stage of the process with minimal delay and without handling damage. For delicate parts that should not be touched post-painting, closed-loop transport systems with air levitation or contact-free carriers are sometimes employed, offering full automation from coating to packaging.
Miniature part painting equipment is also being enhanced by data-driven manufacturing practices. Machines now commonly generate detailed logs of production parameters for every part batch, including spray time, paint consumption, curing temperature, environmental conditions, and inspection outcomes. This traceability is particularly important in regulated industries such as aerospace and medical, where every component’s production history must be documented. The ability to link this data to serial numbers or QR codes on parts further supports end-to-end quality control.
Maintenance strategies have similarly benefited from digitalization. Sensors detect wear on spray nozzles, pressure fluctuations, filter saturation levels, and system diagnostics in real time, feeding into predictive maintenance dashboards. This ensures minimal unplanned downtime and extends the operational life of the machine. Self-cleaning mechanisms and automatic purging cycles reduce operator intervention, which is especially helpful when changing between different paint types or colors.
The versatility of miniature part painting equipment is what makes it particularly valuable in competitive and fast-changing industries. Whether coating a batch of 10,000 microfasteners, a series of custom medical pins, or prototype lots of nano-electronic casings, the same system can be configured to deliver precise results at scale. With tool-less changeovers, quick part-fixture swaps, and recipe-based automation, the machine can pivot from one application to the next with minimal waste or downtime.
As product designs grow smaller and more intricate, the need for flawless finishes at a miniature scale only becomes more critical. Whether the goal is aesthetic perfection, enhanced durability, or specialized functional performance, miniature part painting equipment provides the stability, repeatability, and precision that high-tech manufacturers rely on. It is no longer just a finishing solution—it is a vital part of the production process that enhances product value, ensures compliance, and supports future-ready manufacturing.
Precision Painting Equipment for Small Parts
Precision painting equipment for small parts is engineered to apply controlled, uniform coatings with extremely tight tolerances, often down to the micrometer level. This type of equipment is indispensable in sectors where even the slightest deviation in coating thickness, adhesion, or surface smoothness can affect the functionality, performance, or aesthetic quality of the product. Industries such as electronics, aerospace, optics, medical devices, defense, and precision mechanics rely heavily on these machines to produce consistent results across high volumes and intricate geometries.
These systems are designed from the ground up to meet the unique challenges posed by small parts, which often include tiny features, fragile structures, and the need for exact repeatability. At the core of precision painting equipment is an ultra-consistent spray system. Electrostatic guns, micro-nozzles, or piezoelectric atomizers are frequently used to create finely atomized droplets that distribute evenly over the smallest surfaces. These nozzles are capable of producing spray patterns tailored to tight zones, which is particularly important when parts have recessed areas, threads, sharp edges, or variable contours. Advanced electrostatic systems allow the coating to “wrap” around the part, improving coverage even in hard-to-reach areas.
To support this level of accuracy, the part handling system must be equally refined. Precision fixtures, custom nests, or rotary index tables are used to secure parts in a repeatable position throughout the coating process. Some machines use vacuum or magnetic holding methods, while others rotate or oscillate parts in multiple axes to ensure total coverage without excess buildup in any one area. These movements are often synchronized with the spray system, coordinated by programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and servo drives, ensuring each part is coated identically regardless of batch size.
Environmental control is another crucial aspect. Precision painting requires controlled temperature, humidity, and airflow to maintain coating consistency. Many systems operate within enclosed spray chambers or cleanroom environments to prevent dust contamination or variation in paint behavior. Air pressure, atomization level, paint temperature, and substrate temperature are all monitored in real time to prevent common defects such as orange peel, fisheyes, or overspray halos. Inline viscosity monitors and paint circulation systems help maintain consistency throughout long production runs.
Curing and drying processes are also highly specialized in this type of equipment. IR ovens, UV curing tunnels, and low-temperature convection systems are tailored to the specific needs of the parts and coatings used. The goal is to fully cure the coating without warping or damaging sensitive parts, many of which are made of heat-sensitive materials like thermoplastics or micro-machined metals. Zoned or programmable curing profiles allow different sections of the part to receive different amounts of heat or exposure, depending on their geometry or mass.
Quality assurance is fully integrated into the workflow. High-resolution cameras and laser-based thickness gauges provide inline inspection, checking each coated part for color consistency, surface texture, gloss level, and film thickness. Defective items can be automatically ejected or redirected for rework. This high level of inspection is especially important for parts used in safety-critical or performance-sensitive applications.
One of the hallmarks of modern precision painting systems is modularity and digital intelligence. These machines often include recipe management systems where process parameters for each part type—such as spray duration, gun distance, axis movement paths, and curing cycles—are saved and retrieved as needed. This enables fast changeovers and supports highly flexible production, where different parts are painted in small batches without compromising throughput or quality.
The trend toward smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 is well-represented in precision painting equipment. Sensors across the machine monitor everything from airflow and pump speed to gun wear and overspray recovery. This data is used for predictive maintenance, process optimization, and detailed traceability. Integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) platforms enables real-time production monitoring and synchronization with the broader factory environment.
Sustainability is also built into modern designs. High-efficiency filtration systems, low-VOC and waterborne paint compatibility, energy-efficient curing options, and paint reclaim technology all contribute to environmentally responsible production while maintaining strict coating performance.
In summary, precision painting equipment for small parts is a convergence of high-accuracy spraying, delicate yet reliable part handling, sophisticated environmental control, and intelligent automation. It provides manufacturers with the ability to apply functional and decorative coatings to intricate, high-value components with speed, efficiency, and consistency—qualities that are non-negotiable in today’s demanding production environments.
Precision painting equipment for small parts is continuously evolving, driven by the growing need for ultra-consistent coatings on increasingly complex miniature components. These systems are not limited to aesthetics—they play a crucial role in delivering functional properties like insulation, conductivity, UV resistance, chemical protection, and biocompatibility. As products become more compact and performance-focused, even the thinnest coating layer must be flawlessly applied, especially in high-stakes sectors such as aerospace avionics, implantable medical devices, and micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS).
To meet such high standards, today’s equipment leverages ultra-fine atomization technologies capable of generating microscopic droplets that settle into extremely smooth and even films. Piezoelectric micro-sprayers and advanced electrostatic guns with variable voltage control allow the paint to be applied in layers as thin as a few microns, without sacrificing coverage uniformity or adhesion. These sprayers are calibrated to work with specialty materials, including nano-additive coatings, metallic finishes, ceramic-based paints, or clear protective layers that demand non-reactive and ultra-precise delivery.
Handling these small parts during the process requires exceptional engineering. Fixtures are often custom-machined for a snug, secure fit that does not obscure paint access. In some cases, parts are loaded into high-precision indexing turrets that rotate at synchronized speeds with the spray application, enabling exact pattern alignment. For parts that must be coated 360 degrees without masking, systems may include gyroscopic rotation mechanisms or multi-axis robotic arms that manipulate the part continuously in front of a stationary or moving spray source. Some machines include built-in part flipping and repositioning systems to allow two-sided or complex geometry coverage in one pass.
Environmental integrity is controlled down to the finest detail. Many systems use Class 1000 or better cleanroom-grade enclosures to eliminate airborne particles. Pressurized cabins, laminar airflow, and anti-static grounding are used to protect both the product and coating consistency. These environments also allow paint systems to work with ultra-sensitive substrates that might otherwise attract dust or moisture, which could lead to coating defects or rejection under tight inspection protocols.
In high-volume operations, automation plays an essential role. Fully robotic painting lines feature coordinated systems where parts are picked, painted, cured, inspected, and sorted with minimal human contact. Advanced HMI platforms allow operators to load job files instantly, select predefined coating recipes, and oversee multiple machines through centralized dashboards. When integrated with artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, these systems can self-adjust based on part data, improving process efficiency and first-pass yield rates. For example, a vision system might detect a slight deviation in part shape or location and alter the spray path in real time to ensure the coating remains within specification.
Drying and curing techniques continue to improve to match the demands of delicate parts and specialized coatings. Rapid LED-UV curing is gaining popularity for heat-sensitive applications, offering instant film hardening without exposing parts to thermal stress. For coatings that require solvent flash-off before full cure, zoned convection systems with low-velocity, high-efficiency airflow ensure solvent removal without turbulence. For hybrid applications—such as parts requiring a conductive base coat and a dielectric top layer—multi-stage curing tunnels with precisely tuned temperatures and time delays allow both layers to reach full cure without compromising either’s performance.
Inspection and metrology systems are just as critical as the application tools themselves. In-line quality control now uses high-resolution line-scan cameras, laser triangulation, and spectral imaging to detect flaws invisible to the naked eye. These systems analyze gloss levels, coating depth, surface roughness, and color accuracy while parts are still in motion, reducing bottlenecks and operator dependency. In regulated industries, full traceability is achieved by assigning barcodes or RFID tags to every part or tray, linking coating data with batch records and audit logs.
The flexibility of modern precision painting equipment also extends to materials and coating types. Whether it’s waterborne, solvent-based, epoxy, polyurethane, or functional nano-coatings, modern machines are built with material compatibility in mind. Paint delivery systems with inert construction materials, anti-settling agitation systems, and closed-loop pressure control allow manufacturers to run a wide variety of coating chemistries without cross-contamination or degradation of material properties.
Altogether, the integration of ultra-fine spray technology, intelligent automation, precise part handling, controlled environments, and real-time inspection defines the future of small-part precision painting. These systems make it possible to meet the ever-increasing demands for miniaturization, performance, and consistency. For manufacturers, investing in this equipment is not just a quality decision—it’s a competitive strategy that ensures capability in high-precision markets, supports faster product cycles, and aligns with the global shift toward zero-defect manufacturing.
As the expectations for precision and reliability continue to rise across advanced manufacturing sectors, precision painting equipment for small parts is becoming even more adaptive, data-driven, and tightly integrated into larger production ecosystems. A growing focus on digitalization allows these systems to function not just as isolated workstations but as key nodes within a fully connected smart factory. With real-time data streaming from every subsystem—spray units, conveyors, curing ovens, and inspection modules—manufacturers can monitor, analyze, and optimize every part of the painting process continuously.
Edge computing and AI-based analytics are being deployed to process this data locally, enabling immediate decision-making on the shop floor. For example, if a spray nozzle begins to drift out of specification or a curing zone develops a temperature imbalance, the system can detect the trend, issue alerts, or even self-correct without stopping production. These predictive capabilities reduce downtime, prevent batch rejections, and ensure consistent throughput. When connected to centralized data platforms, this information also supports long-term process improvements and robust documentation for quality audits.
Customizability has also become a major design feature of modern systems. A single precision painting line can now be configured to switch between different product geometries, coating types, or curing methods with minimal manual intervention. This is achieved through the use of modular spray heads, quick-release part fixtures, and reprogrammable movement patterns. Automated tool changers allow spray nozzles or masks to be swapped mid-cycle, while recipe-driven software handles transitions between coating stages or product models. This versatility supports high-mix, low-volume production models that are increasingly common in aerospace components, luxury electronics, and medical device prototyping.
In some systems, augmented reality (AR) interfaces are being introduced for enhanced user interaction. With AR-enabled tablets or smart glasses, operators and technicians can receive overlay instructions directly onto machine components, guiding them through maintenance procedures, part loading configurations, or troubleshooting routines. These tools significantly reduce training times, improve safety, and increase first-time-right setup success, particularly in factories where skilled labor is limited or turnover is high.
Sustainability continues to shape equipment development as well. As environmental regulations tighten globally, especially regarding emissions and chemical usage, precision painting systems are designed with closed-loop air handling, solvent recovery, and material recycling capabilities. Energy-efficient servo motors, insulated curing chambers, and smart standby modes reduce power consumption during idle times without slowing the process restart. In addition, many manufacturers now specify low-VOC, waterborne, or powder-based coating systems, and precision painting equipment is built to handle these with the same degree of accuracy as traditional solvent-based materials.
Collaboration between machine manufacturers and paint formulators is also becoming more common, ensuring that application technology is precisely matched to the chemistry of the coatings being used. This synergy results in shorter development cycles for new products, better control of specialized materials like UV-fluorescent or conductive coatings, and tighter performance tolerances for advanced finishes such as anti-fingerprint, hydrophobic, or thermal-barrier coatings.
Ultimately, the value of precision painting equipment for small parts lies in its ability to apply perfect coatings, consistently and efficiently, on the most delicate and complex items in modern manufacturing. Whether it’s a miniature surgical implant, a sensor housing for an autonomous vehicle, or a connector in a high-density circuit board, these parts often represent a critical failure point if improperly coated. The equipment that handles them must therefore perform with unmatched accuracy, built-in intelligence, and the flexibility to adapt to tomorrow’s manufacturing challenges. This is why the future of precision painting is not just about better finishes—it’s about integrated performance, total process control, and the seamless coordination of quality, speed, and sustainability in one compact, intelligent system.
Small Item Painting Machines
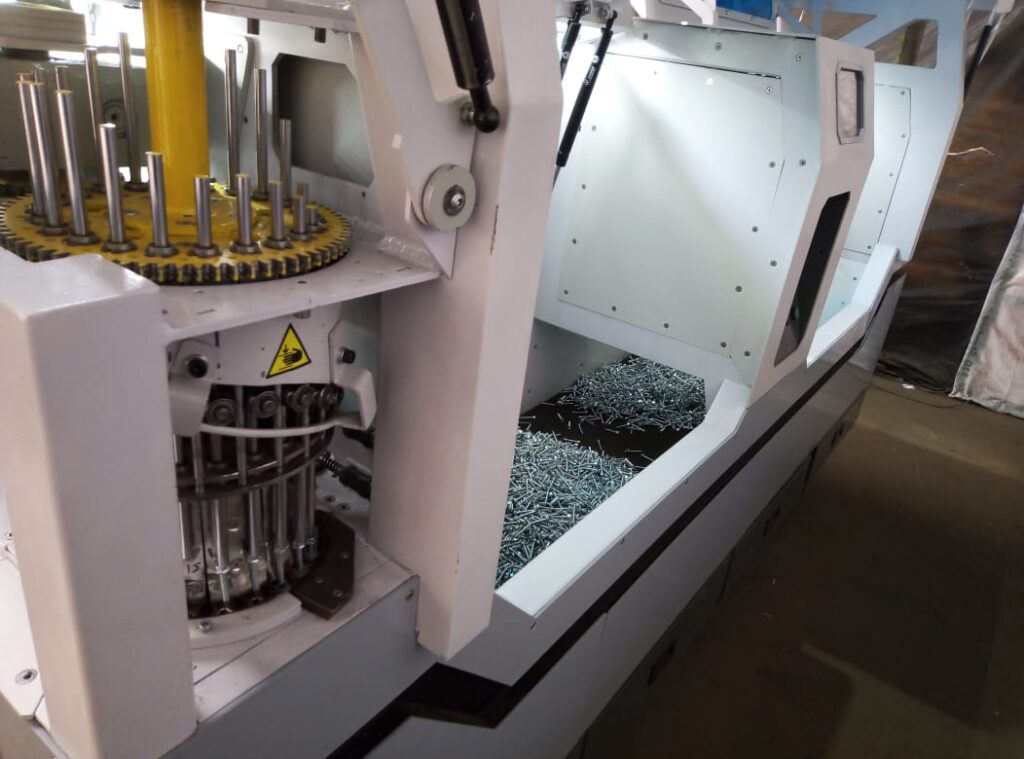

Small item painting machines are specialized systems designed to apply coatings efficiently and uniformly on objects of limited size, ranging from tiny mechanical parts and fasteners to miniature electronics housings and decorative items. These machines serve industries such as electronics manufacturing, automotive components, jewelry, toys, medical devices, and precision instruments, where high-quality surface finishes on small-scale parts are essential for both aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
The core advantage of small item painting machines lies in their ability to handle delicate, intricate parts with precision and care. To accomplish this, these machines are equipped with advanced part handling mechanisms such as vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, or precision conveyor systems that gently orient and transport components through the painting process. By continuously agitating or rotating the parts, the machines ensure complete and even coverage on all surfaces without causing damage or surface defects.
Spray application technologies in these machines include electrostatic spraying, HVLP (high volume low pressure) systems, ultrasonic atomization, and micro-jet spraying. Electrostatic spraying is particularly effective for metal parts, as it charges paint particles to attract them toward grounded components, enhancing transfer efficiency and minimizing overspray. Ultrasonic and micro-jet technologies allow for extremely fine atomization of coating materials, enabling smooth, thin layers that are crucial for small parts with complex geometries.
The painting chamber is designed to maintain consistent environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and airflow to ensure the paint behaves predictably and cures properly. Integrated filtration systems remove overspray and airborne particles, protecting operators and maintaining a clean work environment in compliance with safety regulations.
Drying and curing modules vary depending on the coating type and substrate material. Infrared heaters, UV curing lamps, and convection ovens are commonly employed to rapidly fix the paint layer without exposing sensitive parts to damaging heat levels. These systems are carefully calibrated to balance speed and finish quality, reducing cycle times while avoiding defects like blistering or discoloration.
Automation and control are key components of modern small item painting machines. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) enable operators to set and monitor parameters such as spray duration, conveyor speed, curing temperature, and paint flow rate. Recipe management capabilities allow quick changeovers between different part types or coating specifications, improving production flexibility and reducing downtime.
Quality assurance is often integrated into these machines through inline inspection systems. Cameras, laser scanners, and optical sensors detect coating defects such as uneven thickness, color inconsistencies, or missed areas, allowing immediate process adjustments or rejection of defective parts. This helps maintain high yield rates and minimizes waste.
Sustainability considerations are increasingly important in small item painting machines. Features like paint recovery and recycling systems, low-VOC or waterborne paint compatibility, and energy-efficient curing technologies reduce environmental impact and operational costs. Closed-loop filtration and ventilation systems further support workplace safety and regulatory compliance.
Modular design principles enable these machines to be tailored for a range of production volumes and part complexities. From compact benchtop models for prototyping and small batch production to fully automated, high-throughput lines for mass manufacturing, small item painting machines offer scalability and customization. Optional add-ons such as pre-treatment stations, masking modules, multi-stage coating capabilities, and post-paint inspection units enhance versatility.
In summary, small item painting machines combine gentle, precise handling with advanced spray technologies and intelligent automation to deliver consistent, high-quality coatings on miniature and delicate components. They play a vital role in modern manufacturing by ensuring that small parts meet exacting aesthetic and functional requirements while optimizing efficiency, sustainability, and overall production performance.
Small item painting machines continue to evolve in sophistication, driven by the need for faster production rates, higher precision, and greater process reliability. One key advancement is the integration of robotic automation, where multi-axis robotic arms provide unparalleled control over spray positioning and movement. These robots can adapt spray angles and distances in real time, ensuring even coverage on complex geometries, including recessed areas and sharp edges that traditional fixed spray nozzles might miss. This adaptability reduces paint consumption, minimizes overspray, and enhances finish consistency across large production batches.
Material handling systems are also becoming more refined to accommodate a wide variety of small parts with differing shapes, weights, and fragility levels. Techniques such as vibratory feeders gently move parts into position without causing surface damage, while rotary tumblers and cushioned conveyors ensure continuous exposure of all surfaces to the coating spray. Advanced vision systems combined with robotic pick-and-place mechanisms can orient parts optimally before painting, reducing rejects and improving coating uniformity.
Spray technologies themselves are improving with innovations like ultrasonic atomization, which produces extremely fine droplets for ultra-smooth coatings, and enhanced electrostatic systems that precisely control charge levels to maximize transfer efficiency. These improvements lead to better adhesion, reduced environmental emissions, and lower paint waste. Environmental controls within the painting chamber maintain stable temperature and humidity, critical for consistent paint behavior and curing, while sophisticated filtration units capture airborne particulates and volatile compounds to safeguard worker health and meet stringent regulatory standards.
Drying and curing technologies integrated into small item painting machines have also advanced significantly. Infrared ovens, LED-UV curing lamps, and convection drying systems are optimized to quickly and evenly cure coatings without harming heat-sensitive parts. Zoned heating and precise temperature controls prevent defects like blistering, cracking, or discoloration, ensuring durable and attractive finishes. Energy-efficient designs reduce power consumption and contribute to sustainable manufacturing goals.
Automation and intelligent control systems are at the core of these machines’ enhanced capabilities. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) coordinate every step of the painting process, from part loading and spray sequencing to curing and inspection. Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) offer intuitive touchscreens that simplify setup, monitoring, and troubleshooting, while recipe management features enable rapid changeovers and consistent process replication. Data logging and connectivity support integration with broader manufacturing execution systems (MES), facilitating real-time production tracking, quality assurance, and maintenance scheduling.
Quality control is increasingly embedded directly within painting lines through in-line inspection technologies. High-resolution cameras, laser thickness gauges, and spectral analyzers scan parts immediately after coating to detect defects such as uneven application, color inconsistencies, or surface imperfections. These systems provide instant feedback, allowing automatic process adjustments or sorting out non-conforming parts before they move further down the production line, reducing waste and ensuring high first-pass yield.
Sustainability remains a key focus, with small item painting machines incorporating paint reclaim systems that capture and recycle overspray, reducing material consumption and environmental impact. Compatibility with low-VOC and waterborne paints supports cleaner operations, while efficient curing and airflow designs lower energy use. Enclosed booths and advanced filtration systems protect operators and surrounding environments from exposure to hazardous emissions.
The modular and scalable architecture of these machines allows manufacturers to customize lines to their precise needs. Whether outfitted as compact benchtop units for prototype or small batch runs or as fully automated, high-throughput production cells, small item painting machines can be configured with additional modules such as pre-treatment, masking, multiple coating stages, or advanced inspection systems. This flexibility helps manufacturers respond quickly to changing product portfolios and market demands.
Ultimately, small item painting machines combine precision engineering, advanced spray technologies, robust automation, and environmentally conscious design to meet the complex challenges of coating miniature components. Their ability to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes efficiently makes them essential in today’s manufacturing landscape, where product quality, process speed, and sustainability are more critical than ever.
Small item painting machines are also increasingly designed with connectivity and smart features that align with Industry 4.0 principles. Integrated sensors and IoT-enabled devices continuously monitor critical parameters such as spray pressure, paint viscosity, environmental conditions, and part positioning. This data is transmitted in real time to centralized dashboards, enabling operators and engineers to track machine performance, identify trends, and make proactive adjustments that optimize throughput and maintain consistent coating quality.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are beginning to play a role in predictive maintenance and process optimization within these machines. By analyzing historical and real-time data, the system can forecast when components like spray nozzles, pumps, or filters require servicing or replacement before failures occur. This predictive approach reduces unplanned downtime and extends equipment life, contributing to higher overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
The user experience is enhanced through advanced human-machine interfaces (HMIs) that provide intuitive control panels with customizable views and alerts. Operators can easily switch between preprogrammed painting recipes, adjust parameters on the fly, and receive guided troubleshooting instructions. Augmented reality (AR) tools are being introduced in some systems to assist maintenance personnel by overlaying step-by-step repair instructions directly onto machine components via smart glasses or tablets, reducing training time and minimizing errors.
In addition to coating metals and plastics, small item painting machines are increasingly adapted to apply specialized functional coatings. These include conductive inks for printed electronics, anti-microbial finishes for medical devices, hydrophobic or oleophobic layers for consumer products, and thermal barrier coatings for aerospace components. The versatility to handle diverse coating materials without compromising precision expands the range of applications and industries these machines serve.
Environmental sustainability continues to shape the evolution of small item painting equipment. Paint recycling and solvent recovery systems reduce material waste, while energy-efficient curing technologies minimize power consumption. Machines are often designed with enclosed booths and advanced filtration to limit VOC emissions and protect operator health. Many manufacturers also prioritize the use of waterborne and low-VOC paints, supported by equipment optimized for these environmentally friendly materials.
Customization and scalability are key features that enable manufacturers to tailor painting solutions to their specific production needs. Modular designs allow additional stations or functions—such as pre-cleaning, masking, multi-layer coating, and post-coating inspection—to be added or removed without extensive reconfiguration. This flexibility supports rapid product changeovers and mixed-model production, critical in markets where agility and responsiveness provide competitive advantages.
Ultimately, small item painting machines represent a convergence of precision engineering, automation, environmental stewardship, and smart technology integration. By delivering flawless coatings on tiny, complex parts with speed and reliability, these machines empower manufacturers to meet stringent quality standards, reduce costs, and innovate product offerings. As manufacturing trends continue toward miniaturization, customization, and sustainability, small item painting machines will remain at the forefront of surface finishing technology, driving productivity and quality improvements across diverse industries.
Automated Painting Machine for Tiny Metal Parts
Automated painting machines for tiny metal parts are specialized systems engineered to deliver precise, consistent, and efficient coating application on small-scale components commonly used in industries such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and precision engineering. These machines address the unique challenges posed by miniature metal parts, including complex geometries, delicate surfaces, and strict quality requirements, by combining advanced automation, precise spray technologies, and intelligent process control.
At the core of these machines is a sophisticated handling system designed to gently manage tiny metal parts without causing surface damage or misalignment. Vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, cushioned conveyors, and precision indexing tables are often employed to orient and transport parts smoothly through the painting process. Many systems integrate robotic arms equipped with vision-guided pick-and-place capabilities that enable accurate loading, positioning, and manipulation of parts to ensure full surface exposure during coating.
Spray technology is carefully selected and optimized for tiny metal parts. Electrostatic spray guns are commonly used because they charge paint particles to improve adhesion and reduce overspray, maximizing transfer efficiency. Ultrasonic atomizers and micro-jet spraying techniques create ultra-fine droplets that achieve uniform, thin coatings essential for maintaining tight tolerances on small components. The spray parameters—such as nozzle size, air pressure, and voltage—are digitally controlled to adapt to part shape and size, ensuring consistent coverage without runs, drips, or defects.
Environmental controls within the painting chamber maintain stable temperature, humidity, and airflow, creating ideal conditions for paint application and curing. Advanced filtration systems capture overspray and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), protecting both product quality and operator health while complying with environmental regulations.
Drying and curing stations are seamlessly integrated into the automated line. Technologies such as infrared (IR) ovens, LED-UV curing lamps, and convection dryers provide rapid, uniform curing tailored to the paint type and substrate sensitivity. Zoned heating and programmable curing profiles prevent defects like blistering or cracking while minimizing cycle times to boost throughput.
Automation is governed by programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and managed through intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs) that allow operators to easily set, monitor, and adjust parameters. Recipe management systems store specific coating protocols for different parts, enabling fast changeovers and repeatable quality across production batches. Data logging and connectivity options support integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) for traceability and process optimization.
Inline inspection systems employing high-resolution cameras, laser thickness gauges, and optical sensors verify coating integrity immediately after application. These systems detect defects such as uneven coverage, color variations, or surface imperfections, enabling real-time process adjustments or automatic rejection of non-conforming parts, thereby enhancing yield and reducing waste.
Sustainability features are increasingly incorporated, including paint recovery and recycling units, compatibility with low-VOC and waterborne coatings, and energy-efficient curing technologies. Enclosed booths with advanced air handling and filtration minimize emissions and maintain clean working conditions.
Modular and scalable designs allow manufacturers to configure automated painting machines according to production volume and complexity. Optional modules for pre-treatment, masking, multi-layer coating, and post-paint inspection can be added to meet specific process requirements.
In summary, automated painting machines for tiny metal parts combine precise part handling, advanced spray technologies, intelligent automation, and environmental control to deliver high-quality, consistent coatings efficiently. These systems are vital for manufacturers aiming to meet stringent quality standards, improve productivity, and reduce environmental impact in the production of miniature metal components.
Automated painting machines for tiny metal parts are designed to meet the increasing demands for speed, accuracy, and repeatability in modern manufacturing environments. Their automation capabilities significantly reduce manual labor, minimize human error, and ensure consistent application of coatings across high-volume production runs. By integrating robotics and programmable systems, these machines can handle thousands of parts per hour, maintaining uniform quality even as part complexity and size shrink.
The handling and transport mechanisms are engineered to be both gentle and precise. Soft-touch grippers, vacuum-based pick-and-place devices, and custom-designed nests securely hold parts without scratching or deforming them. These systems ensure that each tiny metal piece is presented to the spray nozzles at the optimal angle and distance, which is critical for achieving full coverage without waste. Some machines use continuous tumbling action combined with synchronized spraying to coat irregularly shaped parts uniformly.
Spray technology is often complemented by electrostatic charging, which enhances paint transfer efficiency by causing charged paint particles to be attracted to grounded metal parts. This process not only improves coating uniformity but also significantly reduces overspray and paint consumption, making it both economically and environmentally beneficial. Advanced controllers adjust electrostatic parameters dynamically to suit variations in part geometry and material, ensuring consistent finish quality.
Precision control extends to the paint delivery system, where pumps and valves maintain exact flow rates and pressure levels. Closed-loop feedback systems monitor variables such as paint viscosity, spray pattern shape, and droplet size, automatically adjusting settings in real time to maintain process stability. This tight control is essential for preventing common defects like runs, sags, or dry spray, which are especially problematic on small parts.
Environmental control within the painting area includes filtered air supply, exhaust systems with VOC capture, and temperature/humidity regulation. These features help maintain the optimal conditions required for different paint chemistries and part materials, reducing variability and ensuring that coatings cure properly. Safety interlocks and enclosed booths protect operators from exposure to harmful fumes and particulates.
Curing processes integrated into these automated lines are designed to be efficient and gentle. LED-UV curing systems provide rapid polymerization of UV-sensitive coatings at low temperatures, preventing heat damage to small metal parts. Infrared and convection ovens are also used with programmable zones to accommodate varied curing requirements across part surfaces. Some machines incorporate inline cooling stations to bring parts to handling temperature quickly after curing, speeding up overall throughput.
Data management is a key aspect of these automated systems. Each production cycle’s parameters, including spray settings, environmental conditions, and inspection results, are recorded and stored for traceability. This capability is crucial in regulated industries where documentation is required for quality assurance and compliance audits. Integration with factory-wide digital systems allows real-time monitoring and analytics, supporting continuous improvement initiatives.
Inline quality inspection tools use high-resolution imaging, laser measurement, and spectral analysis to assess coating thickness, uniformity, and appearance immediately after painting. Defects are detected with high sensitivity, enabling automated rejection or rerouting for rework before parts proceed to subsequent manufacturing stages. This real-time feedback loop minimizes waste and ensures only parts meeting stringent standards continue through production.
Sustainability considerations are increasingly embedded in machine design. Paint recovery systems capture overspray and reclaim material for reuse, reducing waste and lowering costs. Energy-efficient curing methods and smart ventilation controls contribute to lower power consumption. Compatibility with environmentally friendly coatings like waterborne and low-VOC paints aligns these machines with global efforts to reduce industrial environmental impact.
The modularity of automated painting machines for tiny metal parts allows manufacturers to scale production or add functionality as needed. Optional modules such as pre-treatment cleaning, masking for selective coating, multi-layer paint application, and advanced inspection units can be integrated seamlessly. This flexibility supports evolving production requirements and rapid adaptation to new part designs or regulatory demands.
In essence, automated painting machines for tiny metal parts deliver a comprehensive solution that combines gentle part handling, precise spray application, intelligent control, and environmental stewardship. Their ability to provide consistent, high-quality finishes on complex miniature components makes them indispensable tools for manufacturers striving to maintain competitive advantage in sectors demanding exacting standards and efficient, sustainable production processes.
Automated painting machines for tiny metal parts are also increasingly incorporating advanced robotics and artificial intelligence to push the boundaries of precision and efficiency. Robotics arms equipped with multi-axis movement and force-feedback sensors allow for dynamic adjustment during the coating process, ensuring optimal spray angles and distances even as part geometries vary subtly between batches or within complex assemblies. This adaptability reduces the need for manual intervention and shortens setup times when switching between different part types.
Artificial intelligence algorithms analyze real-time data from sensors monitoring paint flow, environmental conditions, and part position to predict and correct deviations before defects occur. Machine learning models trained on historical process data help optimize parameters such as spray velocity, nozzle oscillation frequency, and curing time, leading to improved coating uniformity and reduced material waste. These smart systems can also detect early signs of equipment wear or malfunction, enabling predictive maintenance that minimizes unexpected downtime.
Integration with other automated production systems is becoming standard. Automated painting lines communicate seamlessly with upstream part feeders, robotic assembly stations, and downstream inspection or packaging units through industrial communication protocols. This connectivity supports synchronized workflows, allowing the entire production process to run smoothly and efficiently with minimal human oversight.
User interfaces are evolving toward more intuitive, user-friendly designs featuring touchscreen controls, customizable dashboards, and remote access capabilities. Operators can monitor machine status, adjust parameters, and receive alerts from mobile devices or computers, enabling faster response times and better resource management. Virtual training modules and augmented reality tools enhance operator skill development and maintenance procedures, reducing errors and improving overall equipment effectiveness.
The materials handled by these machines are also diversifying. Beyond traditional solvent-based paints, automated painting systems now accommodate advanced coatings such as conductive inks for printed electronics, biocompatible finishes for medical implants, corrosion-resistant layers for aerospace fasteners, and functional coatings like hydrophobic or anti-fingerprint treatments. Equipment is engineered with flexible delivery systems and corrosion-resistant components to handle these specialized materials without cross-contamination or degradation.
Sustainability remains a core focus, with many automated painting machines incorporating closed-loop solvent recovery systems, high-efficiency particulate filters, and energy-saving curing technologies. The adoption of waterborne and UV-curable coatings reduces environmental impact while maintaining or enhancing coating performance. Manufacturers benefit from lower operating costs and compliance with increasingly strict environmental regulations.
Customization and modularity continue to drive equipment design. Manufacturers can select from a range of options—such as pre-treatment modules including ultrasonic cleaning or plasma activation, selective masking stations, multi-layer coating capabilities, and integrated inline inspection—to build systems tailored precisely to their product mix and production volumes. This flexibility supports rapid innovation and quick adaptation to evolving market demands.
Ultimately, automated painting machines for tiny metal parts represent the convergence of precision engineering, advanced automation, intelligent process control, and sustainable manufacturing practices. Their ability to consistently produce high-quality coatings on delicate, complex components at scale makes them indispensable in industries where product reliability, appearance, and functionality are paramount. As technology advances, these machines will continue to evolve, enabling manufacturers to meet the challenges of tomorrow’s increasingly miniaturized and sophisticated products with confidence and efficiency.
Auto Powder Coating Line for Tiny Goods
Auto powder coating lines for tiny goods are specialized manufacturing systems designed to apply durable, uniform powder coatings efficiently to small-scale items such as miniature metal parts, fasteners, electronic components, and delicate hardware. These lines are engineered to meet the unique challenges posed by tiny goods—including their intricate shapes, high volume requirements, and strict quality standards—by combining automated handling, precise powder application, and optimized curing processes.
At the heart of these lines is a carefully designed part handling system capable of gently and accurately transporting small goods through each stage of the powder coating process. Vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, precision conveyors, and robotic pick-and-place units orient and move parts with minimal risk of damage or contamination. This handling ensures each item is fully exposed to the powder spray and maintains proper spacing to prevent clumping or shadowing during coating.
Powder application typically uses electrostatic spray guns that charge powder particles, causing them to be attracted to grounded metal parts. This electrostatic effect enhances transfer efficiency and provides uniform coverage even on complex geometries, including recessed areas and sharp edges. For tiny goods, specialized nozzles and powder delivery systems are employed to produce fine, controlled powder clouds that minimize waste and ensure thin, even layers without buildup.
Automated powder coating lines integrate sophisticated control systems to manage parameters such as powder flow rate, spray voltage, booth air pressure, and gun positioning. These systems dynamically adjust settings based on part size, shape, and batch requirements, ensuring consistent coating quality across varied production runs. Powder recovery and recycling units capture overspray powder for reuse, reducing material costs and environmental impact.
Following application, parts pass through curing ovens designed to evenly melt and fuse the powder into a tough, continuous coating. Infrared or convection curing ovens with zoned temperature control provide precise thermal profiles tailored to the powder chemistry and substrate material. For tiny goods, the ovens are engineered to maintain gentle heating rates to prevent part distortion or damage while ensuring complete curing in short cycle times.
Environmental controls are critical throughout the line. Enclosed spray booths with high-efficiency filtration systems maintain clean air and capture airborne powder particles, protecting worker health and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Temperature and humidity controls within the curing area optimize powder flow and film formation, contributing to defect-free finishes.
Automation and data integration play key roles in modern auto powder coating lines. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) enable operators to monitor and adjust process parameters, manage recipe storage for different products, and track production metrics. Integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) facilitates traceability, quality control, and real-time reporting.
Inline inspection systems are often incorporated to detect coating defects such as uneven coverage, pinholes, or excessive buildup immediately after curing. High-resolution imaging and laser measurement tools provide fast, non-contact quality assessments, enabling rapid process corrections or sorting of defective parts before packaging or further assembly.
The modular design of auto powder coating lines for tiny goods allows manufacturers to scale capacity and customize configurations according to product complexity and volume. Optional features such as pre-treatment cleaning stations, masking units for selective coating, multi-stage coating booths, and advanced curing tunnels can be added or removed as needed to optimize workflow and accommodate product variations.
Sustainability is a core consideration in these systems. Powder coatings are inherently low in volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and powder recovery systems further minimize waste. Energy-efficient curing technologies and smart airflow management reduce power consumption, aligning with environmental regulations and corporate responsibility goals.
Overall, auto powder coating lines for tiny goods provide manufacturers with a reliable, high-throughput solution for producing durable, attractive, and consistent finishes on miniature parts. Their combination of precise automation, advanced powder application technology, and integrated quality controls make them indispensable in industries demanding excellence in both appearance and performance at a small scale.
Auto powder coating lines for tiny goods continue to advance as manufacturers seek faster production speeds, improved coating quality, and greater process flexibility. One significant development is the integration of robotics and automated material handling, which enhances precision and reduces human intervention. Robotic arms equipped with vision systems can identify, pick, and orient individual parts with exceptional accuracy, ensuring optimal exposure to powder spray and reducing the risk of damage or misplacement.
Powder delivery systems have also evolved to handle the specific demands of tiny goods. Precision pumps and flow controllers regulate powder feed rates, maintaining consistent spray density even at high speeds. Specialized spray guns with adjustable nozzles create finely atomized powder clouds tailored to the size and shape of each part, minimizing overspray and promoting uniform coating thickness. Electrostatic charging parameters are dynamically adjusted by advanced control systems to maximize powder adhesion while conserving material.
The curing ovens incorporated into these lines are designed to offer both efficiency and gentle handling. Zoned temperature controls and programmable conveyor speeds allow for customized thermal profiles that cater to sensitive substrates and complex part geometries. Some lines feature compact, fast-heating infrared ovens that reduce overall cycle time without compromising coating integrity or part quality. Inline temperature sensors monitor curing conditions in real time, enabling rapid adjustments to maintain optimal performance.
Environmental safety and cleanliness remain priorities throughout the powder coating process. Enclosed spray booths with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration systems capture airborne powder particles, protecting operators and preventing contamination. Airflow within booths is carefully managed to prevent turbulence that could cause uneven coating or powder buildup. Reclaimed powder is collected through cyclones or electrostatic precipitators and recycled back into the system, reducing waste and lowering operational costs.
Automation software plays a crucial role in synchronizing all components of the powder coating line. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) coordinate conveyors, spray guns, powder feeders, and curing ovens to maintain smooth, uninterrupted operation. Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide operators with real-time data visualization, alarm notifications, and recipe management tools that simplify setup and ensure repeatable quality. Data collected throughout the process supports traceability and facilitates compliance with quality standards.
Quality assurance is enhanced through inline inspection technologies that scan coated parts immediately after curing. High-resolution cameras, laser scanners, and thickness gauges detect defects such as pinholes, uneven coverage, or excessive buildup, allowing immediate corrective actions. Defective parts are automatically diverted for rework or removal, minimizing waste and ensuring only parts meeting specifications proceed to packaging or assembly.
The modular construction of these powder coating lines offers manufacturers the flexibility to adapt to changing production needs. Additional modules such as pre-treatment washers, masking stations, or multi-stage coating booths can be integrated or removed as product requirements evolve. This scalability supports a wide range of production volumes, from small batch prototyping to high-volume mass production.
Sustainability continues to be a driving factor in the design and operation of auto powder coating lines for tiny goods. Low-VOC powder coatings combined with efficient recovery and recycling systems reduce environmental impact. Energy-saving features such as variable frequency drives on conveyors and ovens, intelligent airflow control, and LED curing technologies further enhance the eco-friendliness of these systems.
In conclusion, auto powder coating lines for tiny goods represent a sophisticated blend of precision automation, advanced powder application technology, and integrated quality and environmental controls. They provide manufacturers with an efficient, reliable, and sustainable method for applying high-quality powder coatings to miniature components, meeting the rigorous demands of industries where durability, appearance, and consistency are paramount.
Auto powder coating lines for tiny goods are increasingly incorporating real-time data analytics and remote monitoring capabilities to elevate process control and operational efficiency. Sensors embedded throughout the system continuously collect data on parameters such as powder flow, spray voltage, conveyor speed, oven temperature, and environmental conditions. This data is transmitted to centralized control platforms or cloud-based services, enabling operators and engineers to monitor line performance remotely, identify trends, and quickly address potential issues before they impact product quality or throughput.
Advanced analytics powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are being deployed to analyze historical and real-time process data, facilitating predictive maintenance and process optimization. By detecting subtle deviations or patterns that precede equipment failures or coating defects, these systems help schedule maintenance proactively, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. Additionally, AI-driven process adjustments can automatically fine-tune spray parameters and curing profiles to maintain optimal coating quality under varying production conditions.
The integration of Industry 4.0 standards allows these powder coating lines to seamlessly communicate with other manufacturing systems, such as material handling robots, quality inspection stations, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. This connectivity supports synchronized production workflows, streamlined inventory management, and comprehensive traceability, enhancing overall factory efficiency and responsiveness.
Ergonomic design features in auto powder coating lines improve operator safety and ease of use. Components like powder spray booths and curing ovens are designed for easy access during maintenance and cleaning, reducing downtime and labor effort. Automated powder reclaim and filtration systems minimize operator exposure to airborne powders and VOCs, creating a safer workplace environment.
Customization remains a hallmark of these systems. Manufacturers can tailor line configurations to specific product characteristics, selecting from options such as high-precision spray guns, multi-axis robotic applicators, selective masking stations, and variable-speed conveyors. This flexibility accommodates diverse product mixes and production scales, ensuring that even the smallest parts receive consistent, high-quality coatings.
The ongoing development of eco-friendly powder coatings—such as low-temperature curing powders, bio-based materials, and coatings with enhanced durability—further complements these advanced coating lines. Equipment designed to handle these innovative materials supports sustainable manufacturing practices without compromising on coating performance or production efficiency.
In summary, auto powder coating lines for tiny goods are evolving into intelligent, connected systems that combine precise automation, sophisticated process control, and sustainable operation. Their ability to deliver uniform, durable coatings rapidly and reliably on miniature components makes them essential for manufacturers striving to meet the demands of modern, high-quality production while embracing Industry 4.0 and environmental responsibility.
High Precision Small Item Coating Machine
High precision small item coating machines are advanced systems specifically designed to apply uniform, defect-free coatings on miniature and intricate parts with exceptional accuracy. These machines serve industries such as electronics, medical devices, aerospace, and precision engineering, where the smallest components require flawless surface finishes for both functional performance and aesthetic quality. Achieving consistent coatings on small items presents unique challenges due to their delicate nature, complex shapes, and tight dimensional tolerances, which high precision coating machines are expertly engineered to overcome.
At the core of these machines is a sophisticated part handling system capable of securely holding, orienting, and transporting small items through the coating process without causing damage or surface contamination. Solutions include custom-designed fixtures, precision robotic grippers, vacuum chucks, and gentle rotary tumblers that ensure continuous and controlled exposure of all part surfaces to the coating medium. Automated loading and unloading reduce human contact, minimizing contamination risk and improving repeatability.
The coating application technologies integrated into these machines are highly refined to deliver ultra-thin, even layers with minimal overspray or material waste. Electrostatic spray guns are commonly employed, utilizing charged particles that adhere efficiently to conductive substrates, improving transfer efficiency and coating uniformity. For non-conductive parts or specialized coatings, ultrasonic atomizers or air-assisted micro-spray nozzles generate fine droplets with precise control over spray patterns and deposition rates. These technologies enable coatings to conform to complex geometries, including recesses, threads, and sharp edges, without pooling or runs.
Environmental controls play a crucial role in maintaining coating consistency. The coating chamber is typically enclosed and equipped with filtered airflow systems to maintain cleanroom-level air quality, regulate temperature and humidity, and prevent airborne particulates from compromising the finish. Anti-static measures are implemented to avoid dust attraction and ensure proper paint deposition, especially important when dealing with microscopic features or sensitive electronics components.
Drying and curing modules integrated within the system are tailored to the coating material and substrate sensitivity. Options include low-temperature infrared ovens, LED-UV curing lamps, and convection dryers, each designed to rapidly and uniformly solidify coatings while minimizing thermal stress on delicate parts. Zoned heating controls allow for fine-tuned temperature management across the curing chamber, ensuring optimal cross-linking or polymerization of the coating materials.
Automation and intelligent process control are central to high precision small item coating machines. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) orchestrate the sequence of operations—part handling, spray application, curing, and inspection—while human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide operators with intuitive control panels for setting parameters, managing recipes, and monitoring system status. Advanced systems include recipe storage for quick changeovers, real-time data logging for quality assurance, and connectivity options for integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES).
Quality inspection is often built into the machine, with inline sensors and vision systems detecting coating defects such as uneven thickness, pinholes, discoloration, or surface contamination immediately after application or curing. These inspections enable rapid feedback and corrective action, reducing scrap rates and enhancing yield. Some machines employ laser-based thickness gauges or spectral analyzers to precisely measure coating properties non-destructively.
Sustainability is an important consideration, with machines designed to optimize material usage through efficient spray technologies and powder recovery systems when applicable. Enclosed coating chambers with advanced filtration protect operators and the environment from harmful emissions and particulate exposure. Compatibility with low-VOC, waterborne, or powder coatings supports environmentally responsible manufacturing practices.
Modular design enables customization and scalability of high precision small item coating machines. Manufacturers can integrate additional modules such as pre-treatment cleaning stations, masking systems for selective coating, multi-layer coating booths, or post-coating inspection units to tailor the machine to specific process requirements and production volumes.
In summary, high precision small item coating machines combine meticulous part handling, advanced spray and curing technologies, intelligent automation, and rigorous quality control to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes on miniature components. These systems are indispensable for manufacturers seeking to meet stringent functional and aesthetic standards while maximizing efficiency and sustainability in the production of small, complex parts.
High precision small item coating machines continue to evolve with technological advancements that enhance their accuracy, speed, and versatility. One major trend is the integration of multi-axis robotic arms, which provide dynamic and adaptive coating capabilities. These robots can maneuver spray nozzles along complex trajectories, adjusting angles and distances in real time to accommodate intricate part geometries. This ensures uniform coating even on challenging features such as deep recesses, fine threads, or irregular surfaces that would be difficult to reach with traditional fixed spray systems.
Sophisticated vision systems play a pivotal role in these machines, enabling automatic recognition, inspection, and alignment of parts before and during coating. High-resolution cameras combined with machine learning algorithms detect part orientation and surface defects, guiding the robotic sprayers to apply coatings precisely where needed and avoid over-application. This level of control reduces material waste and prevents defects, thereby improving yield and lowering production costs.
Environmental control within the coating area has also advanced, with machines now capable of maintaining ISO cleanroom standards when required. Controlled airflow, temperature, and humidity reduce the risk of contamination and promote optimal paint flow and curing characteristics. Anti-static and dust mitigation technologies further enhance coating quality, particularly important when working with sensitive electronics or medical components where even microscopic particles can cause failure.
Curing technologies integrated into high precision coating machines have diversified to accommodate a wide range of coating chemistries and substrate sensitivities. UV and LED-UV curing systems offer rapid polymerization at low temperatures, preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive parts while increasing throughput. Infrared and convection ovens are often equipped with zoned heating elements and real-time temperature monitoring, enabling tailored thermal profiles that minimize stress and deformation.
Automation software is becoming more intelligent, with adaptive process controls that respond dynamically to sensor feedback. Closed-loop control systems adjust spray parameters, conveyor speeds, and curing times based on real-time data to maintain consistent coating thickness and appearance. This minimizes variation between batches and within production runs, ensuring every part meets stringent specifications.
Data connectivity supports Industry 4.0 integration, allowing machines to communicate with broader manufacturing networks for production monitoring, predictive maintenance, and quality analytics. Operators benefit from intuitive dashboards that display key performance indicators and alert them to potential issues before they impact product quality or line uptime.
The modularity of these machines permits easy upgrading or reconfiguration to meet changing production needs. Additional modules such as surface pre-treatment units, selective masking stations, or multi-coat application booths can be added to expand capabilities without requiring complete system replacement. This flexibility supports rapid adaptation to new products or evolving customer requirements.
Sustainability remains a driving factor in machine design. Efficient spray technologies and recovery systems reduce coating material consumption and waste. Enclosed and filtered environments protect worker health and reduce emissions. Compatibility with environmentally friendly coatings, including waterborne and powder formulations, aligns with regulatory standards and corporate responsibility goals.
Ultimately, high precision small item coating machines combine advanced robotics, intelligent control, and environmental stewardship to deliver flawless, consistent finishes on the most delicate and complex miniature components. Their ability to meet exacting quality standards while optimizing throughput and minimizing waste makes them essential assets for manufacturers operating in highly competitive and regulated industries.
High precision small item coating machines are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to further refine process control and enhance product quality. By continuously analyzing data from sensors monitoring parameters such as spray pattern, coating thickness, environmental conditions, and curing progress, AI algorithms can detect subtle deviations that may affect the final finish. These systems can proactively adjust spray angles, flow rates, or curing temperatures in real time, minimizing defects before they occur and ensuring consistent output even amid variations in part batches or ambient conditions.
The use of AI also extends to predictive maintenance, where machine learning models analyze operational data to forecast component wear or potential failures. This allows maintenance teams to service or replace parts like spray nozzles, pumps, or conveyor belts before breakdowns happen, reducing downtime and maintenance costs while maximizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) are becoming more user-centric, featuring customizable dashboards, touch controls, and remote access capabilities. Operators can monitor line status, receive alerts, and adjust parameters from mobile devices or control rooms, increasing responsiveness and operational flexibility. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tools are also being integrated to assist with operator training, maintenance procedures, and troubleshooting, reducing errors and speeding up machine setup and repairs.
In terms of materials, high precision coating machines are adapted to handle an expanding range of advanced coatings. These include conductive inks for electronics, anti-microbial and biocompatible coatings for medical devices, protective layers for aerospace components, and functional finishes such as hydrophobic or anti-fingerprint treatments. The machines are equipped with specialized delivery systems and corrosion-resistant components to handle these diverse materials safely and effectively.
Environmental sustainability continues to guide machine innovation. Manufacturers prioritize energy-efficient curing methods such as LED-UV technology and optimized airflow management to reduce power consumption. Enclosed booths with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration and solvent recovery systems minimize environmental emissions and improve workplace safety. Compatibility with low-VOC and waterborne coatings further supports eco-friendly production practices.
Customization and modularity remain key strengths, enabling manufacturers to configure machines to their exact needs. Options for pre-treatment processes, masking for selective coating, multi-layer applications, and in-line inspection units can be seamlessly integrated or upgraded. This modular approach supports rapid adaptation to new product designs and market demands without extensive capital investment.
Overall, high precision small item coating machines represent a convergence of cutting-edge automation, intelligent process control, advanced materials handling, and environmental responsibility. They empower manufacturers to produce consistently superior finishes on the tiniest and most complex components while optimizing efficiency, quality, and sustainability—critical factors for success in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape.
Automatic Coating Line for Mini Metal Parts
Automatic coating lines for mini metal parts are highly specialized manufacturing systems engineered to provide efficient, consistent, and high-quality surface finishes on small-scale metal components. These lines are crucial in industries such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and precision hardware, where miniature metal parts must meet stringent aesthetic and functional standards. The design of these automatic coating lines addresses unique challenges including the delicate handling of tiny components, complex geometries, high throughput requirements, and precise coating application.
At the foundation of these lines is an advanced automated handling system designed to gently yet reliably transport mini metal parts through every stage of the coating process. Components such as vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, precision conveyors, and robotic pick-and-place units ensure accurate orientation and spacing of parts. This controlled movement minimizes the risk of damage, contamination, or coating defects, and ensures that every surface is accessible to the coating application system.
Coating application typically involves technologies such as electrostatic spray, dip coating, or powder coating, depending on the material and finish requirements. Electrostatic spray systems are particularly effective for mini metal parts because they charge coating particles to increase attraction to grounded components, resulting in superior transfer efficiency and uniform coverage. Specialized spray nozzles and fine atomization techniques create precise, thin coating layers that conform to complex shapes without runs, drips, or buildup.
Environmental control is a key aspect, with enclosed coating booths that regulate airflow, temperature, and humidity to maintain optimal application conditions. High-efficiency filtration systems capture overspray and airborne particulates, protecting both product quality and operator safety while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Curing ovens integrated into the line use technologies such as infrared, convection, or UV curing to rapidly and evenly solidify the coating. Zoned heating controls and programmable temperature profiles accommodate the specific curing requirements of different coating materials and substrate sensitivities, ensuring durable finishes without damaging delicate mini parts.
Automation and control systems coordinate every aspect of the line, from part handling and coating application to curing and quality inspection. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to set parameters, manage multiple coating recipes, monitor process variables, and respond to alarms. Recipe storage enables quick changeovers and consistent replication of coating processes across production batches.
Inline inspection systems employing vision cameras, laser gauges, and other sensors verify coating uniformity, thickness, and appearance immediately after application or curing. Defects such as uneven coverage, color variation, or surface imperfections are detected early, allowing automatic rejection or rework and minimizing waste.
Modular design principles make automatic coating lines highly adaptable. Manufacturers can add or remove modules such as pre-treatment washers, masking stations for selective coating, multi-stage coating booths, and advanced inspection units to customize the line according to product mix, volume, and quality requirements. This flexibility supports rapid adaptation to new products and evolving market demands.
Sustainability features are integrated throughout the line, including powder recovery systems, low-VOC or waterborne coating compatibility, and energy-efficient curing technologies. Enclosed booths and advanced filtration reduce emissions and improve workplace conditions, aligning with increasingly strict environmental standards.
In summary, automatic coating lines for mini metal parts combine gentle, precise part handling with advanced coating application and curing technologies, intelligent automation, and stringent quality control to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes at scale. These systems enable manufacturers to meet demanding product specifications efficiently while minimizing environmental impact and operational costs.
Automatic coating lines for mini metal parts are continuously advancing to meet the growing demands for higher throughput, improved precision, and enhanced process flexibility. Robotics and automated material handling play a central role in these developments, enabling highly accurate and repeatable positioning of parts throughout the line. Multi-axis robotic arms equipped with vision systems can dynamically adjust part orientation and spray paths to ensure complete and uniform coating coverage, even on parts with complex geometries or tight tolerances.
Coating application technologies have evolved to offer greater control and efficiency. Electrostatic spray systems are fine-tuned with adjustable voltage and powder flow parameters that adapt in real time to variations in part size and shape. Some lines incorporate multiple spray stations or combine different coating methods—such as powder coating followed by liquid painting—to achieve multi-layer finishes or specialized functional coatings. Precision nozzle designs and optimized air pressure settings minimize overspray, reducing material waste and environmental emissions.
Environmental and safety controls are integral to the line’s design. Enclosed spray booths equipped with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and powder recovery units maintain a clean work environment while capturing and recycling excess coating materials. Temperature and humidity are carefully regulated within the coating and curing areas to promote consistent film formation and curing quality. These controls also protect operators from exposure to hazardous substances and help meet regulatory compliance.
Curing ovens within automatic coating lines feature zoned temperature control and rapid heating elements to deliver precise, uniform curing profiles tailored to coating chemistry and substrate requirements. Technologies such as infrared, convection, and LED-UV curing are selected based on the specific application to maximize curing speed and coating performance while minimizing thermal stress on delicate parts. Inline sensors monitor curing parameters in real time, allowing for adaptive control and process optimization.
Automation systems orchestrate the entire coating line, integrating part handling, coating application, curing, and inspection. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) coordinate equipment actions with high accuracy, while human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide operators with intuitive control over process parameters and real-time status updates. Recipe management features enable quick setup changes and consistent process replication, supporting mixed-product runs and rapid product development cycles.
Quality assurance is enhanced through advanced inline inspection technologies that detect coating defects such as uneven coverage, color inconsistencies, or surface flaws immediately after coating or curing. High-resolution imaging, laser thickness gauges, and spectral analysis tools provide rapid, non-contact measurement and defect identification. Parts failing inspection are automatically segregated or routed for rework, reducing waste and improving overall yield.
The modularity and scalability of automatic coating lines allow manufacturers to tailor systems to their specific production requirements. Additional modules for pre-treatment cleaning, masking for selective coating, multi-coating applications, or post-coating finishing can be incorporated without major redesigns. This flexibility supports evolving product portfolios and changing market demands while protecting capital investment.
Sustainability considerations are increasingly embedded into these lines. Powder recovery and recycling systems minimize material consumption and environmental impact. Energy-efficient curing technologies and intelligent airflow management reduce power usage. Compatibility with environmentally friendly coatings such as waterborne and low-VOC formulations aligns production with regulatory standards and corporate social responsibility goals.
Overall, automatic coating lines for mini metal parts deliver a sophisticated, integrated solution that combines gentle and precise part handling, advanced coating and curing technologies, intelligent automation, and rigorous quality control. These lines enable manufacturers to consistently produce high-quality, durable finishes on miniature metal components while optimizing throughput, reducing waste, and maintaining compliance with environmental and safety regulations—key factors for success in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape.
Automatic coating lines for mini metal parts are also embracing digital transformation to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. Real-time data collection through embedded sensors and connected devices provides comprehensive visibility into every stage of the coating process. Operators and engineers can access dashboards displaying key performance indicators such as coating thickness, line speed, equipment status, and environmental conditions, enabling proactive decision-making and rapid troubleshooting.
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms further empowers these lines to self-optimize. By analyzing vast amounts of process data, AI can detect subtle patterns and predict deviations before they affect coating quality. This capability facilitates adaptive control, where system parameters like spray voltage, powder feed rate, and curing temperature are automatically adjusted to maintain optimal conditions, even in the face of variable part geometries or environmental fluctuations.
Predictive maintenance is another key benefit of integrating AI into automatic coating lines. Machine learning models analyze equipment performance metrics to forecast wear or impending failures, allowing maintenance to be scheduled during planned downtime. This reduces unplanned stoppages and extends the lifespan of critical components such as spray guns, conveyors, and curing ovens.
Connectivity to factory-wide manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms ensures seamless integration of coating lines within broader production workflows. This integration supports traceability, inventory management, and quality control, essential for regulated industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing. Digital records of coating parameters and inspection results facilitate compliance audits and continuous improvement initiatives.
Operator interfaces have become more intuitive and accessible, often featuring touchscreens with graphical displays, guided workflows, and alarm notifications. Remote monitoring and control capabilities enable supervisors to oversee multiple lines or facilities from centralized locations, improving resource allocation and responsiveness.
Sustainability remains at the forefront of design and operation. Advances in powder recovery technology and booth filtration systems reduce emissions and waste, while energy-efficient curing methods minimize environmental impact. Lines are increasingly compatible with eco-friendly coating materials, such as low-VOC powders and waterborne finishes, aligning with global efforts to reduce industrial carbon footprints.
Customization options allow manufacturers to configure lines precisely to their product mix and volume needs. Modular components for pre-treatment, masking, multi-coat application, and inspection can be added or reconfigured to support new products or process enhancements without significant downtime or capital expense.
Powder coaters for small components are specialized systems designed to apply durable, high-quality powder coatings onto miniature parts with precision and efficiency. These coaters address the unique challenges associated with coating small components, such as intricate geometries, tight tolerances, and delicate surfaces, by combining advanced powder application technologies, precise handling mechanisms, and controlled curing processes.
At the heart of these systems is a carefully engineered part handling mechanism that gently transports and orients small components to ensure complete and uniform powder coverage. Techniques such as vibratory feeders, precision conveyors, rotary tumblers, and robotic pick-and-place units are commonly employed to handle tiny parts without causing damage or surface contamination. This controlled handling facilitates consistent exposure of all surfaces during coating.
Powder application is typically achieved using electrostatic spray guns that charge powder particles, causing them to adhere efficiently to grounded metal components. For small components, the spray system is optimized with fine nozzles and adjustable air pressure to create a precise, finely atomized powder cloud, ensuring thin, even layers without buildup or overspray. Some systems also incorporate tribo charging or corona charging methods to enhance powder adhesion depending on the part material and coating requirements.
Environmental control within powder coating booths is critical for maintaining coating quality. Enclosed booths with filtered airflow minimize contamination, regulate temperature and humidity, and capture overspray powder for recovery and reuse. These features protect operator health, reduce material waste, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Curing ovens integrated into powder coaters provide uniform and efficient heat treatment to melt and fuse the powder coating into a durable, continuous film. Infrared, convection, or UV curing technologies are selected based on coating chemistry and substrate sensitivity. Zoned temperature control and programmable profiles ensure consistent curing without damaging delicate small parts.
Automation and intelligent controls enhance process repeatability and efficiency. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) manage powder flow, spray parameters, conveyor speed, and curing cycles. Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide operators with intuitive controls for recipe management, real-time monitoring, and alarm handling. Data logging capabilities support quality assurance and traceability.
Quality inspection modules using optical sensors, laser gauges, or vision systems can be incorporated to detect coating defects such as uneven coverage, pinholes, or surface imperfections immediately after curing. Defective parts are identified and separated, reducing waste and ensuring only high-quality coated components proceed to packaging or assembly.
Modular designs allow powder coaters to be tailored to specific production volumes and component complexities. Additional modules for pre-treatment cleaning, masking for selective coating, multi-stage powder application, and post-coating finishing can be integrated to meet diverse manufacturing needs.
Sustainability considerations are embedded in powder coater designs, including powder recovery and recycling systems, energy-efficient curing methods, and compatibility with environmentally friendly powder formulations. These features help reduce environmental impact while maintaining operational efficiency and coating performance.
In summary, powder coaters for small components combine precise handling, advanced powder application, controlled curing, and intelligent automation to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes on miniature parts. They play a vital role in industries requiring durable, aesthetically pleasing coatings on small-scale metal components, supporting both functional and decorative applications.
Powder coaters for small components are increasingly equipped with adaptive technologies that automatically adjust to part size, geometry, and coating requirements, ensuring that every component, regardless of complexity, receives an optimal finish. These systems are especially valuable in high-mix, low-volume environments where frequent changeovers are needed. Intelligent controls allow operators to store and switch between coating recipes, minimizing setup time and maintaining consistency across batches. Real-time sensor feedback informs the system of powder flow rates, spray voltage, and booth conditions, which can be adjusted dynamically to respond to changes during the production cycle without operator intervention.
The powder coating process for small components often involves tighter tolerances and more delicate substrates, which necessitate the use of low-velocity, fine-particle spray patterns that reduce the risk of powder buildup, bridging, or uneven coating. These fine-tuned delivery systems are capable of producing extremely smooth finishes, even on parts with complex shapes or recessed features. Precision spray arms or oscillating guns provide consistent application along all contours of the parts, and in some cases, rotary fixtures are used to expose all sides of the item in a continuous motion, improving coating uniformity while conserving powder.
To support efficient powder recovery, many systems are designed with cyclone separators and filter cartridges that capture unused powder from the air, allowing it to be cleaned and reused. This closed-loop recovery not only minimizes waste but also reduces the cost of consumables over time. Modern booth designs facilitate quick color changes by minimizing dead zones and simplifying cleaning procedures, an essential feature when coating different parts with varied powder types in a single shift.
Energy-efficient curing ovens contribute to both environmental sustainability and operational economy. Whether using gas-fired convection ovens or electric infrared heaters, these systems are designed with thermal insulation and optimized airflow to ensure that every small component receives uniform heat exposure. For highly sensitive or heat-intolerant parts, UV-curable powders provide a viable alternative. These powders cure instantly under LED or mercury UV lamps, requiring minimal energy and eliminating the need for high-temperature ovens.
Inspection and quality control are seamlessly integrated into modern powder coater systems for small components. Inline vision systems and thickness measurement tools identify potential coating flaws in real time, allowing defective items to be removed or automatically reprocessed without halting the line. These quality checks are essential in industries where the coating not only serves an aesthetic function but also provides electrical insulation, corrosion resistance, or chemical protection. In applications such as electronics, medical instruments, or aerospace fasteners, even microscopic inconsistencies in coating thickness or adhesion can lead to product failure.
Digital connectivity is another area of rapid development. Powder coaters can now be networked with plant-wide systems via Industry 4.0 protocols, enabling operators to track production, monitor coating trends, predict maintenance needs, and generate automated compliance reports. This level of connectivity enhances traceability and accountability while making the line more resilient to operator variability and process drift.
Ultimately, powder coaters for small components embody a combination of precision, adaptability, and efficiency. Their ability to deliver flawless finishes on complex, delicate items in a controlled and repeatable manner makes them indispensable for modern manufacturers aiming to meet high-quality standards and demanding production schedules. As industries continue to miniaturize and diversify their products, the importance of these high-performance coating systems will only continue to grow.
Powder coaters for small components are also being designed with compact footprints to suit limited factory floor spaces without sacrificing throughput or performance. This space efficiency is especially important for manufacturers producing miniature parts in cleanroom environments or urban facilities where square footage comes at a premium. Despite their size, these compact systems incorporate all the essential components—automated feeders, spray booths, recovery units, and curing modules—into a streamlined, enclosed configuration that maximizes productivity while minimizing environmental contamination and operator exposure.
Another key advantage of modern powder coaters for small components is their flexibility across a wide variety of materials and part types. While traditionally focused on metal substrates, many systems are now capable of handling specially formulated powders for non-metallic components, including heat-resistant plastics and ceramic parts. This expands their applicability to industries such as consumer electronics, telecommunications, and precision optics, where even non-metallic items may require durable, functional coatings.
The surface preparation stage is also receiving more attention in small component coating systems. Integrated pre-treatment modules use techniques such as plasma cleaning, ultrasonic washing, or ionized air blow-off to remove microscopic oils, dust, or oxidation layers. This step is critical for ensuring good powder adhesion and long-term coating performance, particularly in applications where corrosion resistance or dielectric strength is critical.
Cycle times have been significantly reduced thanks to fast-curing powders and highly responsive control systems. With ovens capable of reaching target temperatures rapidly and powder guns that can ramp up or down with minimal lag, these systems are able to coat and cure small parts in seconds rather than minutes. This high speed, combined with the system’s continuous operation mode, allows for massive production volumes with consistent quality and minimal downtime.
As sustainability goals become more stringent across industries, powder coaters for small components have become strong contributors to environmentally responsible manufacturing. Since powder coatings are solvent-free and emit virtually no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), they inherently meet many green manufacturing standards. When paired with energy-saving technologies, smart resource management, and low-waste operation, they help companies meet ISO 14001 standards and corporate sustainability targets without compromising output or finish quality.
Operator training and ease of use are further enhanced by modern user interfaces that guide users through machine setup, calibration, and maintenance routines. These interfaces are often multilingual, touchscreen-based, and supported by video instructions or augmented reality overlays that reduce the learning curve and help maintain consistency even with varying skill levels on the shop floor. Remote diagnostic tools allow service teams to troubleshoot issues quickly without being onsite, reducing service downtime and improving operational reliability.
In the bigger picture, powder coaters for small components have become more than just coating systems—they are now complete, intelligent finishing solutions. Their role goes beyond applying protective or decorative layers; they contribute directly to production efficiency, product reliability, and sustainable operations. Whether applied to batches of micro screws, connector pins, medical pins, or decorative jewelry parts, these systems offer the precision, cleanliness, and speed required by modern manufacturing ecosystems. Their importance will only increase as component sizes shrink and performance expectations rise in the years ahead.
Small Object Coating Equipment Line
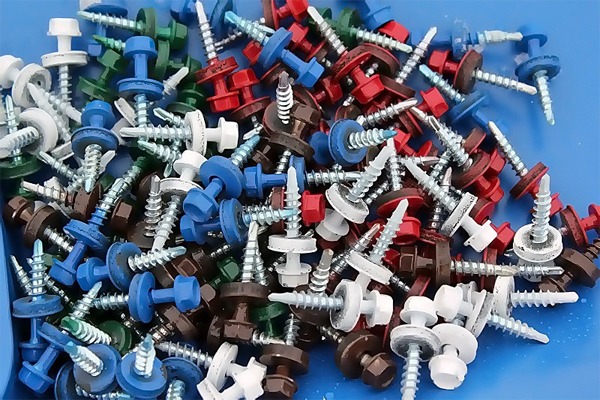

A small object coating equipment line is a fully integrated, automated system designed to apply protective or decorative coatings to miniature items with precision, efficiency, and repeatability. This type of production line is essential in industries such as electronics, medical devices, fasteners, tools, consumer products, and automotive components—where parts are small, often delicate, and manufactured in high volumes. The line typically includes a sequence of operations such as surface preparation, automated loading, coating application, curing, and quality inspection, all configured to handle the specific challenges of coating small-scale components.
The process begins with part feeding and orientation. Small objects are often supplied in bulk, so the line is equipped with vibratory bowl feeders, rotary disk feeders, or robotic pick-and-place arms to separate, align, and position each part correctly. This stage ensures each item moves consistently through the system with the correct orientation for coating. Depending on the part geometry, components may be transported via fixtures, pallets, or mesh belts to keep them secure and avoid damage or misalignment.
Before coating, surface preparation is often necessary to ensure adhesion and surface cleanliness. The line may include modules for degreasing, ultrasonic cleaning, plasma treatment, or ionized air blow-off to eliminate dust, oils, or oxidation. For metal components, abrasive blasting or chemical etching may also be used. This step is critical for achieving durable, defect-free coatings, particularly in applications requiring high performance or long-term reliability.
The coating application stage is the core of the equipment line. Depending on the desired finish, the system may employ powder coating, liquid spray painting, dip coating, or electrocoating (e-coating). For powder or spray coating, electrostatic application guns are used to direct a fine, controlled cloud of coating material onto the small parts. These guns are typically mounted on automated arms or oscillators for consistent movement and precision. Small object coating lines often feature multiple guns or stages to accommodate different coating layers or coverage angles.
To accommodate the complex geometries of small parts, some systems use rotating fixtures or tumbling mechanisms to expose all surfaces evenly during coating. For dip coating, robotic arms lower the parts into the coating bath with controlled timing and withdrawal speeds to avoid dripping or uneven film buildup. Selective coating systems with automated masking may also be included for parts that require partial or patterned coatings.
Curing follows coating and is customized based on the type of material and coating chemistry. Convection ovens, infrared heaters, or UV curing chambers are integrated into the line to solidify or polymerize the coating. These ovens are carefully zoned and controlled to ensure uniform heating without damaging the parts or altering critical dimensions. For delicate or heat-sensitive components, UV-curable coatings offer a low-temperature solution with instant curing.
Once curing is complete, the parts are cooled, conveyed, and directed to inspection modules. Inline vision systems, thickness gauges, and optical sensors are used to verify coating coverage, color uniformity, and surface quality. Systems can detect common defects such as missed spots, bubbles, runs, or excessive buildup. Parts that fail inspection can be automatically diverted for rework or rejection, ensuring that only components meeting specifications proceed to packaging or assembly.
Automation and digital control are central to modern small object coating lines. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) synchronize each stage of the process, while human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide operators with real-time feedback, alarm handling, recipe control, and production analytics. Integration with factory networks or MES systems enables traceability, production planning, and remote diagnostics. Recipes can be stored and recalled for fast changeovers, making the system suitable for high-mix, low-volume production as well as large, continuous runs.
The entire line is designed with efficiency, repeatability, and environmental responsibility in mind. Enclosed spray booths with filtration systems reduce overspray and emissions. Powder recovery units reclaim unused material, and energy-efficient ovens minimize power consumption. Compatibility with eco-friendly coatings, including waterborne and low-VOC formulations, supports sustainable production practices.
In summary, a small object coating equipment line combines precise handling, adaptive coating technology, and advanced automation to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes on miniature components. Its flexibility, scalability, and integration capabilities make it a vital tool for manufacturers seeking to meet modern performance standards while maintaining cost-effectiveness and environmental compliance.
A small object coating equipment line is designed not only to be functionally efficient but also to be highly modular and customizable, allowing manufacturers to tailor the system to their specific part dimensions, coating materials, and production volumes. Many systems are built around a central conveyor system—either continuous or indexing—that connects all modules from start to finish. The conveyor design is carefully chosen to suit the weight and geometry of the small parts being processed. For instance, miniature metallic parts may ride on custom-designed racks, rotating jigs, or perforated trays that ensure exposure of every surface during the coating and curing phases.
One of the key features of a well-designed small object coating line is the ability to handle large quantities of parts with high repeatability and minimal operator intervention. In many lines, multiple parts can be coated simultaneously, with precise spacing and alignment maintained throughout the entire process. This is especially important when dealing with fasteners, connectors, screws, springs, and medical or electronics hardware where dimensional accuracy and coating consistency are critical. Automated systems are capable of tracking thousands of parts per hour, and production can run continuously with minimal downtime due to quick-clean booths, auto gun purging, and touch-free inspection.
The integration of smart control systems adds further advantages to these coating lines. Sensors embedded throughout the line provide live data on temperature, humidity, coating gun voltage, conveyor speed, and curing time, all of which are monitored and adjusted automatically to compensate for external changes or load variations. This feedback loop enables self-correction in the process, maintaining optimal performance even across extended shifts or multi-product runs. Operators can adjust system parameters through intuitive touchscreen interfaces, which also store historical data for each job, supporting traceability and compliance with quality standards like ISO or automotive-grade certifications.
High-end systems also support barcode or RFID tracking of part trays or batches, allowing the line to automatically adjust its settings when a new part type is detected. This is ideal for facilities that run frequent product changeovers. Recipes for each part are stored in the system and loaded instantly, avoiding human error and reducing startup times between runs. This level of automation transforms the coating line into a smart manufacturing asset that not only produces parts but manages process knowledge and enforces consistency across shifts and operators.
Maintenance and serviceability are also built into the design of small object coating lines. The systems include quick-access panels, modular gun mounts, and tool-less cleaning features that reduce downtime and make routine maintenance faster and easier. Remote diagnostics and cloud connectivity enable manufacturers to receive software updates, troubleshoot faults, and get real-time support from equipment suppliers without waiting for a service technician to arrive onsite.
Safety and environmental protection are also central to these systems. Enclosed booths prevent powder or paint particles from escaping into the factory air. Overspray is captured efficiently through filters and recovered where possible. Many powder coating systems now boast recovery rates above 95%, saving material costs and reducing waste. Furthermore, with the push toward environmentally friendly manufacturing, many lines are now being designed to run entirely solvent-free using low-VOC coatings or powder-only systems, which drastically reduce emissions and the need for expensive ventilation or disposal procedures.
From a performance standpoint, the durability and aesthetics of the coatings produced on these lines rival or surpass those achieved through manual processes. Whether the objective is corrosion protection, abrasion resistance, insulation, or simply color and finish, the line can be tuned to produce finishes that meet or exceed OEM and industry standards. Parts coated on these systems typically require no further processing, emerging from the line fully cured and ready for packing, assembly, or shipment.
In practice, these lines can be used to coat everything from tiny gears and implantable medical screws to metal buttons, clips, brackets, phone parts, and sensors. The combination of compact design, smart automation, and flexible modules makes the small object coating equipment line a cornerstone of modern high-precision manufacturing, capable of supporting the increasing demands for miniaturization, speed, and surface quality across industries.
As production trends continue to favor customization, rapid turnaround, and zero-defect manufacturing, small object coating equipment lines are being adapted to support highly flexible, data-driven operations. Many modern systems now feature AI-assisted process optimization that not only automates real-time adjustments but also learns from historical runs to suggest improved settings for future batches. For instance, if a specific type of small part consistently shows minor edge thinning or excessive buildup in a certain area, the system can automatically modify spray patterns or recommend fixture changes to improve coating balance.
Integration with upstream and downstream systems further enhances the value of these coating lines. Upstream, the line may receive real-time data from machining or forming equipment, allowing it to pre-load the correct coating parameters based on part ID or lot history. Downstream, the line may feed directly into robotic assembly cells, packaging machines, or quality laboratories, reducing the need for buffer inventory and manual handling. In fully automated factories, the coating line becomes a tightly synchronized node in a larger production ecosystem where every part is tracked, logged, and processed with surgical precision.
Material compatibility is expanding as well. Beyond conventional powders and solvent-based coatings, the equipment line can be adapted for UV powders, water-based paints, ceramic coatings, and functional formulations such as anti-static, anti-corrosion, low-friction, or heat-resistant materials. These capabilities open the door to advanced applications in aerospace, defense, electronics, and healthcare, where the demands on surface performance are especially high. Some lines can even apply multiple coats in sequence—primer, base, and top coat—without manual transfer or staging, using interlinked application and curing stations that handle layering and flash-off timing automatically.
Lighting and airflow within the coating environment are also optimized for micro-scale operations. Coating booths for small objects often use laminar airflow to maintain a dust-free environment while carefully directing the powder or paint plume. High-lumen LED lighting ensures operators and vision systems can detect even the smallest surface irregularities, while temperature and humidity control systems maintain consistency in electrostatic behavior and drying speed—both of which are sensitive to environmental variation.
From a workforce perspective, the shift toward automated small object coating lines reduces dependency on specialized manual labor and minimizes ergonomic strain. Instead of hand-coating hundreds of tiny parts, operators manage high-level settings, oversee production flow, and respond to quality alarms. This transition helps manufacturers maintain stable production even in regions with tight labor markets or skill shortages, and it also supports the upskilling of the workforce toward more technical roles in automation and systems management.
Overall, small object coating equipment lines represent an intersection of precision engineering, intelligent software, and scalable manufacturing. They are no longer simple conveyor-based tools but rather agile, integrated systems capable of adapting to fast-paced production demands while ensuring the highest levels of quality, consistency, and operational control. As global industries continue to demand smaller, lighter, and smarter components, the need for such coating systems will only intensify—pushing innovation toward even greater speed, flexibility, and functional capability in the miniature domain.
Automatic Powder Coating Line for Tiny Parts
An automatic powder coating line for tiny parts is a highly specialized, fully integrated system engineered to apply durable, uniform powder coatings on miniature components with exceptional precision and efficiency. This type of line caters to industries like electronics, medical devices, aerospace, automotive, and precision hardware, where tiny metal or plastic parts require high-quality protective or decorative finishes. The system is meticulously designed to address the challenges posed by small part handling, intricate geometries, thin coating layers, and rapid throughput demands.
The line begins with automated part feeding and orientation systems tailored to miniature components. Vibratory bowl feeders, micro-conveyor belts, or robotic arms with delicate grippers separate, align, and position parts for consistent presentation to the coating station. Specialized fixtures, such as trays with individual compartments or rotary tumblers, secure parts to prevent damage or misalignment during transport through the coating process.
Powder application is performed using advanced electrostatic spray technology, optimized for tiny parts. Fine-mist powder guns with adjustable voltage and powder flow deliver a controlled cloud of charged powder particles that efficiently adhere to grounded parts, ensuring even coverage with minimal overspray. Multiple spray stations or multi-axis robotic arms may be employed to reach complex part geometries and coat all surfaces uniformly, including recesses, threads, or sharp edges.
The coating booths are enclosed and equipped with filtered airflow systems to maintain a clean, contamination-free environment. Overspray powder is captured by high-efficiency filtration units and recovered for reuse, minimizing material waste and environmental impact. Precise control of temperature and humidity within the booth ensures optimal powder flow and electrostatic behavior, which are critical for consistent coating quality on tiny components.
Following powder application, parts move through curing ovens designed for uniform, efficient heat treatment. Infrared or convection curing technologies are commonly used, with zoned temperature controls that accommodate the thermal sensitivity of small parts. LED-UV curing options may be available for specialized powders requiring low-temperature curing, enabling rapid solidification without risking part deformation.
Automation and control systems coordinate every aspect of the line, utilizing programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) to manage parameters such as conveyor speed, spray voltage, powder flow, and curing temperature. Recipe management features allow operators to store and quickly switch between coating profiles for different part types, facilitating rapid changeovers in high-mix production environments.
Quality assurance is integrated through inline inspection systems using high-resolution cameras, laser thickness sensors, or spectrophotometers to detect coating defects like uneven coverage, pinholes, or color variations immediately after curing. Defective parts are automatically diverted or flagged for rework, ensuring that only compliant components proceed to packaging or assembly.
The modular design of automatic powder coating lines for tiny parts allows customization according to production volume, part complexity, and coating requirements. Additional modules such as pre-treatment cleaning, selective masking, multi-layer coating stations, or post-coating finishing can be incorporated to expand capabilities.
Sustainability features, including powder recovery systems, energy-efficient curing, and compatibility with eco-friendly powders, align these lines with environmental regulations and corporate responsibility goals. Enclosed systems protect operators from exposure to powder particles and minimize emissions.
In summary, automatic powder coating lines for tiny parts combine precise handling, advanced electrostatic powder application, controlled curing, and intelligent automation to deliver high-quality, consistent coatings on miniature components. These systems are essential for manufacturers seeking to balance quality, efficiency, and sustainability in the production of small, complex parts.
Automatic powder coating lines for tiny parts continue to evolve with a focus on increasing throughput while maintaining exceptional quality. To achieve this, manufacturers incorporate multi-stage conveyor systems that allow simultaneous processing of parts at different steps—loading, coating, curing, and unloading—thus maximizing line efficiency and reducing cycle times. Some lines utilize continuous flow conveyors with synchronized speeds, while others employ indexing conveyors that pause parts at critical process points for precise application and curing.
The delicate nature of tiny parts requires that the handling systems be both gentle and precise. Robotic arms with soft grippers or vacuum-based end effectors can pick and place parts without causing scratches or deformation. Advanced vision systems integrated into these robots provide real-time feedback, enabling automatic adjustment of positioning and orientation to ensure consistent coating coverage, even on irregularly shaped or complex components.
Powder delivery systems are optimized to maintain consistent particle flow and charge levels, which is critical when working with small parts that have limited surface area. Closed-loop feedback mechanisms monitor parameters like powder feed rate, gun current, and booth airflow, automatically adjusting them to prevent coating defects such as uneven thickness or buildup. Some lines feature multiple powder hoppers and quick-change color modules to support rapid shifts between coating colors or formulations, minimizing downtime and expanding product flexibility.
Curing ovens are designed with precise thermal control, employing zoned heating elements and advanced insulation to maintain consistent temperatures throughout the chamber. Rapid curing cycles not only improve throughput but also reduce energy consumption. For parts sensitive to heat, low-temperature curing powders and UV-LED curing technologies provide effective alternatives that preserve part integrity while ensuring coating durability.
Environmental control remains a priority, with enclosed booths and filtered ventilation systems preventing powder escape and protecting operator health. High-efficiency powder recovery units capture overspray with recovery rates often exceeding 95%, reducing material waste and lowering operating costs. The use of solvent-free powder coatings further enhances the environmental friendliness of these lines, meeting strict VOC regulations and reducing hazardous waste.
Automation software interfaces are designed for ease of use, featuring graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that allow operators to monitor real-time system status, adjust process parameters, and access maintenance alerts. Data logging and connectivity enable integration with factory-wide manufacturing execution systems (MES), supporting traceability, quality control, and predictive maintenance. This level of digital integration is vital for manufacturers operating in regulated industries where documentation and compliance are essential.
Quality inspection systems employing machine vision and laser sensors provide high-resolution imaging and measurement capabilities, detecting coating flaws with high accuracy. Defective parts are automatically identified and segregated, reducing manual inspection labor and improving overall product yield. Some systems also incorporate in-line thickness gauges and colorimeters to verify coating specifications immediately after curing.
Modularity and scalability allow these powder coating lines to be adapted as production requirements change. Additional modules such as pre-treatment cleaning stations, masking units for selective coating, multi-coat application booths, and post-coating curing tunnels can be added or reconfigured with minimal disruption. This flexibility supports manufacturers in rapidly responding to market demands, product changes, or evolving quality standards.
Training and support are enhanced by integrated diagnostic tools and remote service capabilities. Operators receive guided instructions through touchscreens or augmented reality overlays, reducing human error and accelerating troubleshooting. Remote monitoring allows service teams to identify issues promptly and provide solutions without the need for onsite visits, minimizing downtime.
In conclusion, automatic powder coating lines for tiny parts are sophisticated, highly automated systems that combine precise handling, advanced powder application, efficient curing, and integrated quality control. Their design prioritizes high throughput, flexibility, environmental responsibility, and consistent coating quality, making them indispensable in modern manufacturing environments focused on miniature, complex components.
Automatic powder coating lines for tiny parts are increasingly incorporating cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to further refine process control and quality assurance. These systems analyze vast amounts of real-time data—covering powder flow rates, electrostatic charge levels, conveyor speeds, temperature profiles, and inspection results—to detect subtle trends and predict potential issues before they cause defects. AI-driven adaptive controls can then adjust spray parameters, booth airflow, or curing cycles autonomously, ensuring continuous optimization and minimizing waste.
Robotic automation in these lines is also advancing with collaborative robots (cobots) that can safely work alongside human operators. Cobots handle sensitive loading and unloading tasks, perform quick tool changes, or assist in maintenance, enhancing operational flexibility without requiring extensive safety barriers. Their ability to learn and adapt to new parts or workflows reduces setup times and supports smaller batch sizes, which are common in industries producing a wide variety of tiny components.
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices throughout the powder coating line enables seamless connectivity and data exchange. Sensors embedded on equipment collect operational metrics that feed into centralized monitoring platforms, providing operators and managers with comprehensive dashboards accessible remotely. This connectivity supports proactive maintenance scheduling, energy management, and production planning, contributing to overall operational excellence.
Sustainability remains a focal point in the evolution of these systems. Innovations in powder formulations, such as bio-based powders and enhanced recyclability, complement advanced powder recovery and filtration technologies. Energy-efficient curing methods—like UV-LED curing combined with improved oven insulation and heat recovery systems—reduce the carbon footprint of the coating process. Enclosed booths and automated cleaning procedures minimize emissions and worker exposure, aligning with stricter environmental and safety regulations worldwide.
Customization options allow manufacturers to tailor automatic powder coating lines for tiny parts to meet exacting industry requirements. Whether coating medical implants with biocompatible powders, aerospace components needing corrosion-resistant finishes, or electronic connectors requiring electrical insulation, these systems offer configurable process modules, from surface preparation to multi-layer coating and final inspection. Such flexibility supports innovation and rapid product development cycles without compromising quality.
Training and workforce development benefit from virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tools integrated into these lines. Operators and maintenance personnel can receive immersive, interactive guidance on system operation, troubleshooting, and preventive maintenance. These technologies help reduce errors, accelerate learning curves, and increase equipment uptime.
In sum, automatic powder coating lines for tiny parts represent a convergence of precise mechanical engineering, smart automation, sustainable design, and digital intelligence. They empower manufacturers to achieve consistent, high-quality coatings on miniature components at scale, meeting the stringent demands of today’s advanced industries while preparing for future challenges in manufacturing complexity, customization, and environmental stewardship.
Automated Small Item Powder Coaters
Automated small item powder coaters are specialized coating systems designed to efficiently apply durable, high-quality powder coatings to miniature components with minimal human intervention. These coaters are engineered to address the unique challenges of handling tiny parts—such as delicate geometries, precise coverage requirements, and high throughput demands—while delivering consistent, repeatable finishes that meet strict industry standards.
At the core of these systems is an automated material handling mechanism that carefully separates, orients, and transports small items through the coating process. Technologies such as vibratory feeders, robotic pick-and-place arms, and conveyor fixtures are employed to ensure gentle yet precise movement, preventing damage or contamination. This automated handling enables continuous production with reduced labor costs and enhanced operational safety.
Powder application in automated small item coaters utilizes electrostatic spray technology optimized for miniature parts. Fine atomization nozzles deliver charged powder particles that efficiently adhere to grounded components, providing uniform coverage even on complex shapes and tight spaces. Multiple spray heads and multi-axis robotic systems may be integrated to ensure all surfaces receive adequate coating without excessive overspray or buildup.
The coating booths are enclosed environments equipped with filtered airflow and powder recovery systems to maintain cleanliness, reduce material waste, and protect operators. These features are critical in minimizing environmental impact and ensuring compliance with increasingly strict workplace safety and environmental regulations.
After powder application, parts are conveyed through curing ovens that employ infrared, convection, or UV-LED technologies to solidify and bond the coating. These ovens feature precise temperature control and zoning to accommodate the thermal sensitivities of small components, ensuring optimal curing without deformation or damage.
Automation and control software coordinate the entire powder coating process, from part feeding and powder delivery to curing and quality inspection. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and user-friendly human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to manage recipes, monitor system performance, and quickly switch between product types. Data logging and connectivity enable integration with broader manufacturing execution systems (MES) for traceability and production optimization.
Inline quality assurance systems—such as vision cameras and laser thickness gauges—detect coating defects in real time, facilitating immediate corrective actions or automatic rejection of non-conforming parts. This reduces waste and ensures that only parts meeting stringent quality criteria proceed to downstream processes.
Modular design allows these automated powder coaters to be customized with additional modules for surface pre-treatment, selective masking, multi-layer coating, or post-coating finishing. This flexibility supports diverse manufacturing needs and quick adaptation to new product lines or coating requirements.
Energy efficiency and sustainability are emphasized through powder recovery systems, solvent-free powder formulations, and low-energy curing technologies. These measures reduce operating costs and environmental footprint, aligning with corporate sustainability goals and regulatory demands.
In summary, automated small item powder coaters provide manufacturers with a precise, efficient, and environmentally responsible solution for coating miniature parts. Their integration of advanced handling, coating, curing, and inspection technologies ensures high-quality finishes at scale, supporting the demands of industries focused on small, complex components.
Automated small item powder coaters continue to evolve with advancements that prioritize not only precision and efficiency but also adaptability to diverse production demands. The systems are engineered to handle a wide variety of part sizes, shapes, and materials, making them suitable for industries ranging from medical devices and electronics to automotive components and consumer goods. This adaptability is achieved through configurable conveyors, adjustable fixtures, and versatile robotic applicators that can be reprogrammed or swapped out quickly, enabling fast changeovers and minimizing downtime.
Handling tiny parts poses significant challenges, and to address this, automated coaters use delicate gripping technologies such as vacuum cups with soft seals, micro-clamps, or non-contact magnetic holders. These technologies ensure that parts are held securely without marring or deforming their surfaces. Coupled with precision vision systems, the equipment can detect part orientation and presence, ensuring each item receives the correct coating treatment and preventing errors such as missed coatings or double handling.
The electrostatic powder application process is finely tuned to optimize particle charge, spray patterns, and airflow dynamics. This level of control reduces overspray and powder waste, improving cost-effectiveness and environmental compliance. Some systems incorporate multiple powder feed hoppers with automatic color change capabilities, allowing for rapid switching between different powder types or colors in a single production run. This flexibility is especially valuable for manufacturers offering customized or limited-edition products.
The curing phase integrates advanced thermal management to accommodate the sensitivity of small parts. Infrared and convection ovens with zoned temperature control ensure uniform curing while preventing heat-induced distortion. For heat-sensitive components, UV-LED curing offers a rapid, low-temperature alternative that cures powder coatings instantly, preserving part integrity and accelerating production cycles.
Safety and environmental controls are integral to automated small item powder coaters. Enclosed spray booths with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and powder recovery units maintain air quality and minimize operator exposure to fine particles. Automated cleaning routines and powder reclaim systems help reduce material waste and lower operating costs, supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Control systems utilize programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs) to facilitate easy operation, real-time monitoring, and rapid recipe adjustments. Data acquisition capabilities support traceability and quality assurance, enabling manufacturers to meet stringent regulatory requirements and internal standards. Remote diagnostics and maintenance alerts enhance uptime by allowing proactive service interventions.
Integrated inline inspection technologies ensure consistent coating quality. High-resolution cameras, laser measurement tools, and colorimeters detect surface defects, thickness variations, and color inconsistencies immediately after coating and curing. Defective parts are automatically rejected or rerouted for rework, reducing waste and ensuring compliance with quality specifications.
Modularity and scalability are key features of these systems, enabling manufacturers to start with a basic coating line and expand with additional modules such as surface pre-treatment units, masking stations for selective coating, multi-layer application booths, and post-coating finishing modules. This approach allows companies to invest incrementally while adapting to evolving production requirements.
By combining precise automation, advanced coating technology, efficient curing, and comprehensive quality control, automated small item powder coaters provide a complete solution for manufacturers focused on miniature component finishing. Their ability to deliver consistent, high-quality coatings at scale supports competitive production, regulatory compliance, and environmental stewardship, making them indispensable tools in modern manufacturing environments where small parts play a critical role.
Automated small item powder coaters also incorporate advanced data analytics to enhance process transparency and continuous improvement. By collecting and analyzing operational data—including powder consumption, line speeds, coating thickness variations, and defect rates—manufacturers gain valuable insights into production efficiency and quality trends. These insights enable root cause analysis of recurring issues, facilitate predictive maintenance schedules, and support process optimization efforts, ultimately reducing downtime and improving yield.
The integration of cloud-based platforms allows multiple coating lines, often across different facilities, to be monitored and managed centrally. This connectivity supports remote troubleshooting, software updates, and performance benchmarking, helping organizations maintain consistent standards regardless of location. Such digital ecosystems also enable seamless documentation for audits, certifications, and customer reporting, which is especially critical in highly regulated sectors like aerospace, medical devices, and electronics.
In response to increasing demands for customization and smaller production batches, automated small item powder coaters are designed to support quick changeovers without compromising efficiency. Tool-less fixture changes, recipe recall functions, and automated cleaning cycles reduce downtime between runs, allowing manufacturers to respond rapidly to market shifts and customer needs. This agility is vital for businesses operating in fast-paced industries or serving niche markets.
Energy efficiency is further enhanced through innovations such as regenerative heating systems, variable frequency drives on conveyors and blowers, and smart standby modes that reduce power consumption during idle periods. Coupled with the inherent environmental benefits of powder coating—such as zero VOC emissions and high material utilization—these features help manufacturers lower their carbon footprint and comply with stringent environmental regulations.
Workforce ergonomics and safety are improved by designing systems that minimize manual handling of parts and powders. Automated loading and unloading, enclosed booths, and extraction systems protect operators from repetitive strain and exposure to airborne particles. User interfaces are developed with operator experience in mind, incorporating touchscreens with clear visuals, guided workflows, and multilingual support to accommodate diverse teams.
Finally, the modular architecture of automated small item powder coaters enables future-proofing against evolving manufacturing trends. Manufacturers can upgrade or expand their lines with minimal disruption, integrating new technologies such as AI-driven quality inspection, additive manufacturing-compatible coating modules, or advanced surface preparation units. This adaptability ensures that investments in powder coating infrastructure remain valuable as product portfolios and industry standards change over time.
In summary, automated small item powder coaters represent a convergence of precision engineering, smart automation, sustainable design, and digital integration. They provide manufacturers with reliable, flexible, and environmentally responsible solutions for coating miniature components, supporting high-quality production at scale in today’s demanding manufacturing landscape.
Coating Machine for Micro-Sized Products
A coating machine for micro-sized products is a highly specialized piece of equipment engineered to apply precise, uniform coatings to extremely small components often measuring just fractions of a millimeter. These machines are essential in industries like electronics, medical devices, micro-mechanics, optics, and advanced manufacturing, where micro-sized parts require protective, functional, or decorative coatings with exceptional accuracy and consistency.
Handling micro-sized products presents unique challenges that standard coating systems cannot address. These products often have complex geometries, fragile structures, and require coatings that must be applied with micron-level precision to avoid clogging, bridging, or uneven coverage. The coating machine integrates delicate handling systems such as micro-feeders, high-precision robotic arms, or vibratory micro-tables that carefully orient and transport components without damage or loss.
The coating application process in such machines often employs advanced technologies including electrostatic powder coating, precision spray atomization, or dip coating with tightly controlled immersion and withdrawal speeds. Electrostatic systems use finely tuned charging mechanisms that ensure powder particles are uniformly attracted to microscopic surfaces, achieving even coverage despite the small scale. For liquid coatings, micro-spray nozzles generate ultra-fine mists or droplets controlled by piezoelectric or ultrasonic actuators, enabling thin, consistent films without runoff or pooling.
Environmental control within the coating chamber is critical. These machines are typically enclosed with HEPA-filtered airflow to maintain a contaminant-free environment, preventing particulate intrusion that could compromise coating quality on sensitive micro-components. Temperature and humidity are precisely regulated to maintain optimal coating adhesion and curing performance.
Curing methods are tailored to the sensitivity of micro-sized products. Infrared or UV-LED curing technologies provide rapid and controlled polymerization without exposing parts to excessive heat that could cause deformation or damage. Some machines incorporate vacuum or inert atmosphere chambers to further protect sensitive materials during curing.
Automation and control systems in coating machines for micro-sized products are highly sophisticated. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and advanced motion controllers synchronize component handling, coating application, and curing cycles with microsecond precision. Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) offer detailed process visualization, recipe management, and fault diagnostics, enabling operators to maintain consistent quality and quickly adapt to new product specifications.
Quality assurance is integrated through high-resolution optical inspection systems capable of detecting microscopic coating defects such as pinholes, uneven thickness, or surface contamination. These inspection modules use techniques like laser scanning, machine vision, or interferometry to ensure coatings meet stringent specifications critical in high-reliability applications.
Modular design allows the integration of additional process steps such as surface cleaning with plasma or ultrasonic treatments, selective masking for partial coatings, and multi-layer application capabilities. This flexibility supports complex coating requirements and enables manufacturers to adapt quickly to evolving product designs.
Sustainability considerations include the use of solvent-free powder coatings or water-based liquids, efficient material recovery systems, and energy-saving curing technologies. Enclosed systems minimize operator exposure and environmental emissions, aligning with strict regulatory standards and corporate sustainability goals.
In summary, coating machines for micro-sized products combine ultra-precise handling, advanced application technologies, controlled curing, and intelligent automation to deliver high-quality coatings on the tiniest components. These machines are critical enablers for industries pushing the boundaries of miniaturization and performance, ensuring durable, functional, and defect-free finishes at microscopic scales.
Coating machines for micro-sized products are engineered to operate with exceptional precision and repeatability, ensuring that each tiny component receives an even and consistent coating without damage or loss. The delicate nature of micro-parts requires that handling systems minimize mechanical stress while maintaining throughput efficiency. To achieve this, manufacturers employ a combination of high-precision feeders, robotic micro-manipulators, and gentle transport mechanisms like air bearings or magnetic levitation conveyors, which provide near-frictionless movement and reduce contamination risks.
The coating application process is meticulously controlled using state-of-the-art dispensing technologies. Electrostatic powder coating systems designed for micro-parts adjust voltage and particle charge dynamically to accommodate varying part shapes and surface conditions, maximizing powder adhesion while minimizing overspray and waste. Liquid coating systems use micro-nozzles that deliver droplets in the range of microliters or less, employing piezoelectric or ultrasonic actuation to produce fine, uniform sprays with minimal overspray or dripping. Some machines incorporate aerosol jet or vapor deposition methods to apply ultra-thin, conformal coatings on complex micro-geometries.
Environmental conditions within the coating chamber are tightly regulated. HEPA filtration ensures an ultra-clean environment, free of dust and particulates that could compromise coating integrity on tiny surfaces. Temperature and humidity controls stabilize the coating process, preventing defects caused by condensation, uneven drying, or powder agglomeration. In some setups, inert gas atmospheres such as nitrogen or argon are introduced to prevent oxidation or moisture-sensitive reactions during coating and curing.
Curing technologies integrated into these machines are carefully selected to suit the thermal sensitivities of micro-sized components. UV-LED curing provides rapid polymerization at low temperatures, ideal for heat-sensitive materials or coatings. Infrared and convection ovens with zoned temperature control ensure uniform curing without hotspots that could cause warping or degradation. Vacuum and inert atmosphere curing options further protect delicate micro-assemblies during the hardening phase.
Automation and control systems utilize high-resolution sensors and feedback loops to synchronize every aspect of the coating cycle. Advanced motion control ensures precise timing between part positioning, coating application, and curing, minimizing cycle times while maintaining quality. Human-machine interfaces provide operators with real-time monitoring, recipe management, and predictive maintenance alerts, allowing quick adjustments and minimizing downtime.
Quality assurance in micro-sized product coating machines leverages cutting-edge inspection technologies. Optical and laser-based systems detect microscopic surface defects, thickness variations, and coating uniformity with sub-micron resolution. Some machines employ interferometry or confocal microscopy for three-dimensional surface profiling, ensuring coatings meet stringent industry specifications. Defective parts can be automatically rejected or routed for reprocessing, reducing waste and improving overall yield.
Flexibility is a hallmark of modern micro-sized product coating machines. Modular architectures allow integration of surface pretreatment steps such as plasma cleaning or ultrasonic degreasing to enhance coating adhesion. Selective masking and multi-layer coating stations enable complex coating schemes, including conductive, insulating, or protective layers tailored to specific functional requirements. This adaptability supports rapid product development and customization in sectors where micro-scale innovation is critical.
Sustainability is increasingly embedded in the design of these machines. Solvent-free powders and water-based liquids reduce environmental impact and operator exposure. Efficient material recovery systems capture and recycle overspray, minimizing waste. Energy-efficient curing technologies and enclosed chambers reduce emissions and power consumption, helping manufacturers meet stringent environmental regulations and corporate responsibility goals.
Overall, coating machines for micro-sized products represent the pinnacle of precision manufacturing technology. By combining ultra-fine handling, advanced coating application, controlled curing, and integrated quality control, these systems enable manufacturers to produce durable, high-performance coatings on some of the smallest and most complex components in modern industry. Their capabilities are essential for advancing miniaturization trends and meeting the exacting standards of fields such as medical devices, microelectronics, aerospace, and advanced instrumentation.
Advancements in coating machines for micro-sized products continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in micro-manufacturing. Emerging technologies such as additive manufacturing integration allow these coating systems to work seamlessly with 3D-printed micro-components, enabling complex geometries to be coated uniformly without manual intervention. This integration accelerates product development cycles and opens new avenues for functionalizing micro-parts with tailored surface properties.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being incorporated into coating process control to enhance precision and reliability. By analyzing real-time sensor data and historical production records, AI algorithms can predict optimal coating parameters, detect anomalies, and suggest corrective actions before defects occur. This proactive approach reduces scrap rates, improves process stability, and supports continuous improvement initiatives in high-mix, low-volume manufacturing environments.
The miniaturization of sensors and actuators enables more compact, efficient, and responsive coating systems. Micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) technology is applied to create ultra-precise dispensing valves, environmental sensors, and position feedback devices, improving the machine’s ability to deliver consistent coatings on increasingly smaller features. This technology also allows for the development of portable or benchtop coating systems suitable for specialized research and small-batch production.
Enhanced environmental controls, including cleanroom compatibility and integration with humidity and particulate monitoring systems, ensure that coating processes for micro-sized products meet the rigorous standards required in pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and aerospace industries. These systems often include automated cleaning cycles and protocols for rapid changeover between coating formulations, maintaining cleanliness and preventing cross-contamination.
User interfaces are evolving toward more intuitive, touch-based controls supplemented with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) training modules. Operators can receive real-time guidance on machine setup, maintenance, and troubleshooting, reducing reliance on specialized technicians and minimizing downtime. Remote monitoring and diagnostics enable expert support without the need for onsite visits, further enhancing operational efficiency.
Material science innovations complement advancements in coating machinery. The development of novel powder and liquid coatings with improved adhesion, flexibility, and functional properties—such as antimicrobial, conductive, or hydrophobic characteristics—expands the applications for micro-sized product coatings. Coating machines are adapted to handle these advanced materials, including their specific application and curing requirements.
Safety features continue to improve, with enclosed systems minimizing operator exposure to fine powders and hazardous chemicals. Automated interlocks, emergency stop functions, and fail-safe mechanisms ensure safe operation even in complex, high-speed processes. Compliance with international safety and environmental standards is integral to the design and certification of these machines.
In summary, coating machines for micro-sized products are at the forefront of precision manufacturing, incorporating cutting-edge automation, environmental controls, materials handling, and quality assurance. They enable industries to meet the growing demand for smaller, more sophisticated components with functional, reliable coatings that are essential for performance and longevity. Continuous innovation in this field ensures that manufacturers remain competitive in an increasingly miniaturized and high-tech global market.
Powder Painting Machine for Small Batch Items
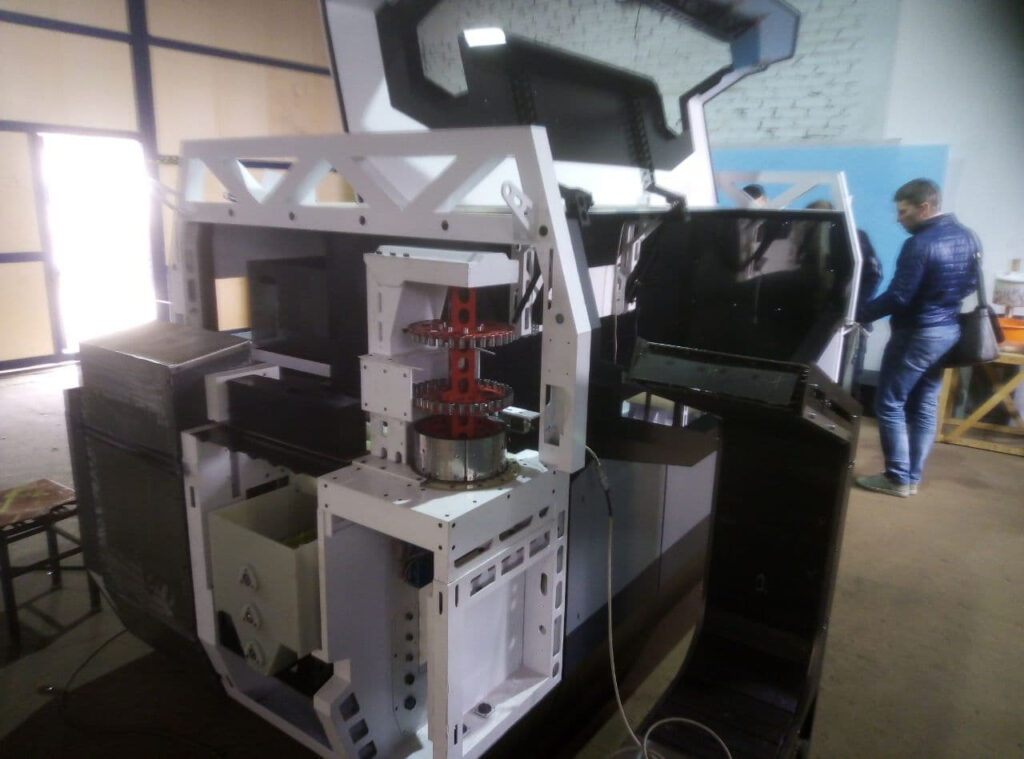

A powder painting machine for small batch items is specifically designed to provide high-quality, efficient coating solutions for limited production runs or customized parts. Unlike large-scale industrial powder coating systems optimized for mass production, these machines focus on flexibility, ease of use, and quick changeovers to accommodate frequent shifts in product types, colors, and batch sizes without compromising coating performance.
Such machines are ideal for manufacturers, prototyping labs, repair shops, and specialized product lines where small batches of metal or plastic components need durable, uniform finishes with minimal setup time. They enable businesses to maintain cost-effectiveness while meeting stringent aesthetic and protective coating requirements for small quantities of items ranging from hardware components and electronic housings to automotive parts and decorative accessories.
Powder painting machines for small batches often feature compact footprints and modular designs, allowing them to fit into limited workspace environments. They utilize user-friendly interfaces with programmable recipes to quickly recall process parameters such as powder type, spray voltage, application time, and curing temperature. This facilitates fast preparation and consistent results even when switching between different products or colors.
The powder application system incorporates electrostatic spray guns capable of fine-tuning powder flow and charge to suit varied part geometries and coating thicknesses. Some machines include manual or automated rotary fixtures and turntables that ensure uniform coverage by rotating the parts during spraying. This is especially useful for complex or irregularly shaped small batch items where consistent coating is critical.
Integrated curing ovens or tunnels with adjustable temperature settings provide controlled, uniform heat treatment necessary to fully cure the powder coating. Depending on space and production requirements, curing units may range from compact infrared ovens for rapid curing to convection ovens that accommodate multiple parts simultaneously.
Powder recovery and filtration systems are often included even in small batch machines to reduce waste and environmental impact. These systems capture overspray powder for reuse, improving material efficiency and lowering operational costs. Additionally, enclosed or semi-enclosed spray booths with proper ventilation protect operators and maintain a clean working environment.
Automation levels in powder painting machines for small batches vary from manual setups requiring operator intervention to semi-automated systems that combine programmable controls with mechanical handling aids. Higher-end units may feature robotic arms or gantries for precise, repeatable spraying, enhancing consistency while reducing labor intensity.
Quality control features such as coating thickness gauges, inspection lighting, and integrated vision systems may be incorporated or added as accessories to verify coating uniformity and adherence. This ensures that even small production runs meet quality standards comparable to large-scale manufacturing.
In summary, powder painting machines designed for small batch items strike a balance between flexibility, precision, and efficiency. They empower manufacturers and service providers to produce high-quality powder-coated finishes on limited quantities of parts without the expense and complexity of full-scale production lines, supporting customization, prototyping, and short-run manufacturing needs.
Powder painting machines for small batch items are increasingly incorporating modular components that enable users to customize their systems according to specific workflow requirements and space constraints. This modularity allows for easy integration of additional features such as pre-treatment stations, masking devices, or multi-color spray booths, enhancing the machine’s versatility without significant reconfiguration or downtime. Manufacturers benefit from this flexibility by adapting their powder coating processes to a wide variety of products and finishing specifications.
Handling systems in these machines are designed to accommodate diverse part sizes and shapes commonly found in small batch production. Fixtures such as adjustable racks, rotary tables, or robotic end-effectors ensure secure positioning of parts during spraying, minimizing manual handling and potential damage. In some setups, quick-change tooling and interchangeable fixtures facilitate rapid switching between different product runs, further reducing setup times and increasing overall productivity.
The powder application technology employed often includes advanced electrostatic spray guns with adjustable parameters like voltage, powder flow rate, and spray pattern. These adjustments are crucial when dealing with small batch items that may vary widely in geometry and surface area, ensuring optimal coating thickness and coverage without excessive powder consumption or overspray. Some systems also feature multi-gun arrangements or robotic spray arms that can be programmed for precise, repeatable application on complex parts.
Curing solutions integrated into powder painting machines for small batches are optimized for efficiency and energy savings. Compact infrared or convection ovens provide rapid and uniform curing, with programmable temperature profiles tailored to different powder formulations and part sensitivities. Some systems incorporate heat recovery features or insulated curing chambers to minimize energy consumption, aligning with sustainability goals and reducing operational costs.
Environmental controls are critical components of these machines, especially in small production environments where operator safety and cleanliness are paramount. Enclosed or semi-enclosed spray booths with high-efficiency filtration capture airborne powder particles, preventing contamination and maintaining air quality. Powder recovery units maximize material reuse, reducing waste and lowering powder costs, which is particularly important for expensive specialty powders often used in small batch applications.
User interfaces on modern powder painting machines for small batch items are designed for intuitive operation, often featuring touchscreen displays with recipe management, real-time process monitoring, and diagnostics. These interfaces simplify training requirements and empower operators to quickly adjust process parameters or troubleshoot issues, enhancing uptime and product consistency. Connectivity options allow integration with broader manufacturing execution systems (MES) for traceability and production management.
Quality assurance in small batch powder coating machines may include inline or offline inspection tools. Thickness gauges measure coating uniformity to ensure compliance with specifications, while visual inspection stations equipped with specialized lighting help detect surface defects or color inconsistencies. Some advanced systems employ machine vision technologies capable of automated defect recognition, which further enhances quality control without increasing labor costs.
Overall, powder painting machines tailored for small batch items enable manufacturers to achieve the benefits of powder coating—such as durability, environmental friendliness, and aesthetic appeal—without the scale or expense of large automated lines. They support flexible production schedules, rapid color changes, and customization, making them ideal for prototype development, specialty manufacturing, and businesses focused on niche markets or bespoke products. By balancing precision, efficiency, and adaptability, these machines help small batch producers compete effectively in increasingly demanding and dynamic industries.
Powder painting machines designed for small batch items also emphasize ease of maintenance and rapid cleaning to support frequent job changes. Components such as spray guns, powder hoppers, and recovery systems are engineered for quick disassembly and cleaning, reducing downtime between batches and minimizing the risk of cross-contamination between different powder colors or formulations. Automated cleaning cycles and blow-back systems further streamline maintenance tasks, allowing operators to focus on production rather than manual cleaning.
Flexibility in powder types is another important feature of these machines. They can handle a broad spectrum of powder formulations—including standard polyester, epoxy, hybrid, and specialty functional powders such as anti-corrosive, heat-resistant, or textured finishes—making them suitable for a wide variety of applications and industries. This adaptability is critical for small batch producers who often work with diverse products requiring different coating properties.
Integration with upstream and downstream processes enhances overall workflow efficiency. For example, some powder painting machines can be linked with pre-treatment systems like washing or phosphating stations to ensure optimal surface preparation before coating. Downstream, coated parts can be transferred automatically to curing ovens, cooling racks, or inspection stations, enabling a smooth, continuous process even at small scales.
Safety is a priority in these machines, with features such as enclosed spray areas, interlocked access doors, emergency stop buttons, and proper ventilation systems to protect operators from powder inhalation and exposure to moving parts. Compliance with relevant health, safety, and environmental regulations is built into the design, providing peace of mind for operators and facility managers alike.
Because small batch production often requires agility and responsiveness to customer demands, many powder painting machines support remote monitoring and control capabilities. Through network connectivity and IoT integration, operators and managers can track production status, adjust parameters, and receive alerts from anywhere, facilitating efficient resource management and timely decision-making.
Training and support services accompany these machines to ensure operators can quickly become proficient with the equipment, maximizing productivity and coating quality. Manufacturers often provide comprehensive documentation, video tutorials, and on-site or remote assistance to minimize learning curves and address issues promptly.
In summary, powder painting machines for small batch items combine compact design, flexible operation, and efficient maintenance to deliver high-quality, consistent coatings on limited runs or specialized parts. Their focus on adaptability, ease of use, and process integration makes them indispensable tools for businesses that require the benefits of powder coating without the constraints of large-scale production lines. By enabling cost-effective, customizable finishing solutions, these machines help small batch manufacturers meet evolving market demands and maintain competitive advantage.
Powder Coating Line for Small Hardware
A powder coating line for small hardware is a specialized production system designed to efficiently apply durable and uniform powder coatings to small metal components such as screws, nuts, bolts, washers, hinges, brackets, and other fasteners or fittings. These lines are tailored to handle the unique challenges associated with coating numerous tiny parts that often have complex shapes, varying sizes, and require consistent, high-quality finishes for corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and enhanced durability.
Such powder coating lines typically feature automated or semi-automated material handling systems that facilitate the careful transfer, orientation, and positioning of small hardware pieces throughout the coating process. Handling methods may include vibratory feeders, rotary tumblers, or conveyor baskets designed to hold multiple parts securely while exposing their surfaces evenly to the coating spray. This ensures comprehensive coverage while minimizing damage or loss during transport.
The powder application stage employs electrostatic spray technology adapted for small hardware items. Powder spray guns with adjustable voltage and powder flow settings generate a charged powder cloud that adheres uniformly to grounded parts. Multiple spray nozzles or robotic applicators may be used to reach intricate geometries and ensure complete surface coverage, even in threaded or recessed areas. The use of specialized spray booths with controlled airflow and powder recovery systems optimizes efficiency and minimizes overspray waste.
Following powder application, coated hardware moves through curing ovens that use infrared, convection, or UV-LED heating methods to solidify and bond the coating. These ovens are designed with zoned temperature controls and appropriate curing cycles to accommodate the thermal sensitivities and volume of small parts, ensuring uniform curing without warping or discoloration.
Powder coating lines for small hardware often integrate pre-treatment stations, such as cleaning, degreasing, and surface preparation modules, which improve coating adhesion and longevity. These can include washing baths, chemical treatments, or abrasive blasting systems depending on the material and contamination level of the hardware components.
Automation and control systems coordinate all aspects of the line, with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) enabling operators to set and monitor process parameters, manage recipes for different hardware types, and ensure repeatable quality. Data logging and connectivity support traceability and integration with broader manufacturing execution systems.
Quality assurance is enhanced through inline inspection equipment such as thickness gauges, optical cameras, and color measurement devices, which verify coating uniformity and adherence to specifications. Defective parts can be automatically rejected or flagged for reprocessing, maintaining overall product quality.
Modularity in design allows these lines to be customized with additional features such as selective masking stations, multi-layer coating capabilities, or post-coating finishing modules to meet specific customer requirements or product standards.
Environmental controls, including powder recovery units and enclosed spray booths with filtered ventilation, ensure operator safety, reduce environmental impact, and comply with regulatory standards. The use of solvent-free powder coatings further contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices.
In summary, powder coating lines for small hardware combine precise handling, advanced electrostatic application, controlled curing, and robust automation to deliver high-quality, consistent coatings on a wide range of miniature metal components. These systems enable manufacturers to efficiently produce durable, attractive, and corrosion-resistant hardware products suited for diverse industrial and commercial applications.
Powder coating lines for small hardware are designed to maximize throughput while maintaining exceptional coating quality on often delicate and intricately shaped parts. The material handling systems play a crucial role by ensuring that hardware pieces are consistently presented to the coating stations with minimal overlap or shadowing, which can cause uneven coverage. Techniques such as vibratory bowls or feeders carefully orient parts before loading them into baskets, trays, or tumblers that rotate or agitate during coating to expose all surfaces evenly. This dynamic handling reduces the need for manual repositioning and improves overall efficiency.
The electrostatic powder application process is finely tuned to accommodate the varied surface textures and geometries of small hardware. Spray guns with adjustable electrostatic charge and powder flow rates are strategically positioned to target all areas, including threads, holes, and recesses, which are challenging to coat uniformly. Some systems use multiple spray booths in sequence or robotic arms with multi-axis movement to reach complex contours, ensuring full coverage without excessive buildup that could interfere with part functionality.
Curing ovens integrated into these lines are engineered to deliver uniform heat distribution across dense loads of small hardware. Infrared ovens offer rapid heat-up and energy efficiency, while convection ovens provide consistent temperature control for larger batches. UV-LED curing ovens are increasingly popular for heat-sensitive parts, offering instant curing at lower temperatures and reducing the risk of thermal distortion. Zoned heating and adjustable conveyor speeds allow for fine control over curing profiles, adapting to different powder types and part materials.
Pre-treatment modules are essential to prepare hardware surfaces for optimal powder adhesion. Cleaning systems may employ ultrasonic baths, chemical degreasing, or phosphate conversion coatings, depending on the metal type and degree of contamination. Automated rinse and drying stations ensure that parts enter the powder coating stage clean and dry, preventing common coating defects such as poor adhesion or surface blemishes.
Automation and control software provide real-time monitoring of line performance, powder usage, curing temperatures, and coating parameters. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) facilitate recipe management, enabling quick changes between different hardware types or coating colors. Data acquisition supports quality traceability and process optimization, essential for meeting industry standards and customer specifications.
Inline inspection systems contribute significantly to maintaining high-quality standards. Thickness measurement tools, colorimeters, and vision systems detect deviations from target specifications early, allowing for immediate corrective actions. Automated rejection stations remove parts with coating defects, ensuring that only conforming products advance to packaging or assembly.
Environmental and safety considerations are integral to line design. Enclosed spray booths equipped with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and powder recovery units capture overspray and minimize airborne particles, protecting operators and reducing material waste. The use of solvent-free powder coatings reduces volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, aligning with environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Modularity and scalability allow manufacturers to tailor powder coating lines for small hardware to their specific production volumes and product diversity. Additional modules, such as selective masking stations or multi-coat application booths, can be integrated as needed, providing flexibility for future product lines or coating requirements without substantial capital investment.
Overall, powder coating lines for small hardware deliver a comprehensive solution combining precise handling, sophisticated coating technology, efficient curing, and rigorous quality control. They enable manufacturers to produce consistently coated, corrosion-resistant, and visually appealing small metal components at high throughput, meeting the demanding requirements of industries such as automotive, electronics, construction, and consumer goods.
Powder coating lines for small hardware also benefit from continuous innovation in automation and digitalization, which enhance their efficiency and reliability. Advanced robotics and vision-guided systems are increasingly employed to handle the loading and unloading of small parts, reducing manual labor and the risk of damage or contamination. These robots can precisely manipulate hardware items, placing them in optimal positions for coating and inspection, even for mixed or complex batches.
Data analytics and machine learning are being integrated into line management software to optimize process parameters dynamically. By analyzing real-time data such as powder flow rates, electrostatic charge levels, conveyor speeds, and oven temperatures, these smart systems can predict maintenance needs, detect process deviations early, and suggest adjustments to improve coating uniformity and reduce waste. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and enhances product quality consistency.
The use of environmentally friendly powders continues to grow, with manufacturers offering a wide variety of specialized powders that provide functional benefits like corrosion resistance, UV protection, or enhanced wear characteristics. These powders are formulated to cure efficiently in the line’s ovens, often requiring lower temperatures or shorter curing times, which improves energy efficiency and throughput.
Sustainability initiatives in powder coating lines for small hardware also focus on reducing material waste through improved powder recovery and recycling systems. Advanced cyclone separators, filter units, and electrostatic recovery technologies enable high rates of powder reclaim, lowering raw material costs and environmental impact. Enclosed systems minimize dust emissions, improving workplace safety and air quality.
Safety features are continually enhanced to comply with stringent industry standards. Lines incorporate interlocked access points, emergency stop mechanisms, and real-time monitoring of ventilation and particulate levels to protect operators. Training programs and intuitive user interfaces help ensure safe operation and quick response in case of anomalies.
Customization remains a key advantage of powder coating lines tailored for small hardware. Manufacturers can configure lines to handle a diverse range of part sizes, shapes, and coating requirements, supporting batch sizes from prototypes to full production runs. This flexibility is vital for industries requiring frequent product updates or specialized finishes.
In summary, powder coating lines for small hardware combine cutting-edge automation, precise electrostatic application, efficient curing technologies, and comprehensive quality control to deliver high-quality, durable finishes on small metal components. Their adaptability, sustainability, and integration with digital tools empower manufacturers to meet evolving market demands with speed and consistency, maintaining competitiveness in industries where performance and appearance of hardware are critical.
Painting Machine for Mini Parts
A painting machine for mini parts is a specialized piece of equipment designed to apply coatings—whether liquid paint, powder coating, or other finishes—to very small components with precision, efficiency, and consistency. These machines cater to industries like electronics, medical devices, watchmaking, automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering, where miniaturized parts require uniform, high-quality coatings that protect, decorate, or add functional properties without compromising their delicate structures.
Handling mini parts requires meticulous care to avoid damage or loss. Painting machines for these components integrate advanced material handling systems such as micro-feeders, vibratory bowls, precision conveyors, or robotic pick-and-place arms that gently orient and transport parts through the coating process. These systems ensure consistent positioning, enabling accurate and repeatable application while minimizing manual handling and potential contamination.
Coating application technologies vary based on the type of finish needed. For liquid paints, machines often use fine atomization spray nozzles or air-assisted micro-spray guns capable of delivering ultra-fine droplets that provide even coverage without excessive overspray or pooling. For powder coatings, electrostatic spray guns with adjustable voltage and flow settings are optimized for miniature parts to ensure charged powder particles adhere uniformly across complex geometries. Some machines also employ dip coating, flow coating, or precision dispensing for selective or controlled application on tiny surfaces.
Enclosed spray booths with controlled airflow and filtration maintain a clean environment during painting, reducing particulate contamination and protecting operators from fumes or powder exposure. These booths are designed with compact footprints and ergonomic access tailored for small parts production environments.
Curing systems integrated with these machines depend on the coating type. Infrared, convection, or UV-LED curing ovens provide rapid, uniform curing tailored to the thermal sensitivity of mini parts and the coating chemistry. Some machines offer programmable temperature profiles and zoning to avoid overheating delicate components while ensuring full cure.
Automation and control systems synchronize handling, application, and curing stages with high precision. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to manage process parameters, switch between different product recipes, and monitor production in real-time. Data logging supports traceability and quality control, which are critical in regulated industries.
Quality assurance is integrated via inline inspection technologies such as high-resolution cameras, laser thickness gauges, and colorimeters that detect coating defects, thickness variations, or color inconsistencies on tiny surfaces. Automated rejection or rework systems enhance yield and reduce waste.
Modular machine designs enable customization with additional features like surface pre-treatment, selective masking, multi-layer coating, or post-paint finishing processes. This flexibility supports rapid adaptation to evolving product designs or finishes.
Safety and environmental considerations are paramount, with enclosed systems, effective ventilation, and powder recovery ensuring operator protection and regulatory compliance. Use of low-VOC paints, water-based formulations, and energy-efficient curing contribute to sustainable operations.
In summary, painting machines for mini parts deliver precise, consistent, and high-quality coatings tailored to the challenges of miniature components. Their advanced handling, application, curing, and inspection technologies enable manufacturers to meet demanding performance, aesthetic, and regulatory requirements while maintaining productivity and cost-effectiveness.
Painting machines for mini parts prioritize precision and consistency throughout every stage of the coating process. Material handling systems are engineered to delicately manage parts that often measure just millimeters or less, ensuring each component is properly oriented and spaced to receive uniform coverage. This careful handling minimizes part loss, damage, or contamination, which are critical concerns when dealing with fragile or intricate miniatures.
The application technologies integrated into these machines are finely tuned to produce ultra-thin, even coatings. Spray systems utilize micro-nozzles or electrostatic powder guns capable of delivering finely atomized particles that conform closely to the part’s surface, including complex shapes and tight recesses. Adjustable spray parameters such as pressure, flow rate, and electrostatic charge enable operators to optimize coverage for different part geometries and coating materials, reducing waste and avoiding defects like runs, sags, or uneven buildup.
Environmental control is crucial in painting mini parts, so coating chambers often feature filtered airflow systems that maintain clean, particle-free atmospheres. This prevents contamination of delicate surfaces and protects operators from exposure to airborne powders or volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Compact, enclosed booths with ergonomic access are designed to fit within limited production spaces typical of precision manufacturing facilities.
Curing technologies matched to mini parts provide rapid, uniform hardening while protecting sensitive components from heat damage. Infrared curing ovens allow targeted heating with minimal thermal stress, convection ovens ensure consistent temperature distribution across batches, and UV-LED curing systems offer near-instant cure times at low temperatures, ideal for heat-sensitive materials or coatings. Programmable curing profiles allow manufacturers to tailor cycles precisely to specific coating chemistries and part tolerances.
Automation and control systems coordinate the entire process, enabling seamless integration of handling, spraying, and curing with minimal operator intervention. Human-machine interfaces provide intuitive recipe management, real-time monitoring, and diagnostic capabilities that facilitate quick changeovers between different part types or finishes. Data logging and connectivity options support traceability and quality assurance, which are essential in regulated industries such as medical devices or aerospace.
Quality inspection is integrated inline or offline, employing high-resolution imaging, laser thickness measurement, and color analysis to detect coating imperfections or deviations from specifications. Automated sorting or rejection mechanisms remove defective parts before packaging or assembly, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing waste.
Flexibility in machine design allows for modular additions such as surface preparation stations, selective masking devices for partial coating, or multi-layer application setups that enable functional or decorative finishes tailored to product requirements. This adaptability supports rapid product development cycles and small batch production runs without sacrificing efficiency.
Safety and environmental considerations are integral to the design of painting machines for mini parts. Enclosed systems, efficient ventilation, and powder recovery minimize operator exposure and environmental emissions. The use of low-VOC paints, water-based coatings, and energy-efficient curing technologies aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices and regulatory compliance.
Overall, painting machines for mini parts combine sophisticated handling, precise application, controlled curing, and rigorous quality control to deliver superior finishes on some of the smallest and most intricate components. These systems enable manufacturers to meet the demanding performance, aesthetic, and regulatory standards of modern industries while maintaining flexibility and cost-effectiveness in their production processes.
Painting machines for mini parts continue to evolve with advancements in automation, robotics, and digital technologies that further enhance precision, throughput, and adaptability. Modern systems often incorporate robotic arms equipped with multi-axis movement, enabling them to coat parts from multiple angles with consistent coverage. These robots can be programmed for complex spraying paths and speeds, reducing human error and increasing repeatability—key advantages when working with delicate, high-value mini components.
Integration of machine learning and AI-driven process control is becoming increasingly common. By analyzing real-time sensor data, such as spray pattern consistency, powder flow, and curing temperatures, intelligent systems can optimize coating parameters dynamically to maintain optimal performance and reduce defects. Predictive maintenance algorithms help minimize downtime by forecasting equipment servicing needs before breakdowns occur, improving overall line efficiency.
Miniaturization of sensors and actuators also allows for more compact, responsive, and precise control within the painting machine. Microfluidic valves, piezoelectric nozzles, and ultrasonic spray heads provide finer control over paint droplet size and placement, enabling ultra-thin, uniform coatings on even the smallest surfaces without waste or overspray. These technologies are especially beneficial in applications demanding extremely high cosmetic or functional finish standards, such as medical implants or precision optics.
Environmental control systems in painting machines for mini parts have advanced to maintain strict cleanroom standards when required. HEPA or ULPA filtration, controlled humidity, and temperature stabilization prevent contamination and ensure coating consistency in sensitive manufacturing environments. Enclosed systems with automated cleaning cycles reduce operator exposure and facilitate quick color or material changes, supporting high-mix, low-volume production scenarios.
User interfaces have become more intuitive and operator-friendly, often featuring touchscreen panels with graphical process visualization, recipe management, and troubleshooting guidance. Remote monitoring and control capabilities allow operators and engineers to supervise processes and adjust parameters via mobile devices or centralized control rooms, enabling faster response times and more efficient production management.
The adoption of environmentally friendly coatings continues to grow, with waterborne paints, UV-curable formulations, and solvent-free powders becoming increasingly compatible with painting machines for mini parts. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but often offer improved durability and faster curing times, enhancing throughput and product quality.
Safety remains paramount, with machines designed to meet rigorous international standards. Features such as interlocked safety doors, emergency stop systems, and continuous monitoring of ventilation and particulate levels protect operators and comply with workplace safety regulations.
In summary, painting machines for mini parts represent a convergence of precision engineering, advanced automation, smart controls, and sustainable design. They enable manufacturers to consistently produce high-quality, functional, and visually appealing coatings on some of the smallest components in modern industries, supporting innovation and competitiveness in sectors where detail and quality are paramount.
Fast Painting Machine for Small Circuit Parts
A fast painting machine for small circuit parts is a highly specialized system engineered to apply precise, uniform coatings rapidly and efficiently to tiny electronic components such as connectors, terminals, printed circuit boards (PCBs), and microelectronic assemblies. These parts require protective coatings that offer insulation, moisture resistance, corrosion protection, and sometimes specific electrical properties—all while preserving the intricate geometry and delicate features crucial to their function.
Speed and precision are paramount in these machines to meet high-volume manufacturing demands without compromising coating quality. Advanced material handling systems carefully transport and orient small circuit parts using micro-feeders, precision conveyors, or robotic arms with vacuum or mechanical grippers. These systems ensure minimal handling damage and consistent positioning to facilitate accurate, repeatable coating application.
The coating application often involves conformal coating technologies such as selective spray, dip, or jetting systems, using specialized liquid materials like acrylics, silicones, urethanes, or epoxy-based coatings formulated for electronics. Spray nozzles are designed to deliver ultra-fine atomization with controlled droplet size, enabling thin, uniform films that avoid pooling or bridging on tiny circuitry features. In some machines, automated selective coating systems use programmable jets or needles that precisely deposit coating only where needed, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste.
Enclosed spray chambers with filtered airflow maintain a clean environment, minimizing particulate contamination and protecting sensitive electronics from exposure to dust or overspray. Temperature and humidity controls further ensure coating consistency and adhesion.
Curing systems integrated into these fast painting machines utilize methods optimized for electronics, such as UV or LED curing that offer rapid polymerization at low temperatures, reducing thermal stress on components. Some setups employ infrared or convection ovens with precise temperature profiling to balance curing speed with part safety.
Automation and control systems coordinate part handling, coating application, and curing stages with high-speed synchronization. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allow for recipe management, real-time process monitoring, and quality control, supporting rapid changeovers and multi-product manufacturing.
Quality assurance incorporates inline inspection technologies like optical cameras, thickness gauges, and fluorescence detection to verify coating coverage, thickness, and uniformity. Automated rejection systems help maintain product integrity by removing parts with coating defects.
Safety and environmental controls include enclosed booths, extraction systems, and low-VOC coating materials to protect operators and minimize emissions. Powder recovery or solvent reclamation may be included in some configurations.
In summary, fast painting machines for small circuit parts combine advanced handling, precise application, rapid curing, and robust automation to deliver high-quality, protective coatings efficiently at scale. These systems are essential for electronics manufacturers seeking to protect miniature components reliably while meeting demanding production schedules and quality standards.
Fast painting machines for small circuit parts are engineered to optimize both throughput and precision, addressing the unique challenges posed by miniature electronic components. The material handling systems are designed to gently but accurately manage delicate parts, often incorporating anti-static measures to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge. High-speed conveyors, vibratory feeders, or robotic pick-and-place units ensure smooth, continuous flow of components through the coating process without bottlenecks or part loss.
The coating application stage utilizes highly controlled spray or jetting technologies capable of depositing ultra-thin, uniform layers. Selective coating systems employ programmable micro-nozzles or needle dispensers that target specific areas on complex circuitry, minimizing material usage and avoiding coating-sensitive contacts or connectors. These systems often include vision-guided robotics to adjust spray paths dynamically based on part geometry and orientation, ensuring consistent quality across variable part designs.
Environmental control within the painting chambers is critical to maintain coating integrity and prevent contamination. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration and controlled airflow create clean conditions, while humidity and temperature are stabilized to enhance adhesion and curing performance. Enclosures also protect operators from exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or fine aerosols produced during spraying.
Curing technologies integrated into these machines prioritize speed and component safety. UV or LED curing offers near-instantaneous polymerization at low temperatures, crucial for heat-sensitive electronics. Infrared and convection ovens with zoned temperature control provide alternative curing methods suited to different coating chemistries or part materials. Some systems incorporate inert atmospheres or vacuum chambers during curing to prevent oxidation and improve coating quality.
Advanced automation systems synchronize part movement, coating application, and curing processes with millisecond precision to maximize throughput without sacrificing coating quality. Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) offer intuitive control, recipe storage, and real-time monitoring, enabling operators to manage multiple product variants and rapidly adjust parameters for new coatings or components. Data logging supports traceability, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance.
Quality assurance features include inline optical inspection, laser thickness measurement, and fluorescence detection to identify coating defects, incomplete coverage, or excessive thickness. Automated rejection or diversion systems help maintain high yields by ensuring only conforming parts proceed to packaging or assembly.
Safety and environmental considerations are integral to machine design. Enclosed booths with extraction and filtration systems protect workers and reduce emissions, while the use of low-VOC or water-based coatings aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices. Interlocks, emergency stops, and safety sensors ensure safe operation in high-speed environments.
Modular design allows manufacturers to customize fast painting machines for small circuit parts according to production needs, integrating pre-treatment stations, selective masking, or multi-layer coating capabilities. This flexibility supports evolving product designs and fast-paced electronics manufacturing cycles.
Overall, these fast painting machines enable electronics manufacturers to achieve rapid, precise, and reliable protective coatings on miniature circuit components. By combining cutting-edge handling, application, curing, and inspection technologies, they help maintain product quality, enhance durability, and meet the demands of high-volume, high-mix production environments.
Fast painting machines for small circuit parts continue to benefit from integration with Industry 4.0 technologies, enabling smarter manufacturing processes and improved operational efficiency. Connectivity through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) allows these machines to communicate with factory-wide systems, providing real-time data on production rates, equipment health, and coating quality. This connectivity facilitates predictive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime, and supports advanced analytics to optimize process parameters for better yield and lower costs.
Robotics and automation are increasingly sophisticated, with multi-axis robotic arms capable of handling a variety of part sizes and shapes with exceptional repeatability. Vision systems integrated with these robots enable dynamic adjustment to part position and orientation, ensuring precise coating application even in mixed or evolving product lines. The use of machine learning algorithms helps the system adapt to subtle variations in parts or environmental conditions, continuously refining coating accuracy and reducing scrap.
The trend toward environmentally sustainable manufacturing has driven the adoption of more eco-friendly coating materials and process improvements. Fast painting machines are now commonly designed to accommodate low-VOC, water-based, or UV-curable coatings, which reduce hazardous emissions and energy consumption. Powder coating variants for electronics provide solvent-free alternatives that offer excellent protection while minimizing environmental impact.
Operator interfaces have evolved to provide enhanced usability through touchscreens, augmented reality (AR) assistance, and remote access capabilities. Training modules integrated into machine software help operators quickly learn complex procedures, while remote diagnostics allow experts to troubleshoot issues without being onsite, speeding up repairs and minimizing downtime.
Safety features remain a priority, with machines incorporating comprehensive monitoring systems that detect abnormal conditions, enforce safe operating procedures, and provide emergency responses. Enclosures, filtered ventilation, and ergonomic designs protect workers from exposure to chemicals and mechanical hazards.
Modularity and scalability are key to future-proofing fast painting lines for small circuit parts. Manufacturers can expand or reconfigure systems easily to accommodate new products, higher volumes, or additional processes such as conformal coating inspection or encapsulation. This flexibility supports agile manufacturing, allowing rapid adaptation to market demands and technological advancements.
In conclusion, fast painting machines for small circuit parts exemplify the convergence of precision engineering, advanced automation, environmental responsibility, and digital intelligence. They empower electronics manufacturers to deliver high-quality, reliable coatings on miniature components at scale, driving product performance and competitive advantage in an increasingly complex and fast-moving industry landscape.
Painting Systems for Tech Components
Painting systems for tech components are specialized setups designed to apply protective and decorative coatings to electronic devices, precision parts, and other high-tech products. These systems cater to the stringent requirements of industries like consumer electronics, telecommunications, aerospace, medical devices, and automotive electronics, where coatings must provide electrical insulation, corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and aesthetic appeal without compromising the delicate functionality of the components.
Such painting systems integrate advanced material handling solutions that carefully transport fragile tech parts through various coating stages, minimizing mechanical stress and contamination risks. Automated feeders, robotic arms, and precision conveyors ensure consistent orientation and spacing, enabling uniform coating application even on miniature, complex geometries.
Coating application methods vary depending on the required finish and material. Techniques include electrostatic powder coating, liquid spray coating, dip coating, and selective jetting. Electrostatic powder coating offers durable, environmentally friendly finishes with minimal waste, while liquid spray and jetting provide thin, conformal coatings necessary for sensitive electronic circuits or optical elements. Selective coating technologies enable precise application to specific areas, protecting critical functional zones while optimizing material usage.
Environmental control is vital, so painting systems often feature enclosed, clean-room compatible booths with HEPA filtration and regulated temperature and humidity to maintain optimal coating conditions and protect sensitive components from particulates or moisture during processing.
Curing technologies integrated into these systems include infrared, convection, and UV or LED curing ovens. These provide rapid, controlled curing tailored to the thermal tolerance and coating chemistry of tech components, ensuring robust adhesion and finish quality without damaging heat-sensitive materials.
Automation and control systems synchronize handling, coating, and curing operations, offering programmable interfaces for recipe management, process monitoring, and quality control. Data logging and traceability features support compliance with industry standards and facilitate continuous improvement.
Quality assurance is enhanced with inline inspection technologies such as high-resolution cameras, laser thickness gauges, and colorimeters that detect coating defects, coverage gaps, or color deviations. Automated sorting systems remove non-conforming parts to maintain high product standards.
Safety and environmental considerations are integral, with systems designed to minimize operator exposure to fumes or powders, control emissions, and reduce waste. Use of low-VOC coatings, powder recovery units, and energy-efficient curing aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices.
Modularity and scalability enable customization of painting systems to specific production volumes, product types, and coating requirements. Additional modules such as surface pre-treatment, masking stations, or multi-layer coating capabilities can be integrated to address diverse application needs.
In summary, painting systems for tech components combine precision handling, versatile application technologies, controlled curing, and rigorous quality control to deliver high-performance, durable, and visually appealing coatings. These systems support manufacturers in meeting the complex demands of modern technology products while optimizing efficiency, quality, and environmental responsibility.
Painting systems for tech components are engineered to maintain a delicate balance between high precision and production efficiency. The handling mechanisms are designed to minimize mechanical stress on fragile or intricate parts, often incorporating soft-grip robotic arms, vacuum fixtures, or gentle conveyors that reduce the risk of scratches, deformation, or contamination. These systems can accommodate a wide range of component sizes and shapes, from tiny sensors and connectors to larger assemblies like circuit boards or device housings.
Coating application technologies are selected and fine-tuned based on the functional and aesthetic requirements of the components. Electrostatic powder coating provides a robust, environmentally friendly finish ideal for metal housings or brackets, delivering excellent corrosion resistance and durability. For more sensitive electronics or plastic parts, liquid spray coating with precision nozzles or selective jetting ensures thin, uniform, and conformal layers that do not interfere with electrical contacts or delicate features. Dip coating may be used for certain applications where complete immersion is beneficial, offering uniform coverage on complex geometries.
Environmental controls within painting systems are critical for consistent quality and operator safety. Enclosed booths with filtered airflow and climate regulation maintain clean processing conditions, reducing particulate contamination and preventing issues like orange peel texture or adhesion failure. Controlled humidity and temperature also help stabilize coating viscosity and drying characteristics, ensuring repeatable results across production batches.
Curing stages are tailored to the thermal and chemical characteristics of both the coatings and the tech components. Infrared and convection ovens provide efficient heat curing for many powder and liquid coatings, while UV and LED curing ovens offer rapid, low-temperature curing solutions ideal for heat-sensitive substrates. Programmable curing profiles enable precise control of ramp-up rates, hold times, and cooling, protecting delicate parts while achieving full polymerization.
Automation and control systems integrate the entire painting process, coordinating material handling, coating application, and curing with high accuracy and repeatability. Human-machine interfaces allow operators to manage process recipes, monitor system status, and quickly adjust parameters for different products or coatings. Data collection and analysis support traceability, quality assurance, and compliance with industry regulations such as IPC standards for electronics manufacturing.
Inline inspection technologies play a vital role in maintaining coating quality and consistency. High-resolution imaging systems detect surface defects, coverage gaps, and color variations, while thickness measurement tools verify that coatings meet specified tolerances. Automated sorting or rejection mechanisms ensure that only conforming components proceed to assembly or shipment, reducing costly recalls or rework.
Safety and environmental sustainability are embedded in system design. Ventilation systems with solvent recovery, powder reclaim units, and sealed coating booths minimize operator exposure and environmental emissions. The adoption of low-VOC, waterborne, and powder coatings aligns with evolving regulatory requirements and corporate sustainability goals.
The modular and scalable architecture of painting systems for tech components allows manufacturers to tailor setups to production volume, product complexity, and evolving market demands. Additional options like surface pre-treatment modules, selective masking stations, or multi-layer coating capability can be incorporated to meet specific technical or aesthetic challenges.
Overall, painting systems for tech components deliver reliable, high-quality coatings that protect and enhance advanced technological products. By combining precise handling, adaptable coating methods, controlled curing, and comprehensive quality assurance, these systems enable manufacturers to meet the demanding standards of modern electronics and technology industries while optimizing efficiency and sustainability.
Painting systems for tech components continue to advance alongside innovations in materials science and manufacturing technology, enabling even greater precision, speed, and environmental performance. The integration of smart sensors throughout the system allows continuous monitoring of critical parameters such as spray patterns, coating thickness, curing temperatures, and environmental conditions. This data-driven approach facilitates real-time process adjustments, reducing variability and enhancing yield.
Robotic automation plays an increasingly central role, with collaborative robots (cobots) working safely alongside human operators to handle delicate components, perform selective coating tasks, or carry out inline inspections. These robots are equipped with force feedback and vision systems, enabling gentle manipulation and adaptive coating strategies tailored to complex or irregular part geometries.
Advanced coating formulations developed specifically for tech applications offer enhanced properties such as improved electrical insulation, chemical resistance, thermal management, and even antimicrobial effects. Painting systems are designed to accommodate these specialty coatings, including conductive paints, transparent protective layers, or functional thin films applied via precise jetting or spray methods.
Environmental stewardship remains a priority, with painting systems adopting closed-loop powder recovery, solvent recycling, and energy-efficient curing technologies to minimize waste and emissions. Compliance with increasingly strict regulations drives ongoing innovation in coating materials and process optimization, helping manufacturers achieve sustainability goals without compromising product quality or throughput.
User interfaces and control software continue to evolve toward greater intuitiveness and integration, supporting features like remote operation, predictive maintenance alerts, and cloud-based analytics. These capabilities empower manufacturers to respond quickly to production changes, optimize resource use, and maintain consistent quality across multiple facilities or production lines.
Training and support services are also integral to successful painting system deployment, ensuring operators and maintenance personnel can efficiently manage complex equipment and respond effectively to process variations or faults. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tools are emerging as valuable aids for hands-on training, troubleshooting, and system upgrades.
In essence, painting systems for tech components embody a fusion of precision engineering, intelligent automation, advanced materials, and sustainable design. They enable manufacturers to produce highly reliable, visually appealing, and functionally robust coatings on a diverse array of technology products, supporting innovation and competitiveness in fast-evolving markets worldwide.
Auto Paint Solutions for Mini Electronics
Auto paint solutions for mini electronics are highly specialized automated systems designed to apply precise, consistent coatings to small electronic components and assemblies, such as connectors, sensors, circuit boards, and miniature housings. These solutions address the unique challenges of coating delicate, densely packed parts that require protection against moisture, dust, corrosion, and electrical interference while maintaining their compact form and functionality.
These automated painting systems incorporate gentle yet accurate material handling equipment—like micro-feeders, vacuum grippers, or robotic arms with soft-touch end effectors—that carefully transport and orient mini electronic parts through the coating process. This minimizes handling damage and ensures consistent positioning for uniform coating application.
Coating methods in these solutions typically include selective spray coating, jetting, dip coating, and electrostatic powder coating, each adapted to the size and sensitivity of the parts. Selective spray and jetting technologies use finely controlled nozzles or needles to deposit ultra-thin, conformal coatings exactly where needed, avoiding sensitive contacts or heat-sensitive areas. Electrostatic powder coating offers durable finishes for metal housings or shielding components with minimal overspray and waste.
Environmental control is essential in auto paint solutions for mini electronics. Enclosed booths with filtered airflow, temperature, and humidity control create clean processing conditions, preventing contamination and ensuring optimal coating adhesion and finish quality. These systems also protect operators from exposure to powders, solvents, or aerosols.
Curing processes are matched to the coating materials and substrate sensitivity, with UV and LED curing becoming popular for their rapid, low-temperature curing capabilities that prevent heat damage to electronic parts. Infrared and convection ovens are also used where appropriate, with precise temperature control and programmable profiles.
Automation and control software synchronize the entire process, coordinating part handling, coating application, and curing with high accuracy. User-friendly interfaces enable recipe management, real-time monitoring, and quick changeovers between products or coatings. Data logging supports quality control, traceability, and compliance with industry standards.
Quality assurance is integrated through inline inspection technologies such as optical imaging, fluorescence detection, and coating thickness measurement, enabling immediate identification and rejection of parts with defects or incomplete coverage.
Safety features include enclosed spray areas, interlocks, emergency stops, and efficient ventilation systems that meet health and environmental regulations. The use of low-VOC coatings and powder recovery systems aligns these solutions with sustainable manufacturing practices.
Modular design allows customization and scalability, enabling manufacturers to configure auto paint lines tailored to specific mini electronics applications, batch sizes, and production rates. Additional options like masking stations, multi-layer coating capabilities, and surface pre-treatment modules can be incorporated as needed.
Overall, auto paint solutions for mini electronics deliver high-precision, consistent, and durable coatings essential for protecting and enhancing small electronic devices. By combining advanced automation, tailored coating technologies, and rigorous quality control, these systems help manufacturers meet the demanding requirements of the fast-paced electronics industry efficiently and reliably.
Auto paint solutions for mini electronics continue to advance through the integration of cutting-edge automation and intelligent control systems that optimize efficiency and precision. Material handling technologies have become increasingly sophisticated, employing vision-guided robotics and adaptive grippers that can handle a wide variety of component shapes and sizes without manual intervention. This flexibility reduces downtime during product changeovers and supports high-mix, low-volume production common in electronics manufacturing.
Coating application processes are enhanced by micro-dispensing and selective jetting technologies, which enable ultra-precise deposition of conformal coatings, sealants, or insulating materials on targeted areas of miniature components. These systems minimize material waste and eliminate the risk of coating critical contact points, connectors, or heat-sensitive areas, ensuring functional integrity alongside protective performance.
The controlled environments within these systems maintain strict cleanroom standards when necessary, utilizing HEPA filtration and climate control to reduce contamination and ensure coating adhesion and finish quality. Automated cleaning and drying modules prepare parts before coating, improving surface receptivity and overall coating durability.
Curing technologies such as UV and LED systems provide rapid, energy-efficient hardening of coatings at low temperatures, protecting sensitive electronic parts from thermal damage while accelerating production cycles. Programmable curing profiles and real-time monitoring ensure consistent curing quality across varying product types and batch sizes.
Advanced software platforms coordinate all aspects of the painting process, integrating part tracking, recipe management, process monitoring, and quality data analytics. This digital connectivity supports traceability, regulatory compliance, and continuous process improvement. Remote access and diagnostics enable swift troubleshooting and maintenance, reducing operational interruptions.
Inline inspection technologies including high-resolution imaging, fluorescence detection, and laser thickness measurement verify coating coverage and uniformity in real time. Defective parts are automatically identified and removed, ensuring only compliant products proceed to downstream assembly or packaging.
Safety systems prioritize operator protection and environmental stewardship, with fully enclosed spray areas, ventilation with solvent recovery, and powder reclamation units minimizing emissions and exposure. The adoption of low-VOC, water-based, and powder coatings further aligns these solutions with sustainable manufacturing goals.
Modular and scalable system architectures allow manufacturers to tailor auto paint solutions for mini electronics according to evolving product designs, production volumes, and quality requirements. This adaptability facilitates rapid response to market changes and technological advancements without significant capital expenditure.
In essence, auto paint solutions for mini electronics represent a convergence of precision engineering, intelligent automation, environmentally responsible materials, and comprehensive quality assurance. These systems empower electronics manufacturers to deliver reliable, high-quality protective coatings on small, complex components efficiently, meeting the stringent demands of today’s fast-paced, innovation-driven market.
Building on these advancements, auto paint solutions for mini electronics increasingly incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence to further enhance process optimization and quality control. By continuously analyzing sensor data—such as spray patterns, coating thickness, curing consistency, and environmental factors—these intelligent systems can predict and correct deviations before they impact product quality, reducing scrap rates and rework costs.
Robotic systems are becoming more versatile, featuring multi-axis arms with tactile sensing and adaptive force control that can handle delicate parts with unparalleled finesse. Combined with vision-guided alignment and barcode or RFID tracking, robots ensure precise positioning and traceability throughout the painting process, even in complex mixed-product lines.
Emerging coating materials designed specifically for mini electronics, including nanocoatings and functional thin films, offer new protective and performance-enhancing properties such as enhanced moisture barriers, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, or anti-reflective surfaces. Auto paint systems are evolving to accommodate these advanced materials, often requiring precise layer thickness control and specialized curing techniques.
Sustainability remains a key driver, with manufacturers striving to reduce environmental impact through innovations such as closed-loop powder recovery, solvent recycling, and energy-efficient LED curing. These eco-friendly practices help companies comply with stricter regulations and meet corporate social responsibility goals without compromising throughput or finish quality.
User experience is improved through intuitive, customizable control interfaces that guide operators through setup, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Integration with factory-wide Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platforms facilitates seamless production planning, inventory management, and quality reporting.
Safety features are enhanced with comprehensive monitoring systems that detect abnormal conditions like solvent leaks, excessive particulate levels, or equipment malfunctions, triggering automatic shutdowns and alerts to protect both personnel and product integrity.
Ultimately, auto paint solutions for mini electronics represent a sophisticated blend of mechanical precision, advanced materials science, intelligent control, and environmental stewardship. They enable manufacturers to meet the demanding requirements of cutting-edge electronic products with speed, accuracy, and reliability, securing competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Paint Line for SMD and Micro Chips
A paint line for SMD (Surface-Mount Devices) and microchips is a highly specialized manufacturing system designed to apply protective coatings to extremely small and sensitive electronic components. These coatings serve multiple purposes: protecting delicate circuitry from moisture, dust, and contaminants; providing electrical insulation; improving mechanical durability; and sometimes enhancing thermal or electromagnetic properties. Given the tiny scale and complexity of SMDs and microchips, the paint line must achieve exceptional precision, uniformity, and repeatability while maintaining high throughput for mass production.
The line begins with advanced material handling systems that gently transport and orient components without damage. Micro-feeders, precision conveyors, or robotic arms equipped with vacuum or soft-touch grippers handle the parts carefully, preventing contamination or mechanical stress. The handling equipment ensures consistent spacing and alignment, critical for uniform coating application and curing.
Coating application technologies in these lines are tailored for micro-scale accuracy. Selective coating methods such as micro-jet dispensing, precision spray nozzles, or needle jetting apply ultra-thin, conformal layers only where needed, avoiding sensitive contacts or bonding pads. These systems minimize coating thickness variations, preventing electrical shorts or mechanical interference. For some components, dip coating or spin coating techniques may be employed when uniform coverage over the entire surface is required.
Environmental control within the paint line is stringent. Enclosed booths with HEPA-filtered airflow reduce particulate contamination that could compromise the coating or component function. Temperature and humidity are carefully regulated to optimize coating adhesion and curing consistency, particularly important for moisture-sensitive microchips.
Curing processes integrated into the paint line use UV or LED curing for rapid polymerization at low temperatures, protecting heat-sensitive substrates while maintaining production speed. Infrared or convection ovens with precise temperature control may also be used depending on the coating chemistry and component tolerance. Programmable curing profiles allow the system to adapt to various materials and production demands.
Automation and control systems synchronize part handling, coating, and curing with high-speed precision. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs) facilitate recipe management, real-time process monitoring, and quick changeovers for different component types or coating formulations. Data logging supports traceability and quality assurance, vital in electronics manufacturing.
Inline inspection technologies play a critical role in maintaining quality. High-resolution imaging, laser thickness measurement, and fluorescence detection identify coating defects, incomplete coverage, or excessive thickness. Automated sorting and rejection systems ensure only fully compliant parts proceed to downstream assembly, reducing scrap and rework.
Safety and environmental considerations are incorporated through enclosed spray areas, solvent or powder recovery systems, and ventilation that protects operators and complies with regulatory standards. The use of low-VOC or powder coatings aligns with sustainable manufacturing initiatives.
Modularity and scalability allow manufacturers to customize paint lines for SMDs and microchips to meet specific production volumes, component sizes, and coating requirements. Additional modules such as surface preparation, selective masking, or multi-layer coating can be integrated to address complex product needs.
Overall, paint lines for SMD and microchips combine delicate handling, precision application, controlled curing, and stringent quality control to deliver high-performance protective coatings on some of the smallest and most critical electronic components. These systems enable manufacturers to meet rigorous industry standards while maintaining efficiency and flexibility in high-volume electronics production.
Paint lines for SMD and microchips are engineered to handle the extreme delicacy and precision required for coating miniature electronic parts without compromising their function or reliability. The material handling systems employ soft-touch robotic grippers, vacuum nozzles, or micro-conveyor belts that minimize mechanical stress and avoid contamination. These systems ensure consistent orientation and spacing, which are critical for uniform coating thickness and effective curing.
Coating application methods focus on delivering ultra-thin, conformal layers that protect sensitive circuitry while avoiding interference with electrical contacts or bonding sites. Micro-jet dispensing and precision spray nozzles deposit coatings with micrometer-level accuracy, allowing selective application only where necessary. This selective coating reduces material consumption and prevents coating-induced defects such as bridging or shorts. Dip or spin coating may be used for components requiring full-surface coverage, but these methods are carefully controlled to prevent excess coating buildup.
Environmental conditions within the paint line are strictly regulated. HEPA-filtered airflow systems maintain a cleanroom-like environment, removing particulates that could cause defects or reduce coating adhesion. Temperature and humidity controls are optimized to ensure consistent coating behavior and curing performance, which is especially important given the sensitivity of microchips to moisture and thermal stress.
Curing technologies are selected to protect delicate substrates and speed production. UV and LED curing ovens provide rapid, low-temperature polymerization of coatings, minimizing thermal impact on components while maintaining throughput. Infrared and convection curing ovens offer alternatives for coatings requiring thermal activation, with programmable profiles to tailor heat exposure precisely.
Automation and process control systems synchronize handling, coating, and curing operations with millisecond accuracy, enabling high-speed production with minimal variability. Intuitive human-machine interfaces allow operators to manage recipes, monitor system status, and quickly switch between product variants. Integrated data logging supports traceability, critical in electronics manufacturing for quality assurance and compliance.
Quality inspection systems embedded in the paint line use high-resolution cameras, laser thickness gauges, and fluorescence detectors to identify coating defects or coverage inconsistencies in real time. Automated rejection or rework stations prevent defective components from advancing in the production flow, improving overall yield and reducing costs.
Safety features include fully enclosed coating chambers, effective ventilation with solvent or powder recovery, and interlocked access points to protect operators from exposure and comply with environmental regulations. The use of environmentally friendly coatings, including low-VOC and powder formulations, aligns with sustainable manufacturing initiatives.
The modular design of paint lines allows easy integration of surface preparation modules such as plasma cleaning or corona treatment to enhance coating adhesion. Selective masking stations can be added for complex multi-layer coatings or to protect sensitive areas. Scalability ensures the line can adapt to varying production volumes or product mixes without major downtime.
In summary, paint lines for SMD and microchips offer a comprehensive solution that balances delicate handling, precise coating application, controlled curing, and rigorous quality control. They enable manufacturers to produce reliable, high-performance electronic components efficiently while meeting the stringent demands of modern electronics industries.
Continuing advancements in paint lines for SMD and microchips focus on integrating smarter automation and real-time data analytics to push precision and efficiency even further. Machine learning algorithms analyze sensor inputs from coating thickness monitors, spray pattern detectors, and environmental sensors to predict and correct deviations instantly, reducing scrap and enhancing product consistency. This proactive approach allows the system to adapt dynamically to variations in part geometry, coating material properties, or environmental conditions without halting production.
Robotic handling systems now often include multi-axis arms with force feedback and vision guidance, enabling gentle manipulation of highly complex or fragile components. These robots can adjust their grip and movement in real time, accommodating slight variations in part shape or position and ensuring optimal coating application every time. Coupled with advanced barcode or RFID tracking, full traceability of each component through the paint line is achievable, which is critical for quality control and regulatory compliance in industries such as medical devices or aerospace electronics.
Emerging coating materials tailored for microelectronics—such as nanocoatings that provide enhanced barrier protection or functional coatings that improve thermal dissipation—are being incorporated into paint lines. The equipment is continually adapted to handle these innovative materials, which may require specialized dispensing techniques or curing profiles to achieve desired performance without damaging sensitive substrates.
Sustainability remains a strong focus, with paint lines adopting closed-loop systems for powder recovery, solvent recycling, and energy-efficient curing solutions like LED systems. These improvements help manufacturers reduce waste, lower energy consumption, and meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations, all while maintaining high throughput and quality.
User interfaces are becoming more intuitive, offering customizable dashboards, remote access for diagnostics, and integration with factory-wide manufacturing execution systems (MES) for seamless production planning and quality management. Operators receive real-time alerts and guided troubleshooting to minimize downtime and maintain consistent operations.
Safety is enhanced through comprehensive monitoring systems that detect hazardous conditions such as solvent leaks or particulate buildup, automatically triggering shutdowns or ventilation adjustments. Ergonomic design features and training tools, including augmented reality (AR) assistance, support safe and efficient operator interactions with complex equipment.
Overall, paint lines for SMD and microchips represent a sophisticated convergence of precision engineering, advanced automation, intelligent control, and environmental responsibility. They empower manufacturers to meet the ever-increasing demands of miniaturized electronics production—delivering high-quality, reliable coatings that protect critical components and enable cutting-edge technologies worldwide.
Automated Painting for PCB Elements
Automated painting for PCB (Printed Circuit Board) elements is a highly specialized process designed to apply protective coatings precisely and consistently to circuit boards and their components. These coatings, often referred to as conformal coatings, serve critical functions such as insulating against moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature variations, while also providing electrical insulation and enhancing the mechanical durability of the board.
The automated painting process begins with careful handling systems that transport PCBs through the coating line. These systems typically include conveyor belts with adjustable guides or robotic arms equipped with vacuum grippers that ensure stable, damage-free movement and accurate positioning of boards for uniform coating application. Precision in handling is essential to maintain alignment for selective coating of complex PCB layouts.
Coating application methods are tailored to the needs of PCB manufacturing. Selective spray coating systems use programmable nozzles or jet dispensers that deposit ultra-thin layers of conformal coating material only onto targeted areas, avoiding connectors, sockets, or other sensitive parts. Alternatively, dip coating or curtain coating may be employed for full-board coverage, ensuring uniform protection even in recessed areas and beneath components.
Environmental controls in automated painting systems for PCBs maintain clean, contaminant-free conditions. Enclosed spray booths equipped with HEPA filtration and controlled airflow prevent particulates from settling on wet coatings, which could cause defects. Temperature and humidity are also regulated to optimize coating flow and curing characteristics.
Curing technologies integrated into automated painting lines include UV and LED curing systems that provide rapid, low-temperature polymerization ideal for sensitive electronic assemblies. Infrared and convection ovens with programmable profiles are used for coatings requiring thermal curing, balancing speed and part safety.
Advanced automation and control systems synchronize the movement of PCBs, coating application, and curing stages with high precision to maximize throughput while maintaining coating quality. Human-machine interfaces allow operators to program coating recipes, monitor process parameters, and quickly adapt to different PCB designs or coating materials.
Quality assurance is supported by inline inspection systems using optical cameras, fluorescence detectors, and thickness gauges to verify coating coverage, detect defects like pinholes or bubbles, and ensure compliance with stringent industry standards. Automated rejection mechanisms remove non-conforming boards, reducing rework and scrap.
Safety and environmental considerations are incorporated through enclosed coating areas, solvent recovery or powder reclamation systems, and ventilation that protects operators and minimizes emissions. Use of low-VOC or water-based coatings aligns with sustainable manufacturing goals.
Modular and scalable designs enable manufacturers to configure automated painting systems for PCB elements according to production volume, board complexity, and coating requirements. Additional modules for surface preparation, selective masking, or multi-layer coatings can be integrated to meet specific application needs.
In summary, automated painting for PCB elements delivers precise, reliable, and efficient application of protective coatings essential for the performance and longevity of electronic assemblies. By combining advanced handling, targeted coating technologies, controlled curing, and rigorous quality control, these systems support the high standards and fast-paced production environments of modern electronics manufacturing.
Automated painting for PCB elements is designed to handle the intricate and delicate nature of circuit boards, where precision and consistency are paramount. Material handling systems use gentle, yet accurate mechanisms such as conveyor belts with adjustable fixtures or robotic arms with vacuum grippers to securely transport PCBs through the coating process without causing damage or contamination. These systems ensure precise positioning for the coating application stage, enabling uniform coverage even on densely populated boards.
Coating application technologies are chosen based on the complexity and functional requirements of the PCBs. Selective spray coating systems employ programmable nozzles or micro-jet dispensers that deliver conformal coatings only to designated areas, protecting vital contacts and connectors from unwanted coverage. This selective approach minimizes material usage, reduces drying time, and prevents coating-related defects such as bridging or shorts. For boards requiring complete coverage, dip coating or curtain coating methods provide uniform layers, even reaching recessed areas beneath components.
Maintaining a clean environment is critical, so automated painting systems feature enclosed spray booths equipped with HEPA filtration and controlled airflow to prevent particulate contamination. Temperature and humidity controls further optimize coating flow characteristics and adhesion, ensuring consistent results across production batches.
Curing processes integrated into these systems include UV and LED curing ovens, which provide rapid, low-temperature polymerization suitable for sensitive electronic assemblies. Infrared and convection curing ovens offer alternative curing methods with programmable temperature profiles to accommodate different coating materials and PCB tolerances, protecting the board from thermal stress.
Automation and control software synchronize the movement of PCBs, coating application, and curing stages, allowing high throughput without compromising quality. Human-machine interfaces provide intuitive control over coating recipes, real-time monitoring of process parameters, and facilitate quick adjustments for varying board designs or coating types. Data logging supports traceability and compliance with quality standards.
Inline inspection systems use high-resolution imaging, fluorescence detection, and thickness measurement to verify coating integrity, coverage uniformity, and defect detection. Automated rejection or rework stations ensure only compliant boards proceed to assembly or shipment, reducing waste and improving overall yield.
Safety measures include fully enclosed coating areas, solvent recovery or powder reclamation systems, and ventilation systems designed to protect operators and meet environmental regulations. The use of low-VOC, water-based, or powder coatings aligns with sustainability goals, reducing emissions and hazardous waste.
Modularity allows manufacturers to customize automated painting lines for PCB elements with additional capabilities such as surface preparation modules (plasma or corona treatment), selective masking stations, or multi-layer coating processes to meet specialized application requirements. Scalability ensures these systems can adapt to different production volumes and evolving product lines.
In essence, automated painting for PCB elements combines precise handling, targeted coating application, controlled curing, and rigorous quality assurance to produce reliable, high-performance conformal coatings. These systems are critical in modern electronics manufacturing, delivering consistent protection to complex assemblies while supporting efficient, high-volume production demands.
Automated painting systems for PCB elements are continuously evolving to incorporate the latest advancements in robotics, sensor technologies, and software intelligence. Modern lines often integrate vision-guided robotics that precisely locate and orient PCBs for optimal coating application, even accommodating variations in board size, shape, and component layout. This flexibility enables manufacturers to handle mixed production runs and rapid product changes without significant downtime.
Coating application techniques are becoming increasingly sophisticated with the introduction of micro-dispensing and jetting technologies, which allow for ultra-precise placement of conformal coatings. These technologies minimize material usage and reduce overspray, which is particularly beneficial for protecting sensitive areas like connectors, switches, and test points. The ability to program complex coating patterns also supports multi-layer applications and functional coatings that provide additional properties such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding or thermal management.
Environmental controls within automated painting systems are enhanced through cleanroom-compatible designs, ensuring that particulate contamination is minimized. Real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and air quality allows for dynamic adjustments to maintain optimal coating conditions, which is crucial for process repeatability and coating performance.
Curing technology advancements focus on reducing cycle times while protecting PCB components from thermal damage. High-intensity UV and LED curing systems enable near-instantaneous hardening of coatings, significantly increasing throughput. Programmable curing profiles provide fine control over exposure levels, accommodating a wide range of coating chemistries and thicknesses.
Automation and control platforms now feature integrated data analytics and machine learning capabilities. These systems analyze process data to identify trends, predict maintenance needs, and optimize coating parameters automatically. Such intelligent automation reduces operator intervention, improves yield, and enhances overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Inline inspection systems have also progressed with the use of high-definition imaging and fluorescence detection to identify coating defects like bubbles, pinholes, or insufficient coverage with greater accuracy and speed. Coupled with automated sorting mechanisms, these inspections maintain product quality and reduce the risk of field failures.
Safety and sustainability remain central concerns. Enclosed booths with advanced filtration, solvent recovery, and powder reclamation systems reduce environmental impact and protect worker health. Many systems support the use of low-VOC, water-based, or powder coatings to further enhance eco-friendliness.
The modular design philosophy allows manufacturers to tailor automated painting lines to specific production needs, easily integrating additional modules such as plasma surface treatment, selective masking, or multi-layer coating capabilities. This adaptability ensures that painting systems remain viable as product designs evolve and market demands shift.
In summary, automated painting for PCB elements leverages cutting-edge technology to deliver precise, reliable, and efficient conformal coating solutions. By combining advanced robotics, environmental controls, rapid curing, intelligent automation, and thorough quality assurance, these systems help manufacturers protect sensitive electronic assemblies while optimizing production speed and flexibility.
Precision Painting Machine for Micro Electronics
A precision painting machine for micro electronics is an advanced automated system engineered to apply ultra-fine, uniform coatings on miniature electronic components such as sensors, microchips, connectors, and other small-scale devices. These coatings provide critical protection against moisture, dust, corrosion, and electrical interference while preserving the delicate functionality and dimensional tolerances of microelectronic parts.
Handling these tiny, fragile components requires highly sensitive and accurate material transport solutions. Precision painting machines utilize micro-robotic arms, vacuum-based grippers, or gentle conveyor systems that ensure damage-free movement and consistent positioning. This careful handling is essential for repeatable coating application and prevents contamination or mechanical deformation.
Coating application technologies focus on delivering extremely thin, conformal layers with exceptional uniformity. Techniques like micro-jet dispensing, electrostatic spray, or precision needle jetting are employed to deposit coatings exactly where needed, avoiding critical contacts or heat-sensitive areas. The system’s fine control over flow rates, spray patterns, and deposition angles enables the creation of coatings just a few microns thick, meeting stringent electrical and mechanical specifications.
Environmental control within precision painting machines is crucial for ensuring coating quality. Enclosed, cleanroom-compatible chambers with HEPA filtration maintain particulate-free atmospheres, while temperature and humidity controls stabilize coating material properties and curing conditions. These factors help minimize defects such as bubbles, uneven coverage, or adhesion failures.
Curing processes are optimized for the sensitivity of microelectronic parts. UV and LED curing ovens provide rapid, low-temperature polymerization, protecting heat-sensitive substrates while enabling high throughput. Programmable curing profiles allow customization for different coating chemistries and thicknesses, ensuring robust performance without compromising part integrity.
Integrated automation and control systems synchronize part handling, coating deposition, and curing with high precision. Intuitive human-machine interfaces enable operators to manage multiple coating recipes, monitor process parameters in real time, and quickly adjust settings for different products. Data logging supports traceability and quality control, essential in regulated industries.
Quality assurance features include inline optical inspection, fluorescence detection, and laser thickness measurement to verify coating uniformity and detect defects immediately. Automated rejection or diversion mechanisms maintain high yields by ensuring only compliant components proceed to assembly.
Safety and environmental considerations are embedded in machine design. Enclosed spray areas with efficient ventilation and solvent or powder recovery systems protect operators and reduce emissions. The use of low-VOC or water-based coatings aligns with sustainability goals.
Modular and scalable designs allow manufacturers to tailor precision painting machines for micro electronics to specific production volumes and product complexities. Additional modules for surface preparation, selective masking, or multi-layer coating can be incorporated to address specialized requirements.
Overall, precision painting machines for micro electronics combine delicate handling, advanced coating technologies, controlled curing, and rigorous quality assurance to deliver reliable, high-performance protective coatings on the smallest electronic components. These systems support manufacturers in meeting the exacting standards of today’s microelectronics industry while optimizing efficiency and flexibility.
Precision painting machines for micro electronics continue to evolve alongside the growing complexity and miniaturization of modern electronic devices. As components become smaller and more densely packed, the tolerances for coating application shrink dramatically, requiring systems capable of depositing coatings with micron-level precision. These machines are built with advanced motion control systems that offer sub-millimeter accuracy, allowing the nozzle or jetting head to trace highly detailed paths around intricate geometries without overspray or missed areas. This level of control is essential in environments like medical electronics, aerospace instruments, or high-density communication devices where even a minor coating defect can compromise performance or cause failure.
Modern systems often integrate machine vision technology, which allows for real-time inspection and dynamic adjustment of coating patterns based on the exact position and orientation of each part. Cameras paired with pattern recognition software identify fiducial markers or geometric references on the components, enabling the system to automatically compensate for part placement deviations or rotational misalignment. This not only improves accuracy but also supports higher throughput, as there is less need for manual alignment or fixturing. Some machines are equipped with artificial intelligence that learns optimal spray trajectories and pressure settings over time, continuously refining the process for each product variant.
Coating materials used in these machines range from traditional conformal coatings to specialized functional formulations such as hydrophobic, anti-static, or EMI-shielding coatings. These materials may have specific viscosity, surface tension, or curing requirements that demand careful process control. The machine’s software allows fine-tuning of spray velocity, atomization air pressure, and flow rate to match the properties of each coating and substrate. Temperature-controlled reservoirs and fluid lines further ensure consistency, especially when working with temperature-sensitive polymers or nano-dispersed solutions.
The curing process is tightly integrated and often occurs in stages, especially for coatings that require flash-off periods or multiple layers. Compact UV or LED curing modules are placed directly after the coating stations to immediately set the applied film, which helps prevent sagging or pooling on complex surfaces. Infrared or thermal curing units are added downstream when necessary for materials that benefit from deeper or longer cure cycles. This stepwise curing approach reduces cycle time while maintaining coating integrity.
To meet the needs of high-reliability industries, precision painting machines are increasingly networked with other production and quality systems. They can be fully integrated into smart factory environments via protocols like OPC-UA, allowing for centralized monitoring, predictive maintenance, and closed-loop process optimization. The machines collect and transmit detailed process data—including ambient conditions, coating parameters, and inspection results—which can be analyzed to identify trends, prevent defects, and document compliance with quality standards such as ISO 9001, IPC-CC-830, or MIL-I-46058C.
These machines also offer modular configurations, which means manufacturers can begin with a single-station setup and scale up as needed. Modules can include additional heads for multi-material coating, masking units for protecting areas from coating exposure, or robotic pick-and-place units that prepare and remove parts automatically. This modularity allows facilities to adapt quickly to changes in product demand or design without major capital investment.
Altogether, a precision painting machine for micro electronics serves as a cornerstone technology in the production of today’s miniature electronic assemblies. It combines mechanical finesse, software intelligence, environmental control, and high-speed automation to deliver ultra-consistent coatings that enhance functionality, durability, and performance of the smallest and most sensitive devices. As electronics continue to shrink in size but grow in complexity, these machines provide the accuracy, adaptability, and reliability needed to keep pace with the future of innovation.
As the demand for smaller, smarter, and more reliable electronic devices continues to rise across industries like wearables, IoT, aerospace, and medical technology, precision painting machines for micro electronics are also becoming more interconnected, adaptive, and autonomous. These systems are increasingly equipped with predictive diagnostics that monitor the health of every mechanical and electronic component in the machine—from nozzle wear to pump pressure variations—and alert maintenance teams before issues affect production. This level of foresight reduces unplanned downtime and supports just-in-time maintenance strategies, which are vital in high-volume or high-mix production environments.
Another key advancement is the seamless integration of digital twins. Manufacturers now often deploy virtual replicas of their coating processes, allowing engineers to simulate and optimize parameters such as spray angles, material usage, airflow, and curing time without disrupting the physical line. This enables faster setup, more efficient recipe tuning, and immediate visualization of the effects of process changes. It also supports remote commissioning and troubleshooting, which is particularly useful for global manufacturing networks and contract manufacturers working under strict timelines.
Human interaction with these machines is also being streamlined. Modern user interfaces are touch-based, multi-language, and logic-driven, allowing even less experienced operators to run complex processes with minimal training. Step-by-step wizards guide users through cleaning routines, recipe setup, part loading, or changeovers, and safety interlocks with real-time feedback prevent misuse. For experienced users, advanced dashboards offer deep process control, historical analytics, and real-time KPI displays. Access can be role-based, ensuring that critical settings are protected while still empowering floor operators with the information they need.
In addition to coating performance, precision painting machines now often support hybrid functions—such as integrated plasma surface treatment prior to coating, or downstream ink marking or laser etching for traceability. These features reduce the need for separate stations, condensing multiple process steps into a single, compact footprint. With cleanroom compatibility and anti-static construction, the machines are suited for deployment in highly controlled environments where component integrity is non-negotiable.
The sustainability aspect of these machines is also becoming increasingly important. Precision painting machines are engineered to minimize overspray, eliminate wasteful purging routines, and recover unused materials. Coating consumption is tracked in real-time, allowing manufacturers to benchmark efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and lower operating costs. Many systems now offer full compliance with environmental regulations such as RoHS, REACH, and WEEE, and can automatically adjust processes when eco-friendly coating variants are introduced.
In summary, precision painting machines for micro electronics are no longer simply tools for applying thin films—they are dynamic, intelligent systems designed to adapt to rapidly changing production landscapes. By combining mechanical delicacy with software sophistication, real-time feedback, predictive analytics, and sustainability, these machines enable manufacturers to meet the strict quality, throughput, and flexibility demands of advanced microelectronic product lines. They support mass production of critical components while offering the precision and reliability needed for tomorrow’s most demanding applications.
Paint Systems for Tiny Electronics
Paint systems for tiny electronics are highly engineered solutions that apply protective or functional coatings to the smallest electronic components—such as microchips, miniature connectors, capacitors, MEMS sensors, and ultra-small circuit boards. These systems are vital for ensuring product durability, electrical reliability, and environmental resistance, especially in devices used in harsh or mission-critical environments like aerospace modules, medical implants, wearables, and compact consumer electronics.
Handling such small and fragile parts requires specialized feeding and positioning technologies. Precision indexing conveyors, robotic pick-and-place systems, and vacuum fixtures hold components securely and accurately throughout the process. Alignment must be extremely precise to avoid coating sensitive areas like solder joints, electrical contacts, or optical interfaces, and to ensure the coating is evenly applied without pooling, bridging, or leaving gaps.
Application methods are specifically adapted for micro-scale requirements. Selective spray systems use ultra-fine nozzles or micro-jetting heads to apply conformal coatings with exacting control over droplet size, pressure, and spray pattern. These coatings—often just a few microns thick—are designed to insulate, waterproof, or shield the electronics without interfering with their compact layout or thermal performance. In some cases, dip coating or misting may be used if uniform coverage is required, but they are tightly controlled to avoid over-coating or capillary action in tight geometries.
Environmental management is critical. Paint systems for tiny electronics operate within sealed, cleanroom-compatible enclosures featuring HEPA filtration, anti-static measures, and climate control to prevent particulate contamination or humidity-related failures. Even minor inconsistencies in environment can cause adhesion issues or visual defects on micro-scale parts.
Curing technologies are fast, efficient, and non-invasive. UV and LED curing systems are widely used because they deliver near-instant curing at low temperatures, which protects temperature-sensitive parts. For thermal cure coatings, systems include IR or convection ovens with programmable profiles that allow for precise ramp-up and cool-down rates, tailored to the thermal tolerance of miniature components.
Automation software coordinates the full workflow, from feeding and alignment to coating and curing, with sub-millisecond timing. User-friendly interfaces allow for rapid setup and recipe changeovers, and process data is logged in real time for traceability. Some systems are equipped with AI or machine learning algorithms that adjust spray parameters automatically based on sensor feedback to maintain consistency even as conditions or parts vary slightly.
Inline inspection is built in using high-resolution cameras, laser thickness measurement, or fluorescence imaging to detect under- or over-coating, missed zones, or contamination. Components that don’t meet specifications are rejected or routed for rework automatically, ensuring high yields and minimizing labor-intensive manual checks.
These systems are also designed with sustainability in mind. They use low-VOC coatings, support powder recovery or solvent recycling, and minimize overspray through high transfer-efficiency nozzles. Compact footprints, energy-efficient curing, and modular designs help manufacturers stay agile and environmentally compliant.
Ultimately, paint systems for tiny electronics are an essential enabler of miniaturized product innovation. By ensuring ultra-precise coating control, maintaining strict cleanliness standards, and enabling rapid, reliable throughput, these systems help electronics manufacturers protect their most delicate and critical components—supporting everything from high-end consumer devices to mission-critical applications where failure is not an option.
Paint systems for tiny electronics must deliver extreme accuracy and consistency, as the slightest deviation in coating thickness or placement can compromise the performance of delicate components. These systems operate at the intersection of materials science, micro-robotics, and digital automation, where every movement and process is tightly controlled. The machines are built with high-precision actuators and servo systems that ensure micron-level repeatability, allowing the applicator heads to follow complex geometries and avoid restricted zones with zero deviation. This becomes even more critical as the density of components on circuit boards increases and the physical space available for coatings shrinks.
Advanced vision systems play a central role in these paint systems. High-speed cameras with microscopic resolution are used not only for pre-application alignment but also to monitor the coating process in real time. These cameras detect inconsistencies in component positioning, surface reflectivity, or existing material buildup and adjust spray parameters accordingly. Some systems use closed-loop visual feedback, where the spray path is actively modified based on what the camera sees moment by moment, ensuring optimal coverage regardless of slight variations between parts. This vision-guided approach is essential for manufacturing processes where high mix and low volume production requires frequent changes in product layout or orientation.
The coatings themselves are engineered for ultra-thin, high-performance applications. These may include acrylics, silicones, polyurethanes, epoxies, and parylenes, each selected for specific environmental or electrical protection properties. In many cases, the coatings are formulated to be transparent, flexible, or resistant to specific chemicals or moisture levels. For high-reliability sectors such as defense or aerospace, nano-coatings with specific dielectric properties or hydrophobic behavior are applied to extend product lifespan under extreme conditions.
Curing stages are seamlessly integrated into the paint systems and optimized to reduce thermal stress. LED-based UV curing systems are favored for their long lifespan, low power consumption, and consistent output, delivering rapid curing without introducing heat buildup. For heat-curable materials, multi-zone ovens with forced convection or IR lamps ensure even thermal distribution and allow the curing profile to be finely tuned to prevent warping or damage. Some systems feature dual-curing capability, combining UV and thermal processes to support hybrid materials or multi-layer coatings that require different activation methods.
Data collection and analytics are deeply embedded in the system architecture. Every step of the process—temperature, humidity, pressure, curing time, coating thickness, material usage—is logged and can be accessed in real-time dashboards. This not only supports traceability and quality control but also allows manufacturers to optimize material usage, predict maintenance intervals, and continuously improve efficiency. These analytics tools are often connected to broader MES or ERP platforms, integrating the coating system into a larger smart manufacturing ecosystem.
Safety systems are comprehensive, incorporating automatic shutoffs, real-time leak detection, fire suppression systems, and solvent vapor control to protect both the operator and the facility. Enclosures are built with antistatic materials and grounded to prevent electrostatic discharge, which could be catastrophic when working with microelectronics. Operator interaction is minimized through intuitive touchscreens, guided maintenance procedures, and auto-cleaning functions that reduce the need for manual intervention in critical areas.
Modular design allows manufacturers to configure each paint system to their exact requirements. For instance, a single platform might combine precision jetting with selective masking, multiple curing stations, and robotic part rotation to handle complex geometries or multilayer coating sequences. These systems can be scaled from small-batch prototyping environments to fully continuous high-speed lines capable of handling thousands of parts per hour with no compromise in accuracy.
In total, paint systems for tiny electronics represent some of the most advanced manufacturing equipment available, combining mechanical precision, smart automation, and deep process control to protect the smallest, most critical components in the world. As electronics continue to get smaller and more powerful, the capabilities of these systems become even more vital, ensuring that every chip, sensor, or micro-module performs reliably from factory to field.
As innovation accelerates in sectors such as wearable technology, smart medical devices, and compact robotics, paint systems for tiny electronics are expected to become even more intelligent and autonomous. The next generation of these systems is being designed with adaptive learning capabilities that allow them to self-tune coating parameters in real time. By analyzing data patterns from previous runs, the system can automatically adjust flow rates, spray patterns, and curing times based on the component’s geometry, material, or the ambient environmental conditions—without any human intervention. This not only eliminates guesswork but also ensures consistent quality across thousands of highly varied or miniaturized parts.
The movement toward complete Industry 4.0 integration is also reshaping how these systems function. Paint lines are now part of fully digitized manufacturing cells where every machine, sensor, and software system communicates continuously. For example, the paint system can receive direct input from upstream inspection equipment to modify its coating behavior dynamically—perhaps increasing the coating thickness on components identified as slightly out of tolerance or skipping parts flagged for rework. Downstream equipment, such as automated optical inspection (AOI) systems or packaging robots, can also provide feedback loops to verify that coatings meet visual and functional standards. This level of synchronization reduces errors, shortens cycle times, and enhances first-pass yield.
Another area of rapid advancement is in multi-functional coatings, which can serve more than one purpose in a single layer. These include coatings that offer both moisture protection and EMI shielding, or those that provide electrical insulation while also enabling thermal dissipation. Precision paint systems are being outfitted with multi-dispense heads and multi-zone curing tunnels to handle these new formulations, allowing for sequential layering or blended coatings within a single pass. This not only saves space on the board but also reduces process steps and improves production efficiency.
As 3D packaging, chip stacking, and heterogeneous integration become more common, the demand for systems that can accurately coat vertically layered or highly contoured surfaces is increasing. To address this, many modern paint systems include 6-axis or even 7-axis robotic arms with adaptive tooling that can move around and between components to apply coatings from unconventional angles. Combined with 3D mapping sensors and laser profiling, the machine can build a complete digital model of each part and then calculate the optimal coating path based on its topography.
In terms of sustainability, precision paint systems for tiny electronics are also setting new benchmarks. They are increasingly equipped with real-time solvent vapor analyzers, closed-loop recycling systems for unused coating material, and low-energy curing modules to reduce environmental footprint. Furthermore, regulatory compliance with standards such as RoHS, REACH, and WEEE is being embedded directly into the process control logic—ensuring every coating material used and every operating parameter meets environmental and safety requirements without requiring manual checks.
Looking forward, the role of these paint systems will expand beyond manufacturing into areas like prototyping, R&D, and failure analysis. Modular tabletop versions of high-end systems are being developed for laboratory use, allowing engineers to test new coatings, refine application patterns, or troubleshoot field failures by simulating production-level coatings on a small scale. These compact units will accelerate product development and support rapid iteration cycles in an increasingly competitive electronics landscape.
Ultimately, paint systems for tiny electronics represent a fusion of precision hardware, intelligent software, advanced materials science, and environmental responsibility. They’re not just machines—they are enablers of innovation, making it possible to produce ever-smaller, more powerful, and more reliable electronic devices that perform flawlessly under increasingly demanding conditions. As the boundaries of microelectronics continue to shrink, these systems will remain critical to defining what is possible in modern technology.
Automactic Painting Line for Electronic Components
An automatic painting line for electronic components is a high-precision, fully integrated system designed to apply protective or functional coatings to a wide range of electronic parts—including PCBs, connectors, sensors, enclosures, relays, and microelectronic modules—with exceptional consistency, speed, and accuracy. These systems are essential in modern electronics manufacturing, where components are becoming smaller, denser, and more complex, and where surface protection is critical to ensure long-term performance in challenging environments such as humidity, heat, dust, chemicals, and electromagnetic interference.
The process begins with automated material handling systems that feed and align the components on carriers or pallets, or directly onto precision conveyors. These mechanisms are designed to gently secure delicate parts and maintain strict positioning tolerances. In many lines, robotic pick-and-place systems are used for accurate component orientation, while optical sensors verify correct placement before coating begins.
Coating application methods vary depending on the size, shape, and sensitivity of the electronic parts. Selective coating systems equipped with programmable spray heads, jet dispensers, or needle applicators are used to apply coatings only where needed, avoiding sensitive areas such as connectors, buttons, and test points. For parts requiring full surface coverage, rotary spray nozzles, electrostatic guns, or dip coating systems may be employed. The system can apply different types of coatings, including conformal coatings (such as acrylic, silicone, polyurethane, or epoxy), insulating layers, hydrophobic films, or EMI-shielding paints.
Each painting zone is enclosed in a clean, ventilated booth to ensure particulate-free application. These booths often use HEPA-filtered airflow, electrostatic neutralizers, and controlled temperature and humidity to prevent contamination and support consistent coating performance. Some systems also include surface pre-treatment modules such as plasma or corona discharge units, which clean or activate the surface to enhance coating adhesion.
Once the coating is applied, the components pass through an integrated curing section. Depending on the coating material, this may include UV or LED curing for fast, low-heat solidification, or thermal curing using infrared or convection ovens with precisely controlled temperature zones. The curing process is tightly coordinated with application to maintain continuous flow and reduce cycle time without compromising quality.
Automation software governs the entire line, from component input to final unloading. It coordinates conveyor movement, coating parameters, curing timing, and inspection results in real time. User-friendly HMIs allow operators to switch between product recipes quickly, adjust spray paths, and monitor live performance metrics. Industry 4.0-compatible interfaces enable connection to MES and ERP systems for traceability, scheduling, and quality control.
Inline inspection systems are critical in automatic painting lines. Vision cameras, laser thickness gauges, and fluorescence detectors verify coating coverage, uniformity, and accuracy. Defective parts are automatically rejected or diverted for rework, ensuring that only qualified components continue to downstream processes such as assembly or packaging.
Safety and environmental sustainability are built into every stage. Exhaust systems and solvent recovery units minimize emissions. Coating reclaim systems reduce material waste. Low-VOC and water-based coatings are increasingly used to meet environmental standards. Enclosures with interlocks, fire suppression systems, and antistatic protection ensure safe operation for both operators and equipment.
These lines are typically modular and scalable, allowing manufacturers to configure them based on specific production needs—whether batch coating of PCBs, high-volume processing of molded components, or hybrid lines handling various part types. Some systems also include automated loading/unloading with barcode scanning or RFID tracking to match each part with the correct coating program.
In essence, an automatic painting line for electronic components is a critical enabler of high-reliability electronics manufacturing. It offers the precision, speed, and repeatability needed to meet the stringent demands of modern applications—ensuring that each component receives the exact protection it needs to function reliably throughout its lifecycle, from consumer gadgets to industrial controls and mission-critical aerospace systems.
Automatic painting lines for electronic components continue to advance with improvements in automation, flexibility, and process intelligence. These systems are engineered to handle increasingly diverse product mixes, allowing manufacturers to switch seamlessly between different component types, sizes, and coating requirements without lengthy downtime. This flexibility is achieved through programmable spray patterns, adjustable conveyor speeds, and modular coating stations that can be added or removed as needed.
A key feature of modern automatic lines is their integration with robotics and vision systems. Robots equipped with multi-axis arms and adaptive tooling handle complex part geometries, orienting components precisely for coating. Vision systems provide real-time feedback on part position, surface condition, and coating quality, enabling closed-loop control that adjusts spray parameters dynamically to ensure consistent application even if components vary slightly in shape or placement.
To maximize throughput while maintaining high quality, these lines often employ parallel processing. Multiple coating stations operate simultaneously, each tailored for specific coating types or application methods, such as selective spraying, dipping, or electrostatic application. Conveyors and robotic handlers synchronize movement to keep components flowing smoothly through the line, reducing bottlenecks and cycle times.
Environmental controls are integral to maintaining coating integrity. Automated lines operate within clean, controlled enclosures that regulate airflow, temperature, and humidity. These measures prevent contamination and ensure optimal curing conditions. Curing modules are designed for rapid, uniform polymerization using UV, LED, infrared, or convection technologies, selected based on coating chemistry and part sensitivity.
Advanced process control software ties the system together, offering comprehensive monitoring, data logging, and diagnostics. Operators can access detailed analytics on coating thickness, material usage, line speed, and defect rates through intuitive interfaces. Integration with factory management systems facilitates production planning, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance.
Safety systems encompass multiple layers of protection, including solvent vapor detection, emergency shutdowns, interlocks, and fire suppression. Materials handling components minimize operator exposure to chemicals, while equipment design incorporates antistatic materials and grounding to prevent electrostatic discharge hazards.
Sustainability considerations drive innovations in material conservation and emissions reduction. Reclaim systems capture overspray and unused coating, returning it to the process to minimize waste. Low-VOC and water-based coatings are preferred where possible, supported by equipment designed to handle these formulations efficiently.
Scalability allows manufacturers to expand or modify lines as production needs evolve. Modular units can be configured for batch or continuous operation, and additional capabilities such as inline surface preparation, masking, or multi-layer coating are integrated as needed. Barcode or RFID tracking systems ensure traceability of each component through the painting process, critical for quality control and audit trails.
Overall, automatic painting lines for electronic components represent a convergence of precision engineering, smart automation, and environmental responsibility. They empower electronics manufacturers to produce reliably coated parts at high volume and with exacting quality—meeting the stringent demands of consumer, industrial, medical, and aerospace markets. As electronics continue to evolve, these lines will remain essential to delivering durable, high-performance devices that perform flawlessly throughout their lifecycle.
Automatic painting lines for electronic components are increasingly embracing smart manufacturing principles, leveraging data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to optimize every aspect of the coating process. Real-time data collected from sensors monitoring parameters such as spray consistency, ambient conditions, curing status, and component positioning feed into sophisticated algorithms that detect subtle deviations and automatically adjust system settings. This predictive capability helps maintain consistent coating quality even as variables like raw material batches or environmental factors change, reducing waste and downtime.
The adoption of digital twins—virtual replicas of the physical painting line—further enhances process development and troubleshooting. Engineers can simulate different coating scenarios, test new materials, or optimize equipment configurations in the digital environment before applying changes on the production floor. This minimizes costly trial-and-error, accelerates product introductions, and allows rapid response to evolving customer requirements.
Connectivity is another hallmark of modern automatic painting lines. Integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP), manufacturing execution systems (MES), and quality management systems (QMS) ensures seamless coordination across the entire production chain. This connectivity facilitates real-time tracking of components, from receipt of raw materials through final coating and inspection, enabling full traceability and compliance with industry standards such as IPC, ISO, and FDA regulations.
Furthermore, user interfaces have become more intuitive and operator-friendly, featuring touchscreen controls, guided workflows, and multi-language support. Remote monitoring and diagnostics capabilities allow technical teams to oversee multiple lines or facilities from centralized locations, enabling rapid troubleshooting and reducing the need for on-site intervention. Augmented reality (AR) tools are also being introduced to assist with maintenance and training, overlaying digital information onto physical equipment to guide users step-by-step.
Sustainability remains a top priority. Automatic painting lines are designed to minimize environmental impact by optimizing coating material usage, reducing solvent emissions through advanced filtration and recovery systems, and supporting eco-friendly coating chemistries. Energy-efficient curing technologies and intelligent process scheduling contribute to lower overall energy consumption.
The modular architecture of these systems enables manufacturers to tailor configurations to specific product needs and production volumes. This adaptability is vital in today’s fast-changing electronics market, where shorter product lifecycles and frequent design changes demand flexible manufacturing solutions. Additional features such as multi-material coating capabilities, in-line surface preparation, selective masking, and multi-step curing processes can be integrated as required.
In conclusion, automatic painting lines for electronic components have evolved into sophisticated, intelligent production platforms that combine precision mechanics, advanced automation, environmental stewardship, and digital connectivity. They play a crucial role in ensuring that electronic parts are reliably protected against environmental and mechanical stresses, thus enabling the high performance and durability required in modern electronics across diverse industries.
Automatic Painting Line for Beauty Products
An automatic painting line for beauty products is a specialized, high-speed manufacturing system designed to apply coatings, finishes, or decorative paints to various cosmetic packaging and components—such as lipstick tubes, compact cases, mascara wands, bottles, jars, and applicator handles—with precision and consistency. This type of line caters to the beauty industry’s demanding standards for aesthetics, durability, and customization, ensuring that products not only function well but also captivate consumers with flawless surface finishes and attractive appearances.
The process begins with automated feeding systems that carefully handle delicate and often irregularly shaped packaging parts. Precision conveyors, robotic arms, or vacuum pick-and-place mechanisms position each item accurately for coating application, minimizing the risk of damage or misalignment. Custom fixtures or adjustable clamps secure the parts during painting, allowing for consistent spray angles and uniform coverage.
Coating application technologies on these lines are diverse, reflecting the variety of finishes demanded by the beauty market. High-quality spray painting systems, including electrostatic spray guns and air-assisted atomizers, deposit smooth, even layers of paint, lacquer, or metallic finishes. Techniques such as pad printing, hot stamping, or UV-curable coatings are often integrated to add logos, patterns, or decorative effects. Selective coating stations enable targeted application to specific areas of the product, preserving clear windows, labels, or functional parts that must remain uncoated.
Environmental controls play a vital role in achieving high-quality finishes. Painting booths feature filtered airflow to eliminate dust and particulates, while temperature and humidity controls maintain optimal conditions for paint adhesion and curing. Many systems include enclosed spray zones with solvent recovery and filtration to protect operators and meet environmental regulations, especially important given the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) often present in beauty product coatings.
Curing modules integrated into the line rapidly solidify coatings using technologies such as UV or LED curing for fast, energy-efficient processing. For solvent-based paints, thermal ovens with carefully controlled temperature profiles ensure thorough drying without warping or damaging sensitive plastic or metal components. The curing step is carefully synchronized with painting to maintain line speed and prevent bottlenecks.
Automation software controls the entire painting line, coordinating part handling, coating application, and curing processes. Operators can quickly switch between different product types or finishes by loading pre-programmed recipes, enabling efficient changeovers and customization. Real-time monitoring and data logging support quality control and traceability, essential for meeting brand standards and regulatory requirements.
Inline inspection systems are often employed to verify coating uniformity, color accuracy, and surface defects. Vision systems with high-resolution cameras detect issues such as runs, sags, or incomplete coverage, allowing defective parts to be removed or reworked promptly. This maintains high production yields and ensures that only flawless products reach the market.
Safety and environmental sustainability are integrated priorities. Advanced solvent recovery, exhaust filtration, and low-VOC or water-based coating options reduce environmental impact. Enclosures with interlocks and fire suppression protect operators and equipment. Some lines incorporate energy-efficient curing technologies and automated cleaning systems to minimize waste and operational costs.
Modularity and scalability are key features, allowing manufacturers to customize lines for small boutique batches or large-scale production. Additional modules such as multi-color painting stations, decorative foil application, or laser engraving can be integrated to meet evolving market trends and brand demands.
In essence, an automatic painting line for beauty products combines precision engineering, sophisticated automation, and environmental stewardship to deliver visually stunning, durable coatings on cosmetic packaging. It enables manufacturers to meet the high expectations of beauty brands and consumers alike—ensuring that every product is not only functional but also a striking expression of brand identity and quality.
Automatic painting lines for beauty products are designed to balance high production speeds with meticulous attention to detail, which is crucial in an industry where aesthetics directly influence consumer purchasing decisions. These lines incorporate flexible automation solutions capable of handling a wide range of product shapes, sizes, and materials, from lightweight plastics to metals and glass. The ability to switch quickly between different product runs or finishes without lengthy downtime is essential to accommodate seasonal trends, limited-edition collections, and customized packaging that are common in the beauty sector.
Robotic systems equipped with multi-axis arms and adaptive grippers enable precise positioning and consistent coating application even on complex or irregularly shaped items. These robots can execute complex spray patterns, including multi-layer coatings and decorative effects, with repeatable accuracy. In addition to painting, these lines often integrate complementary processes such as priming, masking, or surface texturing, creating a seamless workflow that enhances final product quality.
The painting booths themselves are engineered to maintain ultra-clean environments to prevent dust, lint, or other particulates from marring the delicate finishes. Temperature and humidity controls stabilize paint viscosity and curing conditions, ensuring uniform color and gloss levels across thousands of parts. Enclosed systems with efficient solvent recovery and air filtration maintain operator safety and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, addressing concerns over VOC emissions and workplace air quality.
Curing technologies within the line are chosen to optimize both efficiency and finish durability. UV and LED curing units provide rapid, low-heat polymerization suitable for UV-curable coatings, which are favored for their fast processing times and environmental benefits. Thermal curing ovens are precisely controlled to avoid warping heat-sensitive packaging components while ensuring thorough drying of solvent-based paints. The curing step is closely integrated with the coating stations to maintain smooth product flow and maximize throughput.
Automation software serves as the backbone of the line, providing centralized control over all process parameters and enabling quick changeovers between product variants. Operators benefit from user-friendly interfaces with recipe management, real-time diagnostics, and quality control data visualization. Integration with enterprise systems allows for comprehensive traceability, essential for meeting regulatory compliance and brand quality standards.
Quality assurance is enhanced through inline inspection systems that continuously monitor the appearance and integrity of coatings. High-resolution cameras detect color inconsistencies, surface defects, or incomplete coverage, triggering automatic rejection or rework procedures. These inspection systems help maintain high first-pass yields and reduce waste, contributing to cost efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Sustainability considerations drive many design choices in modern automatic painting lines for beauty products. The use of environmentally friendly, low-VOC, or water-based coatings is supported by equipment optimized for these materials. Advanced recycling and reclaim systems minimize paint waste, while energy-efficient curing and ventilation reduce the line’s overall environmental footprint.
Modular and scalable line configurations offer manufacturers the flexibility to expand capacity, incorporate new technologies, or adapt to changing market demands without extensive downtime or capital investment. Additional modules such as multi-color painting, hot stamping, or laser engraving can be integrated to deliver premium finishes and personalized branding options that appeal to discerning consumers.
In summary, automatic painting lines for beauty products represent a harmonious blend of precision engineering, smart automation, and environmental responsibility. They empower cosmetic manufacturers to produce visually striking, high-quality packaging at scale—supporting brand differentiation and delivering the flawless finishes that today’s beauty consumers expect.
These advanced painting lines are also engineered to support high levels of customization, which is becoming a defining feature in the beauty industry. Consumers increasingly expect products that reflect personal style, seasonal themes, or limited-edition designs, and manufacturers must respond quickly without sacrificing quality or production efficiency. Automatic painting systems meet this challenge by enabling rapid changeovers and programmable coating sequences, allowing even short production runs to maintain the same precision and consistency as mass-produced items.
Digital color management systems are integrated into the line to ensure repeatability and accuracy in color matching, which is critical when producing branded packaging. These systems can measure color in real time and make micro-adjustments during the painting process to compensate for variables such as lighting, paint viscosity, or substrate reflectivity. This ensures brand consistency across multiple batches, regardless of production date or location.
Some lines are further enhanced with digital printing heads or hybrid printing-painting modules that allow direct-to-surface decoration. This opens the door for variable data printing—such as QR codes, batch numbers, or personalization—directly onto curved or contoured packaging surfaces. Combining decoration and painting in one seamless process reduces handling, shortens lead times, and allows for intricate, high-resolution graphics that were previously only possible with separate labeling or transfer processes.
The handling systems within these lines are also becoming more intelligent. Vision-guided robotic arms can identify, sort, and orient components of varying geometry without requiring manual adjustments or specialized tooling. These robots adjust grip pressure, motion paths, and rotation angles dynamically, making them ideal for fragile or irregular-shaped containers often found in premium beauty packaging. Smart conveyors with servo-controlled indexing also ensure perfect timing and alignment as components move from one station to the next.
To further improve efficiency, some painting lines for beauty products now incorporate predictive maintenance systems. These use sensors embedded throughout the equipment to monitor vibration, temperature, pressure, and cycle counts. By analyzing this data, the system can anticipate wear or faults and alert operators before a breakdown occurs. This reduces downtime, extends machine life, and ensures uninterrupted production—a vital feature in a market driven by seasonal launches and tight delivery schedules.
The continuous feedback loop between production, inspection, and adjustment also enhances compliance with global quality standards. Every step of the process is logged, and the data is stored for audit purposes, which is especially important for manufacturers supplying multinational brands that demand full traceability and documentation for every product. These records include paint lot numbers, curing temperatures, coating times, and even environmental conditions in the spray booth, enabling complete transparency throughout the supply chain.
Automatic painting lines also help reduce the labor burden in traditionally manual painting operations. With minimal operator intervention, the system can operate around the clock with high consistency, freeing up human workers for supervisory or quality assurance roles. This shift not only reduces costs but also helps address labor shortages or safety concerns associated with manual spraying and solvent handling.
Ultimately, the automatic painting line for beauty products becomes more than a machine—it is a strategic asset that delivers both operational performance and brand value. It enables producers to consistently create high-end, visually perfect packaging that aligns with evolving market trends, environmental responsibilities, and consumer expectations. As beauty packaging continues to evolve in both form and function, these painting lines are at the heart of delivering speed, style, and surface perfection at scale.
Paint Systems for Small Cosmetic Items
Paint systems for small cosmetic items are precision-engineered solutions tailored for decorating and finishing compact beauty product components such as lipstick tubes, mascara caps, compact cases, nail polish bottles, and applicator handles. These systems are designed to meet the high aesthetic standards of the cosmetics industry, where visual appeal and flawless finishes are just as critical as product performance. Given the small size and intricate shapes of these items, the painting process requires extreme accuracy, flexibility, and careful material handling to ensure consistent, high-quality results.
The entire system is built around the idea of delicate yet high-speed processing. Automated feeding and orientation mechanisms gently position each item using custom fixtures, trays, or robotic arms, ensuring they are precisely aligned for uniform coating. These fixtures are often designed to accommodate a wide variety of shapes and sizes without requiring complete tool changeovers, making the line more adaptable to product variation or short-run customization.
Painting is typically carried out using high-resolution spray nozzles, miniaturized rotary atomizers, or electrostatic systems capable of producing ultra-fine droplets for a smooth, even coating without drips or excess buildup. In many cases, multiple painting stations are employed to apply primer, base color, decorative layers, and clear protective topcoats in sequence. Paint types range from traditional solvent-based lacquers and waterborne acrylics to advanced UV-curable coatings that offer superior gloss, hardness, or specialty finishes like pearlescence, metallic shimmer, or soft-touch textures.
Because cosmetic items are designed to be visually perfect, environmental control is a critical factor. Paint booths are fitted with HEPA-filtered air systems to remove dust and contaminants, while humidity and temperature controls maintain stable painting conditions. Some systems include antistatic measures to avoid particle attraction during the coating process, particularly important when dealing with glossy or mirror finishes.
Once painted, the components are conveyed through curing modules that vary depending on the paint chemistry. UV and LED curing systems are common, offering instant hardening without generating excessive heat that could warp plastic parts. Thermal ovens may be used for solvent-based coatings, with precise control over airflow and temperature gradients to prevent defects such as orange peel, wrinkling, or incomplete curing. These curing stages are designed to synchronize with the overall line speed to maintain smooth and efficient operation.
Modern paint systems also include inline quality control modules. Vision inspection systems equipped with high-resolution cameras and optical sensors scan each component to detect coating flaws such as bubbles, runs, gaps, or color mismatches. Items that fall outside of quality thresholds are automatically rejected or sent for rework, ensuring that only flawless pieces continue down the production line. Data from the inspection system is logged and analyzed to identify process drift, enabling timely adjustments and continuous improvement.
Control software acts as the command center for the entire system. Recipes for different products—detailing coating thickness, spray pressure, paint color, curing time, and part orientation—can be loaded or adjusted through a touchscreen interface. Operators can manage everything from part changeovers to process diagnostics and maintenance schedules through a centralized dashboard. These systems often support remote monitoring, cloud-based data storage, and integration with MES or ERP platforms for full traceability and production management.
Efficiency and sustainability are built into the process design. High-transfer-efficiency spray systems minimize overspray and material waste. Paint reclaim systems capture unused material for reuse, and ventilation setups ensure that solvent emissions are filtered and neutralized. Many manufacturers also prioritize low-VOC and water-based coatings to comply with environmental regulations and consumer expectations for cleaner production.
Compact, modular construction allows these systems to fit into constrained production spaces typical of cosmetics factories, while still delivering high throughput. Lines can be scaled by adding parallel stations or incorporating auxiliary processes such as laser marking, screen printing, or automated labeling to offer more comprehensive surface decoration.
Ultimately, paint systems for small cosmetic items combine high-precision engineering, aesthetic finesse, and operational flexibility. They allow beauty brands to create packaging that is visually striking, tactilely appealing, and consistent across high-volume or limited-edition product lines. With the ability to deliver everything from subtle matte effects to bold metallic gloss in a controlled, efficient, and sustainable manner, these systems are vital to maintaining a brand’s image and product appeal in the competitive cosmetics market.
These paint systems are not only about function and finish—they’re about creating an emotional connection between the consumer and the product. The colors, textures, and visual effects applied to small cosmetic items often serve as the first impression a brand makes on a buyer. This is why the ability to deliver mirror-like gloss, soft-touch matte, color gradients, holographic effects, or even velvet finishes on compact, mass-produced parts is critical. Achieving such consistency at speed requires a seamless integration of coating precision, part handling, environmental control, and digital automation.
Automation is the foundation of modern paint systems for cosmetics. The line may include robotic sprayers capable of adjusting angles, distances, and spray durations on the fly. These robots can accommodate design changes or apply different finishes to multiple product lines without requiring lengthy manual setup. Multi-axis arms work in coordination with intelligent software to ensure that even products with curves, contours, or recessed surfaces receive even and defect-free coatings. They are paired with quick-change grippers and adjustable jigs that allow the system to adapt instantly to different sizes and geometries—a crucial advantage when the product mix includes lipsticks, nail polish caps, compacts, and bottles all on the same production floor.
High-end paint systems also account for the intricacies of branding. Brands often require metallic logos, clear windows, embossed surfaces, or contrasting finishes in a single product. The painting line supports these requirements with features like selective masking stations, multi-pass spray heads, and hybrid application modules that combine painting with hot stamping or inkjet decoration. This reduces the need for separate post-processing stages and cuts overall production time.
Throughout the process, digital control ensures consistency. Each coating cycle is governed by preloaded digital recipes that contain every detail—nozzle types, paint flow rates, curing profiles, booth temperature, and humidity limits. These parameters are constantly monitored by sensors and adjusted in real time if deviations are detected. The system flags issues before they result in defects, maintaining yield and minimizing waste. Operators interact with the system through intuitive touch panels, often supported by real-time video feeds, production metrics, and maintenance alerts.
The inspection phase is just as vital. With cosmetic items being subject to close consumer scrutiny, even microscopic flaws can be unacceptable. The system’s integrated vision units inspect every piece under controlled lighting, comparing each to calibrated color and finish standards. Minor flaws can be corrected through rework routes, while major defects are automatically rejected. Inspection data is used not just for quality control but also for statistical process control, helping engineers refine the process and eliminate root causes of defects.
Curing, too, is precisely tailored. LED UV curing is favored for its cool operation and instant results—especially for UV-reactive coatings that need rapid solidification without distorting thin or heat-sensitive parts. These systems are configured with variable intensity and focus settings to match different coating chemistries and product shapes. For solvent or waterborne paints, infrared or convection ovens ensure full drying with uniform heat distribution. All curing units are tightly timed and sequenced with conveyor speeds to support a continuous, uninterrupted flow of parts.
Environmentally, the latest systems embrace sustainability from the start. They minimize overspray using precision nozzles and spray control algorithms, reduce energy consumption with efficient curing technologies, and recover unused coating materials through cyclone separation or filtration units. Many support the use of eco-friendly paints and comply with international standards like REACH and RoHS, helping manufacturers reduce environmental impact and respond to growing consumer demand for green beauty production.
Flexibility and scalability are built in. Manufacturers can start with a compact, semi-automatic system for small batch runs and scale up to fully automated, high-throughput lines as demand grows. The modular structure allows for the addition of new stations—whether for additional color layers, decorative effects, or post-coating operations—without redesigning the entire line. This supports rapid adaptation to new product launches, seasonal packaging, or customer-specific variants.
In total, paint systems for small cosmetic items combine advanced automation, aesthetic excellence, and production efficiency into a single platform. They are critical tools for brands aiming to deliver visually distinctive, emotionally engaging, and consistently high-quality packaging at scale. As consumer expectations evolve and customization becomes more central to brand identity, these systems will continue to define the cutting edge of cosmetic manufacturing.
Beyond production efficiency and visual precision, paint systems for small cosmetic items are increasingly aligned with the branding strategies and market positioning goals of global beauty companies. Packaging is no longer just a container—it is a statement of luxury, youthfulness, sustainability, or innovation. As a result, these systems must support not only technical reliability but also creative freedom. Manufacturers demand the ability to launch dozens of design variations per year with minimal production disruption, which these advanced systems enable through flexible programming and ultra-fast changeovers.
This flexibility extends to multi-finish capabilities within a single cycle. A compact item like a lipstick case might require a high-gloss colored base, a metallic gradient cap, and a soft-touch grip—all achieved within the same system. Advanced paint systems accommodate this by integrating multiple spray booths or color stations, each equipped with its own robotic sprayers, paint feed systems, and filtration controls. Through precise synchronization, each layer is applied and cured in the correct order, with the system maintaining perfect registration between finishes.
Such layering isn’t just visual—it can also add physical functionality. For example, clear coats provide abrasion resistance, matte layers reduce glare and fingerprints, and UV-blocking coatings protect color from fading in sunlight. Some formulations even incorporate anti-bacterial or tactile properties, giving the cosmetic item an added sensory or hygienic appeal. Paint systems are being adapted to handle these advanced materials by using special temperature controls, pressurization, or inert gas environments in specific modules, depending on the coating’s sensitivity to air or moisture.
From a technical point of view, these systems are built with longevity and precision in mind. Components such as servo motors, linear rails, and dosing valves are selected for thousands of cycles per day with minimal maintenance. Self-cleaning spray heads, automatic flush routines, and paint recirculation systems keep performance stable without halting production. Some systems can even identify nozzle clogging through spray pattern recognition and correct it automatically by purging or switching to a backup head.
In terms of user interaction, operators are supported by highly visual, step-by-step control panels that eliminate guesswork. Recipes for each product type are stored with 3D visualizations, live spray paths, and curing profiles, allowing even less-experienced operators to handle production tasks with confidence. System alarms, diagnostics, and maintenance forecasts are presented in real time, often supported by cloud-based dashboards accessible to quality teams and production managers remotely.
Digital traceability continues to grow in importance. Every part that passes through the system can be linked to its batch, coating type, operator, machine status, and even environmental conditions at the time of processing. This not only supports quality control and compliance with cosmetic packaging standards, but also enables trend analysis for yield, material efficiency, and defect patterns. For high-end cosmetic lines or regional variants, this traceability is essential for brand protection and product recalls, should they occur.
Cosmetic brands are also using these paint systems to create exclusivity and limited-run designs that connect with seasonal campaigns, influencer collaborations, or social media trends. Paint systems are being tailored to meet this demand with ultra-fast color change units, minimal cleaning downtime, and automated palette management. Some incorporate RFID-tagged paint canisters and QR-coded fixtures that automatically load the correct process flow based on the SKU, eliminating human error and enabling extreme personalization on a mass-production scale.
Looking toward the future, the integration of AI-driven process optimization will further elevate what these systems can achieve. AI engines are already being developed to analyze environmental conditions, spray performance, and inspection outcomes in real time and fine-tune the application process autonomously. Combined with robotic intelligence and predictive maintenance, these systems will reach new levels of efficiency, allowing cosmetic manufacturers to operate at high volumes while continuously improving quality and reducing costs.
Ultimately, paint systems for small cosmetic items are the silent artists behind the products lining shelves in beauty stores around the world. They turn basic plastics and metals into elegant, tactile, and emotionally resonant objects. They allow beauty brands to deliver visual identity, promise quality, and express creativity—without compromise, and at any scale. These systems are not just tools of decoration—they’re engines of brand expression, driving the success of cosmetic products in an increasingly design-driven marketplace.
Auto Painting Machine for Cosmetic Packaging
An auto painting machine for cosmetic packaging is a fully automated, high-precision system specifically engineered to coat and decorate the surfaces of beauty product containers such as lipstick tubes, compact cases, perfume caps, cream jars, and mascara housings. These machines are built to deliver flawless, uniform finishes at high throughput rates, ensuring that every package leaving the line reflects the luxury, identity, and visual appeal that the cosmetics industry demands. Because packaging is often the first physical interaction a customer has with a product, its finish must convey both quality and desirability—which makes the role of automated painting machines crucial in modern beauty manufacturing.
These machines are equipped with advanced robotic arms, high-efficiency spray guns, or rotary atomizers that are precisely programmed to apply consistent coatings across a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Whether dealing with smooth cylindrical lipstick tubes, contoured compacts, or textured lids, the machine adjusts spray angles, flow rates, and path geometry to ensure full coverage without over-application or waste. For multi-tone finishes, color gradients, metallic effects, or soft-touch coatings, the system can execute multiple painting steps in a single cycle—each with its own parameters and dedicated spray station.
A key aspect of these machines is their use of precision part holders or fixtures. Each packaging item is held in a stable, repeatable position using tailored mounts, often on a rotating axis, so that even curved or asymmetric surfaces are evenly coated. The machine’s motion control system synchronizes part rotation with spray head movement for optimized coverage with minimal overspray. This process ensures high repeatability and finish quality across thousands of units, with minimal manual intervention.
To accommodate the industry’s fast-changing trends and seasonal demands, auto painting machines are designed for flexible, quick changeovers. Tool-less fixture swaps, touchscreen recipe selection, and automated cleaning cycles make it possible to switch between product runs in minutes rather than hours. This enables manufacturers to efficiently produce both high-volume staples and short-run custom or limited-edition packaging lines.
The painting environment is tightly controlled to prevent contamination and defects. Enclosed spray booths with HEPA filtration, antistatic controls, and cleanroom-compatible designs keep particles, lint, or electrostatic interference from affecting surface finishes. For coatings sensitive to temperature or humidity—such as metallic lacquers or UV-reactive paints—the machine may include internal climate regulation to maintain ideal spray conditions throughout production.
Curing technologies are integrated directly into the machine. UV or LED curing modules offer instant solidification for UV-curable coatings, while thermal curing ovens—whether convection, IR, or hybrid—are used for traditional solvent-based or waterborne coatings. These curing zones are aligned to match the painting cycle, preventing bottlenecks while ensuring thorough, even curing that meets cosmetic-grade durability requirements.
Vision inspection is another core component. Auto painting machines typically feature inline camera systems that scan every unit for coating consistency, color accuracy, and surface defects such as runs, pinholes, or bubbles. AI-driven image analysis can identify anomalies with sub-millimeter precision, rejecting flawed parts or triggering real-time adjustments to maintain quality. This reduces rework, protects brand integrity, and ensures compliance with packaging standards for luxury beauty products.
Material efficiency is also built into the system. High transfer-efficiency spray guns reduce paint waste, and advanced reclaim systems recover overspray. Automated flushing and recirculation minimize downtime between paint changes. Many systems are also designed to be compatible with eco-friendly coatings and low-VOC formulations, allowing manufacturers to meet both regulatory and sustainability goals without sacrificing performance or aesthetics.
User interaction is made simple through modern HMI (human-machine interface) systems that allow operators to control all aspects of the machine through intuitive touchscreens. Real-time dashboards display production rates, paint usage, maintenance alerts, and inspection results, while preprogrammed recipes allow for repeatable, consistent output regardless of operator experience.
Compact footprints, modular design, and compatibility with upstream/downstream automation make these machines ideal for integration into larger production environments. Whether used in stand-alone mode for niche products or as part of a high-volume line, they offer the precision, flexibility, and quality assurance that cosmetic brands require to stay competitive in a style-driven market.
In essence, an auto painting machine for cosmetic packaging is not just a piece of equipment—it is a critical asset that bridges artistic expression with industrial efficiency. It enables the transformation of plain containers into glossy, luxurious, and emotionally engaging objects that embody the identity of the beauty product inside.
These machines continue to evolve with the demands of modern cosmetics manufacturing, where personalization, sustainability, and rapid design turnover are becoming essential. Auto painting machines for cosmetic packaging are now designed not only to meet high aesthetic expectations but to do so with speed, adaptability, and intelligence. They support full integration with digital production systems, meaning the machines can receive product specifications, color codes, and decorative patterns directly from the factory’s central control system or even from a customer-facing design interface. This creates a seamless workflow from design concept to finished, shelf-ready packaging.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into these systems allows them to self-optimize over time. As more components are painted and scanned, the system begins to understand slight variations in paint behavior, environmental conditions, or part geometry. The AI uses this knowledge to fine-tune parameters automatically, reducing the need for operator intervention and further enhancing consistency. It also anticipates maintenance needs before failures occur, using predictive analytics to schedule cleanings, nozzle replacements, or part inspections during idle windows, thus reducing unplanned downtime.
In production environments focused on branding flexibility, such as those handling multiple product lines or sub-brands, auto painting machines offer programmable multi-color modules. These can apply different finishes to specific zones of a component—such as a gold gradient on a perfume cap, followed by a soft black matte base and a transparent protective topcoat—all in one uninterrupted sequence. This level of sophistication opens up new creative possibilities for packaging designers while maintaining the mass production benefits of automation.
Lighting effects and surface texture enhancements are another area where these machines add value. Paint systems can be configured to produce gloss and matte contrasts, shimmer, pearlescence, and even tactile finishes that simulate fabric, stone, or rubber. These surface effects are achieved through specialized coatings, precise spray layering, and optional embossing or microtexture application units installed within the machine. This allows brands to elevate packaging from merely functional to a multisensory experience, which is especially valuable in premium product segments.
Many of these machines also support full digital traceability. Each component can be assigned a unique identifier—often via QR code, RFID chip, or barcode—that is tracked through every stage of the painting process. From the type and batch of paint used, to booth temperature, curing times, and inspection results, all data is logged and accessible through centralized reporting tools. This level of traceability supports internal quality assurance programs, regulatory compliance, and external verification for luxury brands that position themselves around craftsmanship and detail.
Environmental and regulatory considerations are addressed through the machine’s design as well. Closed-loop ventilation systems with solvent recovery capture and purify air inside the spray zone, while water-based or low-VOC paint compatibility reduces emissions. Overspray collection and separation systems reclaim excess paint efficiently, lowering material waste and ensuring that only the minimum required amount is used for each component. Energy-efficient LED curing systems reduce power consumption and eliminate the need for long thermal drying cycles, which not only supports green production goals but also increases overall line speed.
Operator safety and ergonomic design are also key priorities. The machines are built with accessible enclosures, quick-swap cartridges, auto-flushing paint lines, and intuitive safety locks. The user interface provides visual feedback and step-by-step assistance for cleaning, loading, or switching jobs. Safety sensors ensure that moving parts stop immediately if the operator accesses protected areas, and fire suppression systems are embedded in any zone where flammable materials are present.
As global cosmetic brands expand into new markets and cater to diverse consumer tastes, the ability to deliver personalized or market-specific packaging quickly becomes a competitive advantage. Auto painting machines enable this responsiveness, allowing factories to switch from bold seasonal colors to classic core products in a matter of minutes. This means product development teams can shorten launch cycles, test new packaging designs rapidly, and even explore direct-to-consumer customization options where packaging is tailored for individual customers at the point of order.
In the future, these machines will likely become even more autonomous and connected, forming part of fully intelligent production cells that operate with minimal human supervision. With vision systems that verify not just the quality of the coating but also the logo placement and label alignment, and AI that recommends paint adjustments or maintenance actions based on live performance metrics, auto painting machines will function as both a creative tool and an operational workhorse. For the cosmetics industry, where the packaging is often as important as the product itself, this type of machine is indispensable for delivering beauty, performance, and brand identity—perfectly, and at scale.
As the beauty and personal care market becomes more competitive and globalized, the demands placed on auto painting machines for cosmetic packaging continue to increase—not just in terms of speed or finish, but in their ability to deliver distinction, authenticity, and traceability at scale. These machines are no longer isolated production units; they are central, intelligent hubs within smart factories that communicate in real time with design departments, quality assurance systems, material supply chains, and even consumer-facing platforms.
For example, integration with digital twins—virtual models of the actual painting system—allows engineers to simulate new paint jobs, test spray parameters, and evaluate part orientation virtually before applying any coating to a physical component. This minimizes material waste and setup time, accelerating development cycles and enabling rapid experimentation with new colors or finishes. This is especially important when launching a new cosmetic line that must meet tight deadlines or reflect fast-changing trends in color, texture, or packaging format.
Personalization has also driven innovation in these systems. With demand rising for monogrammed packaging, influencer-branded limited runs, and region-specific designs, auto painting machines are increasingly paired with high-resolution digital printing modules. These modules apply intricate patterns, names, and visual details over or under paint layers, enabling the creation of serialized, one-of-a-kind cosmetic packaging without interrupting the main production flow. What once required slow, manual decoration or third-party subcontracting can now be executed seamlessly in-line.
In addition to printing, many systems offer value-adding modules like laser etching for permanent branding, foil stamping for metallic detail, or texture-masking devices that create tactile contrast. These decorative layers work together with the paint coatings to produce a final product that not only looks luxurious but feels luxurious, whether it’s a velvety compact case or a shimmering gradient lip balm tube.
Speed and throughput are carefully balanced with detail and control. Today’s top-tier systems can process thousands of items per hour, each with unique coating profiles, without compromising on visual or mechanical quality. Cycle time optimization is achieved through parallel operation—while one component is being sprayed, another is being cured, a third is being inspected, and a fourth is already on its way to packaging. Each stage is monitored and synchronized to avoid bottlenecks and maintain perfect flow.
Packaging diversity is also a challenge that these machines are built to solve. In cosmetics, no two product lines are exactly alike. One brand may use cylindrical mascara tubes, another rectangular foundation bottles, and a third multifaceted perfume caps. With modular jigs, smart part recognition, and AI-driven spray path generation, these systems can accommodate wildly different geometries without requiring a complete tooling change. In fact, some advanced systems use 3D scanning at the input stage to dynamically generate the appropriate spray program for each part—ideal for contract manufacturers handling multiple brands and SKU types in one facility.
Another key feature is the machine’s ability to report on environmental impact. Many auto painting systems now track paint consumption, VOC output, energy usage, and overspray volumes, providing sustainability metrics directly to production managers. These metrics help companies meet ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) targets, which are increasingly scrutinized by both consumers and regulators. In certain cases, these machines can also optimize settings to prioritize low-waste and low-energy operation modes when demand or production goals allow.
Because cosmetic trends move fast, downtime is not acceptable. The machines are built for high reliability, and support packages often include remote diagnostics, predictive analytics, and automated calibration routines. When issues arise, the system often alerts technicians before a fault impacts production, offering video-based tutorials, virtual support, or remote updates from the manufacturer’s service team. The goal is clear: keep the line running, keep the output flawless, and ensure that packaging keeps pace with marketing.
In conclusion, the auto painting machine for cosmetic packaging represents the perfect fusion of automation, artistry, and adaptability. It transforms plain packaging into iconic brand elements—glossy, matte, metallic, velvet, color-shifting, or even glow-in-the-dark—while delivering the speed, efficiency, and environmental responsibility required by modern manufacturing. It is the hidden engine behind a beauty product’s shelf appeal, brand identity, and tactile luxury. As beauty becomes more personalized, sustainable, and digitally connected, the machines applying the paint must be as innovative and elegant as the products they help present to the world.
Mini Item Auto Painting Equipment

Mini item auto painting equipment is a specialized type of automated system engineered for painting very small parts, components, or packaging items with high precision, consistency, and speed. These systems are widely used in industries like cosmetics, electronics, fashion accessories, toys, and hardware—anywhere compact products require an attractive, durable, and uniform surface finish. Unlike conventional coating lines, mini item auto painting equipment is designed specifically to handle delicate, lightweight, and often intricately shaped objects that present unique challenges in handling, orientation, and coating quality.
At the core of such equipment is a tightly integrated automation process that combines advanced part handling mechanisms with high-precision spray technology. Miniature parts are often placed on custom-designed jigs, trays, or rotating fixtures that hold each item in a secure, fixed position. These fixtures are engineered to expose all relevant surfaces to the spray path while minimizing the risk of shadowing, paint pooling, or contact marks. Depending on the size and geometry of the product, the system may utilize robotic arms, vacuum pick-and-place devices, or magnetic mounts to position each item with millimeter-level accuracy.
Spray application systems in mini item painting machines are finely tuned for small-scale coverage. Nozzles are often smaller, more focused, and capable of very fine atomization to ensure a smooth, thin, and even coating without overspray or waste. Electrostatic spray guns, micro rotary atomizers, and high-precision airbrush heads are common tools within the system, delivering excellent coverage even on intricate surfaces such as embossed logos, curved edges, or textured designs. These machines support multiple coating layers—including primers, base colors, decorative finishes, and topcoats—all applied in sequence and aligned for high efficiency.
Due to the small size and tight tolerances involved, environmental control becomes crucial. Enclosed spray booths with laminar airflow, HEPA filtration, and controlled humidity eliminate dust and contaminants that could ruin a fine finish. Some systems include antistatic ionizers to neutralize charge buildup, especially important when painting plastic items prone to attracting dust. The booth design also helps capture and recycle overspray, reducing both material loss and environmental emissions.
Once painted, mini items move through integrated curing systems that are selected based on the type of paint used. UV and LED curing are popular for small parts because they offer instant, energy-efficient drying without subjecting delicate items to prolonged heat. For solvent-based coatings, mini convection ovens or infrared curing tunnels are used, designed with gentle airflow and zoned temperature control to protect thin-walled components from warping or discoloration.
Inline inspection is essential in these compact systems. Mini item auto painting machines are typically equipped with high-resolution vision cameras and optical sensors that check each part for uniformity, coverage, color accuracy, and surface defects. Even the tiniest speck, streak, or undercoated area is detected and flagged automatically. Parts that fail inspection are diverted into a separate track for rework or disposal, ensuring only perfect units continue to final packaging or assembly.
Efficiency is a core advantage of these machines. With cycle times measured in seconds and the ability to coat hundreds or thousands of units per hour, they’re ideal for both high-volume mass production and agile short-run manufacturing. Quick-change fixtures and programmable spray patterns make it possible to switch between product types with minimal downtime—critical for factories serving multiple brands or product lines simultaneously. Many systems offer modular expansion, allowing extra spray booths, curing stations, or inspection zones to be added as production needs grow.
Digital control and connectivity are standard features. Operators can control every aspect of the process through a touchscreen interface or remote dashboard, including part loading, spray timing, nozzle pressure, paint flow rates, and curing parameters. Recipes for each product are stored digitally, so switching between color variants or product SKUs is fast and consistent. Integration with MES or ERP systems enables full traceability and real-time monitoring of output, quality metrics, material usage, and maintenance cycles.
Mini item painting equipment also supports sustainability through reduced material waste, energy-efficient curing, and compatibility with water-based or low-VOC paints. Many systems include paint reclaim features, automatic line purging, and enclosed wash cycles that minimize cleaning time and chemical usage. These features not only lower operating costs but also help manufacturers meet environmental compliance and corporate sustainability goals.
In conclusion, mini item auto painting equipment is an advanced, adaptable solution for applying high-quality finishes to small products at industrial scale. It blends delicate handling, precise coating, and high-speed automation into a compact, clean, and efficient package. For industries where visual appeal, consistency, and branding are paramount—even at miniature sizes—this equipment provides the speed, flexibility, and reliability needed to produce beautifully finished parts on demand.
The growing demand for customization and product differentiation has pushed mini item auto painting equipment to become increasingly intelligent and modular. These machines are now designed not only for efficient bulk processing, but also for fast setup adjustments and recipe-driven automation that allows manufacturers to offer a wide range of color finishes, surface effects, and decorative accents without sacrificing speed or consistency. With one machine able to paint a high-gloss lipstick cap in the morning and then switch seamlessly to a matte-finished microelectronic shell in the afternoon, versatility has become just as essential as precision.
Part recognition systems powered by cameras or sensors can automatically identify the type or orientation of each mini item as it enters the painting zone. This enables the system to dynamically adjust spray parameters such as angle, duration, and atomization level for each object, ensuring optimal coverage across mixed batches. This technology is particularly useful in job-shop settings or contract manufacturing environments where multiple SKUs are handled simultaneously on the same line. It reduces human intervention and practically eliminates the margin for setup errors or coating mismatches.
Some systems are also equipped with rotating spray platforms that allow the object to spin or tilt as it is being painted, which is essential for achieving full coverage on parts with recesses, cutouts, or non-uniform geometry. The synchronization between the part’s motion and the spray path is controlled down to milliseconds, ensuring consistency across thousands of repetitions. In cases where parts have internal surfaces or difficult-to-reach features, these machines may incorporate angled nozzles, side sprays, or multi-axis sprayers to apply paint evenly without dripping or shadowing.
A major trend is the incorporation of multi-stage painting within a single continuous loop. Items may be primed, painted in multiple colors, given a specialty coating like metallic or pearl, and then top-coated—all without leaving the system or requiring manual repositioning. Each station within the machine is calibrated to maintain proper coating thickness and drying time. Integrated drying or UV curing between stations ensures that layers are bonded correctly, and that the next coat can be applied without smearing or uneven adhesion.
The durability of the coating is as important as its appearance. For products that will be frequently handled, like cosmetic caps, wearable electronics, or key fobs, the finish must resist chipping, fading, and abrasion. That’s why coating materials used in mini item painting systems are often specially formulated with additives for scratch resistance, chemical durability, and UV stability. These systems can adjust their process to handle thicker protective coatings or layered finishes that provide both aesthetic and functional benefits.
Automation software also plays a key role in quality control. In many systems, every part is photographed multiple times—before and after coating, and after curing—and these images are analyzed in real time by AI algorithms trained to recognize defects. Over time, the software improves its sensitivity and reduces false rejections, ensuring maximum yield without compromising quality. Collected data is stored and can be audited for batch validation, making the system suitable for industries where traceability and compliance are essential.
From a mechanical standpoint, these machines are built for nonstop use. Every moving part, from the conveyor system to the spray heads, is optimized for minimal wear, easy cleaning, and low maintenance. Lubrication systems, filter monitoring, and temperature control are all automated. Daily maintenance routines are guided by on-screen checklists, while remote diagnostic tools allow for real-time service and troubleshooting by OEM technicians without the need for on-site visits. These features contribute to high uptime and ensure that small-batch or high-mix production doesn’t suffer from avoidable downtime.
Even packaging integration is streamlined. Once the painted mini items pass inspection and curing, they can be automatically transferred to trays, blisters, or feeding systems for downstream processes like assembly, branding, or direct shipment. For high-end consumer products, where packaging and presentation are part of the product experience, the ability to seamlessly transition from painting to packing within one system is a major efficiency booster.
The environmental footprint of these systems has been greatly reduced through closed-loop air circulation, efficient spray pattern control, and reclaim systems that collect unused paint from booths and filters. Solvent recovery, water recirculation, and VOC containment ensure compliance with local environmental regulations and support green manufacturing initiatives. In many regions, investment in such systems may even qualify for sustainability incentives or certifications, which add further value beyond production.
As global markets continue to demand faster lead times, broader customization options, and zero-defect packaging, mini item auto painting equipment is proving essential. It merges the precision of laboratory equipment with the robustness of industrial machinery, allowing manufacturers to produce beautifully finished miniature components with repeatability, elegance, and speed. In industries where appearance, branding, and tactile experience matter as much as the product inside, this type of equipment isn’t just helpful—it’s transformative.
The evolution of mini item auto painting equipment continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in high-speed, high-precision decorative finishing. As industries compete not just on quality but on creativity and brand uniqueness, the role of these machines expands from simple paint application to becoming an integrated part of the product design and manufacturing strategy. They are no longer viewed as just a production tool, but as an enabler of innovation, allowing even the smallest items to carry the full weight of a brand’s identity.
Modern systems increasingly feature hybrid processing capabilities. For instance, alongside paint application, the same machine may apply a gloss clear coat over a matte base, or deposit metallic flakes in only selected zones using digitally masked spray heads. Techniques like two-tone or fade-to-clear transitions, usually reserved for high-end automotive painting, are now achievable on lipstick caps or earbud shells at industrial speeds. What once required artisanal methods or manual masking can now be done in a single uninterrupted cycle with robotic accuracy and perfect repeatability.
Furthermore, the growing importance of tactile design—how a surface feels in the hand—has led to the development of special coatings that go beyond visual appeal. These include soft-touch coatings that mimic the feel of velvet or rubber, textured matte finishes that resist fingerprints, and ultra-smooth surfaces that give a premium, polished impression. Mini item painting machines are calibrated to handle the delicate balance of viscosity, spray angle, and curing time required to achieve these effects without distorting or degrading the base material underneath.
Advanced user interfaces have also made operation simpler and more intuitive. Operators no longer need to manually adjust nozzles or program paint paths. Instead, touchscreen panels with visual guides, pre-loaded product libraries, and smart wizards make setup nearly foolproof. In some cases, a barcode or RFID chip embedded in the part tray instantly loads the correct parameters from the database—color, spray duration, curing type, and inspection criteria—so the machine configures itself on the fly. This automation reduces training time and ensures consistency regardless of who is operating the line.
Another breakthrough is the integration of digital printing with painting, allowing for not only color and texture application but also logos, icons, personalization, or QR codes applied directly onto curved or irregular surfaces. This is particularly valuable in short-run or customized production, such as influencer-branded cosmetics, seasonal gift sets, or serialized promotional items. And because it’s fully inline, there’s no need to manually move parts to a separate decoration area, significantly cutting production time and potential handling errors.
Mini item painting systems are also increasingly used in the microelectronics and wearable tech industries, where aesthetics and miniaturization converge. For smart rings, earbuds, sensor housings, and connectors, color is not just cosmetic—it may indicate function, signal user interaction zones, or coordinate with an app’s design language. Painting machines for these applications must deliver finishes within micron-level tolerances and ensure absolute cleanliness to avoid interference with sensitive electronics. As such, many of these systems are built to cleanroom standards, with antistatic materials, isolated chambers, and non-contaminating lubrication systems.
The rise of sustainable packaging and eco-conscious branding has also changed how these machines are used. Many manufacturers are shifting from multi-material packaging to single-material recyclable units that rely on paint alone to create premium looks. A basic PET cap, for example, can be transformed into a gold-gloss finish with metallic coating rather than needing to be molded in multiple layers or coated in foil. This reduces material complexity, improves recyclability, and supports circular economy initiatives—while keeping the product visually luxurious. Mini item painting equipment supports this transition with minimal waste, high transfer efficiency, and compatibility with water-based or bio-derived coatings.
Even the analytics layer of these machines has become more sophisticated. Production data—such as paint usage per part, line uptime, first-pass yield, and defect causes—can be logged, visualized, and shared in real time. This gives operators and managers immediate insight into production performance, helps identify inefficiencies, and allows for continuous improvement. In multi-site operations, these analytics can be compared across factories to benchmark quality, optimize recipes, and fine-tune throughput.
In sum, mini item auto painting equipment has matured into an advanced, multipurpose platform that enables small parts to achieve big impact. Whether producing glossy beauty product caps, personalized tech gadgets, or premium lifestyle accessories, these machines offer an unmatched combination of speed, precision, and flexibility. They give manufacturers the power to make tiny items look and feel exceptional—visually stunning, perfectly coated, and always consistent—no matter the production volume, product shape, or brand complexity.
Automatic Painting Line for Micro Items
An automatic painting line for micro items is a highly specialized production system designed to apply precise, consistent coatings to extremely small components, often measuring just a few millimeters to a couple of centimeters in size. These micro items are common in industries such as electronics, medical devices, cosmetics, precision hardware, and micro-mechanical assemblies, where surface finish quality directly impacts functionality, durability, and aesthetics.
The core of such a painting line lies in its ability to handle miniature parts with exceptional care and accuracy. Automated feeders or robotic pick-and-place systems deliver individual micro items from bulk storage or trays to custom-designed fixtures or carriers that secure each part firmly without damage. Because micro parts can be fragile, lightweight, or irregularly shaped, these fixtures are engineered to provide stable positioning while maximizing exposure to the spray path.
Spray application in an automatic painting line for micro items employs ultra-fine atomization technologies, including micro electrostatic spray guns, precision airbrush systems, or micro rotary atomizers. These tools produce a finely controlled mist of paint particles, allowing even coverage on complex geometries, recessed areas, and delicate surfaces without flooding or dripping. The electrostatic component helps the charged paint particles adhere efficiently to the part’s surface, reducing overspray and improving transfer efficiency—a critical advantage when working with expensive specialty coatings.
Because many micro items require multiple coatings—such as primers, base colors, functional layers (e.g., anti-corrosion or anti-static coatings), and protective clear coats—the line is modular, with sequential spray booths connected by conveyors or robotic transfer arms. Each booth is optimized for a specific coating step, complete with precise environmental controls for temperature, humidity, and airflow to ensure ideal drying or curing conditions.
Curing processes integrated into the line vary according to the type of paint or coating used. For UV-curable coatings, LED or UV lamps deliver instant polymerization, reducing cycle times and minimizing thermal stress on tiny parts. For solvent or waterborne paints, convection ovens or infrared curing tunnels provide even, controlled drying. Because micro items may be heat sensitive or have thin walls, curing zones are carefully calibrated to avoid deformation or coating defects.
Inline quality inspection is a critical feature of these lines. High-resolution cameras and optical sensors scan each part to detect coating defects such as uneven coverage, runs, pinholes, or discoloration. Some systems incorporate 3D scanning or laser profilometry to assess coating thickness and surface texture. Defective parts are automatically diverted for rework or rejection, ensuring that only flawless components proceed to packaging or assembly.
Given the microscopic scale, environmental controls are stringent. Enclosed spray booths with HEPA filtration, laminar airflow, and ionization systems prevent contamination by dust, fibers, or static electricity. This level of cleanliness is often comparable to cleanroom standards, especially when the micro items are used in medical or electronic applications where contamination could compromise performance.
The line’s automation software enables recipe-based control, storing detailed parameters for each product variant—including spray pressure, paint viscosity, nozzle distance, part rotation speed, and curing profile. This allows rapid changeovers and consistent results even in mixed-model production environments. Integration with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) supports real-time monitoring, traceability, and data analytics, providing transparency and control over production quality and efficiency.
Material efficiency is paramount, as coatings used on micro parts can be costly specialty formulations. Automated paint delivery and reclaim systems minimize waste by precisely metering paint flow and capturing overspray for recycling. Some lines are designed to use eco-friendly, low-VOC paints, helping manufacturers meet environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Space efficiency is another hallmark of these lines. Compact footprints, modular design, and flexible layout options enable installation in facilities where floor space is limited. Despite their small size, these systems can achieve high throughput, often processing thousands of micro items per hour, thanks to fast cycle times, synchronized spraying and curing stations, and continuous part handling.
Operator interfaces are intuitive and support quick training. Touchscreen controls with graphical recipe editors, real-time diagnostics, and remote access facilitate smooth operation and reduce human error. Preventive maintenance schedules, supported by sensor data and predictive analytics, help maintain uptime and extend equipment life.
In summary, an automatic painting line for micro items is a precision-engineered, fully automated solution that meets the demanding quality, speed, and environmental standards required by industries producing tiny, high-value components. By combining advanced spray technology, meticulous handling, controlled curing, and robust inspection, these lines ensure every micro part receives a flawless, durable finish—critical to product performance, aesthetics, and brand reputation.
These automatic painting lines for micro items are increasingly incorporating smart technologies to enhance performance and adaptability. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms analyze data from spray parameters, environmental sensors, and inspection results in real time, enabling the system to self-optimize coating quality and process efficiency. For example, the system can adjust spray pressure, nozzle positioning, or curing times dynamically in response to detected variations in part geometry or environmental conditions, minimizing defects and maximizing yield.
Integration with Industry 4.0 and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms further extends the capabilities of these lines. Connected sensors and devices communicate with centralized manufacturing management software to provide comprehensive visibility into production status, maintenance needs, and material consumption. This connectivity enables predictive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime by alerting technicians before equipment wear affects quality or throughput. It also facilitates seamless coordination with upstream and downstream processes, such as component assembly, packaging, and logistics.
Customization flexibility is another significant advantage. The modular nature of these lines allows manufacturers to tailor the system to specific product requirements, whether applying a single uniform coat or complex multi-layer finishes with different colors, textures, or functional properties. Quick-change fixtures, programmable spray robots, and automated cleaning cycles enable rapid product changeovers, supporting small batch runs and just-in-time production strategies favored by many modern industries.
Environmental sustainability remains a priority. Many automatic painting lines for micro items are designed to minimize solvent emissions and material waste. Enclosed spray booths with efficient air filtration and solvent recovery systems ensure compliance with stringent environmental regulations. Paint reclaim units collect and recycle overspray, while the use of waterborne and UV-curable coatings reduces volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Energy-efficient curing technologies, such as LED UV lamps, contribute to lowering the overall carbon footprint of the painting process.
Operator ergonomics and safety are carefully considered in the design of these lines. User interfaces feature intuitive touchscreens, graphical process visualization, and guided workflows to simplify operation and maintenance. Safety interlocks, emergency stop functions, and protective enclosures prevent accidents, while automation reduces operator exposure to hazardous substances and repetitive tasks.
Scalability is inherent in the design of modern automatic painting lines for micro items. Manufacturers can start with a basic configuration for simple coating tasks and progressively add modules—such as additional spray stations, advanced inspection systems, or integrated packaging solutions—as production demands grow. This scalability ensures long-term investment protection and supports evolving product portfolios.
In sectors like medical devices, electronics, and luxury cosmetics, where regulatory compliance and product traceability are critical, these lines provide comprehensive data logging and reporting. Every part’s coating history—including batch number, process parameters, inspection results, and operator actions—is recorded and easily accessible for audits or quality investigations. This transparency supports certifications and builds trust with end users.
Ultimately, automatic painting lines for micro items are indispensable in today’s high-precision manufacturing landscape. By marrying cutting-edge automation, precise material application, rigorous quality control, and environmental responsibility, these systems enable producers to deliver flawless, functional, and visually appealing finishes on the smallest components at scale. As product designs become ever more intricate and consumer expectations rise, the sophistication and adaptability of these painting lines will continue to advance, driving innovation across multiple industries.
Beyond the immediate production benefits, automatic painting lines for micro items play a pivotal role in fostering innovation and differentiation in highly competitive markets. As product designers explore new materials, finishes, and functional coatings, these lines provide the flexibility and precision necessary to bring complex surface treatments from concept to mass production without compromise. For instance, the ability to precisely deposit conductive or insulating coatings onto tiny electronic connectors or to create biocompatible surface layers on medical microdevices expands the possibilities for product performance and reliability.
Advances in robotics and motion control further enhance the capabilities of these painting lines. Multi-axis robotic arms equipped with adaptive end-effectors can manipulate micro items with exceptional dexterity, enabling complex spray trajectories and angles that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve. This precision ensures that even the most intricate geometries and hard-to-reach areas receive uniform coverage, which is critical for both aesthetics and functional requirements like corrosion resistance or electrical insulation.
Another emerging trend is the integration of additive manufacturing techniques with automatic painting lines. Some facilities combine micro 3D printing and coating processes in a seamless workflow, allowing parts to be printed and then immediately coated in-line. This fusion accelerates prototyping and production cycles while maintaining tight control over surface finish quality, which is especially valuable in customized medical implants or micro-optical components.
The role of automation in reducing human error cannot be overstated. Manual painting or coating of micro items is prone to inconsistencies, contamination, and slow throughput. Automatic painting lines eliminate these issues by providing repeatable, controlled environments where every variable—from paint viscosity to spray pattern—is monitored and adjusted in real time. This not only enhances product quality but also reduces waste, lowers labor costs, and improves workplace safety by minimizing operator exposure to solvents or particulates.
Looking ahead, the integration of advanced sensor technologies and augmented reality (AR) interfaces may revolutionize how operators interact with these systems. Real-time visual overlays could assist technicians in monitoring coating uniformity, diagnosing equipment status, or guiding maintenance procedures with unprecedented clarity and speed. Such technologies would further reduce downtime and ensure that lines operate at peak efficiency.
In addition, growing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles will push manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly paints and processes compatible with automatic painting lines. Biodegradable coatings, solvent-free formulations, and water-based paints are becoming increasingly mainstream, and painting systems are evolving to handle these materials without sacrificing speed or finish quality. Enhanced paint recovery and recycling systems will become standard, contributing to waste reduction and resource conservation.
From a business perspective, the deployment of automatic painting lines for micro items enables companies to be more responsive to market trends and customer demands. The ability to quickly switch between product variants, apply custom finishes, and maintain strict quality standards provides a significant competitive advantage. This agility supports not only mass production but also limited editions, personalized products, and rapid innovation cycles, all of which are increasingly valued in consumer electronics, healthcare, and luxury goods sectors.
In conclusion, automatic painting lines for micro items represent a fusion of advanced engineering, materials science, and digital automation that addresses the unique challenges of coating the smallest, most complex parts. They deliver unparalleled precision, efficiency, and quality control while supporting environmental goals and enabling greater product creativity. As these technologies continue to mature, they will remain at the forefront of manufacturing innovation, helping industries meet the ever-growing demands of a detail-driven, fast-paced global market.
Painting Machine for a Tiny Parts with Precision
A painting machine for tiny parts with precision is a highly specialized piece of equipment engineered to deliver flawless coatings on extremely small components that require meticulous attention to detail and uniformity. These tiny parts—often found in industries such as electronics, medical devices, cosmetics, jewelry, and precision instruments—demand coatings that are not only visually perfect but also functionally reliable, ensuring durability, protection, and aesthetic appeal at a micro scale.
At the heart of such a machine is a combination of precise part handling and advanced spray technology. Handling tiny parts without damage or misalignment requires custom-designed fixtures, micro trays, or robotic grippers capable of positioning each item securely and repeatably. These systems often use vacuum suction, micro clamps, or magnetic holders to ensure that the parts remain immobile during the painting process, allowing consistent application without smudges or uneven coverage.
The spraying mechanism employs ultra-fine atomization techniques, such as electrostatic spray guns, micro airbrushes, or rotary atomizers, designed to produce a highly controlled, mist-like paint distribution. Electrostatic spraying is particularly valuable for tiny parts, as the charged paint particles are attracted to the surface, reducing overspray and increasing transfer efficiency. This ensures that even intricate geometries, recessed surfaces, and delicate edges receive complete and uniform coating layers.
Environmental controls within the machine’s spray booth are critical to maintaining coating quality. Laminar airflow systems prevent dust or airborne contaminants from settling on wet surfaces, while humidity and temperature are regulated to optimize paint drying and curing times. Antistatic ionizers may also be employed to neutralize static charges that could attract particles or cause paint to behave unpredictably on small components.
Because tiny parts often require multiple coatings—such as primers, base coats, decorative layers, and protective clear coats—the machine is usually designed with modular spray stations that allow sequential application without manual intervention. Each station can be calibrated individually to deliver precise amounts of paint, accommodating different colors, textures, or functional finishes as required.
Curing methods integrated into these machines vary based on paint type and material compatibility. UV or LED curing systems provide rapid, energy-efficient drying without exposing delicate parts to excessive heat, making them ideal for temperature-sensitive materials like plastics or thin metals. Infrared or convection ovens may be used for solvent-based coatings, designed to gently dry the paint while avoiding distortion or damage to tiny parts.
Inline inspection systems are integral to precision painting machines for tiny parts. High-resolution cameras and sensors scan each component to detect defects such as uneven coverage, runs, pinholes, or discoloration. Advanced vision software can compare coated parts against digital templates, ensuring that only those meeting strict quality standards proceed to packaging or assembly. This real-time feedback allows for immediate process adjustments, reducing waste and improving yield.
Automation software enables operators to store and recall precise spray recipes for different parts, controlling variables such as spray duration, nozzle pressure, paint flow rate, and curing times. This digital control facilitates rapid changeovers between product types and ensures consistent results, which is especially important in environments producing diverse or high-mix product ranges.
To minimize material waste and environmental impact, precision painting machines for tiny parts often feature paint reclaim systems that capture overspray and excess paint for reuse. Closed-loop air filtration and solvent recovery units reduce emissions, while compatibility with waterborne and low-VOC paints supports sustainable manufacturing practices.
Ergonomics and operator safety are also considered in the design. User-friendly interfaces, guided maintenance protocols, and safety interlocks ensure safe operation while simplifying training and routine tasks. Automation reduces operator exposure to hazardous chemicals and repetitive motions, contributing to healthier work environments.
In sum, a painting machine for tiny parts with precision combines cutting-edge spray technology, delicate handling systems, environmental controls, and intelligent automation to deliver impeccable coatings on miniature components. By providing repeatable, high-quality finishes with minimal waste and downtime, these machines enable manufacturers to meet the exacting standards of modern industries where even the smallest parts must perform flawlessly and look impeccable.
These precision painting machines for tiny parts continue to evolve with the integration of cutting-edge robotics and artificial intelligence, further enhancing their accuracy and efficiency. Advanced robotic arms equipped with multi-axis movement capabilities enable complex spray patterns that conform perfectly to intricate part geometries, ensuring comprehensive coverage even in hard-to-reach areas. The synchronization between robotic movement and spray nozzles is finely tuned to avoid over-application or gaps, preserving both the functional and aesthetic qualities of each piece.
Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of operational data to predict and correct deviations in real time, optimizing spray parameters such as flow rate, pressure, and nozzle distance automatically. This adaptive control minimizes defects and improves first-pass yield, which is especially valuable in high-mix production environments where frequent changes in part design or coating requirements occur.
Customization and flexibility are at the forefront of modern precision painting machines. They accommodate a broad spectrum of part sizes, shapes, and materials, from tiny metal fasteners to delicate plastic components. Quick-change fixtures and programmable spray recipes allow manufacturers to switch between different products with minimal downtime, supporting just-in-time manufacturing and small batch production without sacrificing consistency.
Environmental sustainability is a key design consideration. Precision painting systems incorporate closed-loop spray booths with efficient air filtration and paint recovery technologies that significantly reduce overspray and volatile organic compound emissions. Many are optimized for use with water-based, UV-curable, or low-VOC coatings, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals.
Quality assurance is embedded deeply within these systems. High-resolution vision systems paired with automated defect recognition software inspect each tiny part multiple times throughout the process, identifying flaws such as uneven coating thickness, color inconsistencies, or surface imperfections at micron-level precision. This ensures that only parts meeting exact standards advance, reducing waste and enhancing brand reputation.
Operators benefit from intuitive control interfaces featuring touchscreen displays, visual process monitoring, and guided maintenance prompts. Remote access capabilities allow for diagnostics and updates, reducing downtime and enabling quick troubleshooting even in geographically dispersed manufacturing facilities. Safety features including interlocks, emergency stops, and enclosed spray environments protect workers from exposure to hazardous substances.
Integration with broader manufacturing execution systems (MES) enables comprehensive traceability, linking each coated part to specific process parameters, batch data, and inspection results. This is critical for regulated industries such as medical devices and aerospace, where documentation and compliance are mandatory.
In addition to functional coatings, these machines can apply decorative finishes such as metallics, pearlescents, or textured surfaces with repeatable precision, enabling manufacturers to create visually striking products that stand out in competitive markets. The ability to layer coatings and control finish properties expands design possibilities while maintaining robust protection.
The compact footprint and modular architecture of modern precision painting machines make them adaptable to diverse factory layouts and scalable to production demands. Additional modules such as curing stations, inspection systems, or packaging interfaces can be integrated seamlessly, ensuring future-proof operations.
Ultimately, precision painting machines for tiny parts embody the convergence of advanced automation, material science, and process engineering. They empower manufacturers to meet the growing challenges of producing flawlessly coated micro components efficiently, sustainably, and with unmatched quality—key differentiators in today’s fast-paced, quality-driven markets.
Continued innovation in precision painting machines for tiny parts focuses heavily on enhancing speed without compromising quality. New-generation systems leverage ultra-fast curing technologies, such as LED UV and rapid infrared drying, which drastically reduce cycle times and increase throughput. These fast-curing methods not only accelerate production but also minimize thermal stress on sensitive materials, preserving part integrity and finish durability.
Moreover, adaptive fixture designs have emerged, allowing flexible handling of varying part geometries within the same production run. These fixtures incorporate smart sensors to detect part placement and orientation, enabling dynamic adjustments in spray parameters and ensuring uniform coating regardless of slight variations in part positioning. This adaptability is essential for industries dealing with customized or evolving product lines.
The incorporation of real-time analytics has become standard practice. Operators and engineers receive instant feedback on key performance indicators such as paint usage efficiency, defect rates, and equipment health. Predictive maintenance algorithms forecast component wear or potential failures, allowing maintenance to be scheduled proactively, thus avoiding unexpected downtime and preserving consistent production flow.
Safety and environmental compliance remain central. Modern machines are equipped with sealed systems and advanced filtration to capture volatile compounds and particulates effectively. The trend toward using environmentally friendly coatings is supported by machine compatibility with a wide range of low-impact materials, further reducing the ecological footprint of the painting process.
From a user experience standpoint, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) training modules are beginning to complement traditional operator education. These immersive tools help technicians understand machine operations, troubleshoot issues, and perform maintenance with greater confidence and precision, reducing human error and training costs.
Collaboration between machine manufacturers and paint suppliers is driving tailored coating solutions optimized for these systems, combining improved adhesion, faster curing, and enhanced durability suited specifically for tiny parts. This synergy results in coatings that meet increasingly stringent industry standards while providing manufacturers with a competitive edge.
Finally, integration with Industry 4.0 initiatives ensures that precision painting machines for tiny parts are not isolated assets but part of a fully connected, intelligent manufacturing ecosystem. This connectivity facilitates seamless data exchange across the supply chain, supports flexible manufacturing paradigms like mass customization, and enables rapid response to market demands.
In essence, precision painting machines for tiny parts continue to evolve into highly sophisticated, efficient, and versatile systems that support the production of miniature components with impeccable finish quality. They play a crucial role in advancing manufacturing capabilities, driving innovation, and delivering products that meet the exacting expectations of today’s technology-driven and design-conscious markets.
Paint Line for Tiny Components
A paint line for tiny components is a meticulously engineered manufacturing system designed to apply high-quality coatings to very small parts with consistent precision, efficiency, and minimal waste. These components—found in sectors such as electronics, medical devices, cosmetics, automotive micro-parts, and precision hardware—require specialized handling, application, and curing processes to ensure durable, defect-free finishes that meet stringent industry standards.
At the core of the paint line is a sophisticated material handling system tailored for tiny components. Parts are typically fed into the line via vibratory feeders, bulk trays, or automated pick-and-place robots that carefully position each item into custom-designed fixtures or carriers. These fixtures securely hold the components in optimal orientation to maximize spray coverage while minimizing contact points that could mar freshly applied coatings.
The coating application segment employs advanced spray technologies suitable for miniature parts, such as electrostatic spray guns, micro airbrushes, or rotary atomizers. These devices produce ultra-fine atomization, delivering a controlled and uniform paint mist that adheres evenly even on complex geometries or recessed features. Electrostatic charging enhances transfer efficiency, reducing overspray and paint consumption—a crucial factor given the often expensive specialty coatings used for tiny components.
The paint line is modular, with sequential spray booths allowing multiple coating stages like primers, base colors, functional layers (e.g., anti-corrosive or insulating coatings), decorative finishes, and protective clear coats. Between stages, drying or curing stations use technologies such as UV/LED curing, infrared ovens, or convection heating, precisely calibrated to cure coatings without damaging delicate parts or altering their dimensions.
Environmental controls within the paint line maintain cleanroom-level conditions, utilizing HEPA-filtered laminar airflow to minimize particulate contamination and ionizers to neutralize static charges. Temperature and humidity regulation optimize coating adhesion and curing consistency. Enclosed booths capture and recycle overspray, improving material efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Inline inspection systems equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors continuously monitor coating quality, detecting defects like uneven coverage, runs, pinholes, or color inconsistencies. Automated sorting mechanisms divert defective parts for rework or rejection, ensuring that only components meeting strict quality criteria proceed downstream.
The entire process is managed via advanced automation software that stores detailed coating recipes, controls spray parameters, monitors environmental conditions, and records quality data for each production batch. Integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) enables real-time production tracking, traceability, and analytics, supporting compliance with regulatory requirements and continuous process improvement.
To minimize downtime and facilitate flexibility, the paint line incorporates quick-change fixtures and programmable spray robots, enabling rapid product changeovers. This adaptability is vital for manufacturers handling diverse product portfolios or small batch runs requiring frequent adjustments.
Sustainability is a key consideration, with many paint lines designed for compatibility with low-VOC, waterborne, or UV-curable coatings. Efficient paint recovery systems reclaim unused materials, while energy-efficient curing methods reduce power consumption and carbon footprint.
Safety and ergonomics are integral to design, with enclosed systems reducing operator exposure to hazardous substances, automated handling minimizing repetitive strain injuries, and user-friendly interfaces simplifying operation and maintenance.
Overall, a paint line for tiny components represents a harmonious integration of precision engineering, advanced coating technology, and smart automation. It enables manufacturers to achieve consistently superior finishes on miniature parts, meeting the growing demands for quality, aesthetics, and durability in high-tech, medical, cosmetic, and consumer industries.
These paint lines for tiny components continue to evolve by incorporating cutting-edge robotics and intelligent control systems that further enhance precision and throughput. Robotic arms with multiple degrees of freedom can manipulate parts dynamically, allowing coatings to be applied from optimal angles and distances regardless of the complexity of the component geometry. This ensures uniform paint distribution even on challenging surfaces such as cavities, grooves, or micro-textures.
Real-time monitoring and adaptive process control play a crucial role in maintaining coating quality. Sensors collect data on spray parameters, environmental conditions, and part positioning, feeding information into machine learning algorithms that detect subtle variations or drift. The system can automatically adjust nozzle pressure, spray patterns, or curing times to compensate, reducing defects and maximizing first-pass yield.
The modularity of these paint lines allows for easy integration of additional functional stations, such as digital printing units for applying logos or serial numbers, plasma treatment for surface preparation, or robotic cleaning modules to ensure contaminant-free parts before coating. This flexibility supports complex finishing workflows within a single continuous production sequence, minimizing manual handling and associated risks.
Environmental sustainability remains a priority, with many systems designed to meet or exceed stringent global regulations. Closed-loop air filtration and paint reclaim technologies dramatically reduce volatile organic compound emissions and material waste. Compatibility with eco-friendly coatings like waterborne or UV-curable paints aligns with corporate sustainability initiatives and helps manufacturers reduce their ecological footprint without compromising product quality.
Operator safety and usability are enhanced through advanced interfaces featuring touchscreen controls, guided maintenance prompts, and remote monitoring capabilities. Augmented reality tools are increasingly being explored to assist technicians in diagnostics and repairs, providing virtual overlays that simplify complex tasks and reduce downtime.
Integration with Industry 4.0 frameworks enables seamless communication across the manufacturing ecosystem. Production data is aggregated for detailed analytics, allowing managers to optimize line performance, forecast maintenance needs, and track compliance with quality standards. This connectivity also facilitates rapid response to market changes, enabling agile production adjustments and supporting just-in-time manufacturing models.
In industries such as medical devices and electronics, where traceability and regulatory compliance are paramount, paint lines for tiny components incorporate comprehensive data logging. Every part’s coating history, including batch information, process parameters, and inspection outcomes, is securely stored and easily accessible for audits or quality investigations, ensuring transparency and accountability.
The compact footprint of these systems allows installation in space-constrained environments without sacrificing throughput or quality. Their scalability means manufacturers can start with a basic setup and expand capabilities by adding modules as demand grows or processes evolve, protecting investment and supporting long-term growth.
Ultimately, paint lines for tiny components represent the convergence of precision engineering, advanced materials science, and digital automation. They enable manufacturers to produce impeccably coated miniature parts at high speed and with minimal waste, meeting the exacting demands of modern industries where quality, consistency, and sustainability are critical to success.
Continuous advancements in paint lines for tiny components are driving further improvements in efficiency and product quality. One notable development is the increased use of artificial intelligence (AI) to refine process control. AI systems analyze historical and real-time data to identify patterns and anomalies that might elude human operators. This enables predictive adjustments to coating parameters before defects occur, ensuring stable output and reducing scrap rates.
Enhanced automation now includes vision-guided robotics capable of precise, adaptive part handling. These robots can identify, pick, and orient micro components of varying shapes and sizes directly from bulk feeders or conveyors, eliminating the need for manual loading and reducing the risk of damage. This flexibility supports high-mix manufacturing environments where frequent product changes are required.
The adoption of multi-material coating capabilities is expanding, allowing paint lines to apply different functional and decorative layers in a single pass. For example, a tiny medical device component might receive a biocompatible primer, an antimicrobial coating, and a color-coded topcoat all within one integrated sequence. Such complexity, once achievable only through separate processes, now reduces lead times and handling risks.
Increased emphasis on sustainability is also prompting manufacturers to optimize energy consumption within paint lines. Innovations like variable-speed fans, energy recovery systems, and LED-based curing units contribute to lowering overall power usage. Additionally, water-based and UV-curable coatings continue to gain popularity due to their reduced environmental impact and faster cure times, aligning with eco-friendly production goals.
Maintenance and downtime reduction are addressed through smart diagnostics and remote monitoring. Sensors track equipment wear, paint supply levels, and environmental conditions, alerting maintenance teams proactively. This reduces unplanned stoppages and ensures the paint line operates at peak efficiency, which is vital for high-volume or time-sensitive production.
User training is becoming more interactive and efficient with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. Operators can simulate machine operation, troubleshoot faults, and learn maintenance procedures in immersive virtual environments, accelerating competency development and reducing errors on the actual production floor.
Data integration across the manufacturing chain facilitates traceability and quality assurance. Paint lines for tiny components are connected to enterprise resource planning (ERP) and supply chain systems, enabling seamless coordination from raw material procurement to finished goods delivery. This connectivity supports compliance with regulatory standards and helps manufacturers respond swiftly to recalls or quality issues.
Customization remains a key driver, with paint lines capable of handling bespoke finishes and limited runs without sacrificing efficiency. Quick-change tooling, programmable spray patterns, and flexible conveyor systems enable rapid transitions between product variants, catering to market demands for personalized or niche products.
In summary, paint lines for tiny components are at the forefront of manufacturing innovation, combining precision engineering, intelligent automation, and sustainable practices. They empower producers to deliver high-quality, reliable, and aesthetically pleasing miniature parts that meet the rigorous standards of today’s advanced industries while maintaining operational excellence and environmental responsibility.
Painting Systems for Tiny Pieces
Painting systems for tiny pieces are specialized, highly engineered setups designed to apply consistent, high-quality coatings to miniature components across various industries such as electronics, medical devices, cosmetics, precision machinery, and jewelry. These systems address the unique challenges associated with handling and finishing very small parts, ensuring that each piece receives an even, durable, and defect-free coating that meets exacting functional and aesthetic requirements.
Central to these painting systems is a precision handling mechanism that carefully secures and positions tiny pieces to prevent movement or damage during the coating process. This often involves custom fixtures, micro-trays, or robotic grippers with fine control, capable of adapting to diverse shapes, sizes, and materials. The handling system ensures that parts are oriented optimally for uniform paint coverage while facilitating rapid transfer between stations.
The coating application utilizes advanced spray technologies engineered for miniature parts. Electrostatic spray guns, micro atomizers, or precision airbrushes create ultra-fine paint particles, producing a controlled mist that adheres uniformly even on complex geometries and hard-to-reach surfaces. Electrostatic charging enhances transfer efficiency by attracting paint particles to the target surface, minimizing overspray and conserving expensive coatings.
Painting systems for tiny pieces are often modular, with sequential stations dedicated to different coating layers such as primers, base coats, functional treatments (e.g., corrosion resistance, insulation), decorative finishes, and protective clear coats. Each station is equipped with environmental controls—regulated temperature, humidity, and laminar airflow—to maintain ideal conditions for paint adhesion and curing.
Curing technologies integrated into these systems vary based on the coating materials. UV or LED curing offers rapid, low-heat polymerization suitable for heat-sensitive parts, while infrared or convection ovens provide thorough drying for solvent or water-based paints. The curing process is optimized to preserve part integrity and coating performance.
Quality assurance is embedded through inline inspection systems employing high-resolution cameras and sensors that detect defects such as uneven coverage, color variation, or surface imperfections at a micro scale. Automated rejection or rework mechanisms ensure only compliant pieces proceed, reducing waste and enhancing overall product quality.
Automation software orchestrates the entire process, storing precise recipes that control spray parameters, curing profiles, and inspection criteria for various products. This enables quick changeovers, consistent results, and detailed traceability, essential for regulated industries and high-mix production environments.
Sustainability is addressed through paint reclaim systems, efficient air filtration, and compatibility with low-VOC or waterborne coatings, reducing environmental impact and material waste. Operator safety is enhanced with enclosed spray booths, ventilation systems, and intuitive control interfaces.
Overall, painting systems for tiny pieces combine delicate handling, sophisticated spray technology, controlled curing, and rigorous quality control into a seamless production flow. They enable manufacturers to achieve flawless, functional, and visually appealing finishes on miniature components—critical for meeting the high standards of modern manufacturing across multiple sectors.
These painting systems for tiny pieces continue to advance by integrating intelligent automation and robotics to improve precision and throughput. Robotic arms equipped with fine-motion control and adaptive end-effectors handle parts with exceptional care, allowing for consistent orientation and positioning even when processing diverse shapes or delicate materials. This robotic integration reduces manual intervention, minimizes damage risks, and increases production speed.
Real-time monitoring and adaptive control systems analyze data from sensors measuring spray parameters, environmental conditions, and coating thickness. Machine learning algorithms interpret this data to dynamically adjust spray pressure, nozzle distance, and curing times, ensuring consistent coating quality despite variations in part geometry or external factors. This responsiveness leads to higher first-pass yields and reduces waste.
The modular design of these painting systems allows manufacturers to tailor configurations according to specific product requirements, adding or removing coating stations, curing units, or inspection modules as needed. This flexibility supports small batch production and rapid product changeovers, vital in industries where customization and quick turnaround are common.
Environmental considerations drive the use of enclosed spray booths with advanced air filtration and paint recovery systems that capture overspray and volatile emissions. Many systems are designed for compatibility with eco-friendly coatings such as waterborne or UV-curable paints, aligning with sustainability goals and regulatory compliance. Energy-efficient curing technologies further reduce the environmental footprint of the painting process.
Operator interfaces emphasize usability and safety, featuring touchscreen controls, guided maintenance workflows, and safety interlocks. Remote diagnostics and monitoring enable proactive maintenance and troubleshooting, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational reliability.
Integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms provides comprehensive traceability and production analytics. Every coated piece’s history—from batch data to inspection results—is logged and accessible for quality audits, regulatory compliance, and continuous improvement initiatives.
Incorporating additional functional capabilities such as surface preparation modules, digital printing for marking or decoration, and robotic cleaning stations extends the versatility of painting systems for tiny pieces. These integrated solutions streamline workflows, reduce handling, and ensure that finished parts meet stringent quality and functional standards.
Compact footprints and scalable architectures make these painting systems suitable for a wide range of manufacturing environments, from large industrial plants to smaller specialized facilities. Their adaptability ensures they can grow with production demands and evolving product lines.
Ultimately, painting systems for tiny pieces represent a convergence of precision engineering, advanced materials science, automation, and sustainability. They empower manufacturers to consistently produce miniature components with impeccable finishes, meeting the high standards of modern industries where quality, reliability, and environmental responsibility are paramount.
Continuous innovation in painting systems for tiny pieces is further enhancing their capabilities through the integration of cutting-edge sensor technologies and data analytics. Advanced imaging systems now enable three-dimensional surface mapping and coating thickness measurement at micron-level resolution, allowing even the most subtle defects or inconsistencies to be detected early in the process. This high-precision feedback enables immediate corrections, reducing rework and ensuring uniform quality across every part.
Emerging trends also include the incorporation of augmented reality (AR) tools to support operator training, maintenance, and real-time troubleshooting. AR overlays can guide technicians through complex procedures with visual cues and step-by-step instructions, minimizing human error and accelerating problem resolution. Such immersive technologies improve overall system uptime and contribute to more consistent production outcomes.
Robust connectivity within Industry 4.0 frameworks allows painting systems for tiny pieces to be fully integrated into smart factories. This interconnectedness facilitates seamless data exchange between coating lines, upstream manufacturing processes, and downstream quality control or packaging systems. As a result, manufacturers gain comprehensive visibility and control over their entire production chain, enabling proactive decision-making and agile responses to market demands.
The rise of additive manufacturing and hybrid production methods is prompting the development of painting systems capable of handling components with complex geometries or multi-material compositions. Specialized spray techniques and adaptive handling mechanisms ensure that coatings are applied precisely and uniformly, even on 3D-printed micro parts or assemblies combining metals, plastics, and ceramics.
Sustainability efforts continue to push advancements in coating materials and application technologies. The adoption of biodegradable paints, solvent-free formulations, and ultra-low VOC coatings is expanding, with painting systems evolving to maintain performance while accommodating these greener alternatives. Energy-efficient curing technologies, such as next-generation UV LEDs and plasma-assisted drying, further reduce environmental impact.
From a production standpoint, painting systems are increasingly designed for maximum flexibility, supporting both high-volume runs and small batch or custom orders with equal efficiency. Modular stations and programmable robotics allow quick reconfiguration, while automated recipe management ensures consistent application across product variants.
Safety enhancements remain a priority, with enclosed spray environments, improved ventilation, and comprehensive monitoring of airborne contaminants protecting operators and the surrounding workplace. Automation reduces manual handling, further minimizing exposure to hazardous substances.
In conclusion, painting systems for tiny pieces continue to evolve as sophisticated, adaptable, and environmentally conscious solutions. By combining precision engineering, smart automation, and sustainable practices, these systems enable manufacturers to meet the growing complexity and quality demands of miniature components across a wide spectrum of industries—securing their role as indispensable tools in advanced manufacturing landscapes.
Mini Part Painting Machine
A mini part painting machine is a specialized automated system designed to apply high-quality coatings on very small components with exceptional precision and efficiency. These machines cater to industries like electronics, medical devices, cosmetics, jewelry, and precision engineering, where miniature parts require flawless finishes to meet strict functional and aesthetic standards.
The core challenge addressed by mini part painting machines is the delicate handling and accurate coating of tiny components, which can be easily damaged or improperly coated using conventional painting methods. To overcome this, these machines employ advanced handling solutions such as micro-grippers, vacuum fixtures, or custom trays that securely hold parts in place throughout the process, ensuring stability and repeatability.
Painting application technologies in these machines include electrostatic spray systems, micro airbrushes, and rotary atomizers that generate ultra-fine paint mists for uniform coverage. Electrostatic charging is especially beneficial, as it attracts paint particles to the surface of the tiny parts, reducing overspray and improving transfer efficiency—a critical factor when working with costly or specialized coatings.
The mini part painting machine typically features modular spray stations, enabling multiple layers to be applied sequentially, such as primers, base coats, functional coatings, and protective clear coats. Each station is optimized for precise control of spray parameters like flow rate, pressure, and nozzle position to match the unique requirements of each coating type.
Curing methods integrated into these machines vary according to the coating chemistry and part materials. UV or LED curing offers rapid, low-temperature drying ideal for heat-sensitive plastics or delicate metals. Infrared or convection ovens are used for solvent-based or waterborne paints, carefully balancing drying speed with part integrity.
To ensure consistent quality, these machines incorporate inline inspection systems with high-resolution imaging and sensor arrays that detect coating defects—such as uneven thickness, runs, or color deviations—at micro-scale resolutions. Automated rejection or rework mechanisms prevent defective parts from advancing, maintaining high production standards.
Advanced control software manages the entire painting cycle, storing detailed process recipes for different part types and coating formulations. This facilitates quick changeovers and ensures repeatability, which is vital for manufacturers handling diverse product lines or frequent customization.
Environmental considerations are embedded in the design, with enclosed spray booths, efficient air filtration, and paint reclaim systems minimizing emissions and waste. Many machines support eco-friendly coatings like waterborne or low-VOC paints, aligning with sustainability goals.
Operator safety and usability are enhanced through intuitive interfaces, safety interlocks, and automated handling, reducing exposure to hazardous materials and repetitive strain.
In essence, mini part painting machines deliver precise, consistent, and environmentally responsible coating solutions tailored to the unique demands of miniature components. Their combination of delicate handling, advanced spray technology, and intelligent automation makes them indispensable in modern manufacturing environments where quality and efficiency are paramount.
Mini part painting machines continue to evolve with the integration of sophisticated robotics and intelligent control systems, further enhancing precision and production speed. Robotic arms equipped with micro-manipulators enable delicate handling and accurate positioning of tiny parts, accommodating complex shapes and ensuring consistent exposure to the spray nozzles. This automation reduces human error, lowers the risk of part damage, and allows for continuous operation with minimal supervision.
Advanced sensors and real-time monitoring systems gather data on spray characteristics, environmental conditions, and coating quality throughout the painting cycle. Machine learning algorithms analyze this information to dynamically adjust parameters such as nozzle pressure, spray angle, and paint flow, optimizing coating uniformity and reducing defects. This adaptive approach significantly improves first-pass yield and minimizes material waste.
The modular design of mini part painting machines supports flexible production setups. Manufacturers can configure multiple spray stations to apply primers, base coats, specialty functional layers, and protective topcoats in sequence, all within a compact footprint. Quick-change tooling and programmable recipes facilitate rapid transitions between product variants, supporting both high-volume runs and small batch production common in industries like medical devices and electronics.
Environmental sustainability is a key focus, with machines designed to operate within enclosed spray booths equipped with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration and solvent recovery systems. These features reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and capture overspray, conserving costly materials and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Compatibility with waterborne, UV-curable, and low-VOC coatings further enhances eco-friendly manufacturing.
Operator interfaces emphasize usability and safety, offering touchscreen controls, guided maintenance procedures, and safety interlocks that prevent accidental exposure to hazardous substances. Remote diagnostics and monitoring enable proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime and ensuring consistent machine performance.
Integration with enterprise manufacturing systems provides comprehensive traceability, recording detailed process data and quality inspection results for each mini part. This transparency is critical for meeting regulatory requirements in highly controlled industries and supports continuous process improvement initiatives.
Overall, mini part painting machines combine precision engineering, advanced automation, and environmentally responsible design to deliver impeccable coatings on miniature components. Their ability to handle complex geometries, maintain consistent quality, and adapt to diverse production needs makes them indispensable tools in modern manufacturing environments focused on excellence and efficiency.
Building on these advancements, mini part painting machines are increasingly incorporating augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies to enhance operator training and maintenance. Through immersive simulations, technicians can practice machine operation and troubleshoot potential issues in a safe virtual environment before interacting with the actual equipment. This reduces human errors, accelerates learning curves, and improves overall productivity.
Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 connectivity enables these machines to communicate seamlessly with other production line equipment and factory management systems. Real-time data exchange allows for synchronized workflows, predictive maintenance scheduling, and rapid quality feedback loops. This interconnectedness helps manufacturers respond swiftly to changing production demands and maintain optimal operational efficiency.
Innovations in coating materials are also driving machine capabilities forward. Mini part painting machines are adapting to apply advanced functional coatings, such as antimicrobial layers for medical devices, hydrophobic finishes for electronics, or conductive paints for flexible circuits. The precision application of these specialty coatings requires tightly controlled spray parameters and curing processes, which modern machines deliver reliably.
Additionally, as additive manufacturing grows, mini part painting machines are tailored to coat 3D-printed micro parts with complex geometries. Adaptive fixtures and spray patterns ensure uniform coverage without obscuring fine details or impairing functionality, opening new avenues for customization and rapid prototyping.
Sustainability remains a cornerstone, with ongoing efforts to reduce energy consumption through efficient curing technologies like LED UV systems and optimized airflow management. Paint recovery and recycling systems continue to evolve, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Compact, modular designs allow mini part painting machines to fit into diverse production environments, from large factories to small cleanrooms. Scalability ensures that manufacturers can expand or reconfigure their systems as product lines evolve or new technologies emerge, safeguarding investment over time.
In summary, mini part painting machines are transforming the way miniature components receive coatings, blending precision, adaptability, and sustainability. They empower manufacturers across sectors to meet stringent quality standards while maximizing efficiency and environmental responsibility—key factors for success in today’s competitive, innovation-driven markets.
Tiny Part Painting – Automated
Automated tiny part painting systems are cutting-edge solutions designed to efficiently coat miniature components with exceptional precision and repeatability, meeting the rigorous demands of industries such as electronics, medical devices, cosmetics, and precision engineering. Automation addresses the inherent challenges of handling and finishing tiny parts, where manual painting would be impractical, inconsistent, and prone to errors.
Central to these systems is automated handling technology that uses robotic arms, vacuum grippers, or micro-manipulators to securely pick, position, and transport tiny parts through each stage of the painting process. These handling mechanisms are engineered to prevent damage and ensure consistent orientation, enabling uniform paint application even on complex geometries and delicate surfaces.
Coating is applied via advanced automated spray technologies such as electrostatic spray guns, micro-atomizers, or precision airbrushes that produce a fine, controlled mist. Electrostatic charging enhances paint transfer efficiency by attracting charged paint particles directly to the part surfaces, minimizing overspray and conserving costly coating materials. Automated spray parameters—such as flow rate, nozzle position, and spray duration—are precisely controlled to achieve consistent layer thickness and finish quality.
The automated painting line is typically modular, featuring sequential coating stations that apply primers, base layers, functional coatings, decorative finishes, and protective clear coats as required. Each station incorporates environmental controls, including temperature, humidity, and clean airflow management, ensuring optimal conditions for paint adhesion and curing.
Curing processes integrated into automated systems include UV/LED curing for rapid, low-heat drying, infrared ovens for solvent-based paints, or convection systems tailored to coating chemistries. Automation synchronizes curing times with coating stages to maximize throughput while preserving part integrity.
Quality control is embedded throughout the automated painting process using high-resolution vision systems and sensors that inspect each part for coating defects such as runs, pinholes, uneven coverage, or color variation. Automated sorting diverts nonconforming parts for rework or rejection, maintaining high yield rates and reducing waste.
Software-driven control systems manage the entire automated workflow, storing detailed process recipes for different part types and coatings, enabling quick changeovers and repeatable results. Real-time monitoring and data logging support traceability, process optimization, and compliance with industry regulations.
Environmental and operator safety considerations are integral, with enclosed spray booths, efficient air filtration, and paint reclaim systems minimizing emissions and exposure to hazardous substances. Compatibility with waterborne and low-VOC coatings further aligns with sustainability initiatives.
Overall, automated tiny part painting systems combine precision robotics, advanced coating technologies, and intelligent process control to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes on miniature components. By enhancing efficiency, reducing waste, and ensuring repeatable excellence, these systems are essential in modern manufacturing environments focused on miniaturized product innovation and reliability.
Automated tiny part painting systems continue to advance by integrating intelligent robotics and adaptive process controls that elevate both precision and productivity. Robotic manipulators equipped with fine-motion capabilities handle parts gently yet accurately, accommodating intricate shapes and fragile materials while maintaining consistent positioning throughout the coating sequence. This automation minimizes human intervention, reduces the risk of damage, and supports continuous, high-throughput operation.
Sensors and real-time analytics collect comprehensive data on spray parameters, environmental conditions, and coating quality. Machine learning algorithms analyze this information to automatically adjust nozzle pressure, spray patterns, and curing profiles, ensuring uniform coverage and reducing defects even when part geometries or production conditions vary. This level of responsiveness improves first-pass yield and conserves coating materials.
The modular nature of these systems allows manufacturers to customize their lines with multiple spray and curing stations tailored to specific coating layers, whether primers, functional coatings, or decorative finishes. This flexibility supports a wide range of products and enables rapid changeovers essential for small batch or mixed production environments.
Environmental stewardship is central to design considerations. Enclosed spray booths with advanced air filtration and paint recovery reduce volatile organic compound emissions and overspray waste. Compatibility with eco-friendly coatings such as waterborne, UV-curable, and low-VOC paints aligns with sustainability goals while maintaining exceptional finish quality.
User-friendly control interfaces feature touchscreen displays, guided workflows, and safety interlocks that protect operators from exposure to hazardous substances. Remote monitoring and diagnostics facilitate proactive maintenance and minimize downtime, ensuring reliable and efficient system performance.
Integration with broader manufacturing execution systems enables full traceability, linking each painted part to detailed process data, quality inspection results, and batch information. This comprehensive data management supports regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and continuous improvement initiatives.
Advanced inspection technologies embedded within the painting line use high-resolution cameras and sensors to detect even microscopic coating defects. Automated sorting and rework mechanisms ensure only parts meeting stringent quality criteria advance, reducing waste and boosting customer satisfaction.
Compact footprints and scalable designs make automated tiny part painting systems suitable for diverse production environments, from large-scale industrial plants to specialized cleanroom facilities. Their ability to adapt to evolving manufacturing demands protects investment and enhances operational agility.
In essence, automated tiny part painting systems represent the fusion of precision engineering, smart automation, and sustainable practices. They empower manufacturers to deliver flawless, durable coatings on miniature components at scale, meeting the stringent quality, efficiency, and environmental standards that define modern high-tech industries.
Ongoing developments in automated tiny part painting systems focus on further enhancing customization and process intelligence. Advanced software platforms now incorporate artificial intelligence to analyze historical production data alongside real-time sensor inputs, enabling predictive adjustments that preempt coating inconsistencies before they arise. This proactive control reduces scrap rates and improves overall process stability, especially important when handling delicate or highly intricate parts.
Robotic systems are becoming increasingly dexterous and versatile, with multi-axis arms capable of executing complex spray trajectories tailored to individual part geometries. These robots can seamlessly switch between different parts and coating types without manual intervention, supporting high-mix manufacturing and mass customization trends. Integration of force feedback and tactile sensors enhances the robots’ ability to handle fragile components delicately, further minimizing damage and improving yield.
The push toward sustainability drives innovations in coating materials and application methods. Automated systems are designed to optimize the use of waterborne, UV-curable, and low-VOC coatings, reducing environmental impact without compromising finish durability or appearance. Paint recovery systems have improved, capturing more overspray for reuse, and energy-efficient curing technologies help lower power consumption.
Operator experience benefits from intuitive human-machine interfaces enriched with augmented reality (AR) tools that overlay operational data and maintenance guidance directly onto equipment views. This technology streamlines troubleshooting, reduces downtime, and enhances training effectiveness.
Seamless integration within Industry 4.0 ecosystems enables automated tiny part painting lines to communicate bi-directionally with upstream and downstream processes, ensuring synchronized production schedules, efficient material flows, and comprehensive traceability. Data analytics platforms provide actionable insights to optimize performance, plan maintenance, and ensure compliance with strict regulatory standards.
Furthermore, modular designs allow manufacturers to scale operations easily or reconfigure lines as new product requirements emerge, preserving investment while adapting to market demands. Compact footprints facilitate installation even in space-constrained facilities, expanding access to advanced coating capabilities across diverse manufacturing environments.
In summary, automated tiny part painting systems continue to evolve as intelligent, flexible, and environmentally conscious solutions. By combining cutting-edge robotics, advanced process controls, and sustainable practices, they enable manufacturers to achieve impeccable finishes on miniature components with unmatched efficiency and reliability—key advantages in today’s competitive, innovation-driven industries.
Building further on these advancements, automated tiny part painting systems are increasingly incorporating collaborative robots, or cobots, which work safely alongside human operators to enhance flexibility and precision. These cobots can assist with delicate loading and unloading tasks, complex part handling, or fine-tuning spray parameters based on operator input, blending the strengths of automation with human adaptability.
Integration of real-time 3D scanning and vision-guided systems enables the machines to adjust spraying dynamically to minute variations in part dimensions or surface conditions. This capability ensures uniform coating even when parts have subtle manufacturing tolerances or surface irregularities, which is critical for maintaining quality in high-precision industries such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
In response to growing customization demands, paint lines now support on-demand variable pattern spraying and multi-material application within single production cycles. This allows different coatings or colors to be applied to individual parts or even specific areas on a single tiny component without manual intervention, facilitating mass customization and reducing inventory complexity.
Energy efficiency continues to improve through the use of next-generation LED curing systems that consume less power and generate minimal heat, preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive materials. Air management systems are optimized to reduce energy waste while maintaining consistent environmental conditions, further lowering operational costs and environmental impact.
Data security and compliance gain prominence as these painting systems handle sensitive product information and quality records. Encrypted communication protocols, secure cloud data storage, and user access controls ensure that intellectual property and regulatory data are protected throughout the coating process.
Maintenance strategies evolve with the deployment of digital twins—virtual replicas of the physical painting line that simulate operations, predict failures, and optimize workflows. This technology enables proactive adjustments, remote troubleshooting, and rapid response to production anomalies, minimizing downtime and extending equipment lifespan.
Finally, collaborative development between machine manufacturers, coating formulators, and end-users accelerates innovation in coatings specifically engineered for automated tiny part painting. These coatings exhibit enhanced adhesion, durability, and specialized functionalities like antimicrobial or conductive properties, optimized for application by automated systems to meet evolving industry standards.
Together, these innovations position automated tiny part painting systems at the forefront of manufacturing technology—delivering unmatched precision, adaptability, sustainability, and integration that empower manufacturers to thrive in complex, fast-paced markets demanding excellence in miniature component finishing.
Compact Painters for Tiny Parts
Compact painters for tiny parts are specialized, space-efficient coating systems designed to deliver precise, high-quality finishes on miniature components within limited manufacturing footprints. These machines address the unique challenges posed by very small parts—such as delicate handling requirements, complex geometries, and the need for consistent, defect-free coatings—while optimizing factory space and operational efficiency.
At the heart of compact painters is an advanced handling mechanism that securely holds and positions tiny parts using custom fixtures, micro-grippers, or vacuum-based solutions. This ensures stability and repeatable orientation during the painting process, critical for achieving uniform coverage and protecting fragile components from damage.
Coating application technologies in these compact systems often include electrostatic spray guns, micro atomizers, or precision airbrushes that generate fine, controlled paint mists. The electrostatic charge enhances transfer efficiency by attracting paint particles directly to the part surfaces, reducing overspray and conserving coating materials—an important consideration when working with expensive specialty paints.
These machines typically feature modular spray stations capable of applying multiple coating layers sequentially, such as primers, base coats, functional or decorative finishes, and clear protective topcoats. Integrated curing technologies—such as UV/LED curing or infrared drying ovens—are optimized for the specific coatings used and the sensitivity of tiny parts, enabling rapid, low-heat curing that preserves part integrity.
Environmental controls within compact painters maintain consistent temperature, humidity, and clean airflow to promote optimal paint adhesion and finish quality. Enclosed spray booths with efficient air filtration and paint recovery systems minimize emissions and waste, supporting compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Quality assurance is embedded through inline inspection systems employing high-resolution cameras and sensors that detect coating defects at a micro scale. Automated sorting mechanisms separate nonconforming parts for rework or rejection, ensuring only parts meeting strict quality standards advance.
Advanced control software manages process parameters, stores coating recipes, and facilitates quick changeovers between product variants, enhancing flexibility in high-mix or small-batch production environments. User-friendly interfaces and safety interlocks protect operators while simplifying operation and maintenance.
The compact footprint of these painting systems allows installation in space-constrained facilities or cleanroom environments common in medical, electronics, and precision manufacturing sectors. Their scalable design supports growing production demands without requiring significant factory floor expansion.
By combining precision handling, sophisticated coating technology, and efficient use of space, compact painters for tiny parts enable manufacturers to achieve superior finishes on miniature components while maximizing operational efficiency and environmental responsibility—essential factors in today’s competitive, innovation-driven markets.
Compact painters for tiny parts continue to evolve by integrating more advanced automation and intelligent process controls to further enhance precision, speed, and flexibility within a minimal footprint. Robotic handling systems equipped with micro-grippers and vision guidance improve part placement accuracy, enabling the machines to accommodate a wider variety of shapes and sizes without compromising throughput or quality. This automation reduces manual intervention, lowers the risk of damage, and supports consistent results even in high-mix production environments.
Real-time monitoring technologies capture detailed data on spray patterns, coating thickness, and environmental conditions throughout the painting process. Machine learning algorithms analyze this information to make dynamic adjustments—such as modifying nozzle pressure, adjusting spray angles, or fine-tuning curing times—ensuring uniform coatings and reducing material waste. This adaptability is especially valuable when processing parts with complex geometries or sensitive surfaces.
The modular design philosophy allows manufacturers to customize compact painters by adding or removing coating and curing stations based on product requirements. This flexibility facilitates rapid changeovers and supports both small-batch runs and larger-scale production without the need for additional floor space. Quick-release fixtures and programmable process recipes further streamline transitions between different tiny part models.
Sustainability remains a key focus, with enclosed spray booths featuring high-efficiency air filtration and paint reclaim systems that minimize overspray and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Compatibility with environmentally friendly coatings such as waterborne and UV-curable paints aligns with industry regulations and corporate sustainability goals. Energy-efficient curing technologies, including LED UV systems and optimized airflow management, help reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
User-centric design elements include intuitive touchscreen interfaces, safety interlocks, and guided maintenance workflows that simplify operation and protect personnel from exposure to hazardous substances. Remote diagnostics and monitoring capabilities enable proactive maintenance and troubleshooting, minimizing downtime and ensuring consistent machine performance.
Integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms provides comprehensive traceability and quality assurance. Detailed process data and inspection results for each part are securely recorded and accessible for audits, regulatory compliance, and continuous improvement initiatives.
Compact painters’ small physical footprint makes them suitable for cleanroom environments and facilities where space is at a premium. Their scalability and modularity enable manufacturers to expand or reconfigure lines as product portfolios evolve, protecting investment while adapting to changing market demands.
In summary, compact painters for tiny parts combine advanced robotics, precise coating technology, intelligent controls, and sustainable design within a space-efficient package. These systems empower manufacturers to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes on miniature components while optimizing factory space, operational efficiency, and environmental responsibility—critical advantages in today’s fast-paced, quality-driven industries.
Further advancements in compact painters for tiny parts emphasize seamless integration with smart factory ecosystems and enhanced customization capabilities. These systems increasingly feature connectivity protocols that allow real-time data exchange with upstream and downstream processes, facilitating synchronized production workflows, inventory management, and quality tracking. This integration supports lean manufacturing principles and just-in-time production models, reducing waste and improving responsiveness to market demands.
Emerging innovations include adaptive spray technologies capable of dynamically altering spray patterns and coating thickness based on individual part characteristics detected by integrated sensors. This ensures optimal finish quality even when parts exhibit slight dimensional variations or surface inconsistencies, a common challenge when dealing with miniature components.
The trend toward multi-functional coating capabilities enables compact painters to apply a variety of functional layers—such as corrosion inhibitors, hydrophobic coatings, or conductive paints—alongside decorative finishes within a single compact system. This versatility reduces the need for multiple separate processes, streamlining production and minimizing handling risks.
Sustainability efforts continue to drive improvements in energy efficiency and material usage. Advanced curing technologies with reduced power consumption and rapid cure times help lower operational costs and carbon footprints. Paint recovery systems have become more effective at capturing and recycling overspray, further conserving resources.
User experience enhancements involve augmented reality (AR) tools that assist operators with maintenance, setup, and troubleshooting by overlaying digital instructions and diagnostics onto real-world equipment views. This reduces training time, enhances safety, and accelerates issue resolution.
Compact painters also incorporate robust safety features, including enclosed spray environments, advanced ventilation, and automatic shutdown protocols to protect operators and maintain clean production spaces.
Their modular, scalable architecture enables manufacturers to expand capacity or incorporate new technologies without major facility modifications. This adaptability ensures that compact painting systems remain relevant and efficient as product lines evolve or new market opportunities arise.
In essence, compact painters for tiny parts continue to advance as intelligent, flexible, and environmentally conscious solutions. By merging precision engineering, automation, and connectivity within a small footprint, these systems empower manufacturers to meet the exacting demands of miniature component finishing while optimizing space, efficiency, and sustainability—key drivers of competitiveness in today’s manufacturing landscape.
Small Object Painting Solutions
Small object painting solutions are specialized systems designed to deliver precise, consistent, and high-quality coatings on miniature components used across diverse industries such as electronics, medical devices, cosmetics, jewelry, and precision engineering. These solutions address the unique challenges of painting small objects, including delicate handling requirements, complex shapes, tight tolerances, and the need for uniform finishes that meet stringent functional and aesthetic standards.
At the core of small object painting solutions is advanced handling technology that secures and positions tiny parts accurately during the painting process. Custom fixtures, micro-grippers, vacuum chucks, or conveyor systems ensure that parts remain stable and properly oriented to achieve even paint coverage while minimizing damage or contamination.
The application methods in these solutions utilize sophisticated spray technologies such as electrostatic spray systems, micro-atomizers, precision airbrushes, or ultrasonic spraying. Electrostatic charging improves paint transfer efficiency by attracting charged paint particles directly to the part surface, reducing overspray and material waste. The precision spray techniques generate fine, controlled mists that penetrate complex geometries and ensure uniform layer thickness even on intricate or recessed surfaces.
Modular painting lines often comprise multiple stations, allowing sequential application of primers, base coats, functional or decorative coatings, and protective clear coats. Each station is equipped with environmental controls—such as temperature, humidity, and clean airflow—to optimize paint adhesion and curing. Integrated curing methods vary based on paint chemistry and part sensitivity, including UV/LED curing, infrared drying, or convection ovens, ensuring fast, low-temperature drying that preserves part integrity.
Quality assurance is a fundamental aspect of small object painting solutions, with inline inspection systems employing high-resolution cameras and sensors to detect coating defects like runs, pinholes, or color inconsistencies at microscopic levels. Automated sorting and rework mechanisms ensure that only parts meeting strict quality criteria proceed, minimizing waste and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Process control software orchestrates the entire painting workflow, storing detailed recipes for different products and coatings, facilitating rapid changeovers and ensuring repeatability. Real-time monitoring and data logging support traceability, regulatory compliance, and continuous process improvement.
Sustainability considerations are integral, with enclosed spray booths equipped with efficient air filtration, paint reclaim systems, and compatibility with environmentally friendly coatings such as waterborne or low-VOC paints. Energy-efficient curing technologies further reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
User-friendly interfaces and safety features protect operators by minimizing exposure to hazardous substances and simplifying machine operation and maintenance. Remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance capabilities enhance uptime and operational reliability.
Overall, small object painting solutions combine precision handling, advanced coating technologies, environmental stewardship, and intelligent automation to deliver flawless finishes on miniature components. These integrated systems enable manufacturers to meet demanding quality standards, improve production efficiency, and maintain compliance with environmental and safety regulations—critical factors for success in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape.
Small object painting solutions continue to evolve by embracing innovations in automation, robotics, and intelligent process control to enhance precision, speed, and adaptability while maintaining compact system footprints. Robotic arms with fine motor control and vision-guided positioning handle delicate parts gently yet accurately, enabling consistent orientation and optimal exposure to spray nozzles. This reduces manual handling, minimizes damage risk, and supports high-throughput production even with diverse part geometries and materials.
Advanced sensor technologies monitor spray characteristics, environmental conditions, and coating quality in real time. Data analytics and machine learning algorithms use this information to dynamically adjust spray parameters such as flow rate, nozzle distance, and curing profiles, ensuring uniform coatings and reducing defects. This adaptive control is especially valuable when coating parts with intricate features or varying surface finishes.
Modular system architectures allow manufacturers to customize small object painting lines by adding or removing spray and curing stations to meet specific product requirements. This flexibility supports small batch runs, frequent product changeovers, and mixed production schedules, enabling quick responses to market demands without compromising quality or efficiency.
Sustainability remains a key focus, with enclosed spray booths featuring high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration and paint recovery systems that capture overspray and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Compatibility with waterborne, UV-curable, and low-VOC coatings further reduces environmental impact while maintaining excellent finish performance. Energy-efficient curing technologies and optimized airflow management contribute to lower operational costs and carbon footprints.
Operator interfaces prioritize safety and usability through touchscreen controls, guided workflows, and safety interlocks that minimize exposure to hazardous materials. Remote monitoring and diagnostics enable proactive maintenance and rapid troubleshooting, enhancing machine uptime and production reliability.
Integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms facilitates full traceability of each painted part, linking process parameters and inspection data to batch records for regulatory compliance and quality assurance. Detailed analytics help identify process improvements and support continuous operational excellence.
Compact designs allow small object painting solutions to fit seamlessly into cleanroom environments or space-constrained facilities common in electronics, medical device, and precision manufacturing sectors. Scalable configurations enable manufacturers to expand or reconfigure systems as production volumes grow or product lines evolve, protecting capital investment.
In conclusion, small object painting solutions combine precise handling, advanced coating technologies, intelligent automation, and sustainable design to deliver flawless, repeatable finishes on miniature components. By optimizing quality, efficiency, and environmental responsibility within compact footprints, these systems empower manufacturers to excel in fast-paced, quality-driven markets requiring exceptional miniature part finishing.
Continuing to advance, small object painting solutions increasingly incorporate collaborative robotics—cobots—that safely work alongside human operators to enhance flexibility and precision. These cobots assist with delicate loading, unloading, and fine adjustments, combining human dexterity with automated consistency to improve overall throughput and quality, especially in mixed-production environments.
Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) support operators and maintenance personnel by overlaying real-time operational data, step-by-step procedures, and troubleshooting guides directly onto the equipment view. This immersive assistance reduces training time, minimizes errors, and accelerates problem resolution, thereby maximizing uptime and production efficiency.
Real-time 3D scanning and machine vision systems provide detailed surface mapping of tiny parts, enabling dynamic adaptation of spray patterns and thickness to compensate for part-to-part variations or surface irregularities. This level of customization ensures each part receives an optimal coating, critical for applications where minute deviations can impact performance or aesthetics.
The trend toward multi-functional coatings has prompted integration of systems capable of applying diverse functional layers—such as conductive inks, antimicrobial finishes, or corrosion-resistant coatings—alongside decorative paints. This capability streamlines production by consolidating processes and reducing handling risks, meeting the complex demands of industries like medical devices, electronics, and aerospace.
Energy-efficient curing technologies, including LED UV systems and plasma-assisted drying, reduce cycle times and power consumption while protecting heat-sensitive materials. Advanced paint recovery and recycling systems further enhance sustainability by minimizing waste and VOC emissions.
Connectivity within Industry 4.0 frameworks allows seamless data exchange between painting lines, upstream fabrication equipment, and downstream quality control and packaging systems. This integration facilitates coordinated workflows, predictive maintenance, and comprehensive traceability, supporting lean manufacturing and regulatory compliance.
Modular and scalable system designs enable easy expansion or reconfiguration as product portfolios evolve, safeguarding investments and enabling rapid adaptation to changing market requirements.
In summary, small object painting solutions are becoming smarter, more flexible, and environmentally responsible. By merging cutting-edge automation, advanced materials, and intelligent controls, these systems empower manufacturers to deliver impeccable finishes on miniature components with unmatched efficiency and consistency—essential qualities in today’s highly competitive and innovation-driven manufacturing landscape.
Not only do we manufacture our powder coating equipment, we also ship them worldwide to your facility with care
We’re not just the manufacturers of your powder coating equipment, we’re also your worldwide delivery partners.
At EMS Powder Coating Equipment, we understand that getting your powder coating equipment to you quickly and safely is just as important as manufacturing it to the highest standards. That’s why we offer worldwide delivery services to all of our customers.
We work with a network of experienced and reliable shipping partners to ensure that your equipment arrives on time and in perfect condition. We also offer a variety of shipping options to fit your budget and needs.
Whether you need your equipment shipped to a local address or to an international destination, we can help. We’ll work with you to choose the best shipping option for your needs and to keep you updated on the status of your shipment every step of the way.
So when you choose EMS for your powder coating equipment, you’re not just getting the best products on the market, you’re also getting the best possible delivery experience.
Contact us today to learn more about our worldwide delivery services.









